Abstract
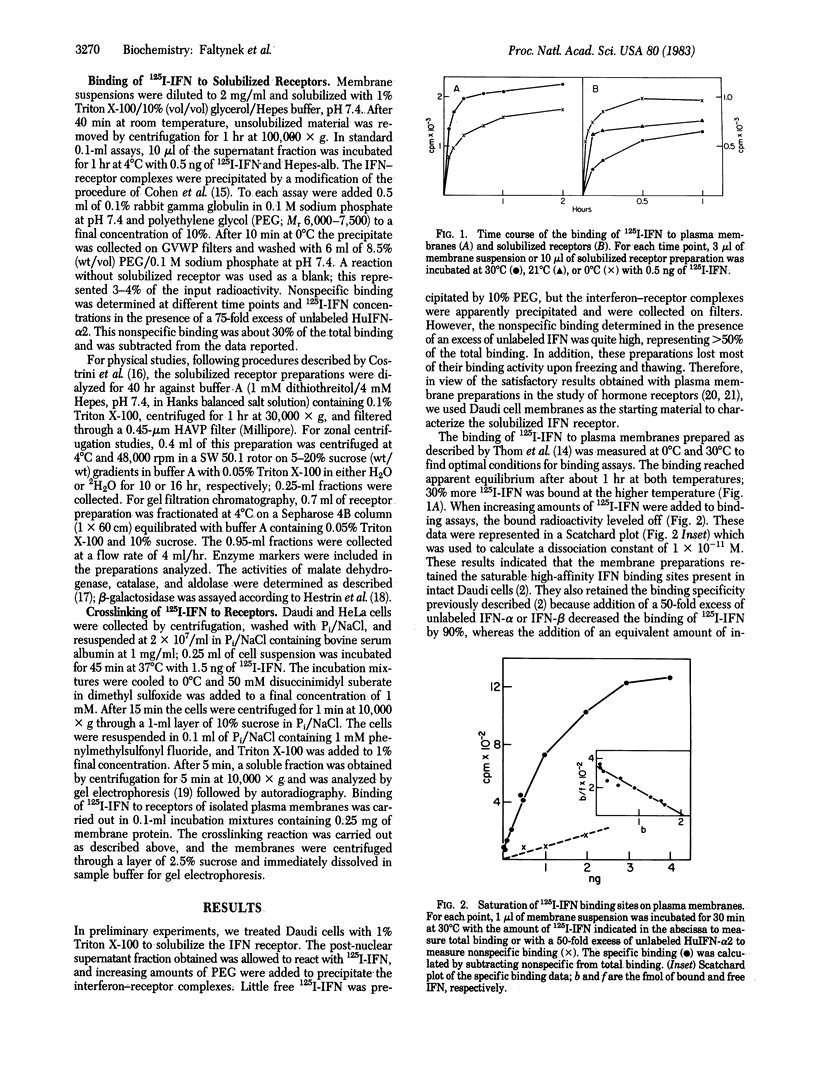
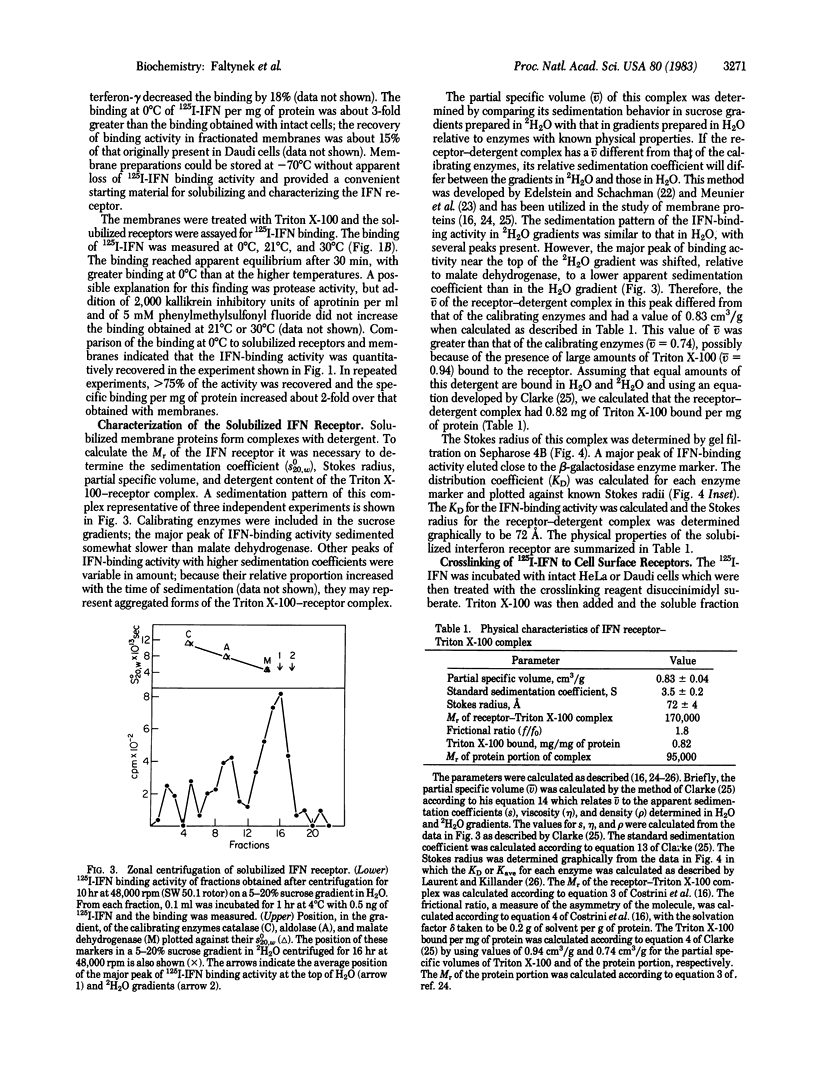
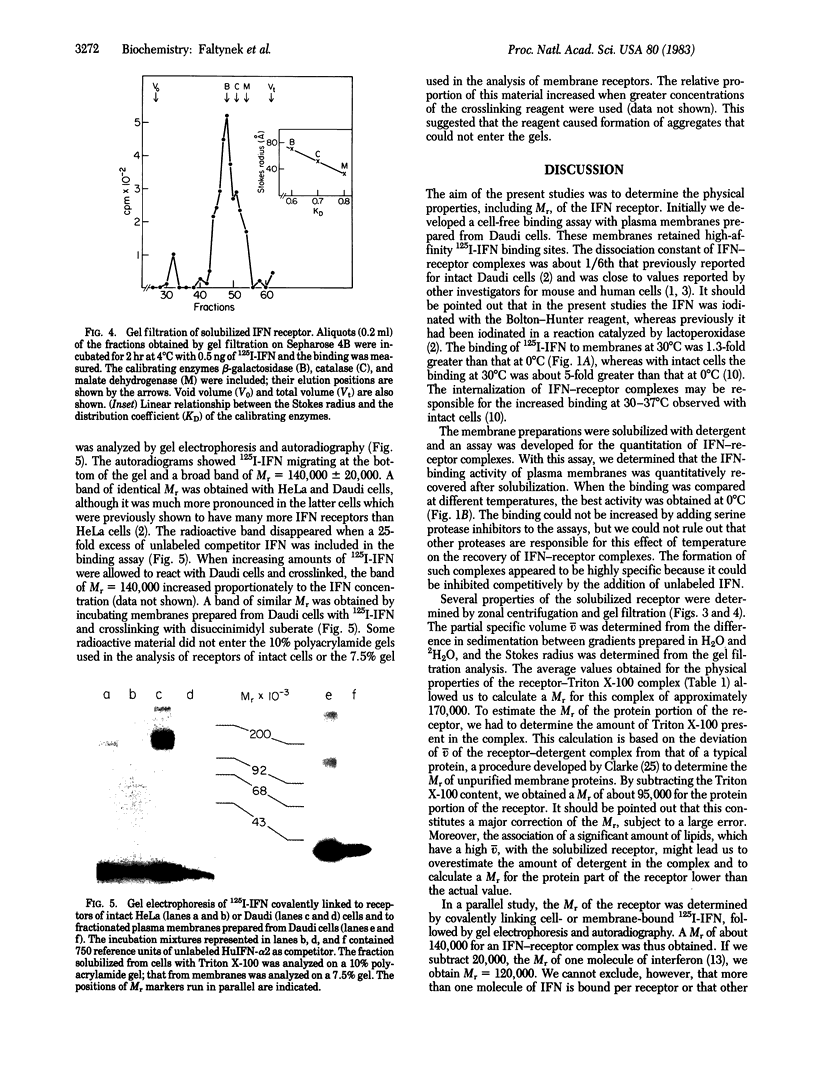
A cell-free assay was developed to measure the binding of iodinated human interferon-alpha 2 to membranes prepared from lymphoblastoid Daudi cells. The kinetics of binding were similar at 0 degrees C and 30 degrees C, with 1.3-fold more interferon bound at the higher temperature. Membrane preparations treated with Triton X-100 proved to be a convenient source of solubilized receptor. An assay was developed to measure the binding of 125I-labeled interferon (125I-interferon) to solubilized receptors, based on the precipitation of interferon-receptor complexes with polyethylene glycol. Optimal binding with this assay was obtained at 0 degrees C. The solubilized receptor was analyzed by zonal sedimentation centrifugation and gel filtration. Sedimentation analysis in H2O and 2H2O gradients provided the sedimentation coefficient and the partial specific volume of the receptor-Triton X-100 complex. Gel filtration chromatography provided the Stokes radius of this complex. From these data we calculated several physical parameters, including Mr = 95,000 for the protein portion of the complex. The receptor is a highly asymmetric and hydrophobic membrane protein. 125I-Interferon could be crosslinked to receptors of intact Daudi cells or of isolated membranes by use of disuccinimidyl suberate. The covalently linked 125I-interferon-receptor complexes were analyzed by gel electrophoresis. A single band with Mr = 140,000 was detected in gel autoradiographs. If one molecule of interferon is present in this complex, the Mr of the receptor is close to 120,000. Possible reasons for the different Mr values obtained with the two analytical procedures used are discussed.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aguet M., Belardelli F., Blanchard B., Marcucci F., Gresser I. High-affinity binding of 125I-labeled mouse interferon to a specific cell surface receptor. IV. Mouse gamma interferon and cholera toxin do not compete for the common receptor site of alpha / beta interferon. Virology. 1982 Mar;117(2):541–544. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90497-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aguet M., Blanchard B. High affinity binding of 125I-Labeled mouse interferon to a specific cell surface receptor. II. Analysis of binding properties. Virology. 1981 Dec;115(2):249–261. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90108-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aguet M., Gresser I., Hovanessian A. G., Bandu M. T., Blanchard B., Blangy D. Specific high-affinity binding of 125I-labeled mouse interferon to interfevon resistant embryonal carcinoma cells in vitro. Virology. 