Abstract
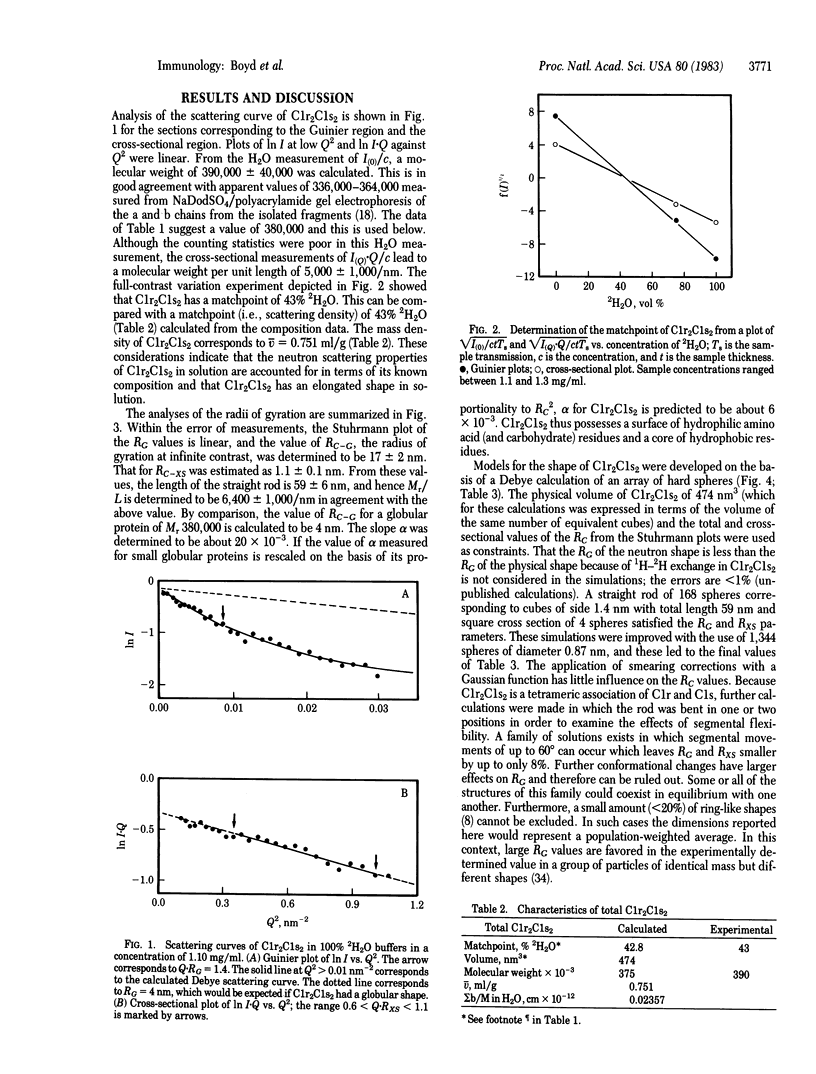
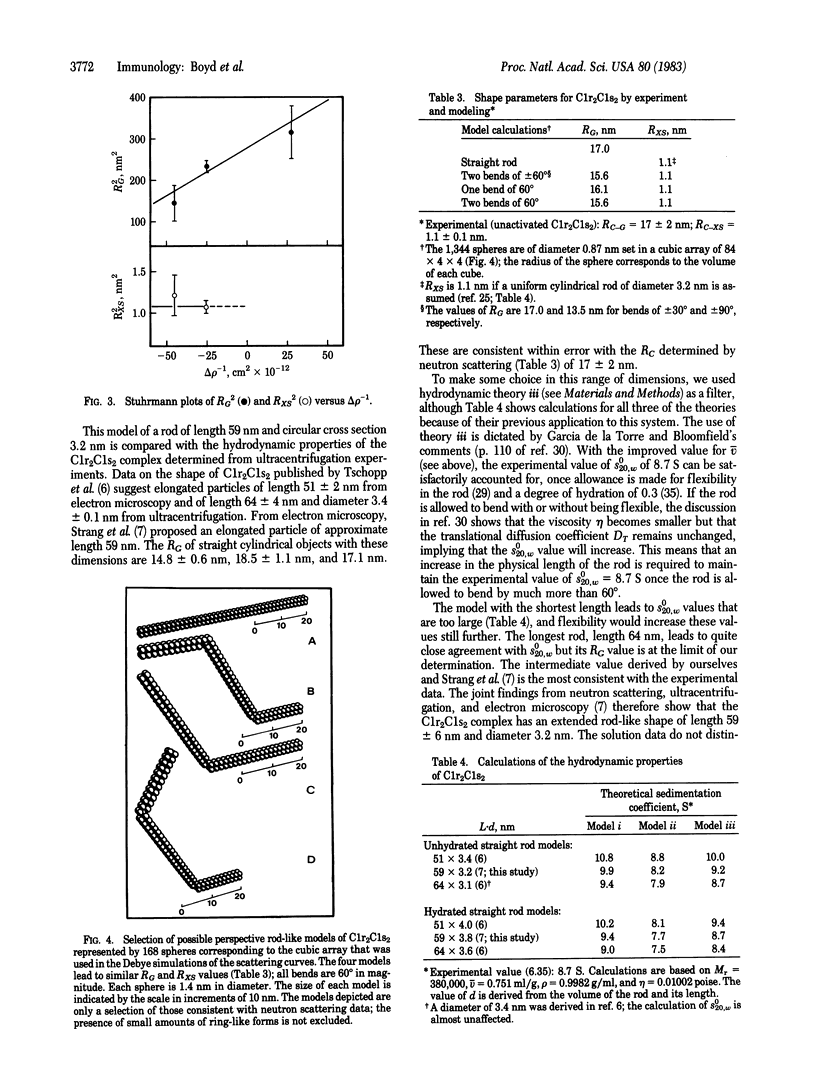
The subunit complex C1r2C1s2 of the first component of complement was investigated by small-angle neutron scattering in both the activated and unactivated forms. From these experiments, a molecular weight of 390,000 for C1r2C1s2 was found. The matchpoint was determined to be 43% 2H2O. Both results are consistent with composition data. The partial specific volume is 0.751 ml/mg. The radius of gyration at infinite contrast was found to be 17 nm for C1r2C1s2 and 1.1 nm for the cross section. Models for C1r2C1s2 were computed by the method of hard spheres, in which C1r2C1s2 was represented by spheres 0.87 nm diameter arranged in a straight rod of length 59 nm and a circular cross section of 3.2 nm. This rod can be bent at one or two places by up to 60 degrees without significant effect on the calculated radii of gyration. The model is in agreement with published ultracentrifugation and electron microscopy data.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amzel L. M., Poljak R. J. Three-dimensional structure of immunoglobulins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:961–997. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.004525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arlaud G. J., Chesne S., Villiers C. L., Colomb M. G. A study on the structure and interactions of the C1 sub-components C1r and C1s in the fluid phase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Nov 6;616(1):105–115. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(80)90268-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arlaud G. J., Gagnon J., Porter R. R. The catalytic chain of human complement subcomponent C1r. Purification and N-terminal amino acid sequences of the major cyanogen bromide-cleavage fragments. Biochem J. 1982 Jan 1;201(1):49–59. doi: 10.1042/bj2010049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arlaud G. J., Sim R. B., Duplaa A. M., Colomb M. G. Differential elution of Clq, Clr and Cls from human Cl bound to immune aggregates. Use in the rapid purification of Cl subcomponents. Mol Immunol. 1979 Jul;16(7):445–450. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(79)90069-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arlaud G. J., Villiers C. L., Chesne S., Colomb M. G. Purified proenzyme C1r. Some characteristics of its activation and subsequent proteolytic cleavage. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Nov 6;616(1):116–129. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(80)90269-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloomfield V., Van Holde K. E., Dalton W. O. Frictional coefficients of multisubunit structures. II. Application to proteins and viruses. Biopolymers. 