Abstract
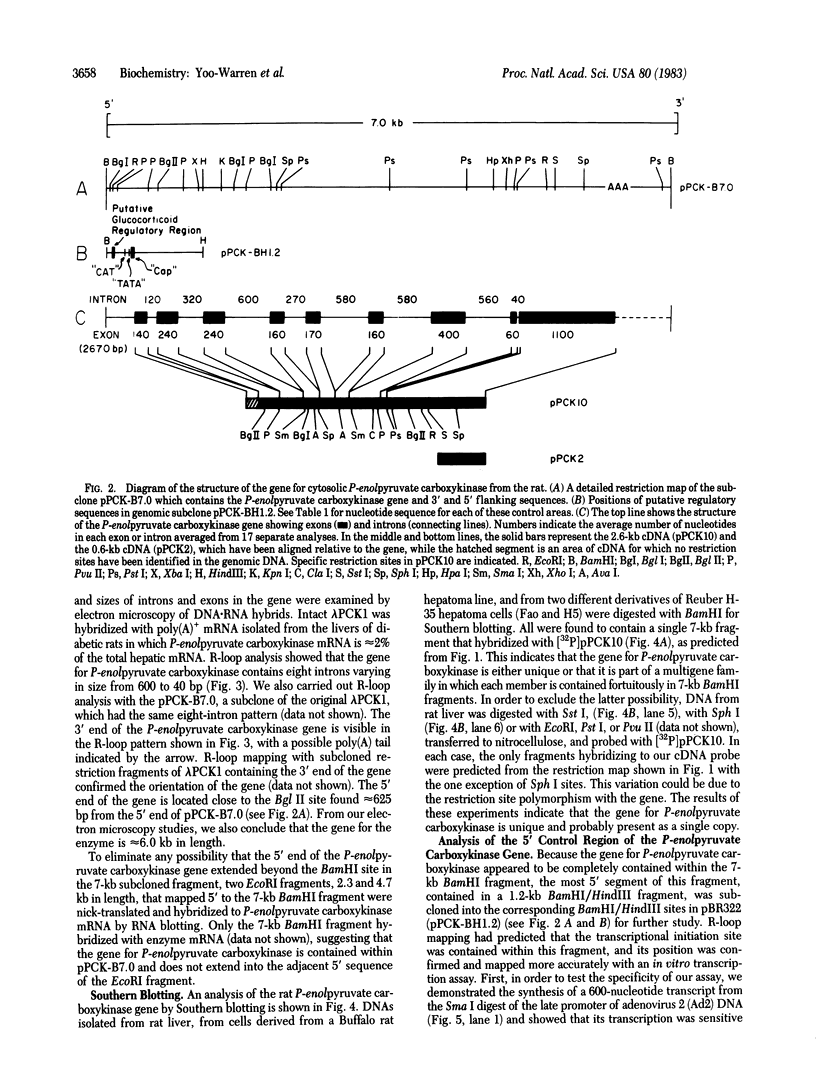
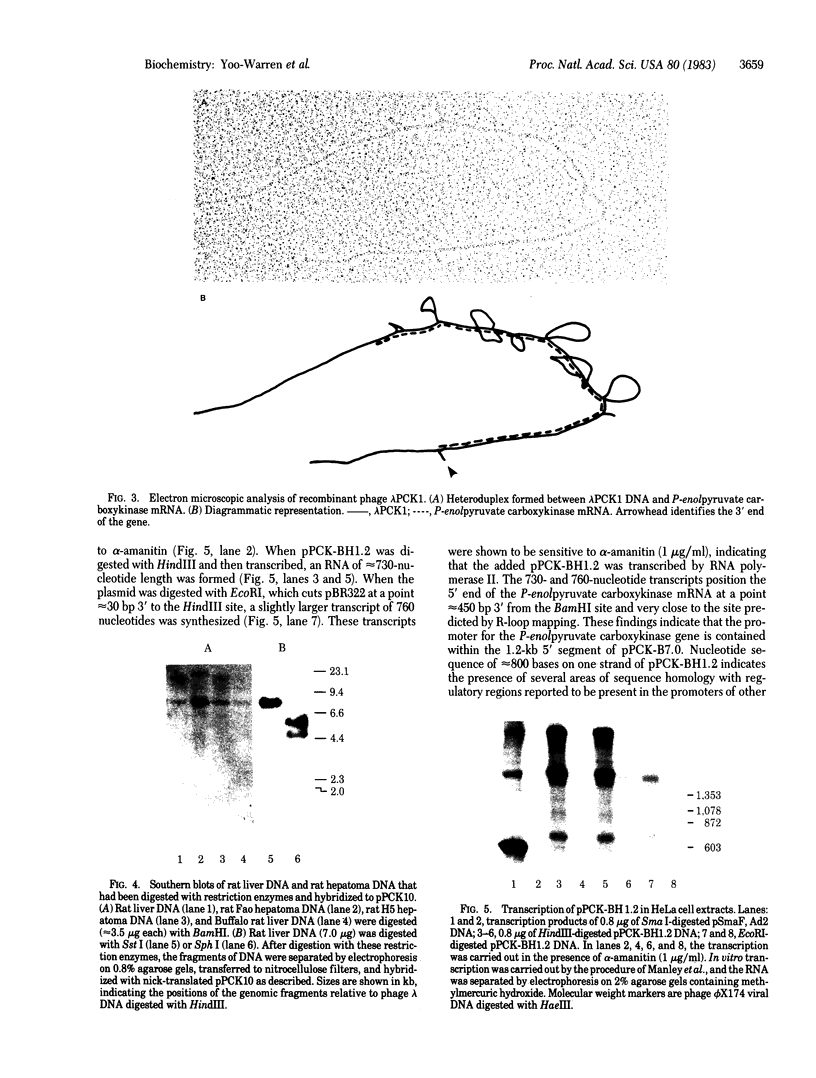
The gene for cytosolic phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (GTP) [GTP:oxaloacetate carboxy-lyase (transphosphorylating), EC 4.1.1.32] from the rat was isolated from a recombinant library containing the rat genome in phage lambda Charon 4A. The isolated clone, lambda PCK1, contains the complete gene for phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase and approximately equal to 7 kilobases (kb) of flanking sequence at the 5' end and 1 kb at the 3' terminus. Restriction endonuclease mapping, R-loop mapping, and partial DNA sequence assay indicate that the gene is approximately equal to 6.0 kb in length (coding for a mRNA of 2.8 kb) and contains eight introns. Southern blotting of rat DNA digested with various restriction enzymes shows a pattern predicted from the restriction map of lambda PCK1. A control region at the 5' end of the gene contained in a 1.2-kb restriction fragment was isolated and subcloned into pBR322. This segment of the gene contains the usual transcription start sequences and a 24-base sequence virtually identical to the sequence found in the 5'-flanking region of the human proopiomelonocortin gene, which is known to be regulated by glucocorticoids. The 1.2-kb fragment of the phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase gene can be transcribed into a unique RNA fragment of predicted size by an in vitro transcription assay.
