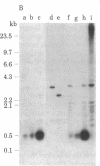
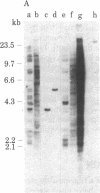
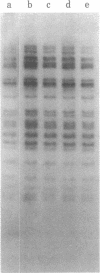
Abstract
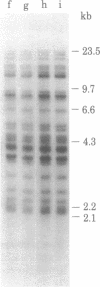
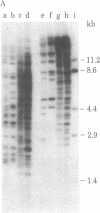
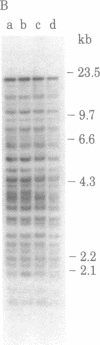
A transposable element, designated Tc1, has been characterized in Caenorhabditis elegans. Tc1 is 1.7 kilobases long, has an inverted terminal repeat of less than 100 base pairs, and is repeated as a highly conserved element. The copy number and genomic positions of Tc1 are extremely variable among strains, implying that Tc1 is mobile. However, progeny of interstrain crosses did not show hybrid dysgenic traits that might be due to Tc1 transposition.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bingham P. M., Kidwell M. G., Rubin G. M. The molecular basis of P-M hybrid dysgenesis: the role of the P element, a P-strain-specific transposon family. Cell. 1982 Jul;29(3):995–1004. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90463-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner S. The genetics of Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics. 1974 May;77(1):71–94. doi: 10.1093/genetics/77.1.71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burr B., Burr F. A. Ds controlling elements of maize at the shrunken locus are large and dissimilar insertions. Cell. 1982 Jul;29(3):977–986. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90461-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calos M. P., Miller J. H. Transposable elements. Cell. 1980 Jul;20(3):579–595. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90305-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cameron J. R., Loh E. Y., Davis R. W. Evidence for transposition of dispersed repetitive DNA families in yeast. Cell. 1979 Apr;16(4):739–751. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90090-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eibel H., Gafner J., Stotz A., Philippsen P. Characterization of the yeast mobile element Ty1. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1981;45(Pt 2):609–617. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1981.045.01.079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emmons S. W., Klass M. R., Hirsh D. Analysis of the constancy of DNA sequences during development and evolution of the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1333–1337. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emmons S. W., Rosenzweig B., Hirsh D. Arrangement of repeated sequences in the DNA of the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. J Mol Biol. 1980 Dec 25;144(4):481–500. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90333-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emmons S. W., Yesner L., Ruan K. S., Katzenberg D. Evidence for a transposon in Caenorhabditis elegans. Cell. 1983 Jan;32(1):55–65. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90496-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Files J. G., Carr S., Hirsh D. Actin gene family of Caenorhabditis elegans. J Mol Biol. 1983 Mar 5;164(3):355–375. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(83)90056-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Files J. G., Hirsh D. Ribosomal DNA of Caenorhabditis elegans. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jun 25;149(2):223–240. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90299-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finnegan D. J., Rubin G. M., Young M. W., Hogness D. S. Repeated gene families in Drosophila melanogaster. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1978;42(Pt 2):1053–1063. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1978.042.01.106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karn J., Brenner S., Barnett L., Cesareni G. Novel bacteriophage lambda cloning vector. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5172–5176. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kidwell M. G., Kidwell J. F., Sved J. A. Hybrid Dysgenesis in DROSOPHILA MELANOGASTER: A Syndrome of Aberrant Traits Including Mutation, Sterility and Male Recombination. Genetics. 1977 Aug;86(4):813–833. doi: 10.1093/genetics/86.4.813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleckner N. Transposable elements in prokaryotes. Annu Rev Genet. 1981;15:341–404. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.15.120181.002013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer J. M., Cox G. N., Hirsh D. Comparisons of the complete sequences of two collagen genes from Caenorhabditis elegans. Cell. 1982 Sep;30(2):599–606. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90256-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCCLINTOCK B. Controlling elements and the gene. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1956;21:197–216. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1956.021.01.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCCLINTOCK B. Intranuclear systems controlling gene action and mutation. Brookhaven Symp Biol. 1956 Feb;(8):58–74. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter S., Truett M., Phillips M., Maher A. Eucaryotic transposable genetic elements with inverted terminal repeats. Cell. 1980 Jul;20(3):639–647. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90310-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prentki P., Karch F., Iida S., Meyer J. The plasmid cloning vector pBR325 contains a 482 base-pair-long inverted duplication. Gene. 1981 Sep;14(4):289–299. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90161-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roeder G. S., Fink G. R. DNA rearrangements associated with a transposable element in yeast. Cell. 1980 Aug;21(1):239–249. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90131-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roeder G. S., Fink G. R. Movement of yeast transposable elements by gene conversion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(18):5621–5625. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.18.5621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin G. M., Kidwell M. G., Bingham P. M. The molecular basis of P-M hybrid dysgenesis: the nature of induced mutations. Cell. 1982 Jul;29(3):987–994. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90462-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spradling A. C., Rubin G. M. Transposition of cloned P elements into Drosophila germ line chromosomes. Science. 1982 Oct 22;218(4570):341–347. doi: 10.1126/science.6289435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strobel E., Dunsmuir P., Rubin G. M. Polymorphisms in the chromosomal locations of elements of the 412, copia and 297 dispersed repeated gene families in Drosophila. Cell. 1979 Jun;17(2):429–439. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90169-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young M. W., Schwartz H. E. Nomadic gene families in Drosophila. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1981;45(Pt 2):629–640. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1981.045.01.081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]