1981 Oct 30;114(2):585–588. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90241-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aguet M. High-affinity binding of 125I-labelled mouse interferon to a specific cell surface receptor. Nature. 1980 Apr 3;284(5755):459–461. doi: 10.1038/284459a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson P., Yip Y. K., Vilcek J. Specific binding of 125I-human interferon-gamma to high affinity receptors on human fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 10;257(19):11301–11304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baglioni C., Branca A. A., D'Alessandro S. B., Hossenlopp D., Chadha K. C. Low interferon binding activity of two human cell lines which respond poorly to the antiviral and antiproliferative activity of interferon. Virology. 1982 Oct 15;122(1):202–206. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90390-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branca A. A., Baglioni C. Evidence that types I and II interferons have different receptors. Nature. 1981 Dec 24;294(5843):768–770. doi: 10.1038/294768a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branca A. A., Faltynek C. R., D'Alessandro S. B., Baglioni C. Interaction of interferon with cellular receptors. Internalization and degradation of cell-bound interferon. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 25;257(22):13291–13296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter G., King L., Jr, Cohen S. Rapid enhancement of protein phosphorylation in A-431 cell membrane preparations by epidermal growth factor. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 10;254(11):4884–4891. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke S. The size and detergent binding of membrane proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jul 25;250(14):5459–5469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S., Carpenter G., King L., Jr Epidermal growth factor-receptor-protein kinase interactions. Co-purification of receptor and epidermal growth factor-enhanced phosphorylation activity. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 25;255(10):4834–4842. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costrini N. V., Kogan M., Kukreja K., Bradshaw R. A. Physical properties of the detergent-extracted nerve growth factor receptor of sympathetic ganglia. J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 25;254(22):11242–11246. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P. Properties of the insulin receptor isolated from liver and fat cell membranes. J Biol Chem. 1972 Apr 10;247(7):1980–1991. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dufau M. L., Charreau E. H., Ryan D., Catt K. J. Soluble gonadotropin receptors of the rat ovary. FEBS Lett. 1974 Feb 15;39(2):149–153. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80038-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelstein S. J., Schachman H. K. The simultaneous determination of partial specific volumes and molecular weights with microgram quantities. J Biol Chem. 1967 Jan 25;242(2):306–311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freychet P., Roth J., Neville D. M., Jr Insulin receptors in the liver: specific binding of ( 125 I)insulin to the plasma membrane and its relation to insulin bioactivity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Aug;68(8):1833–1837. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.8.1833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
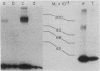
- Joshi A. R., Sarkar F. H., Gupta S. L. Interferon receptors. Cross-linking of human leukocyte interferon alpha-2 to its receptor on human cells. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 10;257(23):13884–13887. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meunier J. C., Olsen R. W., Changeux J. P. Studies on the cholinergic receptor protein from Electrophorus electricus. Effect of detergents on some hydrodynamic properties of the receptor protein in solution. FEBS Lett. 1972 Jul 15;24(1):63–68. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80827-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mogensen K. E., Bandu M. T., Vignaux F., Aguet M., Gressner I. Binding of 125I-labelled human alpha interferon to human lymphoid cells. Int J Cancer. 1981 Nov 15;28(5):575–582. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910280508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neer E. J. The size of adenylate cyclase. J Biol Chem. 1974 Oct 25;249(20):6527–6531. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streuli M., Nagata S., Weissmann C. At least three human type alpha interferons: structure of alpha 2. Science. 1980 Sep 19;209(4463):1343–1347. doi: 10.1126/science.6158094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thom D., Powell A. J., Lloyd C. W., Rees D. A. Rapid isolation of plasma membranes in high yield from cultured fibroblasts. Biochem J. 1977 Nov 15;168(2):187–194. doi: 10.1042/bj1680187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoon K., Zur Nedden D., Arnheiter H. Specific binding of human alpha interferon to a high affinity cell surface binding site on bovine kidney cells. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 10;257(9):4695–4697. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]