Abstract
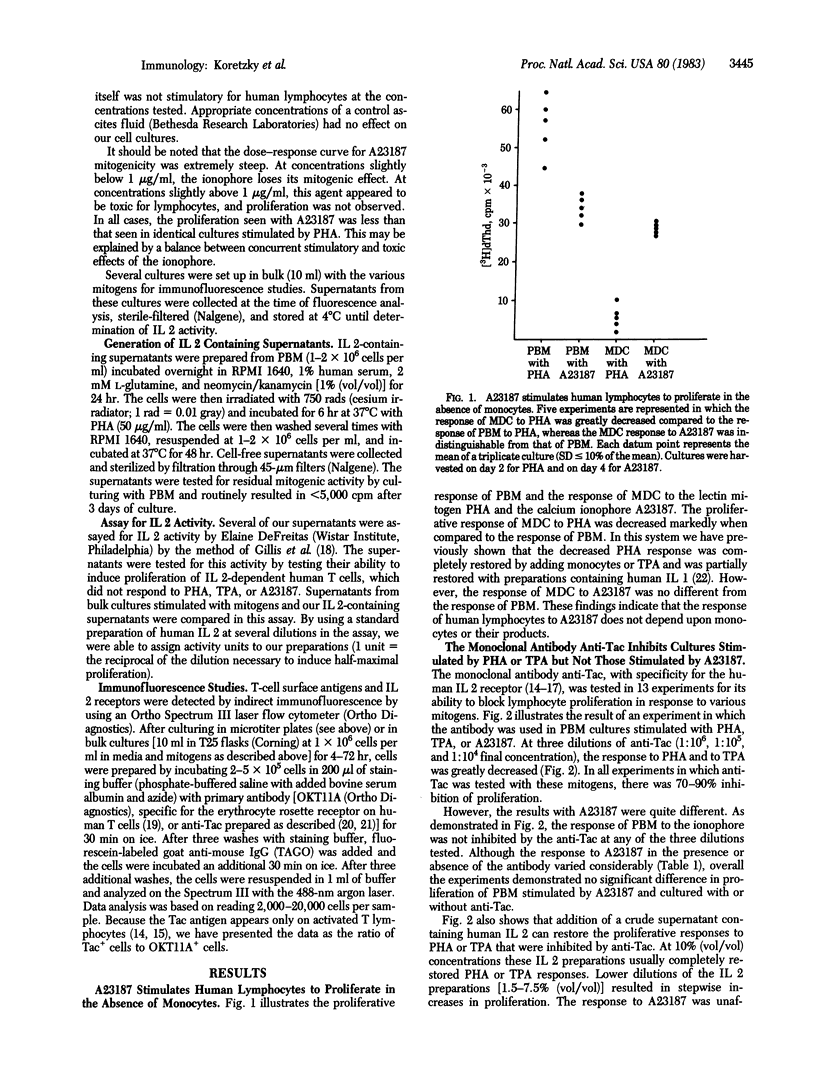
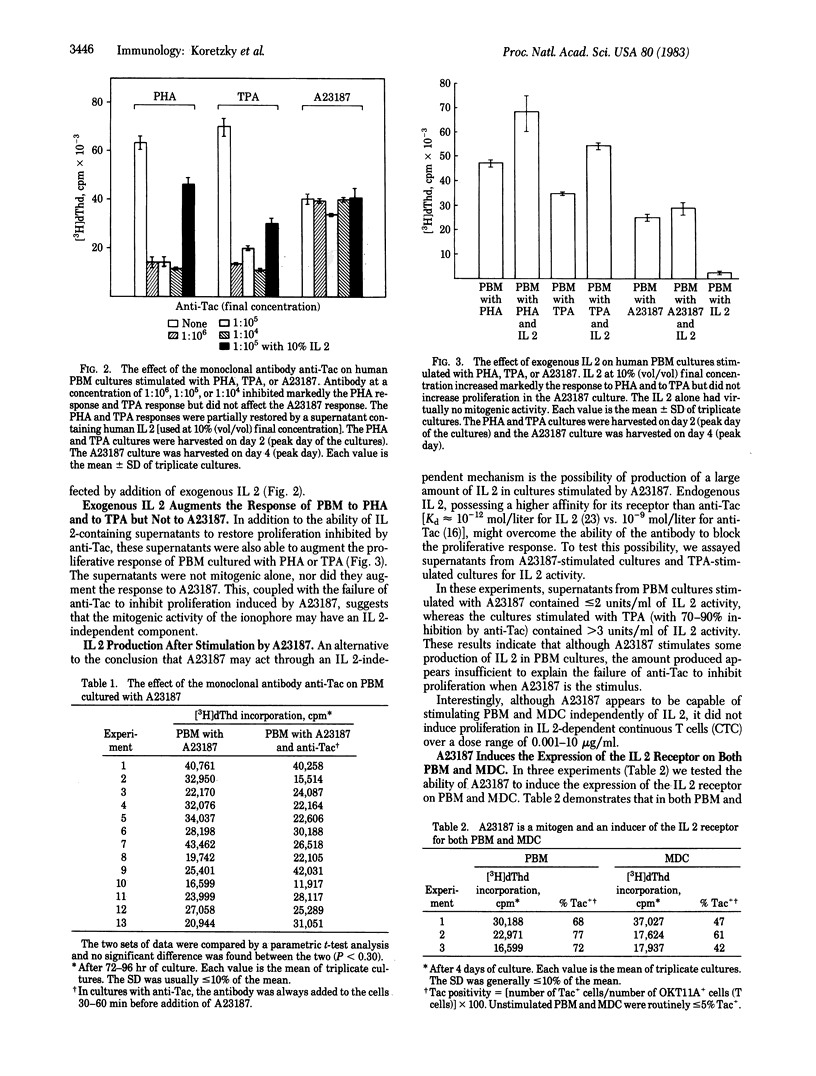
Though lectin mitogen stimulation of T-cell proliferation is an interleukin 1- (IL 1), interleukin 2- (IL 2) dependent process, the calcium ionophore A23187 may be able to initiate T-lymphocyte proliferation by an additional pathway. That the action of A23187 is IL 1 independent was demonstrated by its ability to stimulate monocyte-depleted cells without the addition of exogenous IL 1. The IL 2 independence of A23187 was indicated by (i) the inability of exogenous IL 2 to augment A23187-induced proliferation and (ii) the inability of the monoclonal antibody anti-Tac (with specificity for the human IL 2 receptor) to inhibit proliferation mediated by A23187. By contrast, in cultures stimulated with the lectin mitogen phytohemagglutinin, additional IL 2 considerably increased proliferation, whereas anti-Tac routinely caused 60-90% inhibition. Although the ionophore caused some IL 2 production and resulted in IL 2 receptor expression, quantitative studies showed that our results could not be explained by excessive amounts of endogenous IL 2 interfering with the blocking action of the antibody. Therefore, these data suggest that the action of A23187 as a human lymphocyte mitogen may be the result of at least two pathways--one dependent on the interleukin-cell interactions and the other independent of these mediators.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blondin G. A. Isolation of a divalent cation ionophore from beef heart mitochondria. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Jan;56(1):97–105. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(74)80320-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gery I., Gershon R. K., Waksman B. H. Potentiation of the T-lymphocyte response to mitogens. I. The responding cell. J Exp Med. 1972 Jul 1;136(1):128–142. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.1.128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis S., Ferm M. M., Ou W., Smith K. A. T cell growth factor: parameters of production and a quantitative microassay for activity. J Immunol. 1978 Jun;120(6):2027–2032. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis S., Mizel S. B. T-Cell lymphoma model for the analysis of interleukin 1-mediated T-cell activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):1133–1137. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.1133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis S., Smith K. A. Long term culture of tumour-specific cytotoxic T cells. Nature. 