Abstract
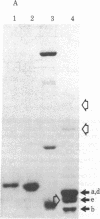
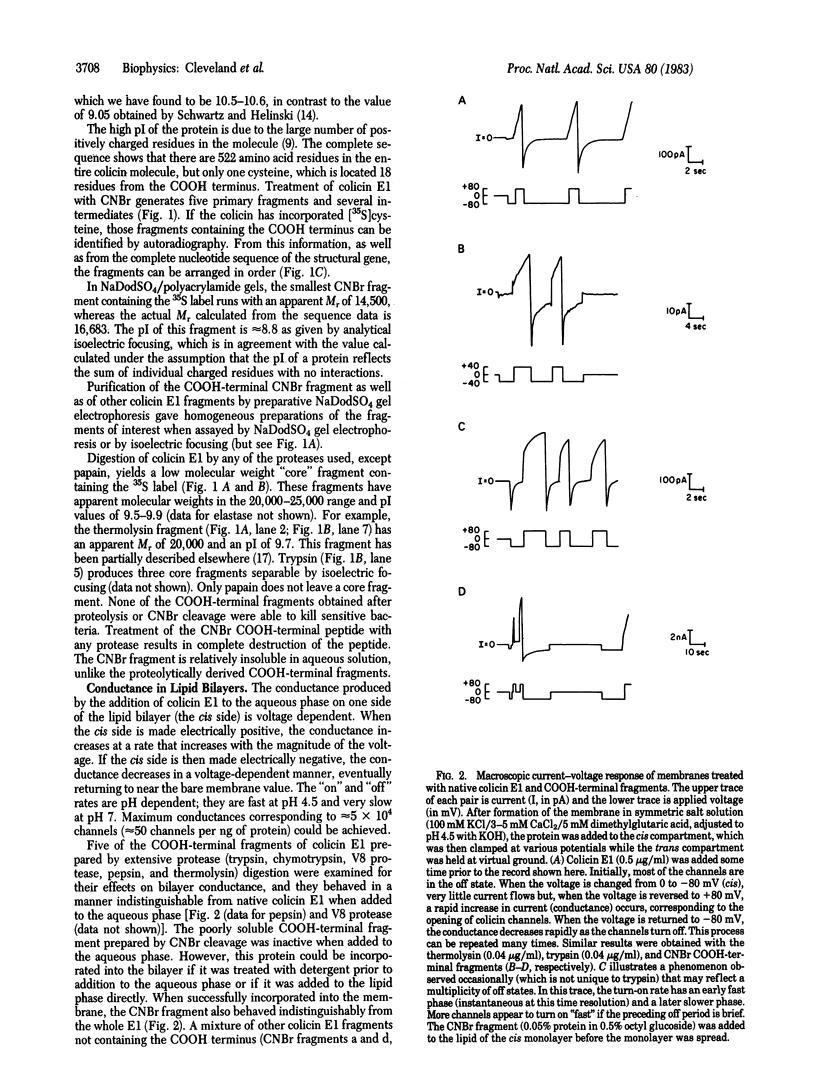
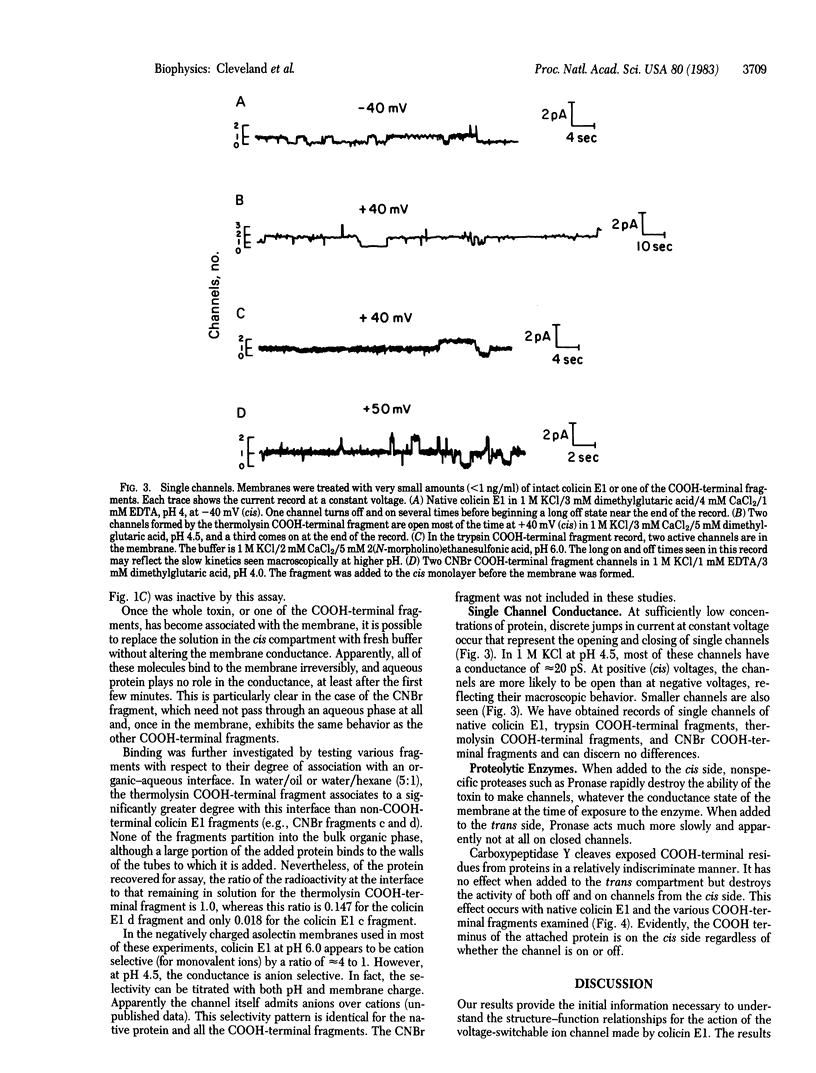
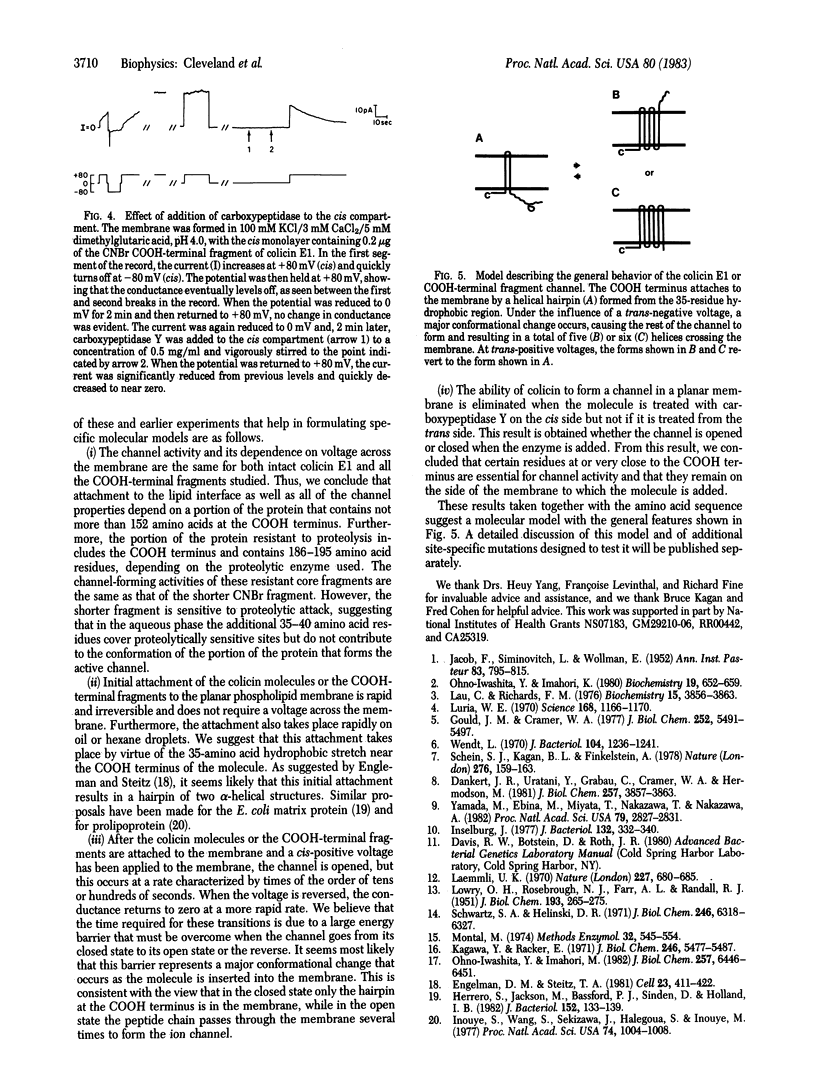
The effects on planar lipid bilayer membranes of carboxyl-terminal fragments derived from the bacteriocin colicin E1 by either proteolysis or CNBr cleavage are indistinguishable from those of the voltage-dependent parent colicin molecule. An upper limit to the length of the COOH-terminal peptide required for channel formation is 152 amino acid residues from the COOH-terminal end, as indicated by the CNBr fragment. In addition, use of carboxypeptidase shows that the COOH-terminal end of the molecule remains on the side of the membrane to which it was added. COOH-terminal peptides of colicin E1 spontaneously associate with oil or hexane droplets in an aqueous system and remain at the interface between the two phases to a significantly greater degree than other colicin E1 fragments or cytochrome c. These results, together with the amino acid sequence, suggest a model wherein the colicin E1 channel is formed first by spontaneous attachment to a membrane of an alpha-helical hairpin centered at a 35-residue hydrophobic region near the COOH-terminal end. Application of a potential of the correct polarity then facilitates a major conformational change in the protein, allowing insertion of the remainder of the COOH-terminal end to form the open channel.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dankert J. R., Uratani Y., Grabau C., Cramer W. A., Hermodson M. On a domain structure of colicin E1. A COOH-terminal peptide fragment active in membrane depolarization. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 10;257(7):3857–3863. