Abstract
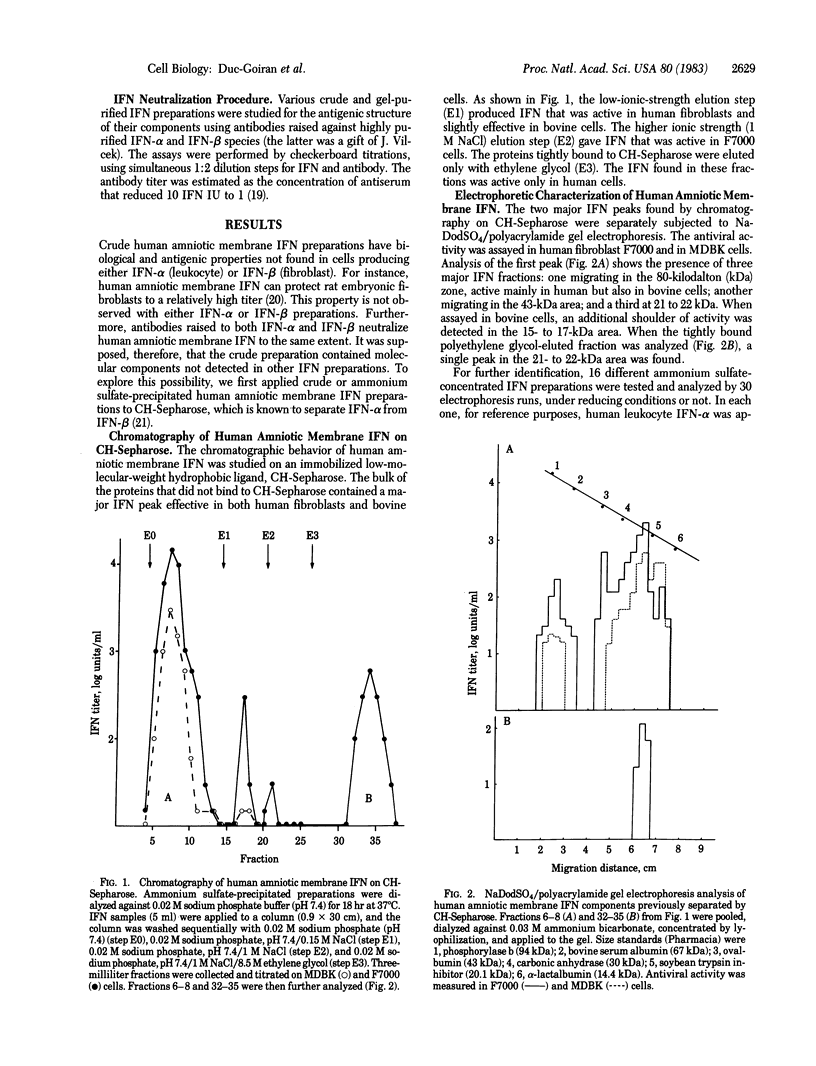
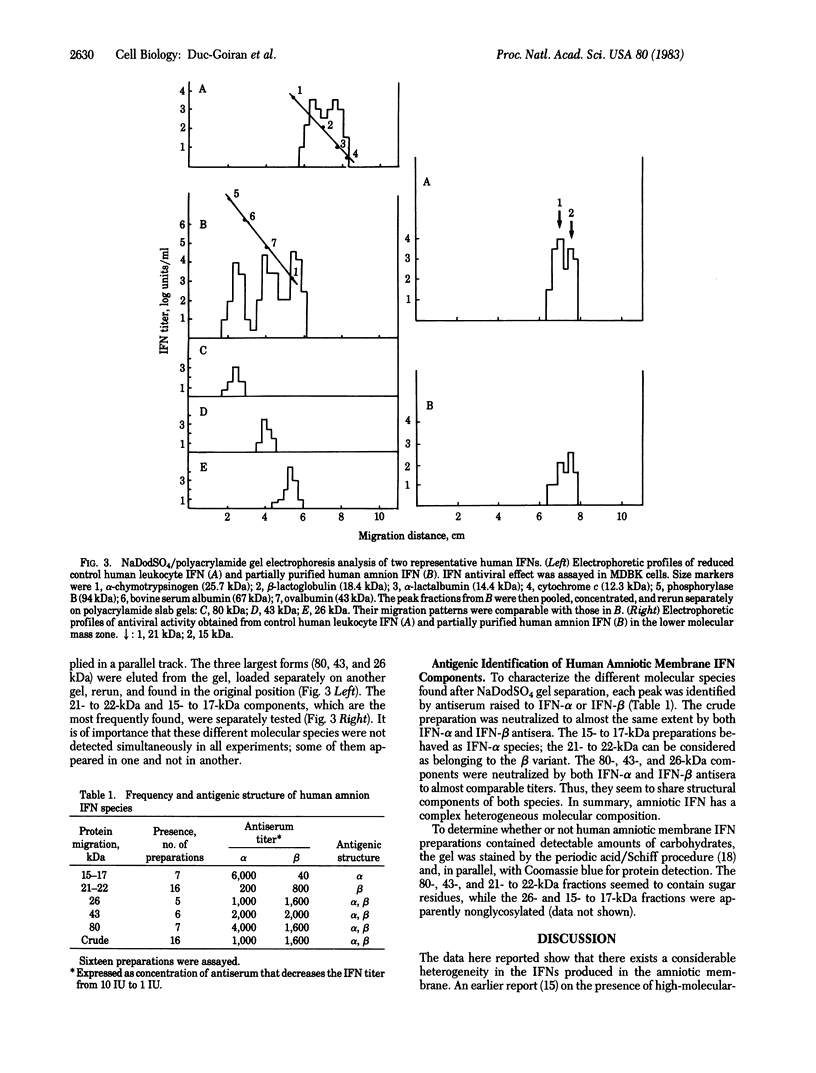
Interferon (IFN) induced in the human amniotic membrane contains at least five different molecular species, as shown by analysis in NaDodSO4/polyacrylamide gels after heating and under reducing conditions. Three of the IFN components reported here--migrating at 26, 43, and 80 kilodaltons--are of unusual antigenic structure because they are neutralized to about the same extent by anti-IFN-alpha and anti-IFN-beta antibodies. The 15- to 17-kilodalton species belongs to the IFN-alpha group, while the 21- to 22-kilodalton species, the most frequently detected major peak, is IFN-beta. In addition to their unusual size and antigenic structure, these IFNs could play a role during embryonic development and in the immune tolerance of the mother with regard to the fetus.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bergeret M., Fouchard M., Gregoire A., Chany C., Zagury D. Interferon effect on cytolytic T lymphocytes in a single cycle assay. Immunology. 1983 Jan;48(1):101–106. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergeret M., Grégoire A., Chany C. Protective effect of interferon on target cells exposed to cellular cytotoxicity. Immunology. 1980 Aug;40(4):637–643. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom B. R. Interferons and the immune system. Nature. 1980 Apr 17;284(5757):593–595. doi: 10.1038/284593a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourgeade M. F., Rousset S., Paulin D., Chany C. Reorganization of the cytoskeleton by interferon in MSV-transformed cells. J Interferon Res. 1981 Feb;1(2):323–332. doi: 10.1089/jir.1981.1.323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chany C., Rousset S., Bourgeade M. F., Mathieu D., Grégoire A. Role of receptors and the cytoskeleton in reverse transformation and steroidogenesis induced by interferon. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1980;350:254–265. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1980.tb20626.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chany C., Vignal M. Etude du mécanisme de l'étst réfractaiere des cellules à l1 production d'interféron, près inductions répétées. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1968 Nov 18;267(21):1798–1800. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duc-Goiran P., Galliot B., Chany C. Studies on virus-induced interferons produced by the human amniotic membrane and white blood cells. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1971;34(3):232–243. doi: 10.1007/BF01242997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira P. C., Paucker M., Golgher R. R., Paucker K. Affinity chromatography of primary human amnion interferon. Arch Virol. 1981;68(1):27–33. doi: 10.1007/BF01315164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fournier F., Falcoff E., Chany C. Demonstration, mass production and characterization of a heavy molecular weight human interferon. J Immunol. 1967 Nov;99(5):1036–1041. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fowler A. K., Reed C. D., Giron D. J. Identification of an interferon in murine placentas. Nature. 1980 Jul 17;286(5770):266–267. doi: 10.1038/286266a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerfaux J., Rousset S., Chany-Fournier F., Chany C. Interferon effect on collagen and fibronectin distribution in the extracellular matrix of murine sarcoma virus-transformed cells. Cancer Res. 1981 Sep;41(9 Pt 1):3629–3634. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jankowski W. J., Davey M. W., O'Malley J. A., Sulkowski E., Carter W. A. Molecular structure of human fibroblast and leukocyte interferons: probe by lectin and hydrophobic chromatography. J Virol. 1975 Nov;16(5):1124–1130. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.5.1124-1130.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapitany R. A., Zebrowski E. J. A high resolution PAS stain for polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1973 Dec;56(2):361–369. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90202-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawade Y. An analysis of neutralization reaction of interferon by antibody: a proposal on the expression of neutralization titer. J Interferon Res. 1980 Fall;1(1):61–70. doi: 10.1089/jir.1980.1.61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King J., Laemmli U. K. Polypeptides of the tail fibres of bacteriophage T4. J Mol Biol. 1971 Dec 28;62(3):465–477. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90148-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebon P., Girard S., Thépot F., Chany C. Présence constante d'interféron de type alpha dans les liquides amniotiques humains. C R Seances Acad Sci III. 1981 Jul 6;293(1):69–71. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebon P., Girard S., Thépot F., Chany C. The presence of alpha-interferon in human amniotic fluid. J Gen Virol. 1982 Apr;59(Pt 2):393–396. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-59-2-393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagata S., Taira H., Hall A., Johnsrud L., Streuli M., Ecsödi J., Boll W., Cantell K., Weissmann C. Synthesis in E. coli of a polypeptide with human leukocyte interferon activity. Nature. 1980 Mar 27;284(5754):316–320. doi: 10.1038/284316a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAUCKER K., CANTELL K., HENLE W. Quantitative studies on viral interference in suspended L cells. III. Effect of interfering viruses and interferon on the growth rate of cells. Virology. 1962 Jun;17:324–334. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(62)90123-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paucker K., Dalton B. J., Törmä E. T., Ogburn C. A. Biological properties of human leukocyte interferon components. J Gen Virol. 1977 May;35(2):341–351. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-35-2-341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeffer L. M., Wang E., Tamm I. Interferon effects on microfilament organization, cellular fibronectin distribution, and cell motility in human fibroblasts. J Cell Biol. 1980 Apr;85(1):9–17. doi: 10.1083/jcb.85.1.9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossi G. B., Matarese G. P., Grappelli C., Belardelli F., Benedetto A. Interferon inhibits dimethyl sulphoxide-induced erythroid differentiation of Friend leukaemia cells. Nature. 1977 May 5;267(5606):50–52. doi: 10.1038/267050a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thang M. N., Thang D. C., Chelbi-Alix M. K., Robert-Galliot B., Commoy-Chevalier M. J., Chany C. Human leukocyte interferon: relationship between molecular structure and species specificity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3717–3721. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


