Abstract
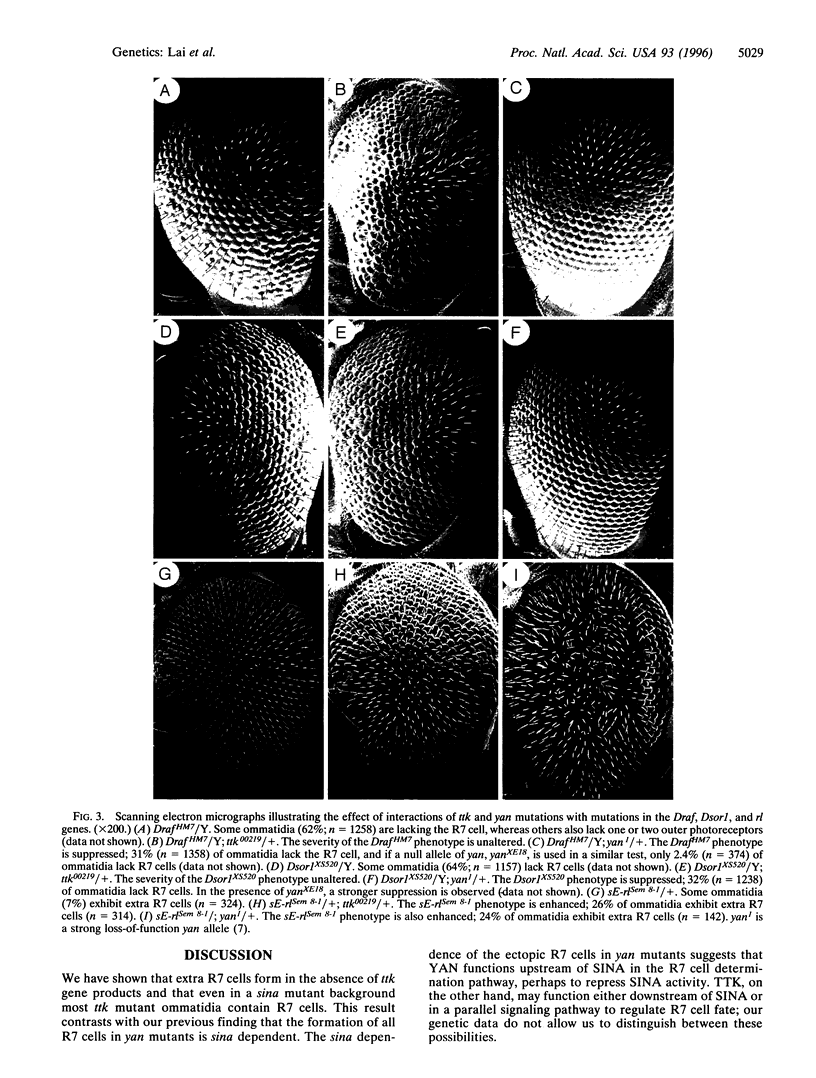
We have screened a collection of transposable-element-induced mutations for those which dominantly modify the extra R7 phenotype of a hypomorphic yan mutation. The members of one of the identified complementation groups correspond to disruptions of the tramtrack (ttk) gene. As heterozygotes, ttk alleles increase the percentage of R7 cells in yan mutant eyes. Just as yan mutations increase ectopic R7 cell formation, homozygous ttk mutant eye clones also contain supernumerary R7 cells. However, in contrast to yan, the formation of these cells in ttk mutant eye tissue is not necessarily dependent on the activity of the sina gene. Furthermore, although yan mutations dominantly interact with mutations in the Ras1, Draf, Dsor1, and rolled (rl) genes to influence R7 cell development, ttk mutations only interact with yan and rl gene mutations to affect this signaling pathway. Our data suggest that yan and ttk both function to repress inappropriate R7 cell development but that their mechanisms of action differ. In particular, TTK activity appears to be autonomously required to regulate a sina-independent mechanism of R7 determination.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Basler K., Christen B., Hafen E. Ligand-independent activation of the sevenless receptor tyrosine kinase changes the fate of cells in the developing Drosophila eye. Cell. 1991 Mar 22;64(6):1069–1081. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90262-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. L., Sonoda S., Ueda H., Scott M. P., Wu C. Repression of the Drosophila fushi tarazu (ftz) segmentation gene. EMBO J. 1991 Mar;10(3):665–674. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07995.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunner D., Oellers N., Szabad J., Biggs W. H., 3rd, Zipursky S. L., Hafen E. A gain-of-function mutation in Drosophila MAP kinase activates multiple receptor tyrosine kinase signaling pathways. Cell. 1994 Mar 11;76(5):875–888. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90362-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carthew R. W., Rubin G. M. seven in absentia, a gene required for specification of R7 cell fate in the Drosophila eye. Cell. 1990 Nov 2;63(3):561–577. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90452-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickson B., Sprenger F., Morrison D., Hafen E. Raf functions downstream of Ras1 in the Sevenless signal transduction pathway. Nature. 1992 Dec 10;360(6404):600–603. doi: 10.1038/360600a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fortini M. E., Rubin G. M. Analysis of cis-acting requirements of the Rh3 and Rh4 genes reveals a bipartite organization to rhodopsin promoters in Drosophila melanogaster. Genes Dev. 1990 Mar;4(3):444–463. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.3.444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fortini M. E., Simon M. A., Rubin G. M. Signalling by the sevenless protein tyrosine kinase is mimicked by Ras1 activation. Nature. 1992 Feb 6;355(6360):559–561. doi: 10.1038/355559a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaul U., Mardon G., Rubin G. M. A putative Ras GTPase activating protein acts as a negative regulator of signaling by the Sevenless receptor tyrosine kinase. Cell. 1992 Mar 20;68(6):1007–1019. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90073-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison S. D., Travers A. A. The tramtrack gene encodes a Drosophila finger protein that interacts with the ftz transcriptional regulatory region and shows a novel embryonic expression pattern. EMBO J. 1990 Jan;9(1):207–216. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08097.