Abstract
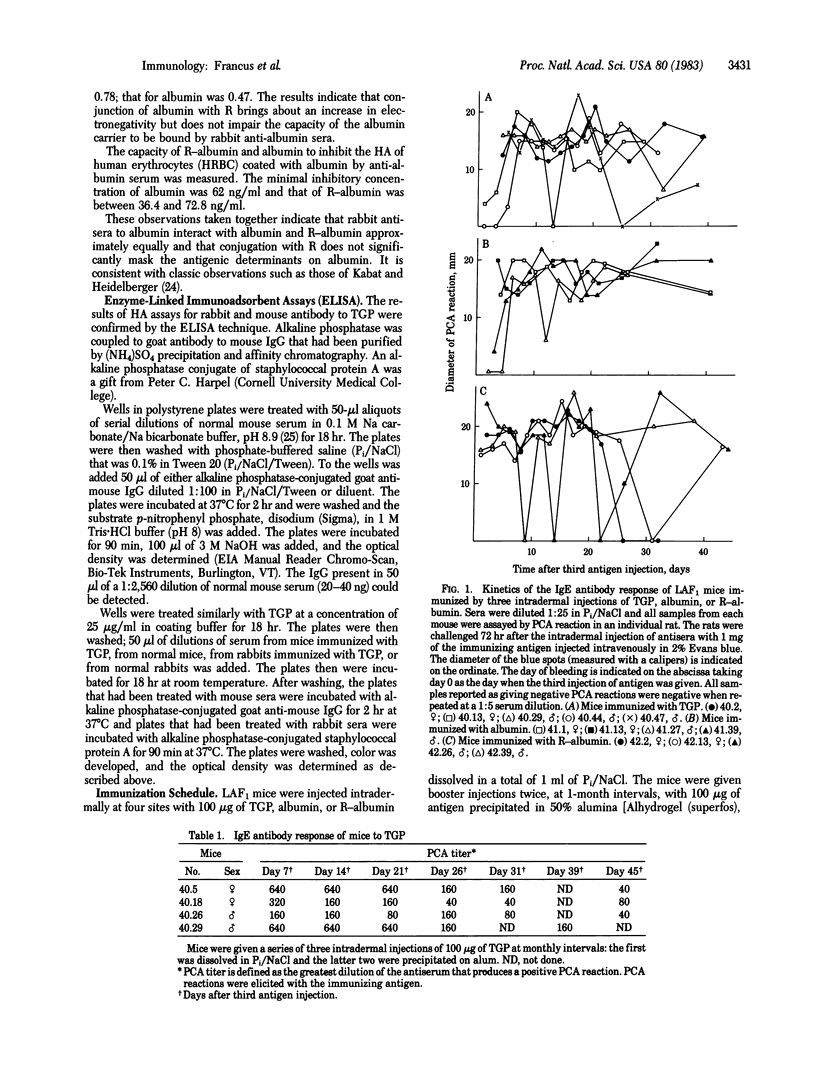
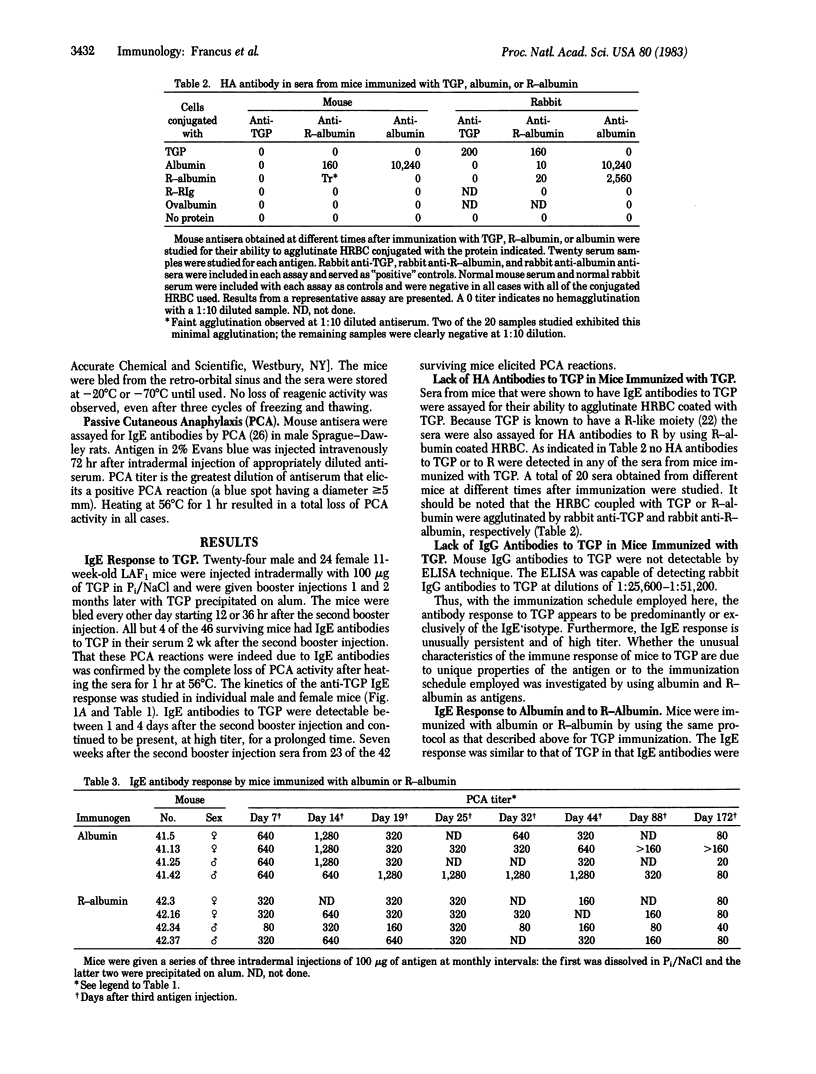
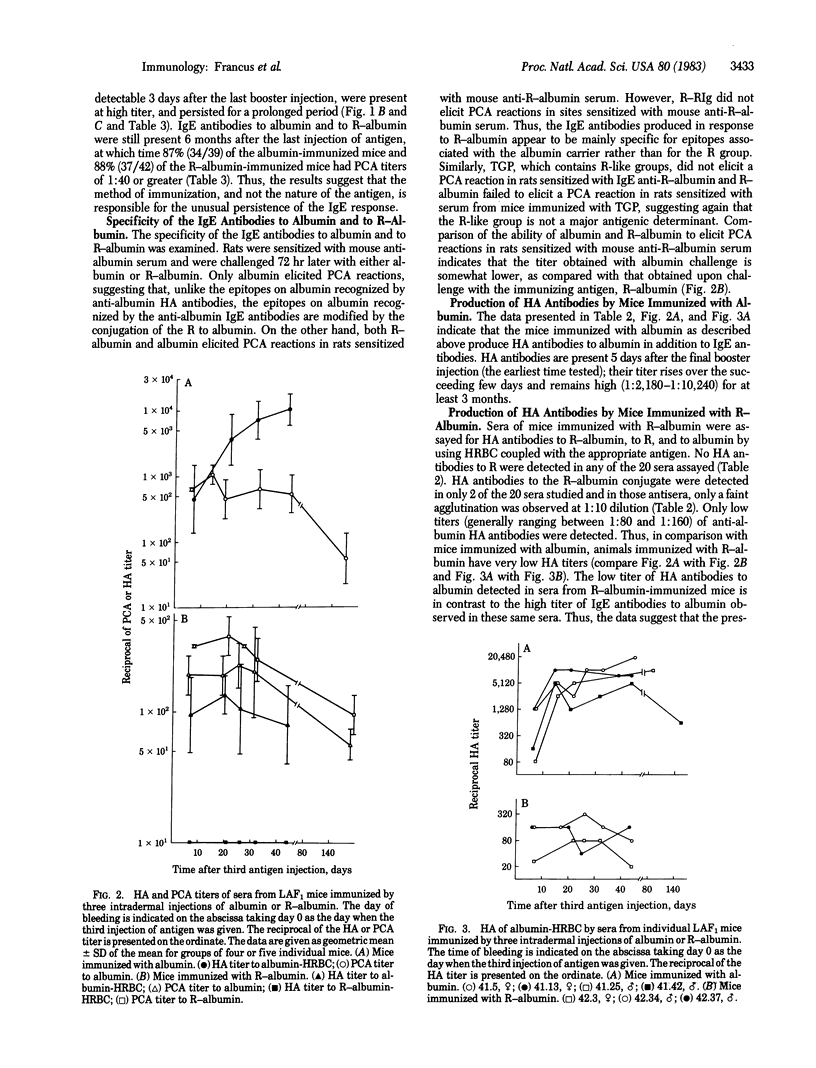
Tobacco glycoprotein (TGP) is a glycoprotein containing rutin-like polyphenol groups that is purified from cured tobacco leaves and can be detected in condensates of tobacco smoke. One-third of normal humans have been shown to manifest immediate, IgE-mediated, wheal and flare reactions to an intradermal injection of TGP. Rutin-like moieties are also found in a wide variety of vegetable foods. The possible importance of sensitivity to TGP in the pathogenesis of the vascular and pulmonary complications of tobacco smoking has stimulated us to study the immune response of mice to TGP and the role of rutin groups in influencing isotype expression. A series of three intradermal injections of TGP elicits a long-lasting IgE antibody response in mice. However, no hemagglutinating antibodies are produced. Similarly, immunization with a rutin derivative of bovine serum albumin stimulates IgE antibodies to bovine serum albumin but little hemagglutinating antibodies. In contrast, mice injected in the same manner with bovine serum albumin produce both IgE and hemagglutinating antibodies. Thus, the rutin moiety is implicated as exerting a regulatory effect on isotype expression by suppressing the production of serum antibodies of isotypes other than IgE. The immunization procedure employed (which involves an initial injection of 100 micrograms of antigen in phosphate-buffered saline, followed, at monthly intervals, by two intradermal injections of 100 micrograms of antigen precipitated on alum) apparently fails to stimulate the normal "down-regulation" of the IgE response so that a persisting high-titered response is obtained.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BINAGHI R. A., BENACERRAF B. THE PRODUCTION OF ANAPHYLACTIC ANTIBODY IN THE RAT. J Immunol. 1964 Jun;92:920–926. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bargatze R. F., Katz D. H. "Allergic breakthrough" after antigen sensitization: height of IgE synthesis is temporally related to diurnal variation in endogenous steroid production. J Immunol. 1980 Nov;125(5):2306–2310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bazin H., Platteau B., Pauwels R. Genetic control of the IgE reaginic immune response. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1981;66 (Suppl 1):19–24. doi: 10.1159/000232861. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker C. G., Dubin T. Activation of factor XII by tobacco glycoprotein. J Exp Med. 1977 Aug 1;146(2):457–467. