Abstract
Objective
To compare maternal and perinatal outcomes in pregnancies complicated by severe preeclampsia, eclampsia, and HELLP (hemolysis, elevated liver enzyme levels, and low platelets) syndrome.
Materials and Methods
Maternal and neonatal charts of 1,222 consecutive pregnancies complicated by severe preeclampsia, eclampsia, or HELLP syndrome at our maternal-perinatal unit were reviewed. Patients were divided into three groups: 903 (73.9%) with severe preeclampsia, 123 (10.1%) with eclampsia, and 196 (16.0%) with HELLP syndrome.
Results
The overall incidence of adverse maternal outcome was 5.9%. The rates of adverse maternal outcomes for women with HELLP syndrome and eclampsia were higher than for severe preeclampsia (13.8% vs. 11.4% vs. 3.4%, respectively) (p=0.000). Birth weight was lower in patients with HELLP syndrome than in patients with eclampsia and severe preeclampsia (p=0.005). No significant difference in neonatal morbidity was found among the three groups. Perinatal mortality tended to be higher in the severe preeclampsia group than in the HELLP syndrome and eclampsia groups (p=0.231).
Conclusion
Pregnancies complicated by HELLP syndrome had significantly higher maternal morbidity than those with severe preeclampsia and eclampsia. Perinatal and neonatal outcomes in pregnancies complicated by severe preeclampsia, eclampsia, and HELLP syndrome were dependent on gestational age rather than being disease dependent.
Keywords: Severe preeclampsia, eclampsia, HELLP syndrome, perinatal and maternal outcome
Özet
Amaç
Şiddetli preeklampsi, eklamsi ve HELLP sendromu ile komplike olmuş gebelerdeki maternal ve perinatal sonuçları karşılaştırmak.
Gereç ve Yöntemler
Maternal-perinatal ünitemizde tedavi olan şiddetli preeklampsi, eklamsi ve HELLP sendromu ile komplike olmuş 1222 gebe incelendi. Olgular üç guruba ayrıldı; 903 (%73.9) şiddetli preeklampsi, 123 (%10.1) eklampsi ve 196 (%16.0) HELLP sendromu.
Bulgular
Toplam maternal komplikasyon oranı % 5.9 olarak bulundu. Maternal komplikasyon oranı HELLP sendromu ve eklampsi ile komplike olmuş geblerde şiddetli preeklampsi ile komplike olmuş geblerden daha yüksek bulundu (%13.8, %11.4, %3.4,) (p=0.000). Doğum ağırlığı HELLP semdromu gurubunda eklampsi ve şiddetli preeklampsi gurubuna gore daha düşüktü (p=0.005). Guruplar arasında neonatal morbitide yönünden istatistiksel anlamda fark bulunamadı (p>0.05). Peritanal mortalite oranı HELLP sendormu ve eklampsi gurubu ile karşılaştırıldığında şiddetli preeklampsi gurubunda daha yüksek oranda meydana gelsede istatistiksel anlamda fark bulunamadı (p=0.231).
Sonuç
HELLP sendromu ile komplike olmuş gebeler şiddetli preeklamapsi ve eklampsi ile komplike olmuş gebelere oranla daha fazla maternal morbiditeye sahiptir. Perinatal ve neonatal sonuçlar ise şiddetli preeklampsi, eklampsi ve HELLP sendromundan çok doğumdaki gestasyonel yaşa bağlıdır.
Introduction
Hypertensive disorders during pregnancy represent a significant public health problem throughout the world, and preeclampsia is the most common of these disorders (1). Villar et al. reviewed available information on the incidence and prevalence of preeclampsia/eclampsia utilizing large epidemiological studies (2). They estimated that hypertension complicates approximately 5% of all pregnancies. Of these, approximately half are due to or associated with preeclampsia. Based on these estimates and case-fatality rates, they calculated that up to 40,000 women, mostly in developing countries, may die due to preeclampsia or eclampsia each year.