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelman D. M., Steitz T. A. The spontaneous insertion of proteins into and across membranes: the helical hairpin hypothesis. Cell. 1981 Feb;23(2):411–422. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90136-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould J. M., Cramer W. A. Studies on the depolarization of the Escherichia coli cell membrane by colicin E1. J Biol Chem. 1977 Aug 10;252(15):5491–5497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrero E., Jackson M., Bassford P. J., Sinden D., Holland I. B. Insertion of a MalE beta-galactosidase fusion protein into the envelope of Escherichia coli disrupts biogenesis of outer membrane proteins and processing of inner membrane proteins. J Bacteriol. 1982 Oct;152(1):133–139. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.1.133-139.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye S., Wang S., Sekizawa J., Halegoua S., Inouye M. Amino acid sequence for the peptide extension on the prolipoprotein of the Escherichia coli outer membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):1004–1008. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.1004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inselburg J. Studies of colicin E1 plasmid functions by analysis of deletions and TnA insertions of the plasmid. J Bacteriol. 1977 Oct;132(1):332–340. doi: 10.1128/jb.132.1.332-340.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau C., Richards F. M. Proteolytic and chemical modification of colicin E3 activity. Biochemistry. 1976 Aug 24;15(17):3856–3863. doi: 10.1021/bi00662a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luria S. E. Phage, colicins, and macroregulatory phenomena. Science. 