Abstract
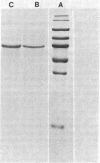
With the use of affinity chromatography, a [3H]-nicotine binding site was purified almost 1,000-fold from a Triton X-100-solubilized extract of rat brain neural membranes. The affinity column was prepared by conjugation of (R,S)-6-(2-hydroxyethyl)nicotine to epoxy-activated Sepharose. Further purification of the material from the affinity column was resolved by using another column of the same affinity gel, resulting in the isolation of a major protein (about 95% purity) that had a Mr of 56,000, as determined by NaDodSO4/polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, with very minor components ranging in Mr from 47,000 to 83,000. With the use of various nicotine analogues, it was shown that the purified material exhibited nearly identical binding characteristics to rat brain membrane preparations, including stereoselectivity for the nicotine enantiomers. The Kd of the purified site, 3.5 x 10(-9) M, was similar to that observed with membrane and Triton X-100-soluble preparations, whereas the binding capacity was greater than 25 pmol/mg of protein, as compared to 0.07 pmol/mg of protein in the starting material. The results are discussed in relation to the purified nicotinic cholinergic receptor from electroplax. It was concluded that the nicotine site in rat brain was different from the cholinergic receptor of electroplax or calf skeletal muscle.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abood L. G., Lowy K., Tometsko A., MacNeil M. Evidence for a noncholinergic site for nicotine's action in brain: psychopharmacological, electrophysiological and receptor binding studies. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1979 Feb;237(2):213–229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abood L. G., Reynolds D. T., Bidlack J. M. Stereospecific 3H-nicotine binding to intact and solubilized rat brain membranes and evidence for its noncholinergic nature. Life Sci. 1980 Oct 6;27(14):1307–1314. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(80)90224-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abood L. G., Reynolds D. T., Booth H., Bidlack J. M. Sites and mechanisms for nicotine's action in the brain. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 1981 Winter;5(4):479–486. doi: 10.1016/0149-7634(81)90018-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aceto M. D., Martin B. R. Central actions of nicotine. Med Res Rev. 1982 Jan-Mar;2(1):43–62. doi: 10.1002/med.2610020104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang H. W. Purification and characterization of acetylcholine receptor-I from Electrophorus electricus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 May;71(5):2113–2117. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.5.2113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conti-Tronconi B. M., Raftery M. A. The nicotinic cholinergic receptor: correlation of molecular structure with functional properties. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:491–530. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.002423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeNoble V. J., Dragan V. P., Carron L. Behavioral effects of intraventricularly administered (-)-nicotine on fixed ratio schedules of food presentation in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1982;77(4):317–321. doi: 10.1007/BF00432762. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dougherty J., Miller D., Todd G., Kostenbauder H. B. Reinforcing and other behavioral effects of nicotine. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 1981 Winter;5(4):487–495. doi: 10.1016/0149-7634(81)90019-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg S. R., Spealman R. D., Goldberg D. M. Persistent behavior at high rates maintained by intravenous self-administration of nicotine. Science. 1981 Oct 30;214(4520):573–575. doi: 10.1126/science.7291998. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotti C., Conti-Tronconi B. M., Raftery M. A. Mammalian muscle acetylcholine receptor purification and characterization. Biochemistry. 1982 Jun 22;21(13):3148–3154. doi: 10.1021/bi00256a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUMMEL J. P., DREYER W. J. Measurement of protein-binding phenomena by gel filtration. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Oct 8;63:530–532. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90124-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall G. H. Pharmacological responses to the intracerebral administration of nicotine. Pharmacol Ther. 1981;15(2):223–238. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(81)90043-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K., Favre M. Maturation of the head of bacteriophage T4. I. DNA packaging events. J Mol Biol. 1973 Nov 15;80(4):575–599. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90198-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansour N. A., Elderfrawi M. E., Eldefrawi A. T. Isolation of putative acetylcholine receptor proteins from housefly brain. Biochemistry. 1977 Sep 6;16(18):4126–4132. doi: 10.1021/bi00637a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin B. R., Aceto M. D. Nicotine binding sites and their localization in the central nervous system. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 1981 Winter;5(4):473–478. doi: 10.1016/0149-7634(81)90017-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen R. W., Meunier J. C., Changeux J. P. Progress in the purification of the cholinergic receptor protein from Electrophorus electricus by affinity chromatography. FEBS Lett. 1972 Nov 15;28(1):96–100. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80686-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds J. A., Karlin A. Molecular weight in detergent solution of acetylcholine receptor from Torpedo californica. Biochemistry. 1978 May 30;17(11):2035–2038. doi: 10.1021/bi00604a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romano C., Goldstein A. Stereospecific nicotine receptors on rat brain membranes. Science. 1980 Nov 7;210(4470):647–650. doi: 10.1126/science.7433991. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosecrans J. A., Meltzer L. T. Central sites and mechanisms of action of nicotine. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 1981 Winter;5(4):497–501. doi: 10.1016/0149-7634(81)90020-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saitoh T., Wennogle L. P., Changeux J. P. Factors regulating the susceptibility of the acetylcholine receptor protein to heat inactivation. FEBS Lett. 1979 Dec 15;108(2):489–494. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80595-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt J., Raftery M. A. Purification of acetylcholine receptors from Torpedo californica electroplax by affinity chromatography. Biochemistry. 1973 Feb 27;12(5):852–856. doi: 10.1021/bi00729a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz R. D., McGee R., Jr, Kellar K. J. Nicotinic cholinergic receptors labeled by [3H]acetylcholine in rat brain. Mol Pharmacol. 1982 Jul;22(1):56–62. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sershen H., Reith M. E., Lajtha A., Gennaro J., Jr Noncholinergic, saturable binding of (+/-)-[3H]nicotine to mouse brain. J Recept Res. 1981;2(1):1–15. doi: 10.3109/10799898109038794. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tripathi H. L., Martin B. R., Aceto M. D. Nicotine-induced antinociception in rats and mice: correlation with nicotine brain levels. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1982 Apr;221(1):91–96. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandlen R. L., Wu W. C., Eisenach J. C., Raftery M. A. Studies of the composition of purified Torpedo californica acetylcholine receptor and of its subunits. Biochemistry. 1979 May 15;18(10):1845–1854. doi: 10.1021/bi00577a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincek W. C., Martin B. R., Aceto M. D., Tripathi H. L., May E. L., Harris L. S. Synthesis of 4,4-ditritio-(+)-nicotine: comparative binding and distribution studies with natural enantiomer. J Pharm Sci. 1981 Nov;70(11):1292–1293. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600701131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wennogle L. P., Oswald R., Saitoh T., Changeux J. P. Dissection of the 66 000-dalton subunit of the acetylcholine receptor. Biochemistry. 1981 Apr 28;20(9):2492–2497. doi: 10.1021/bi00512a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]