Abstract
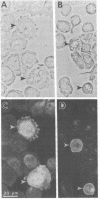
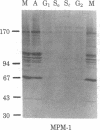
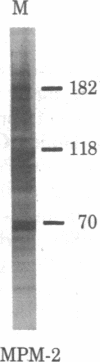
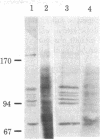
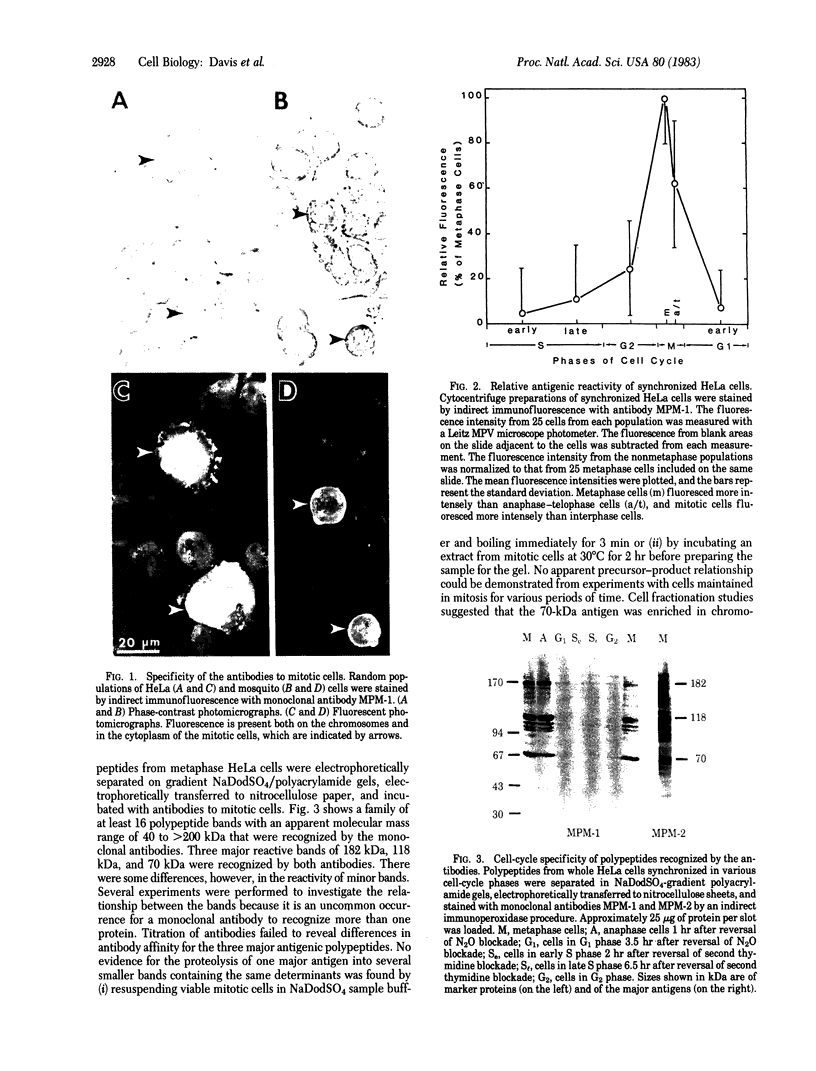
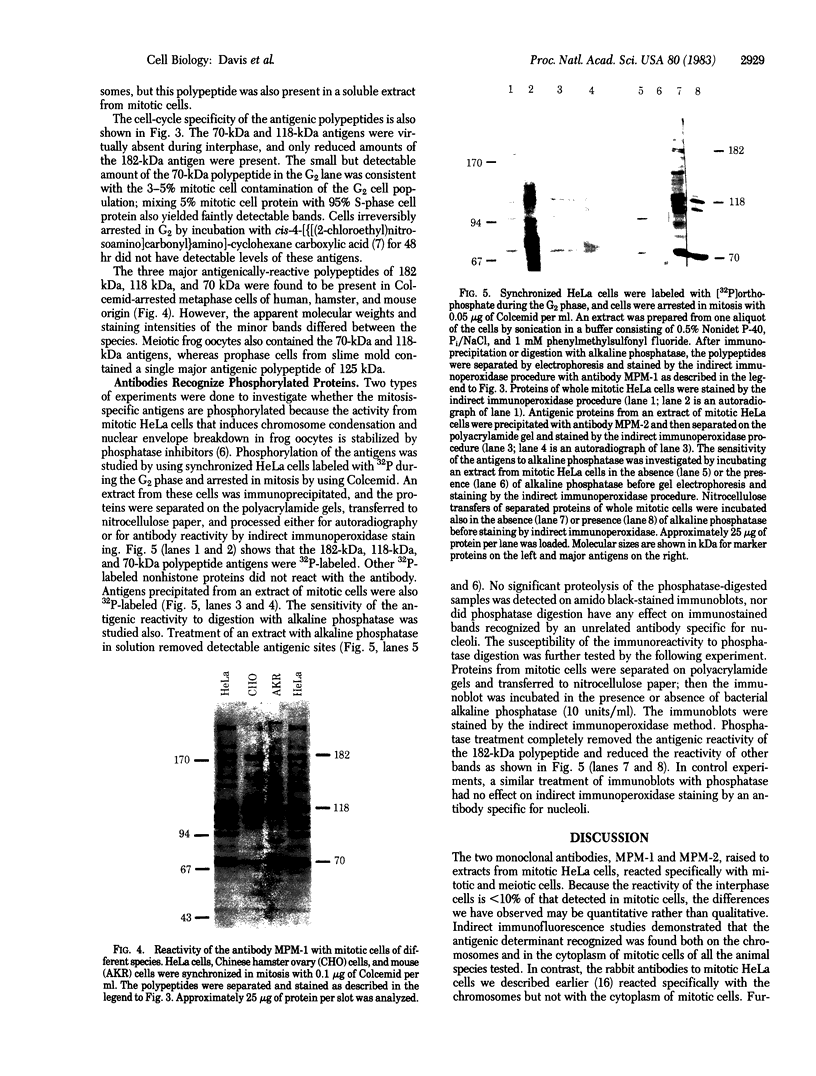
Certain proteins or activities are present in mitotic cells but not in interphase cells. These proteins may be synthesized or activated, or both, just prior to mitosis and are responsible for the breakdown of the nuclear envelope and the condensation of chromosomes. To learn more about the nature of these proteins, we raised monoclonal antibodies to mitotic cells. Spleen cells from mice immunized with a 0.15 M NaCl extract of synchronized mitotic HeLa cells were fused with SP2/0-Ag14 mouse myeloma cells, and hybrids were selected in medium containing hypoxanthine, methotrexate, thymidine, and glycine. Two different hybridoma clones secreting antibodies reactive with mitotic and meiotic cells from every species tested were isolated. Chromosomes as well as cytoplasm in mitotic cells reacted with the antibodies, as detected by indirect immunofluorescence. The proteins from mitotic cells were separated by electrophoresis in NaDodSO4/polyacrylamide slab gels, transferred to nitrocellulose sheets, and stained immunochemically. The two antibodies, designated MPM-1 and MPM-2, recognize a family of polypeptides with apparent molecular masses of 0.40 to greater than 200 kilodaltons (kDa). Both antibodies reacted strongly with three polypeptide bands of 182 kDa, 118 kDa, and 70 kDa. Only mitotic cells exhibited the protein bands that were recognized by the antibodies. All these bands were found to be phosphoproteins as shown by 32P labeling and autoradiography and their removal by alkaline phosphatase treatment.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adlakha R. C., Sahasrabuddhe C. G., Wright D. A., Lindsey W. F., Rao P. N. Localization of mitotic factors on metaphase chromosomes. J Cell Sci. 1982 Apr;54:193–206. doi: 10.1242/jcs.54.1.193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Al-Bader A. A., Orengo A., Rao P. N. G2 phase-specific proteins of HeLa cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):6064–6068. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.6064. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradbury E. M., Inglis R. J., Matthews H. R. Control of cell division by very lysine rich histone (F1) phosphorylation. Nature. 1974 Feb 1;247(5439):257–261. doi: 10.1038/247257a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis F. M., Busch R. K., Yeoman L. C., Busch H. Differences in nucleolar antigens of rat liver and Novikoff hepatoma ascites cells. Cancer Res. 1978 Jul;38(7):1906–1915. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis F. M., Rao P. N. Antibodies specific for mitotic human chromosomes. Exp Cell Res. 1982 Feb;137(2):381–386. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(82)90039-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen R. S., Beavo J. A. Purification of two calcium/calmodulin-dependent forms of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase by using conformation-specific monoclonal antibody chromatography. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(9):2788–2792. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.9.2788. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodge L. D., Mancini P., Davis F. M., Heywood P. Nuclear matrix of HeLa S3 cells. Polypeptide composition during adenovirus infection and in phases of the cell cycle. J Cell Biol. 1977 Jan;72(1):194–208. doi: 10.1083/jcb.72.1.194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodge P. W., Wright F. W. Meteoritic spherules in the soil surrounding terrestrial impact craters. Nature. 1970 Feb 21;225(5234):717–718. doi: 10.1038/225717a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennett R. H. Cell fusion. Methods Enzymol. 1979;58:345–359. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(79)58149-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krystal G. W., Poccia D. L. Phosphorylation of cleavage stage histone H1 in mitotic and prematurely condensed chromosomes. Exp Cell Res. 1981 Jul;134(1):41–48. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(81)90461-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity. Nature. 1975 Aug 7;256(5517):495–497. doi: 10.1038/256495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine L., Van Vunakis H., Gallo R. C. Serologic specificities of methylated base immune systems. Biochemistry. 1971 May 25;10(11):2009–2013. doi: 10.1021/bi00787a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen D. F., Tobey R. A., Anderson E. C. Synchronously dividing mammalian cells. Fed Proc. 1969 Nov-Dec;28(6):1771–1779. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao P. N. Mitotic synchrony in mammalian cells treated with nitrous oxide at high pressure. Science. 1968 May 17;160(3829):774–776. doi: 10.1126/science.160.3829.774. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sunkara P. S., Wright D. A., Rao P. N. Mitotic factors from mammalian cells induce germinal vesicle breakdown and chromosome condensation in amphibian oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2799–2802. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanphaichitr N., Moore K. C., Granner D. K., Chalkley R. Relationship between chromosome condensation and metaphase lysine-rich histone phosphorylation. J Cell Biol. 1976 Apr;69(1):43–50. doi: 10.1083/jcb.69.1.43. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobey R. A., Petersen D. F., Anderson E. C., Puck T. T. Life cycle analysis of mammalian cells. 3. The inhibition of division in Chinese hamster cells by puromycin and actinomycin. Biophys J. 1966 Sep;6(5):567–581. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3495(66)86678-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu M., Gerhart J. C. Partial purification and characterization of the maturation-promoting factor from eggs of Xenopus laevis. Dev Biol. 1980 Oct;79(2):465–477. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(80)90131-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]