Abstract
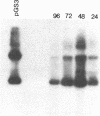
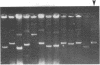
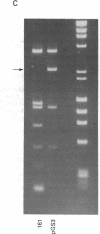
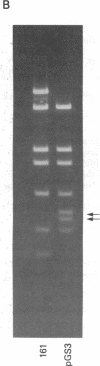
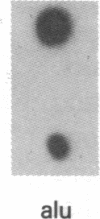
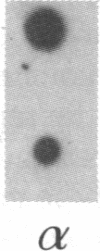
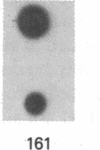
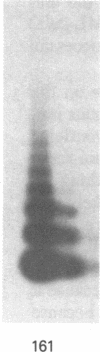
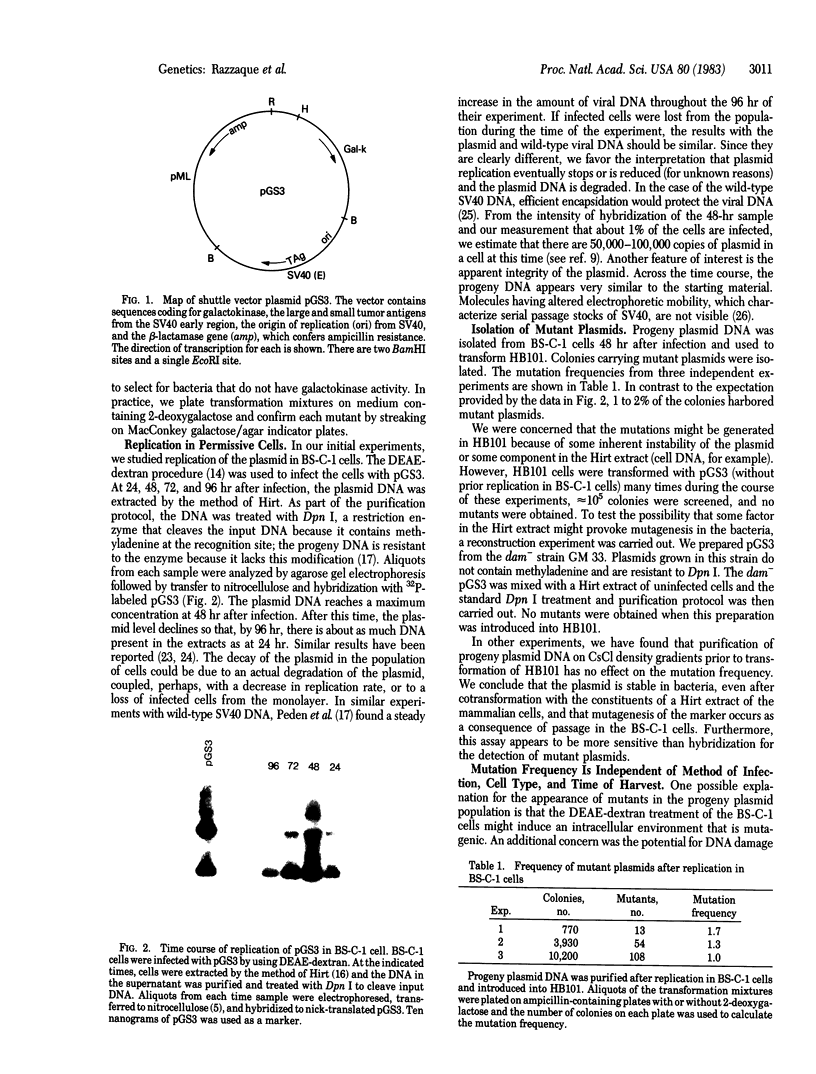
A shuttle vector plasmid that contains sequences from simian virus 40, pBR322, and a bacterial marker gene, galactokinase, has been constructed. After replication in cells permissive for virus progeny, plasmid DNA was introduced into a galactokinase-deficient bacterial strain and the relative frequency of colonies with plasmids but without galactokinase activity was determined. This assay showed that 1% of the plasmids were defective after passage in the mammalian cells. Individual mutant plasmids were examined and found to contain deletions, duplications, point mutations, and insertions of cell DNA.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alper M. D., Ames B. N. Positive selection of mutants with deletions of the gal-chl region of the Salmonella chromosome as a screening procedure for mutagens that cause deletions. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jan;121(1):259–266. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.1.259-266.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baltimore D. Somatic mutation gains its place among the generators of diversity. Cell. 1981 Nov;26(3 Pt 1):295–296. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90196-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calos M. P., Lebkowski J. S., Botchan M. R. High mutation frequency in DNA transfected into mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(10):3015–3019. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.10.3015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiMaio D., Treisman R., Maniatis T. Bovine papillomavirus vector that propagates as a plasmid in both mouse and bacterial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):4030–4034. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.4030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drake J. W., Baltz R. H. The biochemistry of mutagenesis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1976;45:11–37. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.45.070176.000303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garber E. A., Seidman M. M., Levine A. J. The detection and characterization of multiple forms of SV40 nucleoprotein complexes. Virology. 1978 Oct 15;90(2):305–316. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90315-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluzman Y. SV40-transformed simian cells support the replication of early SV40 mutants. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):175–182. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90282-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimaldi G., Queen C., Singer M. F. Interspersed repeated sequences in the African green monkey genome that are homologous to the human Alu family. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Nov 11;9(21):5553–5568. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.21.5553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutai M. W., Nathans D. Evolutionary variants of simian virus 40: Nucleotide sequence of a conserved SV40 DNA segment containing the origin of viral DNA replication as an inverted repetition. J Mol Biol. 1978 Dec 5;126(2):259–274. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90362-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ish-Horowicz D., Burke J. F. Rapid and efficient cosmid cloning. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 10;9(13):2989–2998. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.13.2989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krolewski J. J., Bertelsen A. H., Humayun M. Z., Rush M. G. Members of the Alu family of interspersed, repetitive DNA sequences are in the small circular DNA population of monkey cells grown in culture. J Mol Biol. 1982 Jan 25;154(3):399–415. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(82)80003-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lusky M., Botchan M. Inhibition of SV40 replication in simian cells by specific pBR322 DNA sequences. Nature. 1981 Sep 3;293(5827):79–81. doi: 10.1038/293079a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lübbe L., Strauss M., Scherneck S., Geissler E. The DNA tumor virus SV 40 induces gene mutations in human cells. Reversion of HPRT deficiency. Hum Genet. 1982;61(3):236–241. doi: 10.1007/BF00296449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milman G., Herzberg M. Efficient DNA transfection and rapid assay for thymidine kinase activity and viral antigenic determinants. Somatic Cell Genet. 1981 Mar;7(2):161–170. doi: 10.1007/BF01567655. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizusawa H., Lee C. H., Kakefuda T. Alteration of plasmid DNA-mediated transformation and mutation induced by covalent binding of benzo[alpha]pyrene-7,8-dihydrodiol-9,10-oxide in Escherichia coli. Mutat Res. 1981 Jun;82(1):47–57. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(81)90137-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papamatheakis J., Lee T. N., Thayer R. E., Singer M. F. Recurring defective variants of simian virus 40 containing monkey DNA segments. J Virol. 1981 Jan;37(1):295–306. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.1.295-306.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peden K. W., Pipas J. M., Pearson-White S., Nathans D. Isolation of mutants of an animal virus in bacteria. Science. 1980 Sep 19;209(4463):1392–1396. doi: 10.1126/science.6251547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
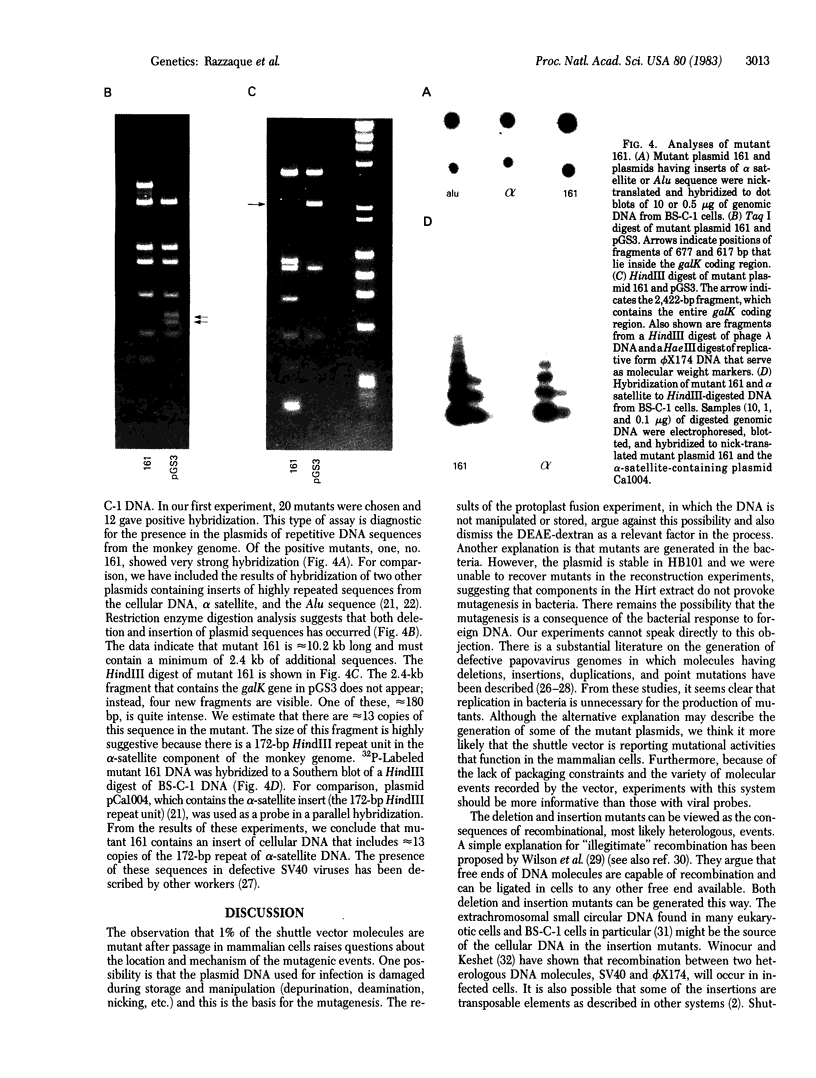