The clinical course of severe preeclampsia results in progressive deterioration of both maternal and fetal conditions. Traditional management of severe preeclampsia has focused on maternal safety, with expedited delivery. Because these pregnancies are associated with high rates of maternal morbidity and mortality and with potential risks for the fetus, it is generally agreed that such patients should be delivered if the disease develops at >34 weeks of gestation (3, 4). In patients with severe preeclampsia at <34 weeks of gestation, several authors have suggested some form of expectant management in an attempt to prolong gestation and improve perinatal outcome (3–7). For patients with severe fetal growth restriction (FGR) with or without oligohydramios or evidence of maternal organ dysfunction (eclampsia, HELLP syndrome), some authors have recommended steroids to enhance lung maturation, with delivery 48 hours after initiating steroid administration (3–9).
The main objective when managing severe preeclampsia, eclampsia, and HELLP syndrome is to reduce maternal mortality and morbidity rates. Current literature emphasizes an increased risk of adverse outcomes for patients with severe preeclampsia, eclampsia, and HELLP syndrome. However, few studies have compared perinatal and maternal outcomes in pregnancies complicated by severe preeclampsia, eclampsia, and HELLP syndrome.
Materials and Methods
The Bakırkoy Women and Children Education and Research Hospital in Istanbul, Turkey serves as a tertiary care facility for western Turkey, where there are approximately 14,000 deliveries annually. During the 6-year period from January 1, 2002 through December 2007, 1,222 of these pregnancies antenatally managed at this hospital were complicated by severe preeclampsia, eclampsia, and HELLP syndrome. This study was approved by the hospital’s Ethics Committee.
Women had severe preeclampsia if they met one or more of the following criteria of The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (10): systolic blood pressure >160 mm/Hg or diastolic blood pressure >110 mm/Hg, headache, visual disturbances, epigastric or right-upper-quadrant pain, pulmonary edema, and proteinuria (urinary protein level >5 g/24 h). Women with severe preeclampsia selected for analysis also met all of the following laboratory criteria: platelet count ≥150,000/mm3, serum lactate dehydrogenase <600 U/L, serum total bilirubin <1.2 mg/dL, and serum aspartate aminotransferase <70 U/L. Eclampsia was defined as tonic-clonic seizures occurring during a hypertensive pregnancy. Patients with any causes for convulsion other than eclampsia were excluded.
HELLP syndrome was divided into three classes by Martin et al. (11). They defined class 1 HELLP syndrome as a platelet nadir below 50,000/mm3, whereas those with platelet nadirs between 51,000 and 100,000/mm3 were defined as class 2. Class 3 HELLP syndrome represented patients with hepatocyte death but a higher platelet count nadir of 101,000–150,000/mm3.
Gestational age was determined using the best obstetric criteria, including either the last menstrual period or ultrasonography (where available) at <20 weeks gestation or both. On admission, hematocrit, hemoglobin, platelet count, and liver enzymes were determined, and 24-h urine collection was started. A hemogram and blood biochemistry tests were repeated daily or at a 2-day intervals. Fetal heart rate monitoring (FHR) was performed at least two to three times per day. Nifedipine and/or alfa-methyldopa were used as antihypertensive agents. An intravenous infusion of magnesium sulfate at a rate of 2 g/h was started, after a loading dose of 4.5 g for 10 min, in patients with persistently elevated systolic or diastolic blood pressure and/or prodromal symptoms and was continued postpartum for 24 h in severe preeclampsia and 48 h in eclampsia. Two doses of betamethasone (12 mg intramuscularly) were also given at 24 h intervals.
Maternal indications for delivery included persistent elevated blood pressure >160/110 mm Hg despite treatment with antihypertensive drugs, persistent or worsening symptoms, deteriorating renal function, severe ascites, abruptio placenta, oliguria, pulmonary edema, preterm labor, preterm rupture of membranes, evidence of class 1–2 HELLP syndrome, and eclampsia. Fetal indications for delivery included a non-reassuring fetal status as determined by the fetal heart rate tracing (decreased variability, repetitive late decelerations, or severe variable decelerations), FGR, oligohydramnios, severe abnormal umbilical artery Doppler findings such as absent or reverse end diastolic flow, and attainment of the 34th or ≥34th week of gestation on admission.
Oligohydramnios was diagnosed with an amniotic fluid index ≤5 cm or a two-diameter pocket <15 cm2. FGR was defined as a birth weight below the 10th percentile for gestational age.