1977 Jul 14;268(5616):154–156. doi: 10.1038/268154a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen P., Winger L., Rasmussen H., Nowell P. The mitogenic effect of A23187 in human peripheral lymphocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Feb 28;496(2):374–383. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(77)90320-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koretzky G. A., Daniele R. P., Nowell P. C. A phorbol ester (TPA) can replace macrophages in human lymphocyte cultures stimulated with a mitogen but not with an antigen. J Immunol. 1982 Apr;128(4):1776–1780. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachman L. B., Hacker M. P., Handschumacher R. E. Partial purification of human lymphocyte-activating factor (LAF) by ultrafiltration and electrophoretic techniques. J Immunol. 1977 Dec;119(6):2019–2023. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson E. L., Coutinho A., Martinez C. A suggested mechanism for T lymphocyte activation: implications on the acquisition of functional reactivities. Immunol Rev. 1980;51:61–91. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1980.tb00317.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard W. J., Depper J. M., Uchiyama T., Smith K. A., Waldmann T. A., Greene W. C. A monoclonal antibody that appears to recognize the receptor for human T-cell growth factor; partial characterization of the receptor. Nature. 1982 Nov 18;300(5889):267–269. doi: 10.1038/300267a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luckasen J. R., White J. G., Kersey J. H. Mitogenic properties of a calcium ionophore, A23187. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Dec;71(12):5088–5090. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.12.5088. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meuer S. C., Hussey R. E., Penta A. C., Fitzgerald K. A., Stadler B. M., Schlossman S. F., Reinherz E. L. Cellular origin of interleukin 2 (IL 2) in man: evidence for stimulus-restricted IL 2 production by T4+ and T8+ T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1982 Sep;129(3):1076–1079. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan D. A., Ruscetti F. W., Gallo R. Selective in vitro growth of T lymphocytes from normal human bone marrows. Science. 1976 Sep 10;193(4257):1007–1008. doi: 10.1126/science.181845. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morita Y., Chiang P. K., Siraganian R. P. Effect of inhibitors of transmethylation on histamine release from human basophils. Biochem Pharmacol. 1981 Apr 1;30(7):785–791. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(81)90166-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morita Y., Siraganian R. P. Inhibition of IgE-mediated histamine release from rat basophilic leukemia cells and rat mast cells by inhibitors of transmethylation. J Immunol. 