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.2.457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker C. G., Dubin T., Wiedemann H. P. Hypersensitivity to tobacco antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 May;73(5):1712–1716. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.5.1712. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker C. G., Levi R., Zavecz J. Induction of IgE antibodies to antigen isolated from tobacco leaves and from cigarette smoke condensate. Am J Pathol. 1979 Jul;96(1):249–255. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker C. G., Van Hamont N., Wagner M. Tobacco, cocoa, coffee, and ragweed: cross-reacting allergens that activate factor-XII-dependent pathways. Blood. 1981 Nov;58(5):861–867. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiorazzi N., Fox D. A., Katz D. H. Hapten-specific IgE antibody responses in mice. VI. Selective enhancement of IgE antibody production by low doses of X-irradiation and by cyclophosphamide. J Immunol. 1976 Nov;117(5 Pt 1):1629–1637. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denburg J., Blajchman J., Gauldie J., Horsewood P., Gill G., Thomson G., Beattie H., Evans G., Bienenstock J. Hypersensitivity to tobacco glycoprotein in human peripheral vascular disease. Ann Allergy. 1981 Jul;47(1):8–13. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorf M. E., Newburger P. E., Hamaoka T., Katz D. H., Benacerraf B. Characterization of an immune response gene in mice controlling IgE and IgM antibody responses to ragweed pollen extract and its 2,4-dinitrophenylated derivative. Eur J Immunol. 1974 May;4(5):346–349. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830040507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E., Perlmann P. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, Elisa. 3. Quantitation of specific antibodies by enzyme-labeled anti-immunoglobulin in antigen-coated tubes. J Immunol. 1972 Jul;109(1):129–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogarth-Scott R. S., Johansson S. G., Bennich H. Antibodies to Toxocara in the sera of visceral larva migrans patients: the significance of raised levels of IgE. Clin Exp Immunol. 1969 Dec;5(6):619–625. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaka K., Ishizaka T. Mechanisms of reaginic hypersensitivity and IgE antibody response. Immunol Rev. 1978;41:109–148. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1978.tb01462.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarrett E., Bazin H. Elevation of total serum IgE in rats following helminth parasite infection. Nature. 