Abstract
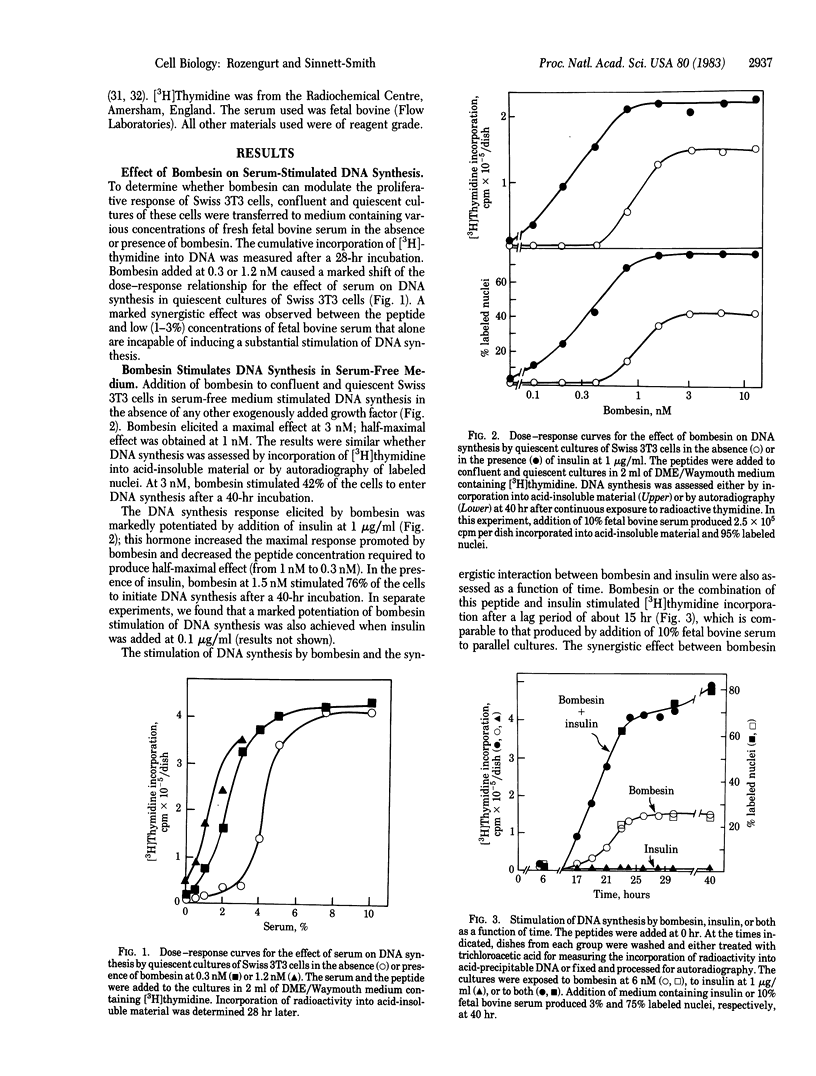
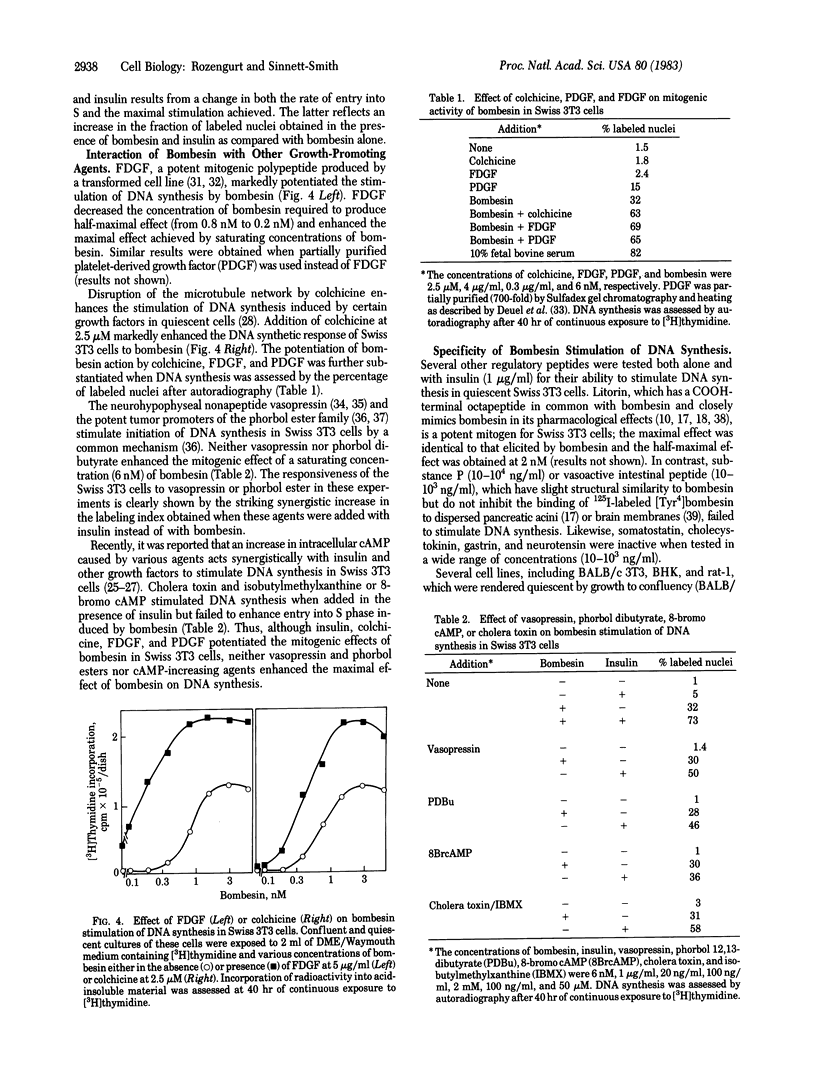
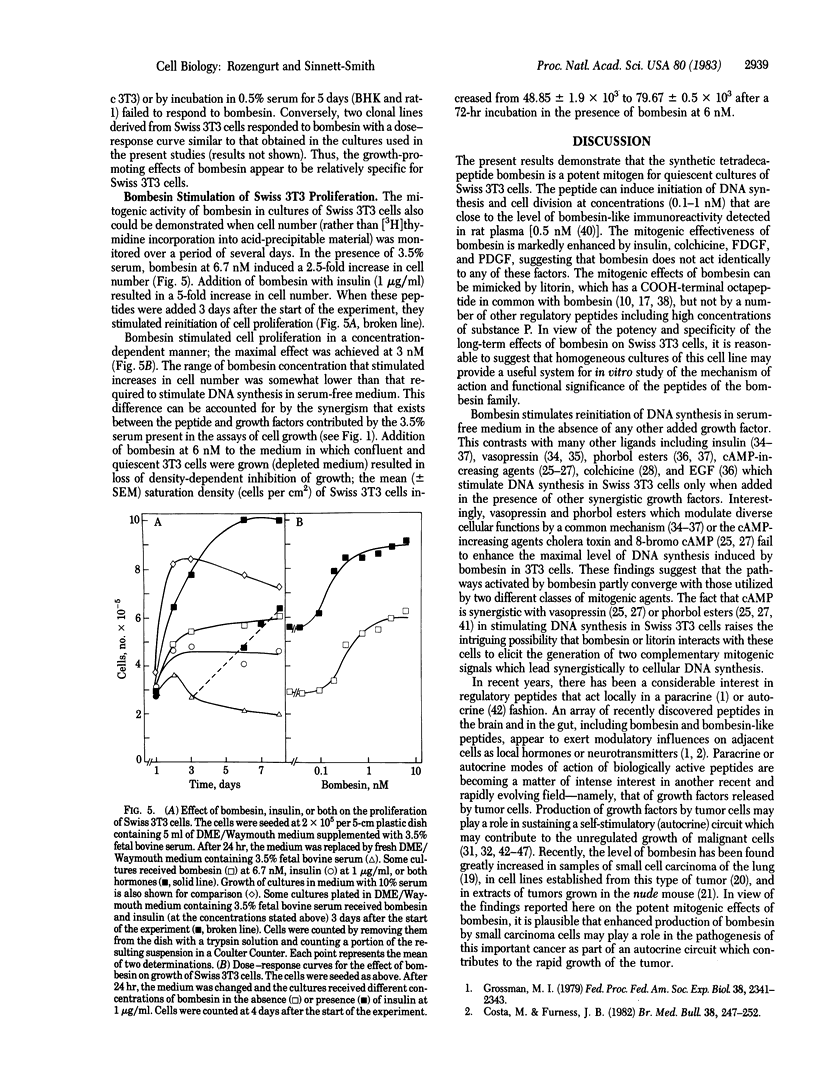
Bombesin is shown to be a potent mitogen for Swiss 3T3 cells. At nanomolar concentrations the peptide markedly enhances the ability of fresh serum to stimulate DNA synthesis in confluent and quiescent cultures of these cells. In the presence of a low concentration (3.5%) of serum, bombesin stimulates 3T3 cell proliferation. In serum-free medium, bombesin induces DNA synthesis in the absence of any other added growth factor; half-maximal effect is obtained at 1 nM. The mitogenic effect of bombesin is dependent on dose and time, is mimicked by litorin, and is markedly potentiated by insulin, colchicine, platelet-derived growth factor, and fibroblast-derived growth factor. These mitogens increase the maximal response elicited by bombesin and decrease the bombesin concentration required to produce half-maximal effect (from 1 nM to 0.3 nM). In contrast, vasopressin, phorbol esters, or cAMP increasing agents fail to enhance the maximal level of DNA synthesis induced by bombesin. Bombesin and litorin may provide useful model peptides for studies on the mechanism(s) by which extracellular ligands control cell proliferation.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anastasi A., Erspamer V., Bucci M. Isolation and structure of bombesin and alytesin, 2 analogous active peptides from the skin of the European amphibians Bombina and Alytes. Experientia. 1971 Feb 15;27(2):166–167. doi: 10.1007/BF02145873. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne H. R., Rozengurt E. An 18,000 molecular weight polypeptide induces early events and stimulates DNA synthesis in cultured cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Dec;73(12):4555–4559. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.12.4555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broccardo M., Falconieri Erspamer G., Melchiorri P., Negri L., de Castiglione R. Relative potency of bombesin-like peptides. Br J Pharmacol. 1975 Oct;55(2):221–227. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1975.tb07631.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M., Allen R., Villarreal J., Rivier J., Vale W. Bombesin-like activity: radioimmunologic assessment in biological tissues. Life Sci. 1978 Dec 31;23(27-28):2721–2728. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(78)90652-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins M. K., Rozengurt E. Binding of phorbol esters to high-affinity sites on murine fibroblastic cells elicits a mitogenic response. J Cell Physiol. 1982 Jul;112(1):42–50. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041120108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins M., Rozengurt E. Stimulation of DNA synthesis in murine fibroblasts by the tumour promoter teleocidin: relationship to phorbol esters and vasopressin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Feb 26;104(4):1159–1166. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91372-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa M., Furness J. B. Neuronal peptides in the intestine. Br Med Bull. 1982 Sep;38(3):247–252. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a071768. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deuel T. F., Huang J. S., Proffitt R. T., Baenziger J. U., Chang D., Kennedy B. B. Human platelet-derived growth factor. Purification and resolution into two active protein fractions. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 10;256(17):8896–8899. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dicker P., Pohjanpelto P., Pettican P., Rozengurt E. Similarities between fibroblast-derived growth factor and platelet-derived growth factor. Exp Cell Res. 1981 Sep;135(1):221–227. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(81)90314-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dicker P., Rozengurt E. Phorbol esters and vasopressin stimulate DNA synthesis by a common mechanism. Nature. 1980 Oct 16;287(5783):607–612. doi: 10.1038/287607a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erisman M. D., Linnoila R. I., Hernandez O., DiAugustine R. P., Lazarus L. H. Human lung small-cell carcinoma contains bombesin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(7):2379–2383. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.7.2379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedkin M., Rozengurt E. The role of cytoplasmic microtubules in the regulation of the activity of peptide growth factors. Adv Enzyme Regul. 1980;19:39–59. doi: 10.1016/0065-2571(81)90008-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghatei M. A., Jung R. T., Stevenson J. C., Hillyard C. J., Adrian T. E., Lee Y. C., Christofides N. D., Sarson D. L., Mashiter K., MacIntyre I. Bombesin: action on gut hormones and calcium in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1982 May;54(5):980–985. doi: 10.1210/jcem-54-5-980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghatei M. A., Sheppard M. N., O'Shaughnessy D. J., Adrian T. E., McGregor G. P., Polak J. M., Bloom S. R. Regulatory peptides in the mammalian respiratory tract. Endocrinology. 1982 Oct;111(4):1248–1254. doi: 10.1210/endo-111-4-1248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs J., Fauser D. J., Rowe E. A., Rolls B. J., Rolls E. T., Maddison S. P. Bombesin suppresses feeding in rats. Nature. 