Abstract
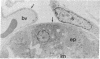
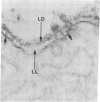
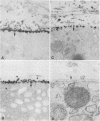
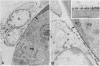
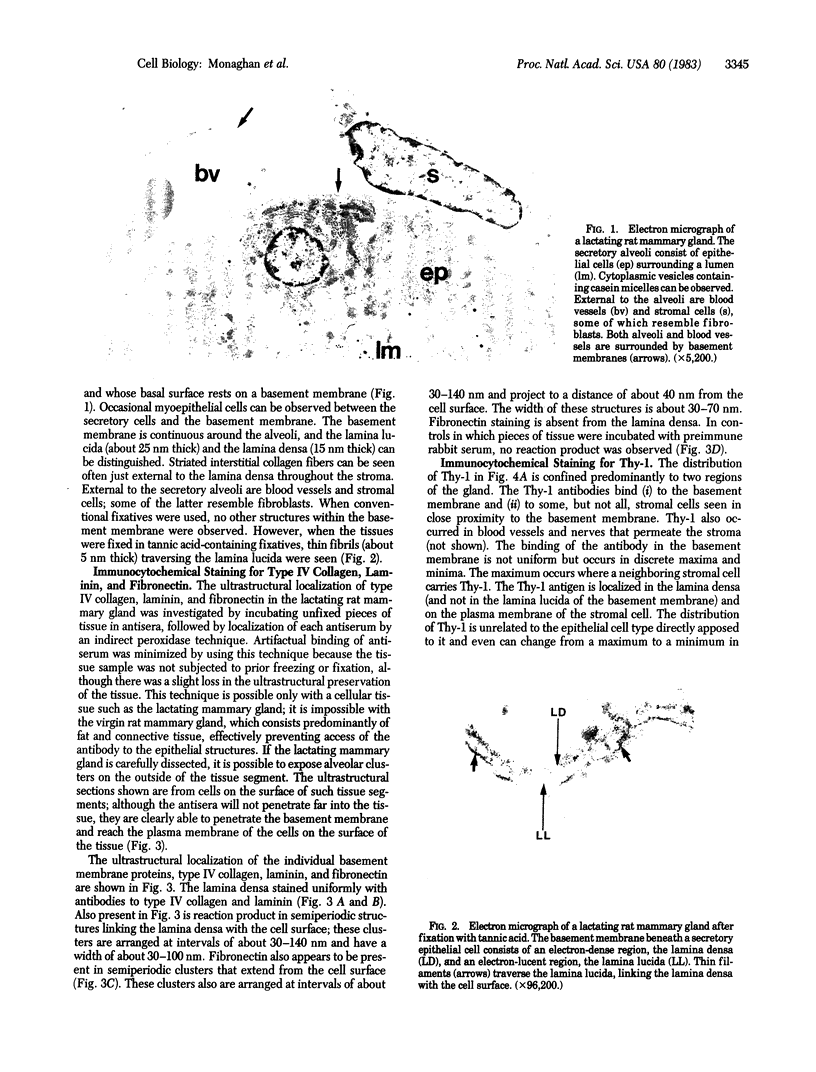
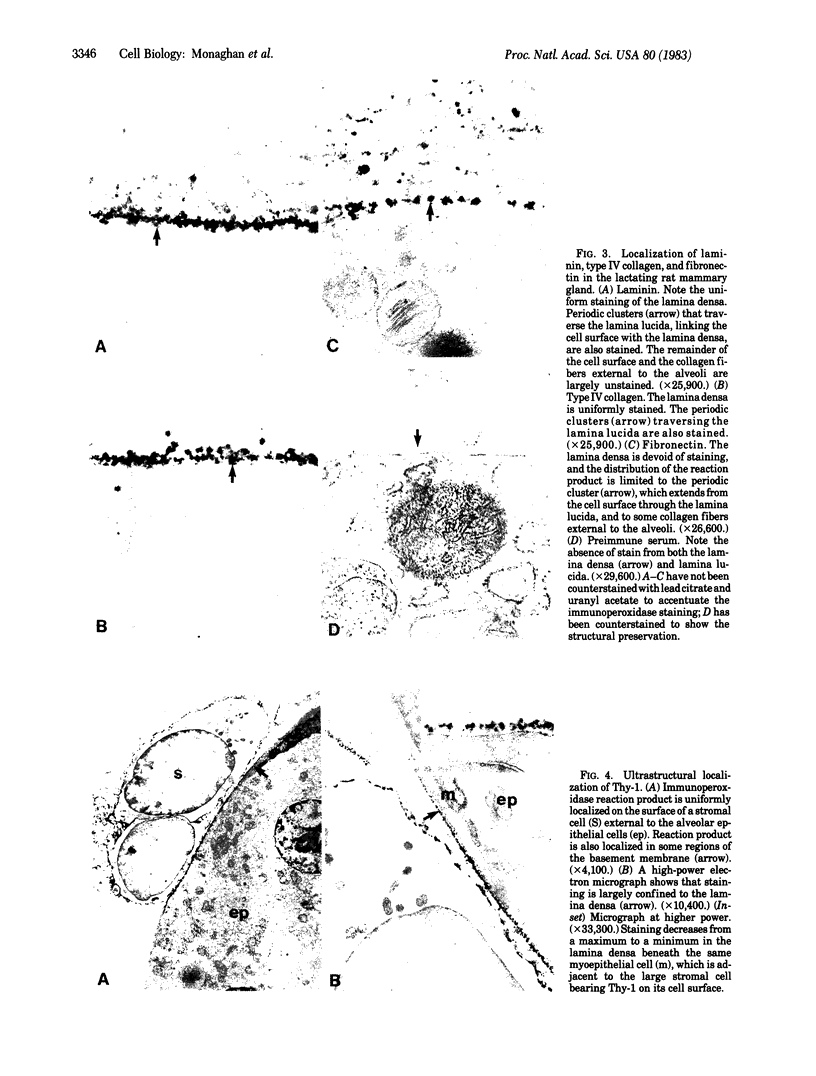
The topographical distribution of type IV collagen, laminin, fibronectin, and the thymocyte differentiation antigen Thy-1 in the basement membrane of the lactating rat mammary gland was investigated. Small cubes of tissue, which had not been subjected to prior fixation or freezing, were incubated with monospecific or monoclonal antibodies to these proteins, and the antibodies were located by an indirect immunoperoxidase staining technique and observed in the electron microscope. The lamina densa stained uniformly with antibodies to type IV collagen and laminin. In addition, both laminin and type IV collagen were present in semiperiodic clusters that traversed the lamina lucida from the cell surface to the lamina densa. Fibronectin was present only in the semiperiodic clusters and not elsewhere in the basement membrane. These clusters were irregularly spaced along the cell surface and heterogeneous in size. It remains to be determined if these three proteins are present in the same clusters. Thy-1 was largely present on the lamina densa and not on the lamina lucida. The Thy-1 staining of the lamina densa occurred in discrete maxima and minima. These maxima occurred in regions adjacent to Thy-1-bearing stromal cells. Thus, the topographical distribution of proteins within a basement membrane varies in a nonrandom manner, and local factors can modify this distribution. We suggest that this topographical variability may play a role in cell recognition and signalling processes that occur across the basement membrane.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Briggaman R. A., Dalldorf F. G., Wheeler C. E., Jr Formation and origin of basal lamina and anchoring fibrils in adult human skin. J Cell Biol. 1971 Nov;51(21):384–395. doi: 10.1083/jcb.51.2.384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brownell A. G., Bessem C. C., Slavkin H. C. Possible functions of mesenchyme cell-derived fibronectin during formation of basal lamina. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3711–3715. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couchman J. R., Gibson W. T., Thom D., Weaver A. C., Rees D. A., Parish W. E. Fibronectin distribution in epithelial and associated tissues of the rat. Arch Dermatol Res. 1979 Nov;266(3):295–310. doi: 10.1007/BF00418575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtoy P. J., Kanwar Y. S., Hynes R. O., Farquhar M. G. Fibronectin localization in the rat glomerulus. J Cell Biol. 1980 Dec;87(3 Pt 1):691–696. doi: 10.1083/jcb.87.3.691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtoy P. J., Timpl R., Farquhar M. G. Comparative distribution of laminin, type IV collagen, and fibronectin in the rat glomerulus. J Histochem Cytochem. 1982 Sep;30(9):874–886. doi: 10.1177/30.9.7130672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEOME K. B., FAULKIN L. J., Jr, BERN H. A., BLAIR P. B. Development of mammary tumors from hyperplastic alveolar nodules transplanted into gland-free mammary fat pads of female C3H mice. Cancer Res. 1959 Jun;19(5):515–520. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foidart J. M., Bere E. W., Jr, Yaar M., Rennard S. I., Gullino M., Martin G. R., Katz S. I. Distribution and immunoelectron microscopic localization of laminin, a noncollagenous basement membrane glycoprotein. Lab Invest. 