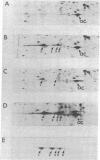
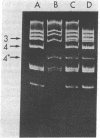
Abstract
Polyoma virus host range transforming (hr-t) mutants are blocked in virion assembly. In normal 3T3 cells, a nonpermissive host, these mutants synthesize 30-40% as much viral DNA and 80-100% as much capsid proteins as does wild-type virus and yet produce only 1-2% as much infectious virus. Intermediates in virion assembly have been followed by [3H]thymidine incorporation. hr-t mutants synthesize 95S replicating minichromosomes, which accumulate as 75S forms. However, the latter fail to undergo efficient transition to 240S virion structures. This block in encapsidation is overcome in permissive hosts such as primary baby mouse kidney (BMK) epithelial cells. The block in assembly of 240S particles is accompanied by a failure to induce a series of acidic isoelectric forms of the major capsid protein, VP1. Multiple species of post-translationally modified VP1 are seen by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis in wild-type virus-infected cells. These acidic VP1 subspecies are decreased 6- to 10-fold in hr-t mutant-infected 3T3 cells but are produced in normal amounts when the same mutants infect BMK cells. When 3T3 cells are coinfected with hr-t mutant and wild-type viruses, normal amounts of the VP1 subspecies are present, and hr-t mutant viral DNA is efficiently packaged into virions. These studies demonstrate an important role of the hr-t gene of polyoma virus in virus assembly. Specifically, we propose that VP1 is a target for hr-t gene-controlled modification and that modified forms of VP1 are essential for encapsidation of viral minichromosomes.
Full text
PDF
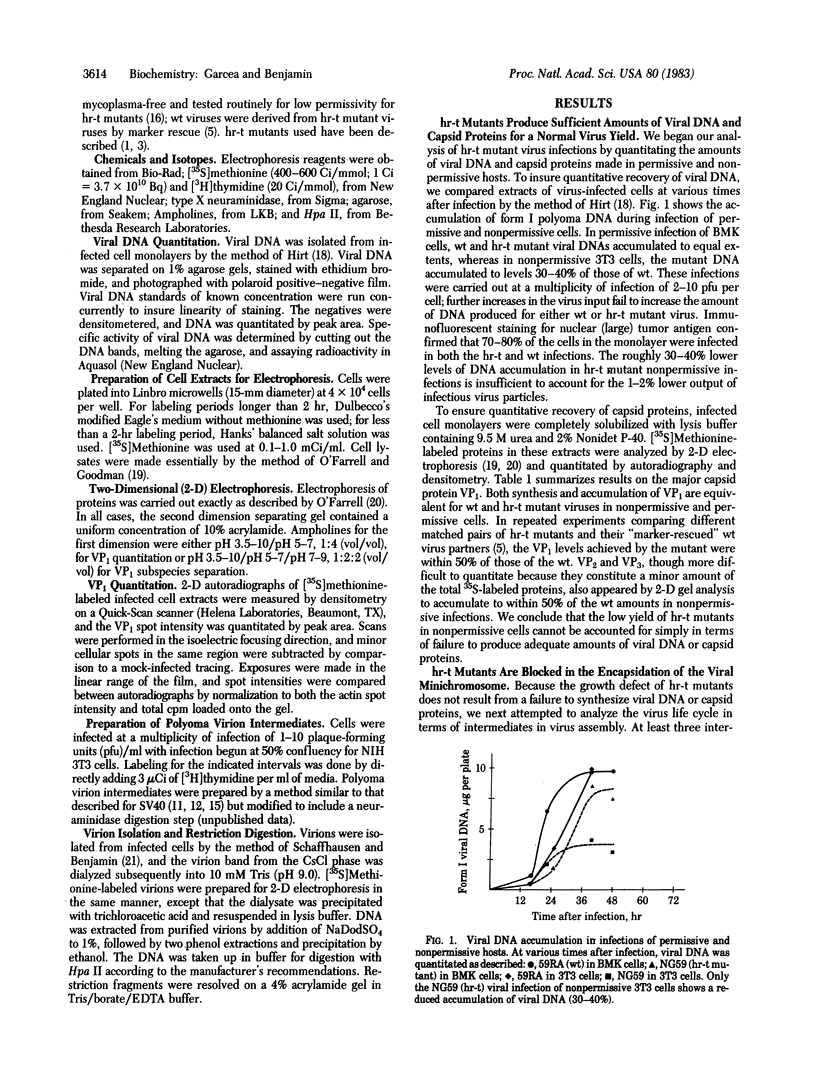
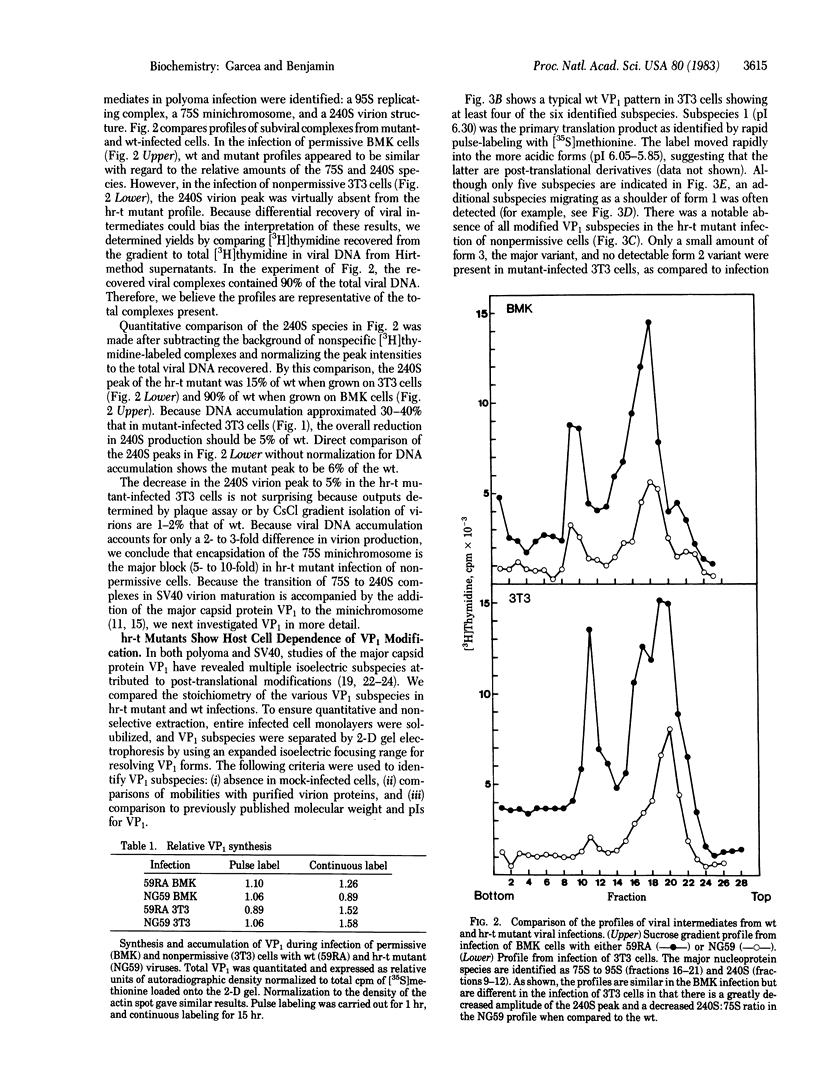


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baumgartner I., Kuhn C., Fanning E. Identification and characterization of fast-sedimenting SV40 nucleoprotein complexes. Virology. 1979 Jul 15;96(1):54–63. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90172-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benjamin T. L. Host range mutants of polyoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Sep;67(1):394–399. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.1.394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benjamin T. L. The hr-t gene of polyoma virus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Dec 21;695(2):69–95. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(82)90018-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolen J. B., Anders D. G., Trempy J., Consigli R. A. Differences in the subpopulations of the structural proteins of polyoma virions and capsids: biological functions of the multiple VP1 species. J Virol. 1981 Jan;37(1):80–91. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.1.80-91.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmichael G. G., Benjamin T. L. Identification of DNA sequence changes leading to loss of transforming ability in polyoma virus. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jan 10;255(1):230–235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fanning E., Baumgartner I. Role of fast-sedimenting SV40 nucleoprotein complexes in virus assembly. Virology. 1980 Apr 15;102(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90064-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez-Munoz R., Coca-Prados M., Hsu M. T. Intracellular forms of simian virus 40 nucleoprotein complexes. I. Methods of isolation and characterization in CV-1 cells. J Virol. 1979 Feb;29(2):612–623. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.2.612-623.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feunteun J., Benjamin T. L. Isolation of transformation-defective host-range mutants of polyoma virus on normal mouse cells. Virology. 