The maternal variables studied included age, gravity, parity, gestational age at delivery, timing of eclampsia onset, and adverse maternal outcome. Maternal outcomes included abruptio placentae, acute renal failure (ARF), pulmonary edema, ascites, acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), neurological deficits, visual changes, intracranial hemorrhage, and maternal death. ARF was diagnosed when oliguria or anuria in association with a creatinine clearance ≤20 mL/min was present with an elevated serum creatinine level ≥2 mg/dL. Pulmonary edema was assessed based on clinical findings and chest radiography. A diagnosis of severe ascites was made by estimation during an ultrasonographic examination, cesarean delivery, or laparotomy (≥1000 mL of fluid measured by a suction apparatus).
Neonatal and fetal medical records were reviewed for the following outcomes: FGR, oligohydramnios, mode of delivery, intrauterine fetal death, perinatal (fetal death and early neonatal death at <7 postnatal days) and neonatal (postnatal 0–28 days) mortality, ARDS, grade 3–4 intraventricular hemorrhage (IVH), stage 2–3 necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC), sepsis, admission to the intensive care unit (ICU), duration of stay in the ICU, and duration of hospitalization. ARDS was defined by the presence of characteristic radiographic findings and oxygen requirements at 24 h. Grade 3 intraventricular hemorrhage was defined as hemorrhage with ventricular dilation, and grade 4 as hemorrhage with parenchymal involvement. NEC was defined by radiographic findings of grade 2 pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis and a grade 3 pneumoperitoneum. Intrauterine death and intrapartum loss of nonviable fetuses during pregnancy termination due to maternal indications were accepted as fetal death.
Data are presented as rates, percentiles, medians (interquartile ranges), and means±SDs. Statistical comparisons were performed using analysis of variance, Kruskal-Wallis test, and χ2 test, as appropriate. P-values < 0.05 were considered significant. Because double comparisons cannot be performed with the Kruskal-Wallis test, the groups significant in this analysis were compared as groups of two using the Mann-Whitney U-test. Levels of significance were evaluated with the Bonferroni correction (n/a=0.05/3=0.017), and p<0.017 was considered significant.
Results
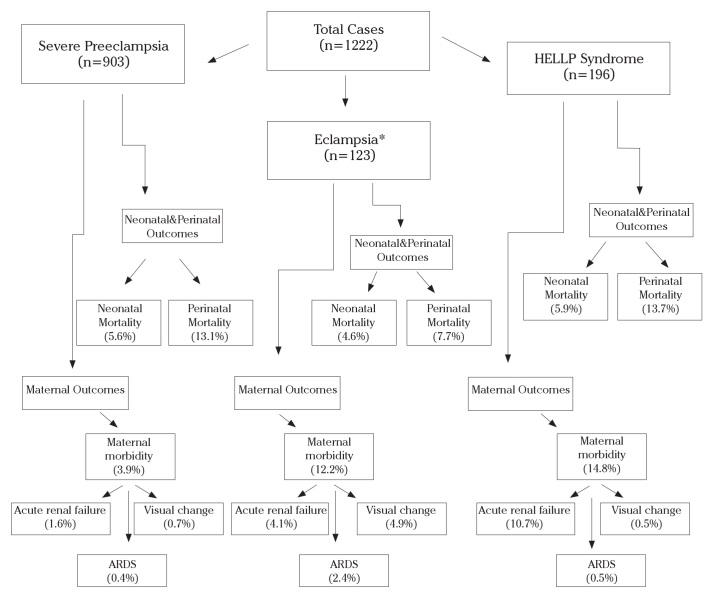
During the study period, 1222 cases of severe preeclampsia, eclampsia, or HELLP syndrome were treated at our institute. Among these, 123 (10.1%) had eclampsia, 903 (73.9%) had severe preeclampsia, and 196 (16.0%) had HELLP syndrome (Fig. 1). This classification was determined based on the patients’ initial presentation. Patients with HELLP syndrome and eclampsia were evaluated as the eclampsia group. Forty-one cases of eclampsia experienced HELLP syndrome. A total of 734 (60.0%) patients (601 with severe preeclampsia, 57 with eclampsia, and 76 with HELLP syndrome) were referred from surrounding hospitals and clinics, 297 (24.4%) were given antenatal care at our hospital (213 with preeclampsia, 35 with eclampsia, 49 with HELLP syndrome), and 191 (15.6%) patients received no antenatal care prior to admission (89 patients with severe preeclampsia, 31 with eclampsia, 71 with HELLP syndrome).