1974 Oct 18;251(5476):613–614. doi: 10.1038/251613a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kabat E. A., Heidelberger M. A QUANTITATIVE THEORY OF THE PRECIPITIN REACTION : V. THE REACTION BETWEEN CRYSTALLINE HORSE SERUM ALBUMIN AND ANTIBODY FORMED IN THE RABBIT. J Exp Med. 1937 Jul 31;66(2):229–250. doi: 10.1084/jem.66.2.229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz D. H. The allergic phenotype: manifestation of 'allergic breakthrough' and imbalance in normal 'damping' of IgE antibody production. Immunol Rev. 1978;41:77–108. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1978.tb01461.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelsoe G., Cerny J. Reciprocal expansions of idiotypic and anti-idiotypic clones following antigen stimulation. Nature. 1979 May 24;279(5711):333–334. doi: 10.1038/279333a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi R., Zavecz J. H., Burke J. A., Becker C. G. Cardiac and pulmonary anaphylaxis in guinea pigs and rabbits induced by glycoprotein isolated from tobacco leaves and cigarette smoke condensate. Am J Pathol. 1982 Mar;106(3):318–325. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine B. B., Stember R. H., Fotino M. Ragweed hay fever: genetic control and linkage to HL-A haplotypes. Science. 1972 Dec 15;178(4066):1201–1203. doi: 10.1126/science.178.4066.1201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine B. B., Vaz N. M. Effect of combinations of inbred strain, antigen, and antigen dose on immune responsiveness and reagin production in the mouse. A potential mouse model for immune aspects of human atopic allergy. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1970;39(2-3):156–171. doi: 10.1159/000230343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOTA I. THE MECHANISM OF ANAPHYLAXIS. I. PRODUCTION AND BIOLOGICAL PROPERTIES OF 'MAST CELL SENSITIZING' ANTIBODY. Immunology. 1964 Nov;7:681–699. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mongini P. K., Paul W. E. T cell regulation of the IgG2a response to TNP-Ficoll: evidence that allotype congenic mice contain both helper cells that preferentially enhance IgG2a synthesis and suppressor cells that specifically suppress IgG2 synthesis. J Immunol. 1982 Jun;128(6):2405–2410. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mongini P. K., Stein K. E., Paul W. E. T cell regulation of IgG subclass antibody production in response to T-independent antigens. J Exp Med. 1981 Jan 1;153(1):1–12. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mota I., Peixoto J. M. A skin-sensitizing and thermolabile antibody in the mouse. Life Sci. 1966 Sep;5(18):1723–1728. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(66)90108-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogilvie B. M. Reagin-like antibodies in rats infected with the nematode parasite Nippostrongylus brasiliensis. Immunology. 