FIG 4 .
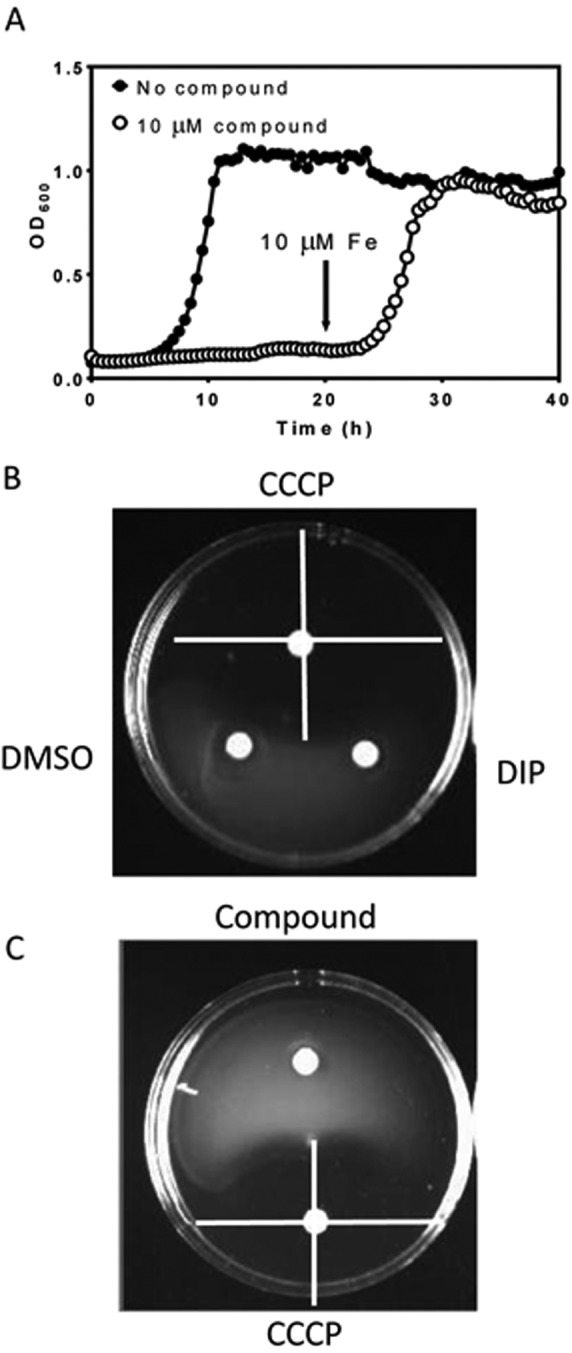
Iron acquisition inhibitors are bacteriostatic and do not inhibit the proton motive force. (A) Representative growth curves of E. coli CFT073 ΔtolC in the presence of iron acquisition inhibitors. Cultures in MOPS with (closed circles) or without (open circles) additional iron were allowed to grow for 40 h in the presence of each of the compounds. For all compounds, growth was not inhibited when excess iron was added to the medium. At 20 h, 10 µM FeSO4 was added. Addition of excess iron to E. coli CFT073 ΔtolC cells in the presence of inhibitory compounds restores growth. Curves are means ± SD for 5 independent replicates. (B) Swimming motility controls. Neither DMSO (10 µl) nor 10 µM dipyridyl (10 µl) inhibited swimming motility of CFT073 ΔtolC. CCCP (10 µl of a 10 µM solution in DMSO) inhibits swimming motility. Inhibition of the PMF is seen as a halo of swimming inhibition surrounding the paper disk. (C) Iron acquisition inhibitors do not inhibit the PMF. Swimming agar plates were inoculated with CFT073 ΔtolC as described. Compounds were tested by pipetting 10 µl of a 10 µM solution in DMSO into paper disks and placing them between the inoculation point and the edge of the plate. The positive control was CCCP (10 µl of a 10 µM solution in DMSO).