Full text
PDF


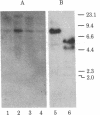
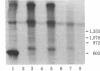
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andreone T. L., Beale E. G., Bar R. S., Granner D. K. Insulin decreases phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (GTP) mRNA activity by a receptor-mediated process. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jan 10;257(1):35–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barta A., Richards R. I., Baxter J. D., Shine J. Primary structure and evolution of rat growth hormone gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):4867–4871. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.4867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blin N., Stafford D. W. A general method for isolation of high molecular weight DNA from eukaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Sep;3(9):2303–2308. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.9.2303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cimbala M. A., Lamers W. H., Nelson K., Monahan J. E., Yoo-Warren H., Hanson R. W. Rapid changes in the concentration of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase mRNA in rat liver and kidney. Effects of insulin and cyclic AMP. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7629–7636. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cimbala M. A., van Lelyveld P., Hanson R. W. Regulation of the levels of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (GTP) mRNA in rat liver by insulin and glucagon. Adv Enzyme Regul. 1980;19:205–214. doi: 10.1016/0065-2571(81)90016-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochet M., Chang A. C., Cohen S. N. Characterization of the structural gene and putative 5'-regulatory sequences for human proopiomelanocortin. Nature. 1982 May 27;297(5864):335–339. doi: 10.1038/297335a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson E. H., Jacobs H. T., Britten R. J. Very short repeats and coordinate induction of genes. Nature. 1983 Feb 10;301(5900):468–470. doi: 10.1038/301468a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donehower L. A., Huang A. L., Hager G. L. Regulatory and coding potential of the mouse mammary tumor virus long terminal redundancy. J Virol. 1981 Jan;37(1):226–238. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.1.226-238.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunn J. M., Hanson R. W., Meyuhas O., Reshef L., Ballard F. J. Glucocorticoids and the regulation of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (guanosine triphosphate) in the rat. Biochem J. 1975 Aug;150(2):195–203. doi: 10.1042/bj1500195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iynedjian P. B., Hanson R. W. Increase in level of functional messenger RNA coding for phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (GTP) during induction by cyclic adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jan 25;252(2):655–662. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kioussis D., Eiferman F., van de Rijn P., Gorin M. B., Ingram R. S., Tilghman S. M. The evolution of alpha-fetoprotein and albumin. II. The structures of the alpha-fetoprotein and albumin genes in the mouse. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 25;256(4):1960–1967. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamers W. H., Hanson R. W., Meisner H. M. cAMP stimulates transcription of the gene for cytosolic phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase in rat liver nuclei. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(17):5137–5141. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.17.5137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Hardison R. C., Lacy E., Lauer J., O'Connell C., Quon D., Sim G. K., Efstratiadis A. The isolation of structural genes from libraries of eucaryotic DNA. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):687–701. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90036-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manley J. L., Fire A., Cano A., Sharp P. A., Gefter M. L. DNA-dependent transcription of adenovirus genes in a soluble whole-cell extract. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3855–3859. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller M. J., Thomsen A., Sibrowski W., Seitz H. J. 3,5,3'-Triiodothyronine-induced synthesis of rat liver phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase. Endocrinology. 1982 Nov;111(5):1469–1475. doi: 10.1210/endo-111-5-1469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargent T. D., Wu J. R., Sala-Trepat J. M., Wallace R. B., Reyes A. A., Bonner J. The rat serum albumin gene: analysis of cloned sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3256–3260. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilghman S. M., Hanson R. W., Reshef L., Hopgood M. F., Ballard F. J. Rapid loss of translatable messenger RNA of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase during glucose repression in liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1304–1308. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Stern M., Stark G. R. Efficient transfer of large DNA fragments from agarose gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and rapid hybridization by using dextran sulfate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3683–3687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wicks W. D., Lewis W., McKibbin J. B. Induction of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase by N 6 , O 2 '-dibutyryl cyclic AMP in rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Mar 30;264(1):177–185. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(72)90129-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woychik R. P., Camper S. A., Lyons R. H., Horowitz S., Goodwin E. C., Rottman F. M. Cloning and nucleotide sequencing of the bovine growth hormone gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Nov 25;10(22):7197–7210. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.22.7197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]