Figure 1.
Flow diagram of the study
(*Patients with HELLP syndrome and eclampsia were evaluated in the eclampsia group. 41 cases of eclampsia experienced HELLP syndrome.)
Table 1 compares the clinical characteristics of the cases. Maternal age, gravity, and parity were higher in patients with HELLP syndrome than in those with severe preeclampsia or eclampsia, and women with eclampsia were more likely to deliver by cesarean section than were those with HELLP syndrome or severe preeclampsia (p=0.005).
Table 1.
Clinical characteristics in 3 study groups
| Severe Preeclampsia (n=903) | Eclampsia (n=123) | HELLP syndrome (n=196) | P | P1b | P2b | P3b | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (year, median, Q1–Q3) | 27 (24–32) | 25 (22–29) | 28 (25–33) | <0.0001a | <0.0001 | 0.144 | <0.0001 |
| Gravidity (median, Q1–Q3) | 2 (1–3) | 1 (1–2) | 2 (1–3) | 0.0002a | 0.0003 | 0.355 | 0.0003 |
| Parity (median, Q1–Q3) | 0 (0–2) | 0 (0–1) | 1 (0–2) | 0.0006a | 0.0012 | 0.358 | 0.0009 |
| Nulliparity, % | 49.8 | 35 | 53.1 | 0.004* |
According to the Kruskal–Wallis test (triple comparison) P<0.05
Mann-Whitney U test P1=Severe Preeclampsia versus Eclampsia, P2=Severe preeclampsia versus HELLP Syndrome, P3=Eclampsia versus HELLP Syndrome Significant p value after Bonferroni correction <0.017
According to χ2 test for trend
Major maternal complications are presented in Table 2. The overall incidence of adverse maternal outcome was 5.9%. Statistical differences were found among the three groups for all adverse maternal outcomes studied. The rate of adverse maternal outcomes for women with HELLP syndrome and eclampsia were higher than those for women with severe preeclampsia (14.8% vs. 12.2% vs. 3.9%, respectively) (p=0.000). The rate of abruptio placentae tended to be higher among women with HELLP syndrome than among women with severe preeclampsia and eclampsia, but the difference was not significant (9.1% vs. 8.1% vs. 7.1%; p=0.581). Two maternal deaths occurred, producing a case fatality rate of 0.2% (one in the HELLP syndrome group and another in the severe preeclampsia group). Death was related to intracranial hemorrhage in one case and to an ARDS complication in another case.
Table 2.
Clinical characteristics in 3 study groups
| Maternal outcomes | Severe Preeclampsia (n=903) | Eclampsia (n=123) | HELLP syndrome (n=196) | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maternal morbidity | 35 (3.9%) | 15 (12.2%) | 29 (14.8%) | p<0.0001 |
| ARDS | 4 (0.4%) | 3 (2.4%) | 1 (0.5%) | 0.038 |
| Acute renal failure | 14 (1.6%) | 5 (4.1%) | 21 (10.7%) | p<0.0001 |
| Neurologic deficits | 1 (0.8%) | 3 (0.3%) | 2 (1%) | 0.0015 |
| Visual change | 6 (0.7%) | 6 (4.9%) | 1 (0.5%) | p<0.0001 |
| Pulmonary edema | 5 (0.6%) | 0 | 2 (1%) | 0.496 |
| Ascites | 3 (0.3%) | 0 | 1 (0.5%) | 0.738 |
| Intracranial hemorrhage | 0 | 0 | 1 (0.5%) | 0.072 |
| Abruptio placentae | 64 (7.1%) | 10 (8.1%) | 18 (9.2%) | 0.581 |
| Cesarean delivery | 617 (68.3%) | 105 (86.3%) | 150 (76.5%) | 0.005 |
| Maternal death | 1 (0.1%) | 0 | 1 (0.5%) | 0.407 |
According to the χ2 test for trend
Fetal findings are presented in Table 3. Birth weights were lower in infants of patients with HELLP syndrome than in infants of those with eclampsia or severe preeclampsia (p=0.005). Infant gestational age at delivery was lower for patients with HELLP syndrome than for those with eclampsia or severe preeclampsia (p=0.036). The percentage of oligohydramnios and of absent or reversed end diastolic flow, and the 5-min Apgar score, except FGR, were not different among women with eclampsia, severe preeclampsia, or HELLP syndrome. FGR was higher in patients with severe preeclampsia than in those with eclampsia and HELLP syndrome (p=0.013). A total of 105 intrauterine fetal deaths occurred, but no significant difference in fetal mortality was found among the three groups (p=0.153). No significant differences in neonatal morbidity (admission to ICU, RDS, grades 3 and 4 IVH, grades 2 and 3 NEC, sepsis, duration in the neonatal ICU) were found among the three groups (Table 4). The duration of hospitalization was similar for patients with severe preeclampsia and eclampsia, but was significantly shorter for those with severe preeclampsia than for those with HELLP syndrome. Perinatal mortality tended to be higher in the severe preeclampsia group than in the HELLP syndrome and eclampsia groups, but the difference was not significant (p=0.231).
