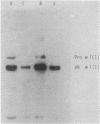
Abstract
Chicken embryo skin of different ages and adult skin were labeled with antibodies against the amino propeptide and carboxyl propeptide of type I collagen and processed for indirect immunoelectron microscopy by the ferritin technique. The results indicate that the formation of thin collagen fibrils involves polymerization of pN-collagen. Fibrils that are thicker than 35-40 nm do not appear to contain the amino propeptide. How fibrils increase in size is not clear, but growth may involve mechanisms such as lateral aggregation of subfibril structures or fusion of thin fibrils. Carboxyl propeptides were localized near or in contact with thin collagen fibrils, but they did not appear to be arranged in a periodic manner along the fibrils. In experiments using antibodies against the amino propeptides of type III collagen, fibrils 20-40 nm in diameter were also labeled in a periodic fashion. pN-Collagen chains were extracted from embryonic skin and identified by NaDodSO4/polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and by immunoblotting. The presence of significant amounts of pN-collagen in skin from 10- and 12-day chicken embryos agreed well with the labeling of amino propeptides by immunoelectron microscopy. This study provides evidence for the role of the amino propeptide in collagen fibrillogenesis in embryonic skin.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Engel J., Bruckner P., Becker U., Timpl R., Rutschmann B. Physical properties of the amino-terminal precursor-specific portion of type I procollagen. Biochemistry. 1977 Sep 6;16(18):4026–4033. doi: 10.1021/bi00637a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fessler J. H., Fessler L. I. Biosynthesis of procollagen. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:129–162. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.001021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fessler L. I., Timpl R., Fessler J. H. Assembly and processing of procollagen type III in chick embryo blood vessels. J Biol Chem. 1981 Mar 10;256(5):2531–2537. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischmajer R., Timpl R., Tuderman L., Raisher L., Wiestner M., Perlish J. S., Graves P. N. Ultrastructural identification of extension aminopropeptides of type I and III collagens in human skin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7360–7364. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDBERG B., GREEN H. AN ANALYSIS OF COLLAGEN SECRETION BY ESTABLISHED MOUSE FIBROBLAST LINES. J Cell Biol. 1964 Jul;22:227–258. doi: 10.1083/jcb.22.1.227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROSS J., KIRK D. The heat precipitation of collagen from neutral salt solutions: some rate-regulating factors. J Biol Chem. 1958 Aug;233(2):355–360. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg B. Binding of soluble type I collagen molecules to the fibroblast plasma membrane. Cell. 1979 Feb;16(2):265–275. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90004-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King J., Laemmli U. K. Polypeptides of the tail fibres of bacteriophage T4. J Mol Biol. 1971 Dec 28;62(3):465–477. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90148-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapiere C. M., Nusgens B. Polymerization of procollagen in vitro. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Apr 11;342(2):237–246. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(74)90078-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenaers A., Lapiere C. M. Type III procollagen and collagen in skin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Jul 21;400(1):121–131. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(75)90132-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung M. K., Fessler L. I., Greenberg D. B., Fessler J. H. Separate amino and carboxyl procollagen peptidases in chick embryo tendon. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jan 10;254(1):224–232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyahara M., Njieha F. K., Prockop D. J. Formation of collagen fibrils in vitro by cleavage of procollagen with procollagen proteinases. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 25;257(14):8442–8448. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowack H., Gay S., Wick G., Becker U., Timpl R. Preparation and use in immunohistology of antibodies specific for type I and type III collagen and procollagen. J Immunol Methods. 1976;12(1-2):117–124. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(76)90101-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen B. R., Berg R. A., Kishida Y., Prockop D. J. Further characterization of embryonic tendon fibroblasts and the use of immunoferritin techniques to study collagen biosynthesis. J Cell Biol. 1975 Feb;64(2):340–355. doi: 10.1083/jcb.64.2.340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen B. R., Guzman N. A., Engel J., Condit C., Aase S. Purification and characterization of a peptide from the carboxy-terminal region of chick tendon procollagen type I. Biochemistry. 1977 Jun 28;16(13):3030–3036. doi: 10.1021/bi00632a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pesciotta D. M., Silkowitz M. H., Fietzek P. P., Graves P. N., Berg R. A., Olsen B. R. Purification and characterization of the amino-terminal propeptide of Pro alpha 1(I) chains from embryonic chick tendon procollagen. Biochemistry. 1980 May 27;19(11):2447–2454. doi: 10.1021/bi00552a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timpl R., Glanville R. W., Nowack H., Wiedemann H., Fietzek P. P., Kühn K. Isolation, chemical and electron microscopical characterization of neutral-salt-soluble type III collagen and procollagen from fetal bovine skin. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1975 Nov;356(11):1783–1792. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1975.356.2.1783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trelstad R. L., Hayashi K., Gross J. Collagen fibrillogenesis: intermediate aggregates and suprafibrillar order. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Nov;73(11):4027–4031. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.11.4027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trelstad R. L., Hayashi K. Tendon collagen fibrillogenesis: intracellular subassemblies and cell surface changes associated with fibril growth. Dev Biol. 1979 Aug;71(2):228–242. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(79)90166-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veis A., Anesey J., Yuan L., Levy S. J. Evidence for an amino-terminal extension in high-molecular-weight collagens from mature bovine skin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 May;70(5):1464–1467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.5.1464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOOD G. C., KEECH M. K. The formation of fibrils from collagen solutions. 1. The effect of experimental conditions: kinetic and electron-microscope studies. Biochem J. 1960 Jun;75:588–598. doi: 10.1042/bj0750588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]