Abstract
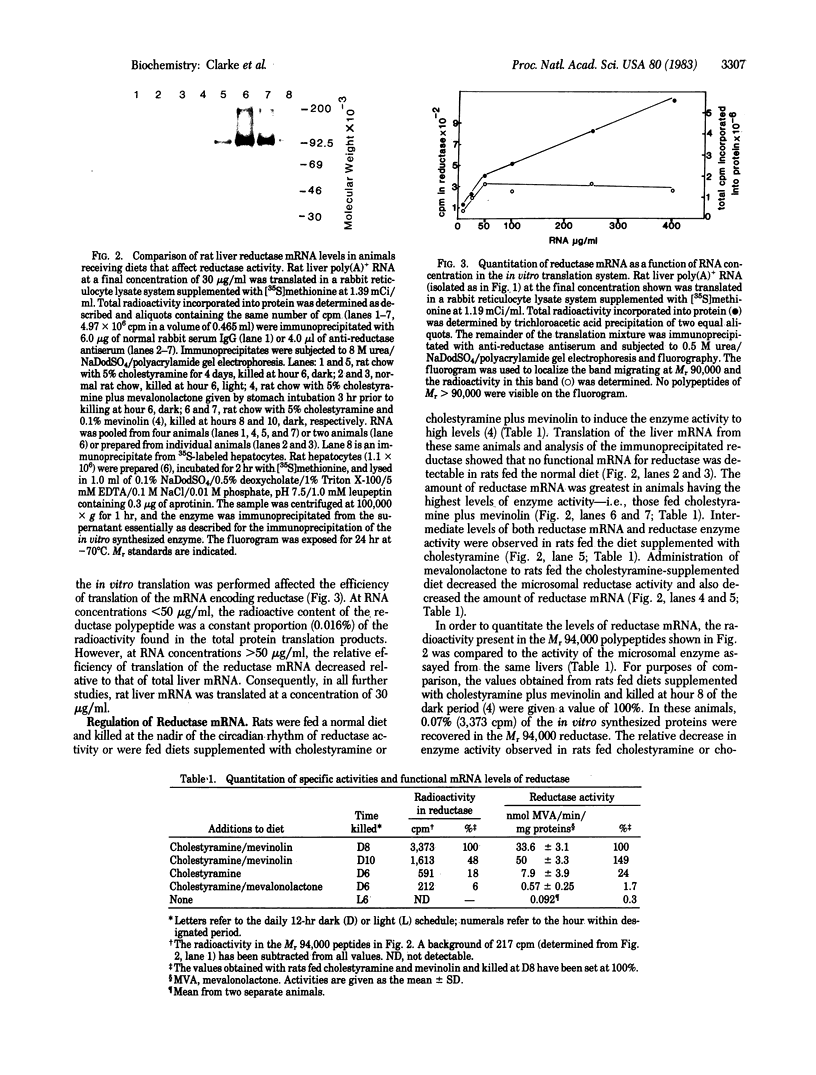
Addition of cholestyramine or cholestyramine plus mevinolin to the diet has been reported to increase the activity and mass of rat liver 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase. The present data show that these same dietary manipulations cause an induction of functional reductase mRNA. RNA was isolated from rat livers and added to an in vitro translation system, and the reductase was immunoprecipitated and analyzed by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis under denaturing conditions. One protein was specifically immunoprecipitated and was found to have a Mr of 90,000 on 0.5 M urea/sodium dodecyl sulfate/polyacrylamide gels and a Mr of 94,000 on 8 M urea/sodium dodecyl sulfate/polyacrylamide gels. In animals fed rat chow supplemented with 5% cholestyramine and 0.1% mevinolin, reductase mRNA levels were 5.7-fold higher than in animals fed rat chow with 5% cholestyramine and were 16-fold higher than in animals fed rat chow with 5% cholestyramine and given mevalonolactone by stomach intubation. RNA isolated from animals fed a normal diet and killed at the nadir of the diurnal cycle of enzyme activity contained no detectable amounts of reductase mRNA as determined by this assay.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beale E. G., Katzen C. S., Granner D. K. Regulation of rat liver phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (GTP) messenger ribonucleic acid activity by N6, O2'-dibutyryladenosine 3',5'-phosphate. Biochemistry. 1981 Aug 18;20(17):4878–4883. doi: 10.1021/bi00520a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. Multivalent feedback regulation of HMG CoA reductase, a control mechanism coordinating isoprenoid synthesis and cell growth. J Lipid Res. 1980 Jul;21(5):505–517. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlain J. P. Fluorographic detection of radioactivity in polyacrylamide gels with the water-soluble fluor, sodium salicylate. Anal Biochem. 1979 Sep 15;98(1):132–135. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90716-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chin D. J., Luskey K. L., Faust J. R., MacDonald R. J., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. Molecular cloning of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme a reductase and evidence for regulation of its mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7704–7708. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R. E., Martin G. G., Barton M. C., Shapiro D. J. Production and characterization of monoclonal antibodies to rat liver microsomal 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jun;79(12):3734–3738. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.12.3734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards P. A., Lemongello D., Fogelman A. M. Improved methods for the solubilization and assay of hepatic 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase. J Lipid Res. 1979 Jan;20(1):40–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards P. A., Lemongello D., Kane J., Shechter I., Fogelman A. M. Properties of purified rat hepatic 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase and regulation of enzyme activity. J Biol Chem. 1980 Apr 25;255(8):3715–3725. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards P. A., Popják G., Fogelman A. M., Edmond J. Control of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase by endogenously synthesized sterols in vitro and in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1057–1063. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goding J. W. Conjugation of antibodies with fluorochromes: modifications to the standard methods. J Immunol Methods. 1976;13(3-4):215–226. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(76)90068-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ness G. C., Way S. C., Wickham P. S. Proteinase involvement in the solubilization of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Sep 16;102(1):81–85. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)91491-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payvar F., Schimke R. T. Methylmercury hydroxide enhancement of translation and transcription of ovalbumin and conalbumin mRNA's. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 25;254(16):7636–7642. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Jackson R. J. An efficient mRNA-dependent translation system from reticulocyte lysates. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Aug 1;67(1):247–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10656.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodwell V. W., Nordstrom J. L., Mitschelen J. J. Regulation of HMG-CoA reductase. Adv Lipid Res. 1976;14:1–74. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-024914-5.50008-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka R. D., Edwards P. A., Lan S. F., Knöppel E. M., Fogelman A. M. The effect of cholestyramine and Mevinolin on the diurnal cycle of rat hepatic 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase. J Lipid Res. 1982 Sep;23(7):1026–1031. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]