- Sandri-Goldin R. M., Goldin A. L., Levine M., Glorioso J. C. High-frequency transfer of cloned herpes simplex virus type 1 sequences to mammalian cells by protoplast fusion. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Aug;1(8):743–752. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.8.743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarver N., Byrne J. C., Howley P. M. Transformation and replication in mouse cells of a bovine papillomavirus--pML2 plasmid vector that can be rescued in bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7147–7151. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid S. E., Daune M. P., Fuchs R. P. Repair and mutagenesis of plasmid DNA modified by ultraviolet irradiation or N-acetoxy-N-2-acetylaminofluorene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):4133–4137. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.4133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spandidos D. A., Siminovitch L. The relationship between transformation and somatic mutation in human and Chinese hamster cells. Cell. 1978 Apr;13(4):651–662. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90215-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thayer R. E., Singer M. F., McCutchan T. F. Sequence relationships between single repeat units of highly reiterated African Green monkey DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 10;9(1):169–181. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.1.169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theile M., Strauss M., Luebbe L., Scherneck S., Krause H., Geissler E. SV40-induced somatic mutations: possible relevance to viral transformation. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1980;44(Pt 1):377–382. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1980.044.01.042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsui L. C., Breitman M. L., Siminovitch L., Buchwald M. Persistence of freely replicating SV40 recombinant molecules carrying a selectable marker in permissive simian cells. Cell. 1982 Sep;30(2):499–508. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90247-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Upcroft P., Carter B., Kidson C. Mammalian cell function mediating recombination of genetic elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Dec 11;8(23):5835–5844. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.23.5835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varmus H. E., Quintrell N., Ortiz S. Retroviruses as mutagens: insertion and excision of a nontransforming provirus alter expression of a resident transforming provirus. Cell. 1981 Jul;25(1):23–36. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90228-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakamiya T., McCutchan T., Rosenberg M., Singer M. Structure of simian virus 40 recombinants that contain both host and viral DNA sequences. I. The structure of variant CVPS/1/P2 (EcoRI res). J Biol Chem. 1979 May 10;254(9):3584–3591. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson J. H., Berget P. B., Pipas J. M. Somatic cells efficiently join unrelated DNA segments end-to-end. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Oct;2(10):1258–1269. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.10.1258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winocour E., Keshet I. Indiscriminate recombination in simian virus 40-infected monkey cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4861–4865. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]