Abstract
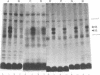
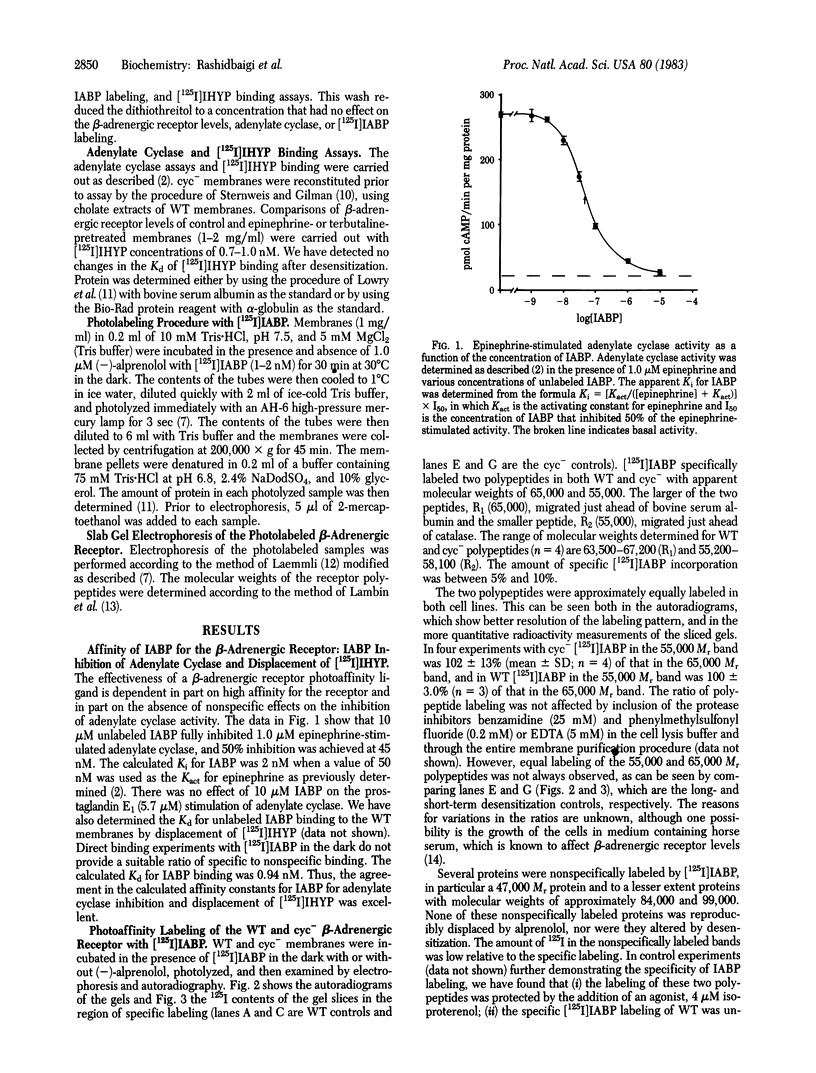
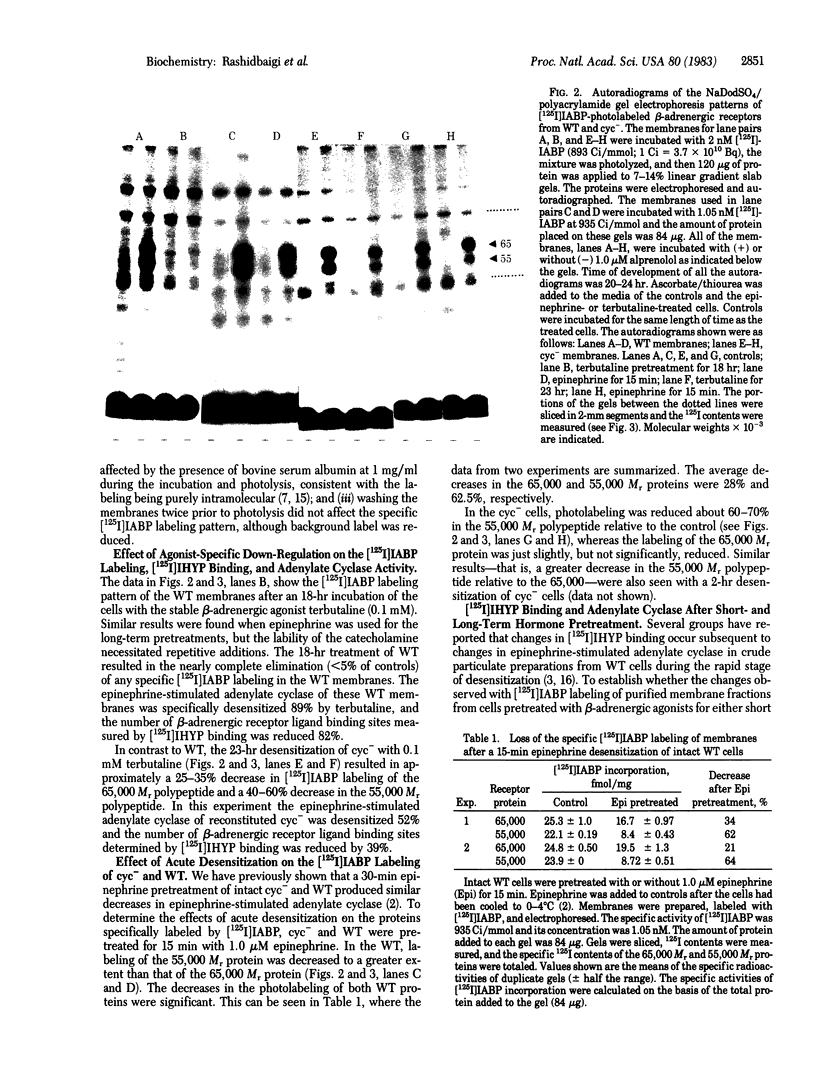
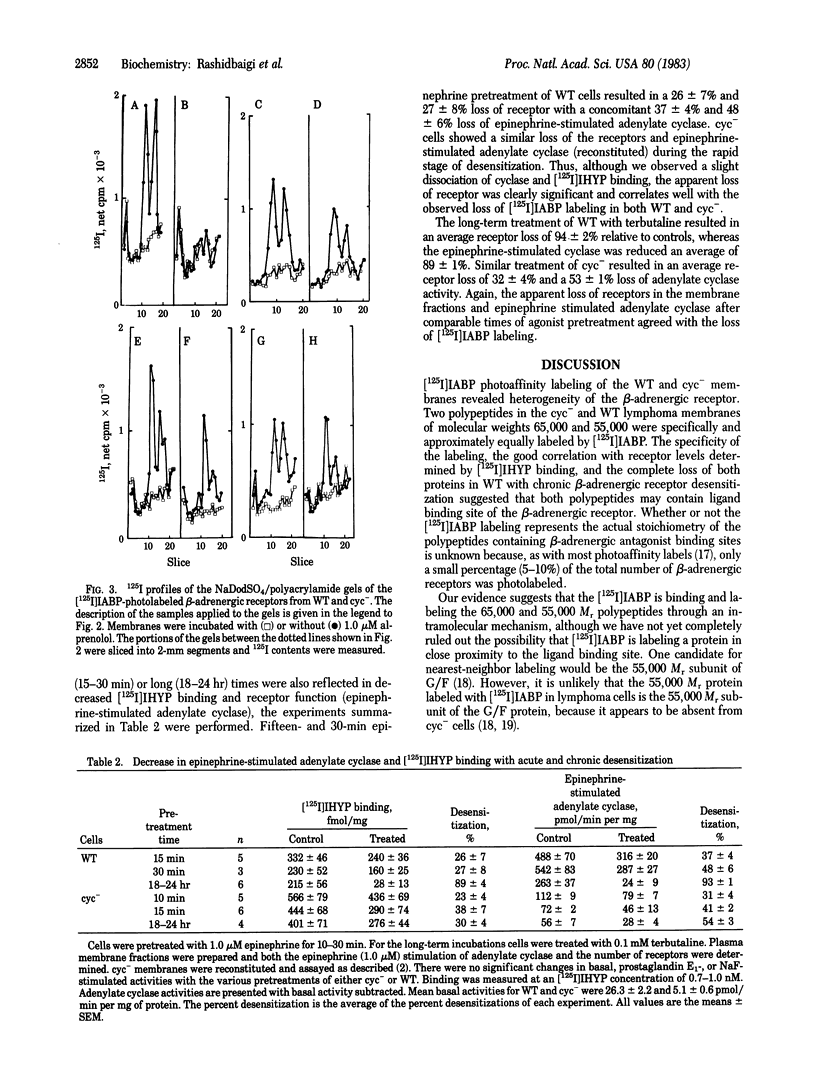
The beta-adrenergic antagonist [125I]iodoazidobenzylpindolol ( [125I]IABP) specifically photolabeled two polypeptides in membrane preparations from wild-type (WT) and coupling protein-deficient cyc- cultured lymphoma cells. The molecular weights of the two polypeptides determined by sodium dodecyl sulfate/polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis were 65,000 and 55,000. They were labeled in a ratio of approximately 1:1. Pretreatment of intact WT or cyc- cells with 1.0 microM epinephrine for 15 min (desensitization) resulted in a greater loss of the 55,000 Mr polypeptide (40-60%) relative to the 65,000 Mr peptide (10-30% loss). An 18- to 24-hr pretreatment of WT cells with terbutaline (down-regulation) led to a greater than 90% reduction of the photolabeling of both polypeptides, whereas a similar pretreatment of cyc- cells resulted in no further loss of labeled receptor than that observed after only a 15-min pretreatment with epinephrine. There was no indication of a change in the electrophoretic mobility of the [125I]IABP-labeled receptors after either short- or long-term agonist pretreatment. These data provide direct evidence for heterogeneity of the beta-adrenergic receptor in lymphoma cells. The differential loss of the [125I]IABP labeling in the two polypeptides suggests a functional heterogeneity as well.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brunton L. L., Maguire M. E., Anderson H. J., Gilman A. G. Expression of genes for metabolism of cyclic adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate in somatic cells. beta-Adrenergic and PGE1 receptors in parental and hybrid cells. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 25;252(4):1293–1302. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhry V., Westheimer F. H. Photoaffinity labeling of biological systems. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:293–325. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.001453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R. B., Goka T. J., Green D. A., Barber R., Butcher R. W. Differences in the forskolin activation of adenylate cyclases in wild-type and variant lymphoma cells. Mol Pharmacol. 1982 Nov;22(3):609–613. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dibner M. D., Insel P. A. Serum catecholamines desensitize beta-adrenergic receptors of cultured C6 glioma cells. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jul 25;256(14):7343–7346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green D. A., Clark R. B. Adenylate cyclase coupling proteins are not essential for agonist-specific desensitization of lymphoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1981 Mar 10;256(5):2105–2108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green D. A., Friedman J., Clark R. B. Epinephrine desensitization of adenylate cyclase from cyc- and S49 cultured lymphoma cells. J Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1981;7(3):161–172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harden T. K., Cotton C. U., Waldo G. L., Lutton J. K., Perkins J. P. Catecholamine-induced alteration in sedimentation behavior of membrane bound beta-adrenergic receptors. Science. 1980 Oct;210(4468):441–443. doi: 10.1126/science.6254143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iyengar R., Bhat M. K., Riser M. E., Birnbaumer L. Receptor-specific desensitization of the S49 lymphoma cell adenylyl cyclase. Unaltered behavior of the regulatory component. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 25;256(10):4810–4815. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson G. L., Kaslow H. R., Bourne H. R. Genetic evidence that cholera toxin substrates are regulatory components of adenylate cyclase. J Biol Chem. 1978 Oct 25;253(20):7120–7123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambin P., Rochu D., Fine J. M. A new method for determination of molecular weights of proteins by electrophoresis across a sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS)-polyacrylamide gradient gel. Anal Biochem. 1976 Aug;74(2):567–575. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90239-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rashidbaigi A., Ruoho A. E. Iodoazidobenzylpindolol, a photoaffinity probe for the beta-adrenergic receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1609–1613. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rashidbaigi A., Ruoho A. E. Photoaffinity labeling of beta-adrenergic receptors: identification of the beta-receptor binding site(s) from turkey, pigeon, and frog erythrocyte. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 May 14;106(1):139–148. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)92069-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rashidbaigi A., Ruoho A. E. Synthesis and characterization of iodoazidobenzylpindolol. J Pharm Sci. 1982 Mar;71(3):305–307. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600710310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross E. M., Gilman A. G. Biochemical properties of hormone-sensitive adenylate cyclase. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:533–564. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.002533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoho A. E., Kiefer H., Roeder P. E., Singer S. J. The mechanism of photoaffinity labeling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Sep;70(9):2567–2571. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.9.2567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shear M., Insel P. A., Melmon K. L., Coffino P. Agonist-specific refractoriness induced by isoproterenol. Studies with mutant cells. J Biol Chem. 1976 Dec 10;251(23):7572–7576. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stadel J. M., De Lean A., Mullikin-Kilpatrick D., Sawyer D. D., Lefkowitz R. J. Catecholamine-induced desensitization in turkey erythrocytes: cAMP mediated impairment of high affinity agonist binding without alteration in receptor number. J Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1981;7(1):37–47. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stadel J. M., Nambi P., Lavin T. N., Heald S. L., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Catecholamine-induced desensitization of turkey erythrocyte adenylate cyclase. Structural alterations in the beta-adrenergic receptor revealed by photoaffinity labeling. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 25;257(16):9242–9245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternweis P. C., Gilman A. G. Reconstitution of catecholamine-sensitive adenylate cyclase. Reconstitution of the uncoupled variant of the S40 lymphoma cell. J Biol Chem. 1979 May 10;254(9):3333–3340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su Y. F., Harden T. K., Perkins J. P. Catecholamine-specific desensitization of adenylate cyclase. Evidence for a multistep process. J Biol Chem. 1980 Aug 10;255(15):7410–7419. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]