1967 Feb;12(2):113–131. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okumura K., Tada T. Regulation of homocytotropic antibody formation in the rat. 3. Effect of thymectomy and splenectomy. J Immunol. 1971 Apr;106(4):1019–1025. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orr T. S., Blair A. M. Potentiated reagin response to egg albumin and conalbumin in Nippostrongylus brasiliensis infected rats. Life Sci. 1969 Oct 15;8(20):1073–1077. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(69)90459-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ovary Z., Itaya T., Watanabe N., Kojima S. Regulation of IgE in mice. Immunol Rev. 1978;41:26–51. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1978.tb01459.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Revoltella R., Ovary Z. Preferential production of rabbit reaginic antibodies. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1969;36(3):282–289. doi: 10.1159/000230749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Revoltella R., Ovary Z. Reaginic antibody production in different mouse strains. Immunology. 1969 Jul;17(1):45–54. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slack J., Der-Balian G. P., Nahm M., Davie J. M. Subclass restriction of murine antibodies. II. The IgG plaque-forming cell response to thymus-independent type 1 and type 2 antigens in normal mice and mice expressing an X-linked immunodeficiency. J Exp Med. 1980 Apr 1;151(4):853–862. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.4.853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tada T., Taniguchi M., Okumura K. Regulation of homocytotropic antibody formation in the rat. II. Effect of X-irradiation. J Immunol. 1971 Apr;106(4):1012–1018. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi M., Tada T. Regulation of homocytotropic antibody formation in the rat. IV. Effects of various immunosuppressive drugs. J Immunol. 1971 Aug;107(2):579–585. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaz N. M., Phillips-Quagliata J. M., Levine B. B., Vaz E. M. H-2-linked genetic control of immune responsiveness to ovalbumin and ovomucoid. J Exp Med. 1971 Nov 1;134(5):1335–1348. doi: 10.1084/jem.134.5.1335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe N., Kojima S., Ovary Z. Tolerizing effect of DNP-ficoll on IgE antibody production. J Immunol. 1977 Jan;118(1):251–255. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weigle W. O. Cyclical production of antibody as a regulatory mechanism in the immune response. Adv Immunol. 1975;21:87–111. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60219-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


