Abstract
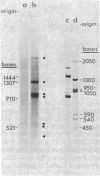
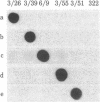
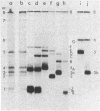
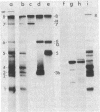
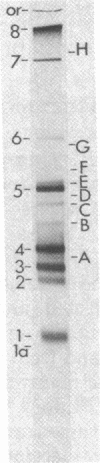
We have isolated cDNA clones representing nine unique poly(A)+ RNAs transcribed from the genome of human respiratory syncytial virus, a paramyxovirus. A cDNA library was constructed by using poly(A)+ RNA from virus-infected cells as template and the Escherichia coli plasmid pBR322 as vector. Viral cDNA clones were identified by hybridization with cDNA probes prepared from viral genomic RNA. The viral clones were grouped into nine different families by hybridization with individual size-selected reverse transcripts representing the major classes of poly(A)+ RNA from virus-infected cells. The largest clone from each family was selected for analysis. These nine clones, molecular sizes ranging from 520 to 2,600 base pairs, were shown to be unrelated on the basis of reciprocal hybridization using dot-blots. These cDNA clones were then used as hybridization probes to analyze intracellular viral RNAs that had been separated by gel electrophoresis and transferred to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper. All nine clones hybridized with intracellular viral genomic RNA, confirmation of virus specificity. Nine unique intracellular viral poly(A)+ RNAs were identified [molecular sizes ranging from 720 to 7,500 nucleotides, including poly(A)]. Comparison of the sizes of these major RNAs and the cDNA clones indicated that a number of the clones represented nearly complete copies of the corresponding RNAs. Several other intracellular viral poly(A)+ RNAs appeared to be polycistronic by the criteria of molecular weights and homologies to various combinations of cDNA clones. The sizes and sequence contents of these polycistronic RNAs were used to prepare a transcriptional map whose significance is discussed.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Collins P. L., Hightower L. E., Ball L. A. Transcriptional map for Newcastle disease virus. J Virol. 1980 Sep;35(3):682–693. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.3.682-693.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins P. L., Hightower L. E. Newcastle disease virus stimulates the cellular accumulation of stress (heat shock) mRNAs and proteins. J Virol. 1982 Nov;44(2):703–707. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.2.703-707.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins P. L., Wertz G. W., Ball L. A., Hightower L. E. Coding assignments of the five smaller mRNAs of Newcastle disease virus. J Virol. 1982 Sep;43(3):1024–1031. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.3.1024-1031.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dagert M., Ehrlich S. D. Prolonged incubation in calcium chloride improves the competence of Escherichia coli cells. Gene. 1979 May;6(1):23–28. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(79)90082-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis N. L., Wertz G. W. Synthesis of vesicular stomatitis virus negative-strand RNA in vitro: dependence on viral protein synthesis. J Virol. 1982 Mar;41(3):821–832. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.3.821-832.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubovi E. J. Analysis of proteins synthesized in respiratory syncytial virus-infected cells. J Virol. 1982 May;42(2):372–378. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.2.372-378.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernie B. F., Gerin J. L. Immunochemical identification of viral and nonviral proteins of the respiratory syncytial virus virion. Infect Immun. 1982 Jul;37(1):243–249. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.1.243-249.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glazier K., Raghow R., Kingsbury D. W. Regulation of Sendai virus transcription: evidence for a single promoter in vivo. J Virol. 1977 Mar;21(3):863–871. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.3.863-871.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorecki M., Rozenblatt S. Cloning of DNA complementary to the measles virus mRNA encoding nucleocapsid protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3686–3690. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M., Wallis J. Colony hybridization. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:379–389. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68027-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herman R. C., Adler S., Lazzarini R. A., Colonno R. J., Banerjee A. K., Westphal H. Intervening polyadenylate sequences in RNA transcripts of vesicular stomatitis virus. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):587–596. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90027-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herman R. C., Schubert M., Keene J. D., Lazzarini R. A. Polycistronic vesicular stomatitis virus RNA transcripts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4662–4665. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4662. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes D. S., Quigley M. A rapid boiling method for the preparation of bacterial plasmids. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jun;114(1):193–197. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90473-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang Y. T., Wertz G. W. The genome of respiratory syncytial virus is a negative-stranded RNA that codes for at least seven mRNA species. J Virol. 1982 Jul;43(1):150–157. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.1.150-157.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kafatos F. C., Jones C. W., Efstratiadis A. Determination of nucleic acid sequence homologies and relative concentrations by a dot hybridization procedure. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1541–1552. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb R. A., Choppin P. W. Determination by peptide mapping of the unique polypeptides in Sendai virions and infected cells. Virology. 1978 Feb;84(2):469–478. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90263-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert D. M., Pons M. W., Mbuy G. N., Dorsch-Hasler K. Nucleic acids of respiratory syncytial virus. J Virol. 1980 Dec;36(3):837–846. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.3.837-846.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrach H., Diamond D., Wozney J. M., Boedtker H. RNA molecular weight determinations by gel electrophoresis under denaturing conditions, a critical reexamination. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 18;16(21):4743–4751. doi: 10.1021/bi00640a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leppert M., Rittenhouse L., Perrault J., Summers D. F., Kolakofsky D. Plus and minus strand leader RNAs in negative strand virus-infected cells. Cell. 1979 Nov;18(3):735–747. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90127-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paramyxovirdae. Intervirology. 1978;10(3):137–152. doi: 10.1159/000148979. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peeples M., Levine S. Respiratory syncytial virus polypeptides: their location in the virion. Virology. 1979 May;95(1):137–145. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90408-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peluso R. W., Lamb R. A., Choppin P. W. Infection with paramyxoviruses stimulates synthesis of cellular polypeptides that are also stimulated in cells transformed by Rous sarcoma virus or deprived of glucose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):6120–6124. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.6120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pringle C. R., Shirodaria P. V., Gimenez H. B., Levine S. Antigen and polypeptide synthesis by temperature-sensitive mutants of respiratory syncytial virus. J Gen Virol. 1981 May;54(Pt 1):173–183. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-54-1-173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose J. K., Gallione C. J. Nucleotide sequences of the mRNA's encoding the vesicular stomatitis virus G and M proteins determined from cDNA clones containing the complete coding regions. J Virol. 1981 Aug;39(2):519–528. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.2.519-528.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowekamp W., Firtel R. A. Isolation of developmentally regulated genes from Dictyostelium. Dev Biol. 1980 Oct;79(2):409–418. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(80)90126-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roychoudhury R., Jay E., Wu R. Terminal labeling and addition of homopolymer tracts to duplex DNA fragments by terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Jan;3(1):101–116. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.1.101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J. M., Illmensee R., Summers J. Efficeint transcription of RNA into DNA by avian sarcoma virus polymerase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Sep 6;442(3):324–330. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(76)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varich N. L., Lukashevich I. S., Kaverin N. V. Newcastle disease virus-specific RNA: an analysis of 24 S and 35 S RNA transcripts. Acta Virol. 1979 Jul;23(4):273–283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss S. R., Bratt M. A. Polyadenylate sequences on Newcastle disease virus mRNA synthesized in vivo and in vitro. J Virol. 1974 Jun;13(6):1220–1230. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.6.1220-1230.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wertz G. W., Davis N. Characterization and mapping of RNase III cleavage sites in VSV genome RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6487–6503. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wertz G. W. Isolation of possible replicative intermediate structures from vesicular stomatitis virus-infected cells. Virology. 1978 Mar;85(1):271–285. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90431-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickens M. P., Buell G. N., Schimke R. T. Synthesis of double-stranded DNA complementary to lysozyme, ovomucoid, and ovalbumin mRNAs. Optimization for full length second strand synthesis by Escherichia coli DNA polymerase I. J Biol Chem. 1978 Apr 10;253(7):2483–2495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]