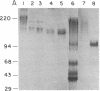
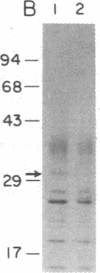
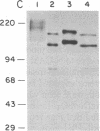
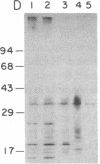
Abstract
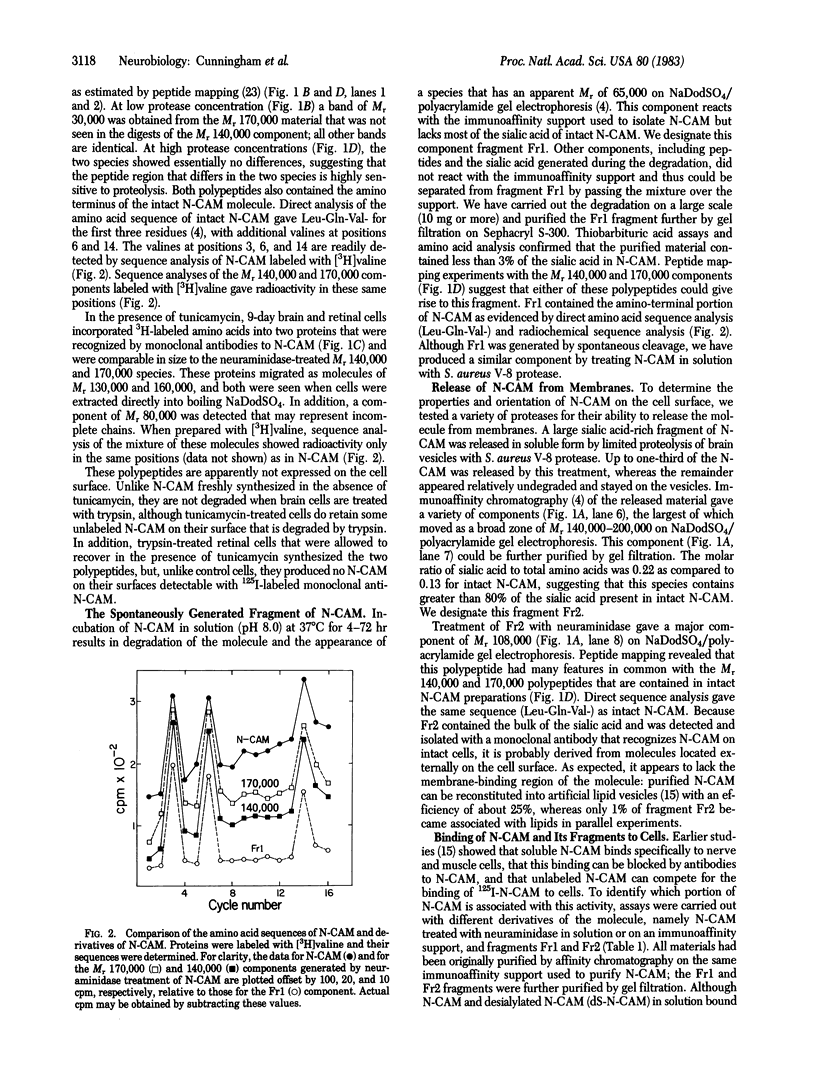
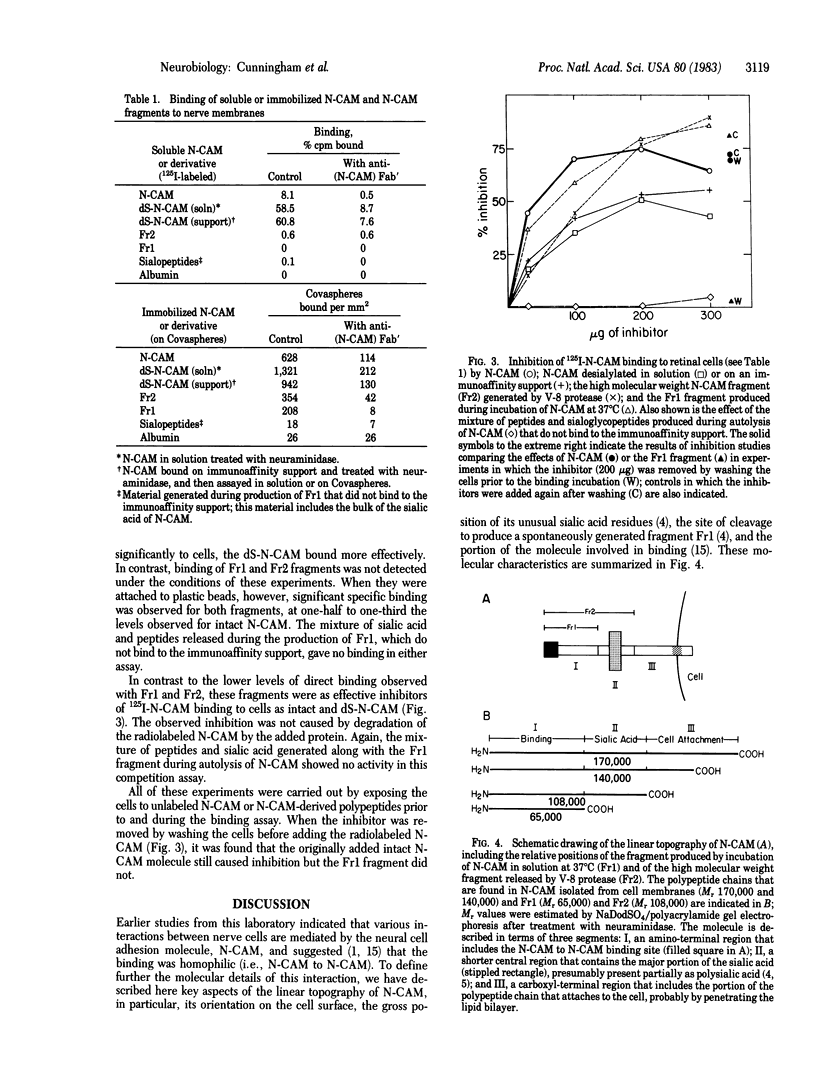
Chemical analyses and binding studies have been correlated to clarify the relationship of structure to function in the neural cell adhesion molecule (N-CAM) from embryonic chicken brain. N-CAM isolated from the cell surface appears to include two closely related polypeptide chains. Treatment with neuraminidase of such preparations of N-CAM bound by antibodies on solid supports yielded components of Mr 140,000 and 170,000. These components each had the same amino-terminal sequence as N-CAM and gave nearly identical profiles on peptide maps. Immunoprecipitation of N-CAM from 9-day brain cells treated with tunicamycin yielded corresponding components of Mr 130,000 and 160,000, suggesting that the differences between these two components of N-CAM are in the polypeptide rather than the carbohydrate portions of the molecules. N-CAM appears to be oriented with the amino terminus extending away from the cell surface and with the bulk of the sialic acid near the middle of the peptide chain. As shown previously, incubation of N-CAM at 37 degrees C generates a fragment (Fr1) of Mr 65,000 that lacks most of the sialic acid. Treatment of membranes with Staphylococcus aureus V-8 protease released a fragment (Fr2) of N-CAM that contained most of the sialic acid; this fragment had an Mr of 108,000 after neuraminidase treatment. Both of these fragments contain the amino-terminal portion of the polypeptide chain. At least a portion of the N-CAM binding site was found to be located in the amino-terminal region of the peptide chain. Most or all of the sialic acid was not directly involved in binding, although it can influence binding, as indicated by the finding that neuraminidase-treated N-CAM (desialylated-N-CAM) bound to cells to a greater extent than untreated N-CAM. The Fr1 and the Fr2 fragments in solution did not bind to cells but were as effective as N-CAM and desialylated-N-CAM as competitors for N-CAM binding to cells. When fixed covalently to beads, N-CAM, desialylated-N-CAM, and the Fr1 and Fr2 fragments bound specifically to cells. In contrast, the N-CAM autolysis products released along with Fr1 neither bound to cells nor competed for N-CAM binding. In addition to suggesting a location for the N-CAM binding region, the accumulated results raise the possibility that valence may play a key role in N-CAM binding.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brackenbury R., Rutishauser U., Edelman G. M. Distinct calcium-independent and calcium-dependent adhesion systems of chicken embryo cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):387–391. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brackenbury R., Thiery J. P., Rutishauser U., Edelman G. M. Adhesion among neural cells of the chick embryo. I. An immunological assay for molecules involved in cell-cell binding. J Biol Chem. 1977 Oct 10;252(19):6835–6840. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buskirk D. R., Thiery J. P., Rutishauser U., Edelman G. M. Antibodies to a neural cell adhesion molecule disrupt histogenesis in cultured chick retinae. Nature. 1980 Jun 12;285(5765):488–489. doi: 10.1038/285488a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chuong C. M., McClain D. A., Streit P., Edelman G. M. Neural cell adhesion molecules in rodent brains isolated by monoclonal antibodies with cross-species reactivity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):4234–4238. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.4234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman G. M. Cell adhesion molecules. Science. 1983 Feb 4;219(4584):450–457. doi: 10.1126/science.6823544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman G. M., Chuong C. M. Embryonic to adult conversion of neural cell adhesion molecules in normal and staggerer mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):7036–7040. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.7036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman G. M., Rutishauser U. Specific fractionation and manipulation of cells with chemically derivatized fibers and surfaces. Methods Enzymol. 1974;34:195–225. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(74)34018-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grumet M., Rutishauser U., Edelman G. M. Neural cell adhesion molecule is on embryonic muscle cells and mediates adhesion to nerve cells in vitro. Nature. 1982 Feb 25;295(5851):693–695. doi: 10.1038/295693a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemperly J. J., Hopp T. P., Becker J. W., Cunningham B. A. The chemical characterization of favin, a lectin isolated from Vicia faba. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jul 25;254(14):6803–6810. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemperly J. J., Mostov K. E., Cunningham B. A. In vitro translation and processing of a precursor form of favin, a lectin from Vicia faba. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7903–7909. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman S., Sorkin B. C., White P. C., Brackenbury R., Mailhammer R., Rutishauser U., Cunningham B. A., Edelman G. M. Chemical characterization of a neural cell adhesion molecule purified from embryonic brain membranes. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7720–7729. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jørgensen O. S., Delouvée A., Thiery J. P., Edelman G. M. The nervous system specific protein D2 is involved in adhesion among neurites from cultured rat ganglia. FEBS Lett. 1980 Feb 25;111(1):39–42. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80756-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClain D. A., Edelman G. M. A neural cell adhesion molecule from human brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(20):6380–6384. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.20.6380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConahey P. J., Dixon F. J. A method of trace iodination of proteins for immunologic studies. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1966;29(2):185–189. doi: 10.1159/000229699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendel-Hartvig I. B. A simple and rapid method for the isolation of peptides from sodium dodecyl sulfate-containing polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1982 Mar 15;121(1):215–217. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90579-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothbard J. B., Brackenbury R., Cunningham B. A., Edelman G. M. Differences in the carbohydrate structures of neural cell-adhesion molecules from adult and embryonic chicken brains. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 25;257(18):11064–11069. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutishauser U., Edelman G. M. Effects of fasciculation on the outgrowth of neurites from spinal ganglia in culture. J Cell Biol. 1980 Nov;87(2 Pt 1):370–378. doi: 10.1083/jcb.87.2.370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutishauser U., Gall W. E., Edelman G. M. Adhesion among neural cells of the chick embryo. IV. Role of the cell surface molecule CAM in the formation of neurite bundles in cultures of spinal ganglia. J Cell Biol. 1978 Nov;79(2 Pt 1):382–393. doi: 10.1083/jcb.79.2.382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutishauser U., Hoffman S., Edelman G. M. Binding properties of a cell adhesion molecule from neural tissue. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):685–689. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutishauser U., Thiery J. P., Brackenbury R., Edelman G. M. Adhesion among neural cells of the chick embryo. III. Relationship of the surface molecule CAM to cell adhesion and the development of histotypic patterns. J Cell Biol. 1978 Nov;79(2 Pt 1):371–381. doi: 10.1083/jcb.79.2.371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiery J. P., Brackenbury R., Rutishauser U., Edelman G. M. Adhesion among neural cells of the chick embryo. II. Purification and characterization of a cell adhesion molecule from neural retina. J Biol Chem. 1977 Oct 10;252(19):6841–6845. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]