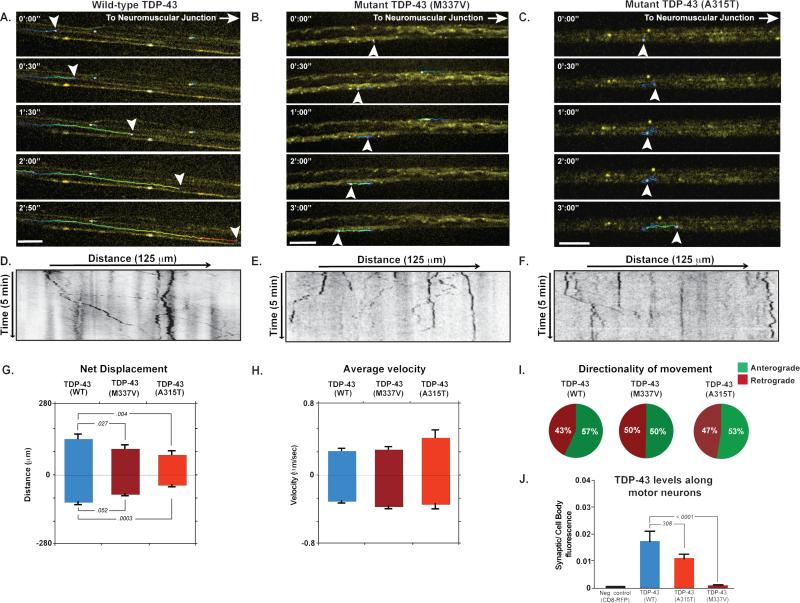
Fig. 1. Localization and transport kinetics of TDP-43 granules in Drosophila motor neurons.
(A-C) Venus-TDP-43WT, Venus-TDP-43M337V, and Venus-TDP-43A315T granules (arrowheads) displayed dynamic bidirectional movement along motor neuron axons of 3rd instar larvae. Transport of mutant TDP-43 granules showed normal instantaneous velocities, but an increased frequency of reversals and diminished net anterograde movement. Scale bar: 10 μm. (D-F) Kymographs tracing TDP-43 granules in motor neuron axons. (G-E) Quantification of displacement and instantaneous velocities of wild type and mutant granules along Drosophila motor neuron axons. Anterograde and retrograde movements are represented as positive or negative values on the y-axis, respectively. (I) Analysis of movement directionality shows a reduced ratio of anterograde to retrograde movement for mutant TDP-43 granules as compared to TDP-43WT. (J) Quantification of fluorescence intensities in Drosophila motor neuron axons. The ratio of average fluorescence intensity per pixel at the synaptic terminal divided by the fluorescence at the cell body shows that Venus-TDP-43WT signal is higher than that of mutant TDP-43. Error bars are shown as mean ± SEM.