Abstract
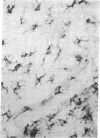
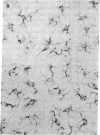
Langerhans cells are Ia-bearing antigen-presenting cells in the epidermis that share many functions with macrophages. We have used monoclonal antibodies to the macrophage antigens, Mac-2 and-3, Ia antigen, Fc fragment receptor and the common leukocyte antigen CLA to compare the cell surface antigens of these cells with those of interdigitating and follicular dendritic cells and of macrophages in lymphoid tissues. Immunoperoxidase staining was carried out with epidermal sheets from BALB/c mice and epidermal cell suspensions enriched for Langerhans cells by Fc rosetting. Langerhans cells stained for all of these antigens. Comparison with the staining properties of other dendritic cells and macrophages, in combination with previous observations, indicates a close relationship of Langerhans cells to the interdigitating cells of lymphoid tissues.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barclay A. N. Different reticular elements in rat lymphoid tissue identified by localization of Ia, Thy-1 and MRC OX 2 antigens. Immunology. 1981 Dec;44(4):727–736. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beller D. I., Springer T. A., Schreiber R. D. Anti-Mac-1 selectively inhibits the mouse and human type three complement receptor. J Exp Med. 1982 Oct 1;156(4):1000–1009. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.4.1000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berken A., Benacerraf B. Properties of antibodies cytophilic for macrophages. J Exp Med. 1966 Jan 1;123(1):119–144. doi: 10.1084/jem.123.1.119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berman B., Gigli I. Complement receptors on guinea pig epidermal Langerhans cells. J Immunol. 1980 Feb;124(2):685–690. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharya A., Dorf M. E., Springer T. A. A shared alloantigenic determinant on Ia antigens encoded by the I-A and I-E subregions: evidence for I region gene duplication. J Immunol. 1981 Dec;127(6):2488–2495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke K., Gigli I. Receptors for complement of Langerhans cells. J Invest Dermatol. 1980 Jul;75(1):46–51. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12521115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CORMANE R. H., KALSBEEK G. L. ATP-HYDROLYZING ENZYMES IN NORMAL HUMAN SKIN. Dermatologica. 1963;127:381–397. doi: 10.1159/000254884. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cocchia D., Michetti F., Donato R. Immunochemical and immuno-cytochemical localization of S-100 antigen in normal human skin. Nature. 1981 Nov 5;294(5836):85–87. doi: 10.1038/294085a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eikelenboom P. Dendritic cells in the rat spleen follicles. A combined immuno- and enzyme histochemical study. Cell Tissue Res. 1978 Jun 26;190(1):79–87. doi: 10.1007/BF00210038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flotte T. J., Springer T. A., Thorbecke G. J. Dendritic cell and macrophage staining by monoclonal antibodies in tissue sections and epidermal sheets. Am J Pathol. 1983 Apr;111(1):112–124. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho M. K., Springer T. A. Mac-1 antigen: quantitative expression in macrophage populations and tissues, and immunofluorescent localization in spleen. J Immunol. 1982 May;128(5):2281–2286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho M. K., Springer T. A. Mac-2, a novel 32,000 Mr mouse macrophage subpopulation-specific antigen defined by monoclonal antibodies. J Immunol. 1982 Mar;128(3):1221–1228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphrey J. H., Grennan D. Isolation and properties of spleen follicular dendritic cells. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1982;149:823–827. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-9066-4_113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juhlin L., Shelley W. B. New staining techniques for the Langerhans cell. Acta Derm Venereol. 1977;57(4):289–296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamperdijk E. W., Raaymakers E. M., de Leeuw J. H., Hoefsmit E. C. Lymph node macrophages and reticulum cells in the immune response. I. The primary response to paratyphoid vaccine. Cell Tissue Res. 1978 Aug 25;192(1):1–23. doi: 10.1007/BF00231019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klinkert W. E., LaBadie J. H., Bowers W. E. Accessory and stimulating properties of dendritic cells and macrophages isolated from various rat tissues. J Exp Med. 1982 Jul 1;156(1):1–19. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kürzinger K., Ho M. K., Springer T. A. Structural homology of a macrophage differentiation antigen and an antigen involved in T-cell-mediated killing. Nature. 1982 Apr 15;296(5858):668–670. doi: 10.1038/296668a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kürzinger K., Reynolds T., Germain R. N., Davignon D., Martz E., Springer T. A. A novel lymphocyte function-associated antigen (LFA-1): cellular distribution, quantitative expression, and structure. J Immunol. 1981 Aug;127(2):596–602. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang P. G., Ada G. L. Antigen in tissues. IV. The effect of antibody on the retention and localization of antigen in rat lymph nodes. Immunology. 1967 Nov;13(5):523–534. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lay W. H., Nussenzweig V. Receptors for complement of leukocytes. J Exp Med. 1968 Nov 1;128(5):991–1009. doi: 10.1084/jem.128.5.991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILLER J. J., 3rd, NOSSAL G. J. ANTIGENS IN IMMUNITY. VI. THE PHAGOCYTIC RETICULUM OF LYMPH NODE FOLLICLES. J Exp Med. 1964 Dec 1;120:1075–1086. doi: 10.1084/jem.120.6.1075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Hermelink H. K., Heusermann U., Stutte H. J. Enzyme histochemical observations on the localization and structure of the T cell and B cell regions in the human spleen. Cell Tissue Res. 1974;154(2):167–179. doi: 10.1007/BF00223162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nossal G. J., Abbot A., Mitchell J., Lummus Z. Antigens in immunity. XV. Ultrastructural features of antigen capture in primary and secondary lymphoid follicles. J Exp Med. 1968 Feb 1;127(2):277–290. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.2.277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nussenzweig M. C., Steinman R. M., Unkeless J. C., Witmer M. D., Gutchinov B., Cohn Z. A. Studies of the cell surface of mouse dendritic cells and other leukocytes. J Exp Med. 1981 Jul 1;154(1):168–187. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.1.168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rausch E., Kaiserling E., Goos M. Langerhans cells and interdigitating reticulum cells in the thymus-dependent region in human dermatopathic lymphadenitis. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol. 1977 Nov 21;25(4):327–343. doi: 10.1007/BF02889443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richman L. K., Klingenstein R. J., Richman J. A., Strober W., Berzofsky J. A. The murine Kupffer cell. I. Characterization of the cell serving accessory function in antigen-specific T cell proliferation. J Immunol. 1979 Dec;123(6):2602–2609. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowden G., Lewis M. G., Sullivan A. K. Ia antigen expression on human epidermal Langerhans cells. Nature. 1977 Jul 21;268(5617):247–248. doi: 10.1038/268247a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz R. H., Dickler H. B., Sachs D. H., Schwartz B. D. Studies of Ia antigens on murine peritoneal macrophages. Scand J Immunol. 1976;5(6-7):731–743. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1976.tb03023.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silberberg-Sinakin I., Thorbecke G. J., Baer R. L., Rosenthal S. A., Berezowsky V. Antigen-bearing langerhans cells in skin, dermal lymphatics and in lymph nodes. Cell Immunol. 1976 Aug;25(2):137–151. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(76)90105-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer T., Galfrè G., Secher D. S., Milstein C. Monoclonal xenogeneic antibodies to murine cell surface antigens: identification of novel leukocyte differentiation antigens. Eur J Immunol. 1978 Aug;8(8):539–551. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830080802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer T., Galfré G., Secher D. S., Milstein C. Mac-1: a macrophage differentiation antigen identified by monoclonal antibody. Eur J Immunol. 1979 Apr;9(4):301–306. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830090410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinman R. M., Cohn Z. A. Identification of a novel cell type in peripheral lymphoid organs of mice. I. Morphology, quantitation, tissue distribution. J Exp Med. 1973 May 1;137(5):1142–1162. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.5.1142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinman R. M., Cohn Z. A. Identification of a novel cell type in peripheral lymphoid organs of mice. II. Functional properties in vitro. J Exp Med. 1974 Feb 1;139(2):380–397. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.2.380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stingl G., Katz S. I., Clement L., Green I., Shevach E. M. Immunologic functions of Ia-bearing epidermal Langerhans cells. J Immunol. 1978 Nov;121(5):2005–2013. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stingl G., Katz S. I., Shevach E. M., Wolff-Schreiner E., Green I. Detection of Ia antigens on Langerhans cells in guinea pig skin. J Immunol. 1978 Feb;120(2):570–578. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stingl G., Wolff-Schreiner E. C., Pichler W. J., Gschnait F., Knapp W., Wolff K. Epidermal Langerhans cells bear Fc and C3 receptors. Nature. 1977 Jul 21;268(5617):245–246. doi: 10.1038/268245a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi K., Yamaguchi H., Ishizeki J., Nakajima T., Nakazato Y. Immunohistochemical and immunoelectron microscopic localization of S-100 protein in the interdigitating reticulum cells of the human lymph node. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol. 1981;37(2):125–135. doi: 10.1007/BF02892562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamaki K., Stingl G., Gullino M., Sachs D. H., Katz S. I. Ia antigens in mouse skin are predominantly expressed on Langerhans cells. J Immunol. 1979 Aug;123(2):784–787. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamaki K., Stingl G., Katz S. I. The origin of Langerhans cells. J Invest Dermatol. 1980 May;74(5):309–311. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12543533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tew J. G., Thorbecke G. J., Steinman R. M. Dendritic cells in the immune response: characteristics and recommended nomenclature (A report from the Reticuloendothelial Society Committee on Nomenclature). J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1982 May;31(5):371–380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unkeless J. C. Characterization of a monoclonal antibody directed against mouse macrophage and lymphocyte Fc receptors. J Exp Med. 1979 Sep 19;150(3):580–596. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.3.580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Furth R., Thompson J. Review of the origin and kinetics of the promonocytes, monocytes, and macrophages and a brief discussion of the mononuclear phagocyte system. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1971 Mar;120(3):337–355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Voorhis W. C., Hair L. S., Steinman R. M., Kaplan G. Human dendritic cells. Enrichment and characterization from peripheral blood. J Exp Med. 1982 Apr 1;155(4):1172–1187. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.4.1172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veerman A. J. On the interdigitating cells in the thymus-dependent area of the rat spleen: a relation between the mononuclear phagocyte system and T-lymphocytes. Cell Tissue Res. 1974 Apr 11;148(2):247–257. doi: 10.1007/BF00224586. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff K. Die Langerhans-Zelle. Ergebnisse neuerer experimenteller Untersuchungen. I. Arch Klin Exp Dermatol. 1967;229(1):54–75. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]