Table 3.
Fetal findings of study groups
| Fetal findings | Severe Preeclampsia (n=903) | Eclampsia (n=123) | HELLP syndrome (n=196) | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gestational age at delivery (wk, median, Q1–Q3) | 34.4 (31.7–36.7) | 34 (30.7–36.9) | 34 (31.05–35.9) | 0.009a P1b 0.574 P2b 0.001 P3b 0.165 |
| Birth weight, (g, median, Q1–Q3) | 975 (835–1315) | 1145 (760–1320) | 940 (700–1200) | 0.005a P1b 0.308 P2b 0.003 P3b 0.006 |
| Fetal growth restriction, % | 53.4 | 39.2 | 50.8 | 0.013t |
| Oligohydramnios, % | 23.9 | 21.7 | 25.4 | 0.755t |
| Absent or reverse end diastolic flow, % | 11.3 | 8.3 | 12.4 | 0.521t |
| 5-min Apgar score <7, % | 6.1 | 11.9 | 4.8 | 0.048t |
| Female infant, % | 52.9 | 50.0 | 52 | 0.829t |
| Placental weight (g, median, Q1–Q3) | 230 (150–310) | 265 (195–320) | 180 (140–250) | 0.591 |
| Fetal mortality (IUFD), % | 10.5 | 5.1 | 11.6 | 0.153t |
| ≤32 weeks, % | 29.4 | 7.7 | 29.6 | 0.016t |
| >32 weeks, % | 3.8 | 3.8 | 3.4 | 0.979t |
IUFD: Intrauterine fetal death
According to the Kruskal–Wallis test (triple comparison) P<0.05
Mann–Whitney U test P1=Severe Preeclampsia versus Eclampsia, P2=Severe preeclampsia versus HELLP Syndrome, P3=Eclampsia versus HELLP Syndrome. Significant p value after Bonferroni correction <0.017
According to the χ2 test for trend
Table 4.