1981 Oct;127(4):1339–1344. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palacios R. Concanavalin A triggers T lymphocytes by directly interacting with their receptors for activation. J Immunol. 1982 Jan;128(1):337–342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robb R. J., Munck A., Smith K. A. T cell growth factor receptors. Quantitation, specificity, and biological relevance. J Exp Med. 1981 Nov 1;154(5):1455–1474. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.5.1455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenstreich D. L., Mizel S. B. The participation of macrophages and macrophage cell lines in the activation of T lymphocytes by mitogens. Immunol Rev. 1978;40:102–135. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1978.tb00403.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruscetti F. W., Gallo R. C. Human T-lymphocyte growth factor: regulation of growth and function of T lymphocytes. Blood. 1981 Mar;57(3):379–394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith K. A., Lachman L. B., Oppenheim J. J., Favata M. F. The functional relationship of the interleukins. J Exp Med. 1980 Jun 1;151(6):1551–1556. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.6.1551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. Y., Pozzan T., Rink T. J. T-cell mitogens cause early changes in cytoplasmic free Ca2+ and membrane potential in lymphocytes. Nature. 1982 Jan 7;295(5844):68–71. doi: 10.1038/295068a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchiyama T., Broder S., Waldmann T. A. A monoclonal antibody (anti-Tac) reactive with activated and functionally mature human T cells. I. Production of anti-Tac monoclonal antibody and distribution of Tac (+) cells. J Immunol. 1981 Apr;126(4):1393–1397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchiyama T., Nelson D. L., Fleisher T. A., Waldmann T. A. A monoclonal antibody (anti-Tac) reactive with activated and functionally mature human T cells. II. Expression of Tac antigen on activated cytotoxic killer T cells, suppressor cells, and on one of two types of helper T cells. J Immunol. 1981 Apr;126(4):1398–1403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Wauwe J., Goossens J., Decock W., Kung P., Goldstein G. Suppression of human T-cell mitogenesis and E-rosette formation by the monoclonal antibody OKT11A. Immunology. 1981 Dec;44(4):865–871. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vries J. E., Caviles A. P., Jr, Bont W. S., Mendelsohn J. The role of monocytes in human lymphocyte activation by mitogens. J Immunol. 1979 Mar;122(3):1099–1107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