1970 Jun 5;168(3936):1166–1170. doi: 10.1126/science.168.3936.1166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montal M. Formation of bimolecular membranes from lipid monolayers. Methods Enzymol. 1974;32:545–554. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)32053-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno-Iwashita Y., Imahori K. Assignment of the functional loci in colicin E2 and E3 molecules by the characterization of their proteolytic fragments. Biochemistry. 1980 Feb 19;19(4):652–659. doi: 10.1021/bi00545a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno-Iwashita Y., Imahori K. Assignment of the functional loci in the colicin E1 molecule by characterization of its proteolytic fragments. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 10;257(11):6446–6451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schein S. J., Kagan B. L., Finkelstein A. Colicin K acts by forming voltage-dependent channels in phospholipid bilayer membranes. Nature. 1978 Nov 9;276(5684):159–163. doi: 10.1038/276159a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz S. A., Helinski D. R. Purification and characterization of colicin E1. J Biol Chem. 1971 Oct 25;246(20):6318–6327. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wendt L. Mechanism of colicin action: early events. J Bacteriol. 1970 Dec;104(3):1236–1241. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.3.1236-1241.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada M., Ebina Y., Miyata T., Nakazawa T., Nakazawa A. Nucleotide sequence of the structural gene for colicin E1 and predicted structure of the protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(9):2827–2831. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.9.2827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]