Perinatal and neonatal outcomes of study groups
| Perinatal and neonatal outcomes | Severe Preeclampsia (n=903) | Eclampsia (n=123) | HELLP syndrome (n=196) | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Admission to ICU, % | 14.8 | 21.6 | 17.3 | 0.169a |
| Duration of ICU (d, median, Q1–Q3) | 13.5 (6–23.7) | 8 (3.2–26.7) | 15 (9–32.5) | 0.345a |
| RDS, % | 13.2 | 19.5 | 16.0 | 0.169* |
| IVH grades 3 and 4, % | 1.3 | 2.7 | 2.6 | 0.379* |
| NEC grades 2 and 3, % | 4.1 | 4.4 | 7.7 | 0.159* |
| Sepsis, % | 6.7 | 6.2 | 8.3 | 0.735* |
| Duration of hospitalization (d, median, Q1–Q3) | 4 (2–12) | 4 (3–15) | 6 (3–15) | 0.0001a P1b 0.025 P2b 0.0001 P3b 0.182 |
| Perinatal mortality, % | 13.1 | 7.7 | 13.7 | 0.231* |
| ≤32 weeks, % | 36.5 | 15.4 | 36.4 | 0.034* |
| >32 weeks, % | 4.9 | 3.8 | 3.3 | 0.706* |
| Neonatal mortality, % | 5.6 | 4.6 | 5.9 | 0.890* |
| ≤32 weeks, % | 21 | 11.4 | 21.6 | 0.415* |
| >32 weeks, % | 1.7 | 1.4 | 0.9 | 0.815* |
| >28 days mortality, % | 1.1 | 1.9 | 4.8 | 0.009* |
According to Kruskal–Wallis test (triple comparison) P<0.05
Mann-Whitney U test P1=Severe Preeclampsia versus Eclampsia, P2= Severe preeclampsia versus HELLP Syndrome, P3=Eclampsia versus HELLP Syndrome. Significant p value after Bonferroni correction <0.017
According to χ2 test for trend
Discussion
We examined maternal and perinatal outcomes for severe preeclampsia, eclampsia, and HELLP syndrome and found the following. 1) The mean gestational age and birth weight at delivery in the HELLP syndrome group were lower than those in the severe preeclampsia and eclampsia groups. 2) No significant differences were found for neonatal mortality and morbidity. 3) Abruptio placentae tended to be higher among women with HELLP syndrome than in the other groups, but the difference was not significant. 4) Perinatal and fetal mortality tended to be higher in the severe preeclampsia and HELLP syndrome groups than in the eclampsia group, but the difference was not significant. 5) When an analysis was performed according to gestational age before and after the 32nd week, perinatal mortality at ≤32 weeks for patients with severe preeclampsia and HELLP syndrome was higher than that in the eclampsia group. 6) Significantly higher maternal morbidity was observed in the HELLP syndrome group than that in the other groups.
Primaparous young women with low socioeconomic status are the most typical preeclamptic and eclamptic cases. Our study also revealed clinical and sociodemographic data similar to the patient profiles in the extant literature. Most of these patients had had no regular antenatal visits, were primiparous, and young. HELLP syndrome has classically been described as a disease process that occurs more often in older, multigravid women than in younger nulliparous women with typical preeclampsia (13, 14). In our study, maternal age, gravity, and parity were higher in patients in HELLP syndrome than in those with severe preeclampsia and eclampsia, which agreed with a previous study (12).
Pregnancies complicated by severe preeclampsia/eclampsia or HELLP syndrome are associated with an increased risk for maternal morbidity and mortality. Complications leading to maternal morbidity include severe bleeding from abruptio placentae, pulmonary edema, ARF, cerebrovascular hemorrhage, and liver rupture. These complications are usually seen in women who develop severe preeclampsia, eclampsia, or HELLP syndrome before 32 weeks gestation (14). Women with HELLP syndrome have an increased risk for adverse maternal outcome compared with those who have severe preeclampsia/eclampsia (10, 15). The differences in the outcomes observed in these studies may be related to the earlier gestation in women with HELLP syndrome than in women with severe preeclampsia/eclampsia. In this study, the overall adverse maternal outcome rate was 5.9%. Statistical differences were found among the three groups for all adverse maternal outcomes studied. As expected, HELLP syndrome was associated with an increased risk for adverse maternal outcome (14.8%) compared with the risk associated with severe preeclampsia/eclampsia.
ARF, the most common adverse outcome in our study, was noted in 0.33% of patients. HELLP syndrome is the most frequent cause leading to ARF during pregnancy (16, 17). As expected, we found that the most frequent cause of ARF during pregnancy was HELLP syndrome (10.7%), which agreed with previous studies (16, 17). Maternal deaths associated with hypertensive disorders of pregnancy assumed greater importance than etiologies that were previously more frequently encountered, such as infection and hemorrhage. In our study, maternal deaths were due to intracranial hemorrhage and ARDS.
