Abstract
31P NMR studies on the brains of living rabbits were carried out at 32 MHz in a spectrometer having a 200-mm clear bore. Paralyzed pump-ventilated animals under nitrous oxide analgesia were inserted into the 1.89-T field and signals were focused in the brain by using a 4-cm surface coil. Several conventional physiological variables were monitored together with 31P spectra during induction and reversal of insulin shock and hypoxic hypoxia sufficient to abolish the electroencephalogram and during status epilepticus. A reversible decrease in phosphocreatine stores accompanied by an increase in Pi was detected during hypoglycemia and hypoxia. Similar changes were observed in prolonged status epilepticus but were not reversed. ATP levels fell about 50% in hypoglycemia but only slightly in the other two metabolic stresses. Intracellular pH rose in hypoglycemia; in status epilepticus and hypoxia it fell, but only when cardiovascular function was severely impaired. From the measured NMR parameters and the assumptions (i) that creatine kinase was at equilibrium and (ii) that the creatine/phosphocreatine pool was constant, it was possible to calculate the relative changes in cytoplasmic ADP levels associated with these metabolic disturbances.
Full text
PDF
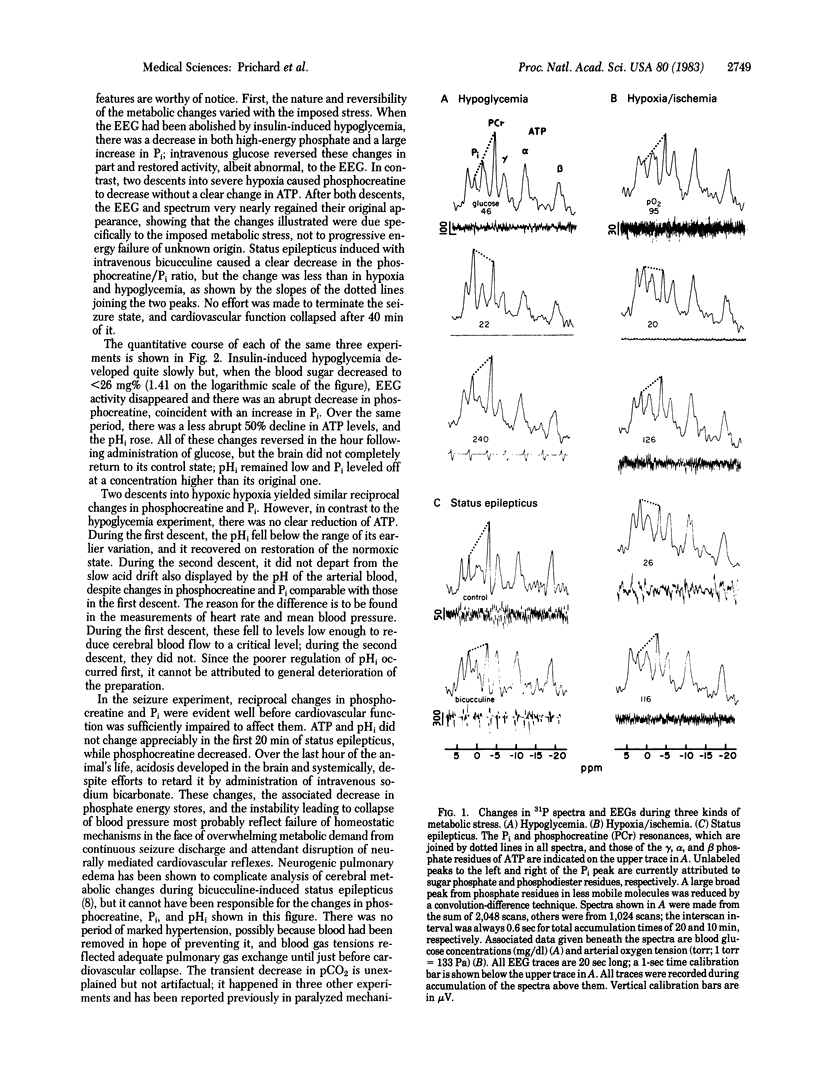
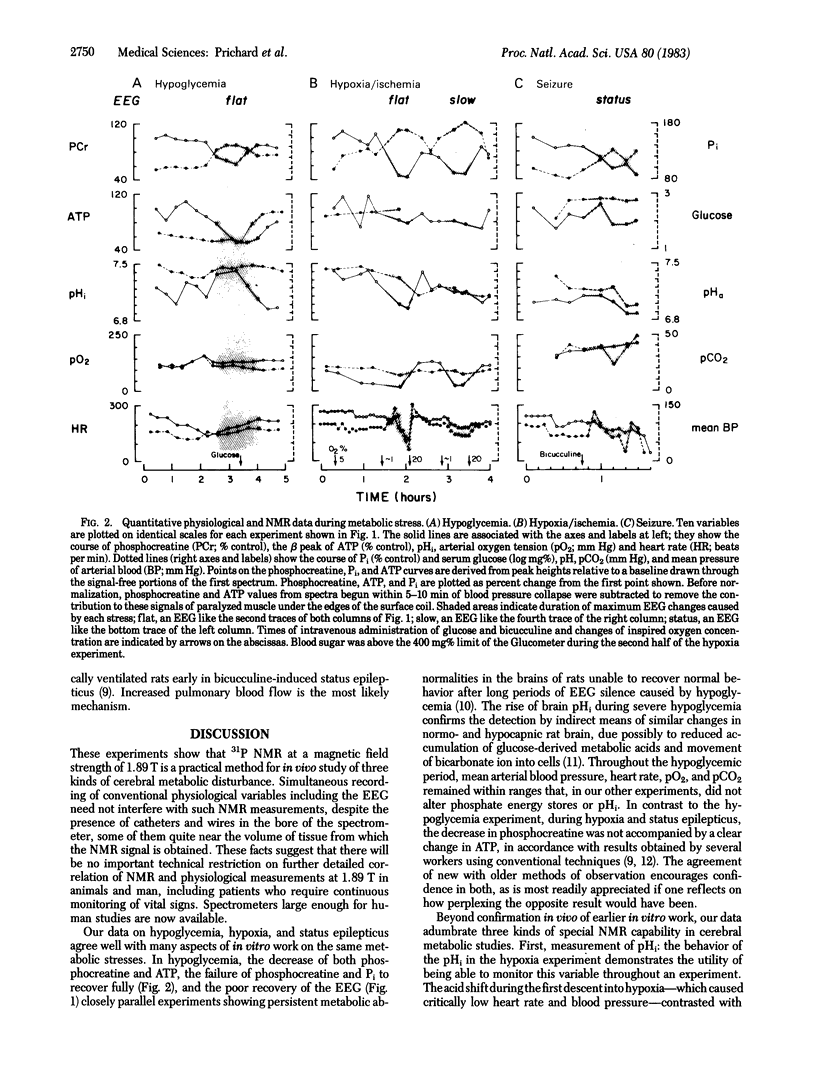

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ackerman J. J., Grove T. H., Wong G. G., Gadian D. G., Radda G. K. Mapping of metabolites in whole animals by 31P NMR using surface coils. Nature. 1980 Jan 10;283(5743):167–170. doi: 10.1038/283167a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Budinger T. F. Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) in vivo studies: known thresholds for health effects. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1981 Dec;5(6):800–811. doi: 10.1097/00004728-198112000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chance B., Nakase Y., Bond M., Leigh J. S., Jr, McDonald G. Detection of 31P nuclear magnetic resonance signals in brain by in vivo and freeze-trapped assays. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4925–4929. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman A. G., Meldrum B. S., Siesjö B. K. Cerebral metabolic changes during prolonged epileptic seizures in rats. J Neurochem. 1977 May;28(5):1025–1035. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1977.tb10665.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delpy D. T., Gordon R. E., Hope P. L., Parker D., Reynolds E. O., Shaw D., Whitehead M. D. Noninvasive investigation of cerebral ischemia by phosphorus nuclear magnetic resonance. Pediatrics. 