Abstract
Cultures of neurite-bearing pheochromocytoma (PC12) cells and of sympathetic neurons have been examined by time-lapse video microscopy. In the presence of nerve growth factor (NGF), the neurites of such cultures elongated and their growth cones changed geometry, via microspike and lamellipodial motion, on a time scale of minutes. Withdrawal of NGF caused process extension to cease and a progressive reduction in growth-cone area as a result of retraction of lamellipodia and microspikes. By approximately equal to 4 hr after NGF withdrawal, most neurite tips were smooth sided, devoid of conical expansions at their termini, and virtually immobile. Addition of NGF to cultures from which it had been withdrawn induced motion of microspikes and projections from the upper surface of growth cones within 2 min, while lamellipodial spreading and neurite reextension were induced after approximately equal to 20 min. For PC12 cells, these responses to replacement of NGF could not be mimicked by addition of dibutyryl cAMP (less than or equal to 2 mM) or the Ca2+ ionophore A23187 (less than or equal to 5 microM) to NGF-deprived cultures nor inhibited by the presence of EGTA (less than or equal to 2 mM) or calcium antagonists in the culture medium. Since neurite fragments formed by transection of processes of PC12 cells deprived of NGF responded to its replacement in a manner similar to intact neurites, it is concluded that the effects are focal to the neurite and growth cone and independent of the cell body. This influence of NGF on growth-cone shape and motility represents short-term local activation of this structure and has significance for control of neurite extension.
Full text
PDF

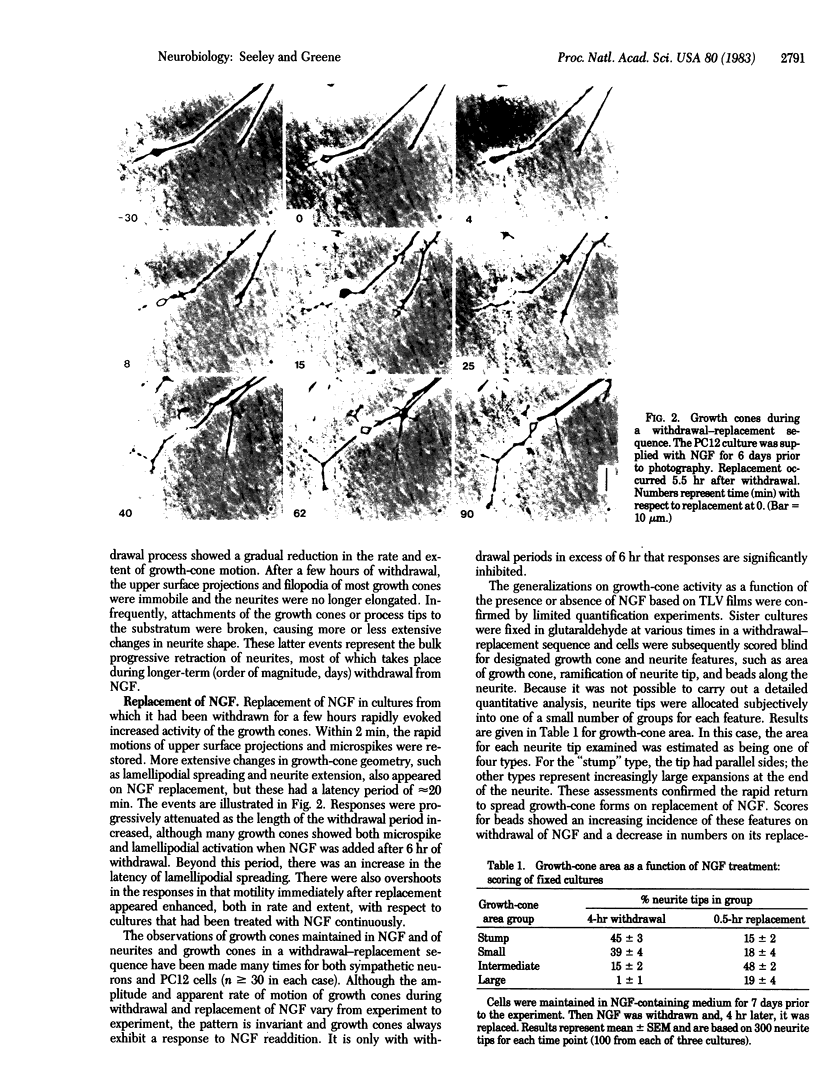


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burstein D. E., Greene L. A. Evidence for RNA synthesis-dependent and -independent pathways in stimulation of neurite outgrowth by nerve growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):6059–6063. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.6059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campenot R. B. Local control of neurite development by nerve growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4516–4519. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4516. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connolly J. L., Green S. A., Greene L. A. Pit formation and rapid changes in surface morphology of sympathetic neurons in response to nerve growth factor. J Cell Biol. 1981 Jul;90(1):176–180. doi: 10.1083/jcb.90.1.176. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connolly J. L., Greene L. A., Viscarello R. R., Riley W. D. Rapid, sequential changes in surface morphology of PC12 pheochromocytoma cells in response to nerve growth factor. J Cell Biol. 1979 Sep;82(3):820–827. doi: 10.1083/jcb.82.3.820. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desmedt J. E., Hainaut K. Inhibition of the intracellular release of calcium by Dantrolene in barnacle giant muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1977 Feb;265(2):565–585. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene L. A., Rukenstein A. Regulation of acetylcholinesterase activity by nerve growth factor. Role of transcription and dissociation from effects on proliferation and neurite outgrowth. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jun 25;256(12):6363–6367. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene L. A., Shooter E. M. The nerve growth factor: biochemistry, synthesis, and mechanism of action. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1980;3:353–402. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.03.030180.002033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin C. G., Letourneau P. C. Rapid retraction of neurites by sensory neurons in response to increased concentrations of nerve growth factor. J Cell Biol. 1980 Jul;86(1):156–161. doi: 10.1083/jcb.86.1.156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gundersen R. W., Barrett J. N. Characterization of the turning response of dorsal root neurites toward nerve growth factor. J Cell Biol. 1980 Dec;87(3 Pt 1):546–554. doi: 10.1083/jcb.87.3.546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUGHES A. The growth of embryonic neurites; a study of cultures of chick neural tissues. J Anat. 1953 Apr;87(2):150–162. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halegoua S., Patrick J. Nerve growth factor mediates phosphorylation of specific proteins. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(2 Pt 2):571–581. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90367-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horii Z. I., Varon S. Nerve growth factor action on membrane permeation to exogenous substrates in dorsal root ganglionic dissociates from the chick embryo. Brain Res. 1977 Mar 18;124(1):121–133. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90868-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huff K., End D., Guroff G. Nerve growth factor-induced alteration in the response of PC12 pheochromocytoma cells to epidermal growth factor. J Cell Biol. 1981 Jan;88(1):189–198. doi: 10.1083/jcb.88.1.189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohlhardt M., Bauer B., Krause H., Fleckenstein A. Differentiation of the transmembrane Na and Ca channels in mammalian cardiac fibres by the use of specific inhibitors. Pflugers Arch. 1972;335(4):309–322. doi: 10.1007/BF00586221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee V. M., Shelanski M. L., Greene L. A. Characterization of antisera raised against cultured rat sympathetic neurons. Neuroscience. 1980;5(12):2239–2245. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(80)90140-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGuire J. C., Greene L. A., Furano A. V. NGF stimulates incorporation of fucose or glucosamine into an external glycoprotein in cultured rat PC12 pheochromocytoma cells. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):357–365. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90004-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGuire J. C., Greene L. A. Rapid stimulation by nerve growth factor of amino acid uptake by clonal PC12 pheochromocytoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1979 May 10;254(9):3362–3367. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mobley W. C., Schenker A., Shooter E. M. Characterization and isolation of proteolytically modified nerve growth factor. Biochemistry. 1976 Dec 14;15(25):5543–5552. doi: 10.1021/bi00670a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NAKAI J. Studies on the mechanism determining the course of nerve fibers in tissue culture. II. The mechanism of fasciculation. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1960;52:427–449. doi: 10.1007/BF00339758. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savage C. R., Jr, Cohen S. Epidermal growth factor and a new derivative. Rapid isolation procedures and biological and chemical characterization. J Biol Chem. 1972 Dec 10;247(23):7609–7611. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schechter A. L., Bothwell M. A. Nerve growth factor receptors on PC12 cells: evidence for two receptor classes with differing cytoskeletal association. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):867–874. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90112-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schubert D., LaCorbiere M., Whitlock C., Stallcup W. Alterations in the surface properties of cells responsive to nerve growth factor. Nature. 1978 Jun 29;273(5665):718–723. doi: 10.1038/273718a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varon S. S., Bunge R. P. Trophic mechanisms in the peripheral nervous system. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1978;1:327–361. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.01.030178.001551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wessells N. K., Johnson S. R., Nuttall R. P. Axon initiation and growth cone regeneration in cultured motor neurons. Exp Cell Res. 1978 Dec;117(2):335–345. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(78)90147-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yankner B. A., Shooter E. M. Nerve growth factor in the nucleus: interaction with receptors on the nuclear membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1269–1273. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu M. W., Tolson N. W., Guroff G. Increased phosphorylation of specific nuclear proteins in superior cervical ganglia and PC12 cells in response to nerve growth factor. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 10;255(21):10481–10492. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]