1979 Nov 8;282(5735):208–210. doi: 10.1038/282208a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossman M. I. Chemical messengers: a view from the gut. Fed Proc. 1979 Aug;38(9):2341–2343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwatsuki N., Petersen O. H. In vitro action of bombesin on amylase secretion, membrane potential, and membrane resistance in rat and mouse pancreatic acinar cells. A comparison with other secretagogues. J Clin Invest. 1978 Jan;61(1):41–46. doi: 10.1172/JCI108923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen R. T., Moody T., Pert C., Rivier J. E., Gardner J. D. Interaction of bombesin and litorin with specific membrane receptors on pancreatic acinar cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):6139–6143. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.6139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaneto A., Kaneko T., Nakaya S., Kajinuma H., Kosaka K. Effect of bombesin infused intrapancreatically on glucagon and insulin secretion. Metabolism. 1978 May;27(5):549–553. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(78)90021-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald T. J., Jörnvall H., Nilsson G., Vagne M., Ghatei M., Bloom S. R., Mutt V. Characterization of a gastrin releasing peptide from porcine non-antral gastric tissue. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Sep 12;90(1):227–233. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91614-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moody T. W., Pert C. B. Bombesin-like peptides in rat brain: quantitation and biochemical characterization. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Sep 12;90(1):7–14. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91582-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moody T. W., Pert C. B., Gazdar A. F., Carney D. N., Minna J. D. High levels of intracellular bombesin characterize human small-cell lung carcinoma. Science. 1981 Dec 11;214(4526):1246–1248. doi: 10.1126/science.6272398. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moody T. W., Pert C. B., Rivier J., Brown M. R. Bomebesin: specific binding to rat brain membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5372–5376. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moses H. L., Branum E. L., Proper J. A., Robinson R. A. Transforming growth factor production by chemically transformed cells. Cancer Res. 1981 Jul;41(7):2842–2848. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozanne B., Fulton R. J., Kaplan P. L. Kirsten murine sarcoma virus transformed cell lines and a spontaneously transformed rat cell-line produce transforming factors. J Cell Physiol. 1980 Oct;105(1):163–180. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041050118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polak J. A., Bloom S. R. Localization of regulatory peptides in the gut. Br Med Bull. 1982 Sep;38(3):303–307. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a071777. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivier C., Rivier J., Vale W. The effect of bombesin and related peptides on prolactin and growth hormone secretion in the rat. Endocrinology. 1978 Feb;102(2):519–522. doi: 10.1210/endo-102-2-519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivier J. E., Brown M. R. Bombesin, bombesin analogues, and related peptides: effects on thermoregulation. Biochemistry. 1978 May 2;17(9):1766–1771. doi: 10.1021/bi00602a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts A. B., Anzano M. A., Lamb L. C., Smith J. M., Sporn M. B. New class of transforming growth factors potentiated by epidermal growth factor: isolation from non-neoplastic tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5339–5343. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozengurt E. Adenosine receptor activation in quiescent Swiss 3T3 cells. Enhancement of cAMP levels, DNA synthesis and cell division. Exp Cell Res. 1982 May;139(1):71–78. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(82)90319-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozengurt E., Brown K. D., Pettican P. Vasopressin inhibition of epidermal growth factor binding to cultured mouse cells. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 25;256(2):716–722. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozengurt E., Collins M., Brown K. D., Pettican P. Inhibition of epidermal growth factor binding to mouse cultured cells by fibroblast-derived growth factor. Evidence for an indirect mechanism. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 10;257(7):3680–3686. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozengurt E., Heppel L. A. Serum rapidly stimulates ouabain-sensitive 86-RB+ influx in quiescent 3T3 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Nov;72(11):4492–4495. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.11.4492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozengurt E., Legg A., Pettican P. Vasopressin stimulation of mouse 3T3 cell growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1284–1287. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozengurt E., Legg A., Strang G., Courtenay-Luck N. Cyclic AMP: a mitogenic signal for Swiss 3T3 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4392–4396. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozengurt E. Stimulation of DNA synthesis in quiescent cultured cells: exogenous agents, internal signals, and early events. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1980;17:59–88. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-152817-1.50007-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozengurt E. Stimulation of Na influx, Na-K pump activity and DNA synthesis in quiescent cultured cells. Adv Enzyme Regul. 1980;19:61–85. doi: 10.1016/0065-2571(81)90009-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozengurt E. Synergistic stimulation of DNA synthesis by cyclic AMP derivatives and growth factors in mouse 3T3 cells. J Cell Physiol. 1982 Aug;112(2):243–250. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041120213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TODARO G. J., GREEN H. Quantitative studies of the growth of mouse embryo cells in culture and their development into established lines. J Cell Biol. 1963 May;17:299–313. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.2.299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taché Y., Vale W., Rivier J., Brown M. Brain regulation of gastric secretion: influence of neuropeptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5515–5519. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todaro G. J., De Larco J. E., Fryling C., Johnson P. A., Sporn M. B. Transforming growth factors (TGFs): properties and possible mechanisms of action. J Supramol Struct Cell Biochem. 1981;15(3):287–301. doi: 10.1002/jsscb.1981.380150306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todaro G. J., Fryling C., De Larco J. E. Transforming growth factors produced by certain human tumor cells: polypeptides that interact with epidermal growth factor receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5258–5262. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh J. H., Wong H. C., Dockray G. J. Bombesin-like peptides in mammals. Fed Proc. 1979 Aug;38(9):2315–2319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westendorf J. M., Schonbrunn A. Bombesin stimulates prolactin and growth hormone release by pituitary cells in culture. Endocrinology. 1982 Feb;110(2):352–358. doi: 10.1210/endo-110-2-352. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wharton J., Polak J. M., Bloom S. R., Ghatei M. A., Solcia E., Brown M. R., Pearse A. G. Bombesin-like immunoreactivity in the lung. Nature. 1978 Jun 29;273(5665):769–770. doi: 10.1038/273769a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood S. M., Wood J. R., Ghatei M. A., Lee Y. C., O'Shaughnessy D., Bloom S. R. Bombesin, somatostatin and neurotensin-like immunoreactivity in bronchial carcinoma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1981 Dec;53(6):1310–1312. doi: 10.1210/jcem-53-6-1310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