1982 Jun;119(2):310–316. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90091-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feunteun J., Sompayrac L., Fluck M., Benjamin T. Localization of gene functions in polyoma virus DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Nov;73(11):4169–4173. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.11.4169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fluck M. M., Staneloni R. J., Benjamin T. L. Hr-t and ts-a: two early gene functions of polyoma virus. Virology. 1977 Apr;77(2):610–624. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90486-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garber E. A., Seidman M. M., Levine A. J. Intracellular SV40 nucleoprotein complexes: synthesis to encapsidation. Virology. 1980 Dec;107(2):389–401. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90306-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman E., Benjamin T. L. Analysis of host range of nontransforming polyoma virus mutants. Virology. 1975 Aug;66(2):372–384. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90210-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman E., Hattori J., Benjamin T. Cellular and C-type viral factors in infections by polyoma virus hr-t mutants. Virology. 1979 Jun;95(2):373–384. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90492-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori J., Carmichael G. G., Benjamin T. L. DNA sequence alterations in Hr-t deletion mutants of polyoma virus. Cell. 1979 Mar;16(3):505–513. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90025-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Gibson W. Characterization of the mRNA's for the polyoma virus capsid proteins VP1, VP2, and VP3. J Virol. 1978 Oct;28(1):240–253. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.1.240-253.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakobovits E. B., Aloni Y. Isolation and characterization of various forms of simian virus 40 DNA-protein complexes. Virology. 1980 Apr 15;102(1):107–118. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90074-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. Z., Goodman H. M. Resolution of simian virus 40 proteins in whole cell extracts by two-dimensional electrophoresis: heterogeneity of the major capsid protein. Cell. 1976 Oct;9(2):289–298. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90119-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponder B. A., Robbins A. K., Crawford L. V. Phophorylation of polyoma and SV40 virus proteins. J Gen Virol. 1977 Oct;37(1):75–83. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-37-1-75. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffhausen B. S., Benjamin T. L. Deficiency in histone acetylation in nontransforming host range mutants of polyoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Apr;73(4):1092–1096. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.4.1092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver J., Schaffhausen B., Benjamin T. Tumor antigens induced by nontransforming mutants of polyoma virus. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):485–496. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90018-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staneloni R. J., Fluck M. M., Benjamin T. L. Host range selection of transformation-defective hr-t mutants of polyoma virus. Virology. 1977 Apr;77(2):598–609. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90485-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WINOCOUR E. Purification of polyoma virus. Virology. 1963 Feb;19:158–168. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(63)90005-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]