1967 Feb;5(2):149–159. doi: 10.1002/bip.1967.360050203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodsky-Doyle B., Leonard K. R., Reid K. B. Circular-dichroism and electron-microscopy studies of human subcomponent C1q before and after limited proteolysis by pepsin. Biochem J. 1976 Nov;159(2):279–286. doi: 10.1042/bj1590279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chothia C. Structural invariants in protein folding. Nature. 1975 Mar 27;254(5498):304–308. doi: 10.1038/254304a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colomb M. G., Bensa J. C., Villiers C. L., Arlaud G. J. Aspects biochimiques de l'activation intrinsèque de C1. Ann Immunol (Paris) 1982 Mar-Apr;133C(2):155–164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmour S., Randall J. T., Willan K. J., Dwek R. A., Torbet J. The conformation of subcomponent C1q of the first component of human complement. Nature. 1980 Jun 12;285(5765):512–514. doi: 10.1038/285512a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber R., Deisenhofer J., Colman P. M., Matsushima M., Palm W. Crystallographic structure studies of an IgG molecule and an Fc fragment. Nature. 1976 Dec 2;264(5585):415–420. doi: 10.1038/264415a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ibel K. Comparison of neutron and X-ray scattering of dilute myoglobin solutions. J Mol Biol. 1975 Apr 5;93(2):255–265. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90131-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knobel H. R., Villiger W., Isliker H. Chemical analysis and electron microscopy studies of human C1q prepared by different methods. Eur J Immunol. 1975 Jan;5(1):78–82. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830050119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch M. H., Stuhrmann H. B. Neutron-scattering studies of ribosomes. Methods Enzymol. 1979;59:670–706. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)59121-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman J., Swinney H. L., Day L. A. Hydrodynamic properties and structure of fd virus. J Mol Biol. 1977 Nov 5;116(3):593–603. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90086-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins S. J., Miller A., Hardingham T. E., Muir H. Physical properties of the hyaluronate binding region of proteoglycan from pig laryngeal cartilage. Densitometric and small-angle neutron scattering studies of carbohydrates and carbohydrate-protein macromolecules. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jul 25;150(1):69–95. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90325-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter R. R., Reid K. B. Activation of the complement system by antibody-antigen complexes: the classical pathway. Adv Protein Chem. 1979;33:1–71. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60458-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid K. B., Porter R. R. The proteolytic activation systems of complement. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:433–464. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shelton E., Yonemasu K., Stroud R. M. Ultrastructure of the human complement component, Clq (negative staining-glutamine synthetase-biologically active Clq). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jan;69(1):65–68. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.1.65. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sim R. B., Porter R. R., Reid K. B., Gigli I. The structure and enzymic activities of the C1r and C1s subcomponents of C1, the first component of human serum complement. Biochem J. 1977 May 1;163(2):219–227. doi: 10.1042/bj1630219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sim R. B. The human complement system serine proteases C1r and C1s and their proenzymes. Methods Enzymol. 1981;80(Pt 100):26–42. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(81)80006-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strang C. J., Siegel R. C., Phillips M. L., Poon P. H., Schumaker V. N. Ultrastructure of the first component of human complement: electron microscopy of the crosslinked complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):586–590. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.586. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tschopp J., Villiger W., Fuchs H., Kilchherr E., Engel J. Assembly of subcomponents C1r and C1s of first component of complement: electron microscopic and ultracentrifugal studies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7014–7018. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villiers C. L., Arlaud G. J., Painter R. H., Colomb M. G. Calcium binding properties of the C1 subcomponents C1q, C1r and C1s. FEBS Lett. 1980 Aug 11;117(1):289–294. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80964-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villiers C. L., Duplaa A. M., Arlaud G. J., Colomb M. G. Fluid phase activation of proenzymic C1r purified by affinity chromatography. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Jan 4;700(1):118–126. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(82)90299-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