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karpen G. H., Spradling A. C. Analysis of subtelomeric heterochromatin in the Drosophila minichromosome Dp1187 by single P element insertional mutagenesis. Genetics. 1992 Nov;132(3):737–753. doi: 10.1093/genetics/132.3.737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimmel B. E., Heberlein U., Rubin G. M. The homeo domain protein rough is expressed in a subset of cells in the developing Drosophila eye where it can specify photoreceptor cell subtype. Genes Dev. 1990 May;4(5):712–727. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.5.712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai Z. C., Rubin G. M. Negative control of photoreceptor development in Drosophila by the product of the yan gene, an ETS domain protein. Cell. 1992 Aug 21;70(4):609–620. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90430-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neill E. M., Rebay I., Tjian R., Rubin G. M. The activities of two Ets-related transcription factors required for Drosophila eye development are modulated by the Ras/MAPK pathway. Cell. 1994 Jul 15;78(1):137–147. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90580-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Read D., Manley J. L. Alternatively spliced transcripts of the Drosophila tramtrack gene encode zinc finger proteins with distinct DNA binding specificities. EMBO J. 1992 Mar;11(3):1035–1044. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05142.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rebay I., Rubin G. M. Yan functions as a general inhibitor of differentiation and is negatively regulated by activation of the Ras1/MAPK pathway. Cell. 1995 Jun 16;81(6):857–866. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90006-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M. A., Bowtell D. D., Dodson G. S., Laverty T. R., Rubin G. M. Ras1 and a putative guanine nucleotide exchange factor perform crucial steps in signaling by the sevenless protein tyrosine kinase. Cell. 1991 Nov 15;67(4):701–716. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90065-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spradling A. C., Stern D. M., Kiss I., Roote J., Laverty T., Rubin G. M. Gene disruptions using P transposable elements: an integral component of the Drosophila genome project. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Nov 21;92(24):10824–10830. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.24.10824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomlinson A., Ready D. F. Cell fate in the Drosophila ommatidium. Dev Biol. 1987 Sep;123(1):264–275. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(87)90448-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wassarman D. A., Therrien M., Rubin G. M. The Ras signaling pathway in Drosophila. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1995 Feb;5(1):44–50. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(95)90052-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiong W. C., Montell C. tramtrack is a transcriptional repressor required for cell fate determination in the Drosophila eye. Genes Dev. 1993 Jun;7(6):1085–1096. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.6.1085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu T., Rubin G. M. Analysis of genetic mosaics in developing and adult Drosophila tissues. Development. 1993 Apr;117(4):1223–1237. doi: 10.1242/dev.117.4.1223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zipursky S. L., Rubin G. M. Determination of neuronal cell fate: lessons from the R7 neuron of Drosophila. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1994;17:373–397. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.17.030194.002105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]