It is generally accepted that perinatal and neonatal morbidity and mortality rates increase in pregnancies complicated by severe preeclampsia, eclampsia, or HELLP syndrome. Different perinatal morbidity and mortality rates are presented in the literature (18–20). Although neonatal morbidity was generally similar across groups in our study, perinatal mortality was higher in pregnancies complicated by HELLP syndrome or severe preeclampsia before 32 weeks of gestation due to an increased number of stillbirths. Interestingly, the eclampsia group performed somewhat better considering early (<32 weeks) fetal losses. This was probably due to more abdominal deliveries and fewer growth-restricted fetuses in the eclampsia group. The high number of patients in the study population who did not have regular prenatal follow-ups may explain the high fetal and perinatal mortality. These findings suggest that perinatal morbidity and mortality are gestational-age dependent rather than disease dependent in cases with severe preeclampsia, eclampsia, or HELLP syndrome. Magann et al. determined that fetal morbidity and mortality are dependent on gestational age and reported similar and nonsignificant relationships between HELLP syndrome, severe preeclampsia, and eclampsia (21). Romero et al. showed that the majority of neonatal complications are due to prematurity (22).
Severe preeclampsia, eclampsia, or HELLP syndrome manifest on average between 32 and 34 weeks of gestation. It is common clinical practice that a 32–34-week pregnancy should be delivered immediately. Before 32–34 weeks, expectant management is generally possible for selected patients in a perinatal center (23). Steroids are administered to induce fetal lung maturity. We prefer aggressive management in cases involving HELLP syndrome and eclampsia. In our study, we determined a median gestational age of 34 weeks (range, 31.05–35.9 weeks) for the appearance of HELLP syndrome, which was lower than that for severe preeclampsia and eclampsia.
The only effective treatment for severe preeclampsia/eclampsia and HELLP syndrome is delivery, but no randomized trial has been conducted to determine the optimal method of delivery. The rate of cesarean delivery increases with increased occurrence of hypertensive disorders during pregnancy (24). Vaginal delivery is recommended for severely preeclamptic cases in the absence of obstetric indications for a cesarean section. In our study, women with eclampsia were more likely to deliver by cesarean section than were those with HELLP syndrome or severe preeclampsia. Fetal distress was the most frequent indication for cesarean section.
In summary, as expected, this study demonstrated that pregnancies complicated by HELLP syndrome have significantly higher maternal morbidity than do those with severe preeclampsia and eclampsia. Perinatal and neonatal mortality as neonatal morbidity were similar among the groups. When an analysis was performed according to gestational age, a significant difference was observed in perinatal and fetal mortality before compared with after 32 weeks of gestation. These findings indicate that perinatal and neonatal outcomes of severe preeclampsia, eclampsia, and HELLP syndrome are dependent on the gestational age of delivery and are not diagnosis dependent.
Footnotes
Conflict of interest
No conflict of interest was declared by the authors.
References
- 1.Roberts JM, Pearson G, Cutler J, Lindheimer M. Summary of the NHLBI Working Group on Research on Hypertension during Pregnancy. Hypertension. 2003;41:437–45. doi: 10.1161/01.HYP.0000054981.03589.E9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Villar J, Say L, Gulmezoglu AM, Marialdi M, Lindheimer MD, Betran AP, et al. Pre-eclampsia eclampsia: a health problem for 2000 years. In: Critchly H, MacLean A, Poston L, Walker J, editors. Preeclampsia. London, England: RCOG Press; 2003. pp. 189–207. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Bergström S, Povey G, Songane F, Ching C. Seasonal incidence of eclampsia, its relationship to meteorological data in Mozambique. J Perinat Med. 1992;20:153–8. doi: 10.1515/jpme.1992.20.2.153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Odendaal HJ, Pattinson RC, Bam R, Grove D, Kotze TJ. Aggressive or expectant management for patients with severe preeclampsia between 28–34 weeks’ gestation: A randomized controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol. 1990;76:1070–5. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Sibai BM, Akl S, Fairlie F, Moretti M. A protocol for managing severe preeclampsia in the second trimester. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1990;163:733–8. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(90)91058-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Chua S, Redman CW. Prognosis for preeclampsia complicated by 5 g or more of proteinuria in 24 hours. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 1992;43:9–12. doi: 10.1016/0028-2243(92)90236-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Oláh KS, Redman CW, Gee H. Management of severe, early preeclampsia: is conservative management justified? Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 1993;51:175–80. doi: 10.1016/0028-2243(93)90032-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.İmir GA, Kol İO, Kaygusuz K, Cetin A, Cetin M, Guvenal T, et al. Perinatal Outcomes in HELLP Syndrome. J Turkish-German Gynecol Assoc. 2008;9:89–93. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Börekçi B, Bebek Z, İngeç M, Kadanalı S. Effects of Postpartum Corticosteroids in Patients with HELLP Syndrome. J Turkish- German Gynecol Assoc. 2008;9:79–83. [Google Scholar]