1982 Aug;70(2):310–313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gadian D. G., Radda G. K., Brown T. R., Chance E. M., Dawson M. J., Wilkie D. R. The activity of creatine kinase in frog skeletal muscle studied by saturation-transfer nuclear magnetic resonance. Biochem J. 1981 Jan 15;194(1):215–228. doi: 10.1042/bj1940215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghajar J. B., Plum F., Duffy T. E. Cerebral oxidative metabolism and blood flow during acute hypoglycemia and recovery in unanesthetized rats. J Neurochem. 1982 Feb;38(2):397–409. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1982.tb08643.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinzen D. H., Müller U. Energiestoffwechsel und Funktion des Kaninchengehirns während Insulinhypoglykämie. Pflugers Arch. 1971;322(1):47–59. doi: 10.1007/BF00586664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiessling M., Hossmann K. A., Kleihues P. Pulmonary edema during bicuculline-induced seizures in rats. Exp Neurol. 1981 Nov;74(2):430–438. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(81)90181-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norberg K., Siesjö B. K. Cerebral metabolism in hypoxic hypoxia. I. Pattern of activation of glycolysis: a re-evaluation. Brain Res. 1975 Mar 14;86(1):31–44. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90635-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelligrino D., Siesjö B. K. Regulation of extra- and intracellular pH in the brain in severe hypoglycemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1981;1(1):85–96. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1981.9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoubridge E. A., Briggs R. W., Radda G. K. 31p NMR saturation transfer measurements of the steady state rates of creatine kinase and ATP synthetase in the rat brain. FEBS Lett. 1982 Apr 19;140(2):289–292. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80916-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoubridge E. A., Briggs R. W., Radda G. K. 31p NMR saturation transfer measurements of the steady state rates of creatine kinase and ATP synthetase in the rat brain. FEBS Lett. 1982 Apr 19;140(2):289–292. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80916-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TARR M., BRADA D., SAMSON F. E., Jr Cerebral high-energy phosphates during insulin hypoglycemia. Am J Physiol. 1962 Oct;203:690–692. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1962.203.4.690. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thulborn K. R., du Boulay G. H., Duchen L. W., Radda G. A 31P nuclear magnetic resonance in vivo study of cerebral ischaemia in the gerbil. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1982 Sep;2(3):299–306. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1982.31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veech R. L., Lawson J. W., Cornell N. W., Krebs H. A. Cytosolic phosphorylation potential. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jul 25;254(14):6538–6547. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