1980 Mar;42(3):336–342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J. R., Bernfield M. R. The basal lamina of the postnatal mammary epithelium contains glycosaminoglycans in a precise ultrastructural organization. Dev Biol. 1980 Jan;74(1):118–135. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(80)90056-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hassell J. R., Robey P. G., Barrach H. J., Wilczek J., Rennard S. I., Martin G. R. Isolation of a heparan sulfate-containing proteoglycan from basement membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4494–4498. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4494. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinman H. K., Klebe R. J., Martin G. R. Role of collagenous matrices in the adhesion and growth of cells. J Cell Biol. 1981 Mar;88(3):473–485. doi: 10.1083/jcb.88.3.473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kratochwil K. Organ specificity in mesenchymal induction demonstrated in the embryonic development of the mammary gland of the mouse. Dev Biol. 1969 Jul;20(1):46–71. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(69)90004-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kratochwil K., Schwartz P. Tissue interaction in androgen response of embryonic mammary rudiment of mouse: identification of target tissue for testosterone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Nov;73(11):4041–4044. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.11.4041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurie G. W., Leblond C. P., Martin G. R. Localization of type IV collagen, laminin, heparan sulfate proteoglycan, and fibronectin to the basal lamina of basement membranes. J Cell Biol. 1982 Oct;95(1):340–344. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.1.340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lennon V. A., Unger M., Dulbecco R. Thy-1: a differentiation marker of potential mammary myoepithelial cells in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):6093–6097. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.6093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madri J. A., Roll F. J., Furthmayr H., Foidart J. M. Ultrastructural localization of fibronectin and laminin in the basement membranes of the murine kidney. J Cell Biol. 1980 Aug;86(2):682–687. doi: 10.1083/jcb.86.2.682. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez-Hernandez A., Fink L. M., Pierce G. B. Removal of basement membrane in the involuting breast. Lab Invest. 1976 May;34(5):455–462. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer B. W., Jr, Hay E. D., Hynes R. O. Immunocytochemical localization of fibronectin in embryonic chick trunk and area vasculosa. Dev Biol. 1981 Mar;82(2):267–286. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(81)90451-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris R. J., Ritter M. A. Association of thy-1 cell surface differentiation antigen with certain connective tissues in vivo. Cell Tissue Res. 1980;206(3):459–475. doi: 10.1007/BF00237975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NANDI S. Endocrine control of mammarygland development and function in the C3H/ He Crgl mouse. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1958 Dec;21(6):1039–1063. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novikoff A. B., Novikoff P. M., Quintana N., Davis C. Diffusion artificats in 3,3'-diaminobenzidine cytochemistry. J Histochem Cytochem. 1972 Sep;20(9):745–749. doi: 10.1177/20.9.745. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozzello L. Epithelial-stromal junction of normal and dysplastic mammary glands. Cancer. 1970 Mar;25(3):586–600. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197003)25:3<586::aid-cncr2820250314>3.0.co;2-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radnor C. J. Myoepithelium in the prelactating and lactating mammary glands of the rat. J Anat. 1972 Sep;112(Pt 3):337–353. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritter M. A., Morris R. J. Thy-1 antigen: selective association in lymphoid organs with the vascular basement membrane involved in lymphocyte recirculation. Immunology. 1980 Jan;39(1):85–91. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudland P. S., Warburton M. J., Monaghan P., Ritter M. A. Thy-1 antigen on normal and neoplastic rat mammary tissues: changes in location and amount of antigen during differentiation of cultured stem cells. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1982 May;68(5):799–811. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanes J. R. Laminin, fibronectin, and collagen in synaptic and extrasynaptic portions of muscle fiber basement membrane. J Cell Biol. 1982 May;93(2):442–451. doi: 10.1083/jcb.93.2.442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seligman A. M., Shannon W. A., Jr, Hoshino Y., Plapinger R. E. Some important principles in 3,3'-diaminobenzidine ultrastructural cytochemistry. J Histochem Cytochem. 1973 Aug;21(8):756–758. doi: 10.1177/21.8.756. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley J. R., Woodley D. T., Katz S. I., Martin G. R. Structure and function of basement membrane. J Invest Dermatol. 1982 Jul;79 (Suppl 1):69s–72s. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12545830. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trelstad R. L., Hayashi K., Toole B. P. Epithelial collagens and glycosaminoglycans in the embryonic cornea. Macromolecular order and morphogenesis in the basement membrane. J Cell Biol. 1974 Sep;62(3):815–830. doi: 10.1083/jcb.62.3.815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warburton M. J., Mitchell D., Ormerod E. J., Rudland P. Distribution of myoepithelial cells and basement membrane proteins in the resting, pregnant, lactating, and involuting rat mammary gland. J Histochem Cytochem. 1982 Jul;30(7):667–676. doi: 10.1177/30.7.6179984. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warburton M. J., Ormerod E. J., Monaghan P., Ferns S., Rudland P. S. Characterization of a myoepithelial cell line derived from a neonatal rat mammary gland. J Cell Biol. 1981 Dec;91(3 Pt 1):827–836. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.3.827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wicha M. S., Lowrie G., Kohn E., Bagavandoss P., Mahn T. Extracellular matrix promotes mammary epithelial growth and differentiation in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(10):3213–3217. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.10.3213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaoita H., Foidart J. M., Katz S. I. Localization of the collagenous component in skin basement membrane. J Invest Dermatol. 1978 Apr;70(4):191–193. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12541313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]