- 10.American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists: Hypertension in Pregnancy. Washington: The College; 1996. (Tech Bull No. 219). http://mail.ny.acog.org/website/SMIPodcast/ChronicHypertension.pdf. [Google Scholar]
- 11.Martin JN, Jr, Rinehart BK, May WL, Magann EF, Terrone DA, Blake PG. The spectrum of severe preeclampsia: Comparative analysis by HELLP (hemolysis, elevated liver enzyme levels, and low platelet count) syndrome classification. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1999;180:1373–84. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9378(99)70022-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Isler CM, Rinehart BK, Terrone DA, Martin RW, Magann EF, Martin JN., Jr Maternal mortality associated with HELLP (hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, and low platelets) syndrome. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1999;181:924–8. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9378(99)70343-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Martin JN, Jr, Blake PG, Perry KG, Jr, McCaul JF, Hess LW, Martin RW. The natural history of HELLP syndrome: patterns of disease progression and regression. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1991;164:1500–13. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(91)91429-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Levine RJ, Hauth JC, Curet LB, Sibai BM, Catalano PM, Morris CD, et al. Trial of calcium to prevent preeclampsia. N Engl J Med. 1997;337:69–76. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199707103370201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Audibert F, Friedman SA, Frangieh AY, Sibai BM. Clinical utility of strict diagnostic criteria for the HELLP (hemolysis, elevated liver enzyme levels, and low platelets) syndrome. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1996;175:460–4. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9378(96)70162-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Sibai BM, Ramadan MK, Usta I, Salama M, Mercer BM, Friedman SA. Maternal morbidity and mortality in 442 pregnancies with hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, and low platelets (HELLP syndrome) Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1993;169:1000–6. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(93)90043-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Haddad B, Barton JR, Livingston JC, Chahine R, Sibai BM, et al. Risk factors for adverse maternal outcomes among women with HELLP (hemolysis, elevated liver enzyme levels, and low platelets) syndrome. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2000;183:444–8. doi: 10.1067/mob.2000.105915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Yücesoy G, Özkan S, Bodur H, Tan T, Çalışkan E, Vural B, et al. Maternal and perinatal outcome in pregnancies complicated with hypertensive disorder of pregnancy: a seven year experience of a tertiary care center. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2005;273:43–9. doi: 10.1007/s00404-005-0741-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Gul A, Cebeci A, Aslan H, Polat I, Ozdemir A, Ceylan Y. Perinatal outcomes in severe preeclampsia – eclampsia with and without HELLP syndrome. Gynecol Obstet Invest. 2005;59:113–8. doi: 10.1159/000082648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Raval DS, Co S, Reid MA, Pildes R. Maternal and neonatal outcome of pregnancies complicated with maternal HELLP syndrome. J Perinatol. 1997;17:266–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Magann EF, Perry KG, Chauhan SP, Graves GR, Blake PG, Martin JN., Jr Neonatal salvage by weeks’ gestation in pregnancies complicated by HELLP syndrome. J Soc Gynecol Invest. 1994;1:206–9. doi: 10.1177/107155769400100305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Romero R, Mazor M, Lockwood CJ, Emamian M, Belanger KP, Hobbins JC, et al. Clinical significance, prevalence and natural history of thrombocytopenia in pregnancy-induced hypertension. Am J Perinatol. 1989;6:32–8. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-999540. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Sibai BM, Mercer BM, Schiff E, Freidman SA. Aggressive versus expectant management of severe preeclampsia at 28 to 32 weeks’ gestation: a randomized controlled trial. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1994;171:818–22. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(94)90104-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Gofton EN, Capewell V, Natale R, Gratton RJ. Obstetrical intervention rates and maternal and neonatal outcomes of women with gestational hypertension. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2001;185:798–803. doi: 10.1067/mob.2001.117314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]