Abstract
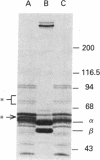
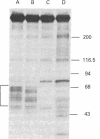
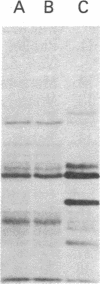
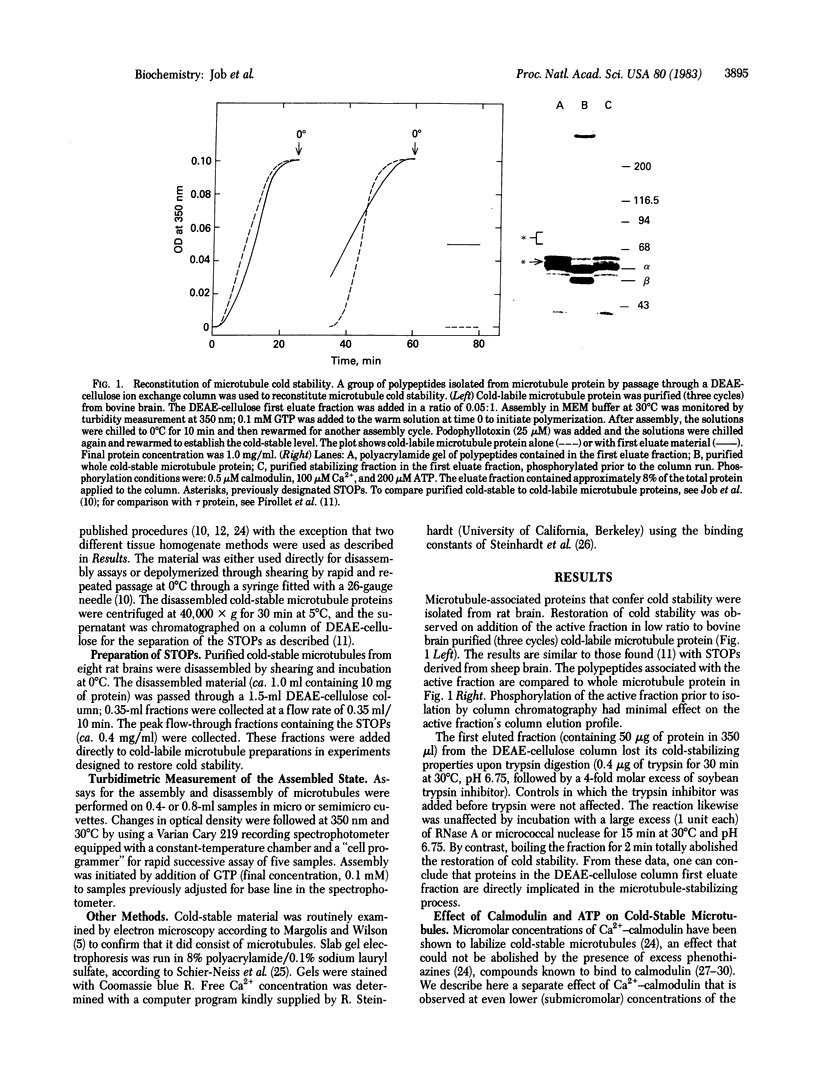
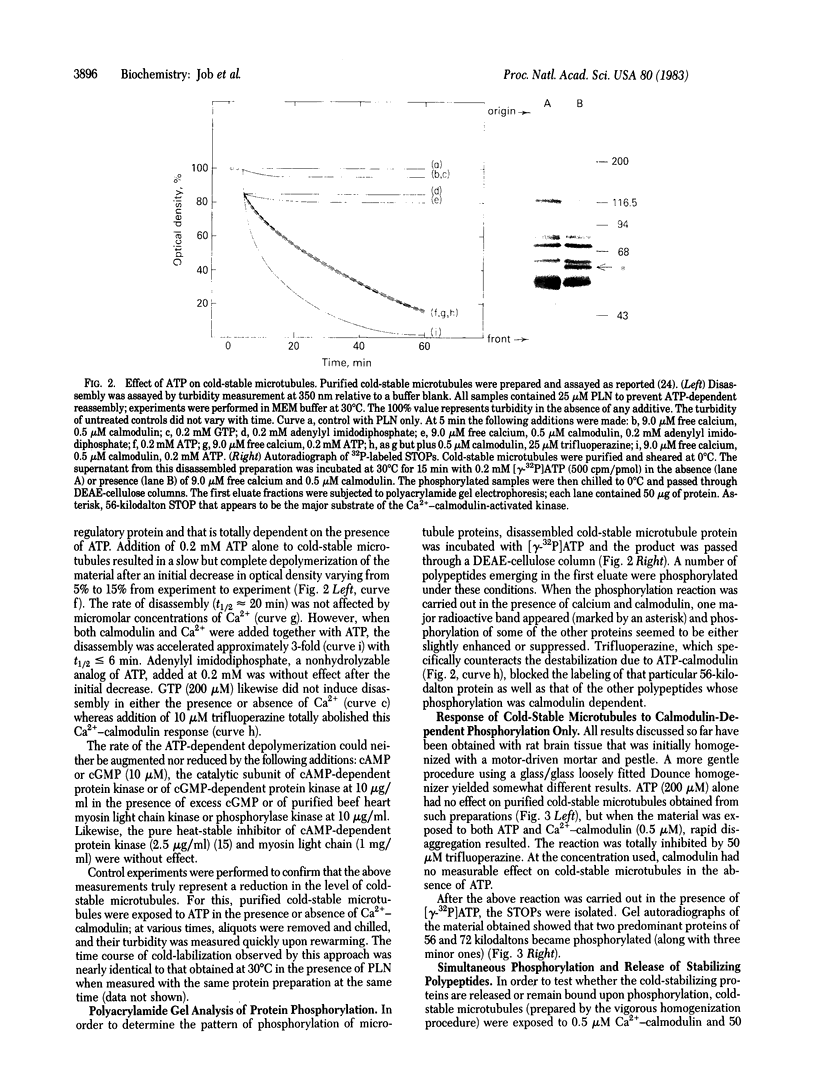
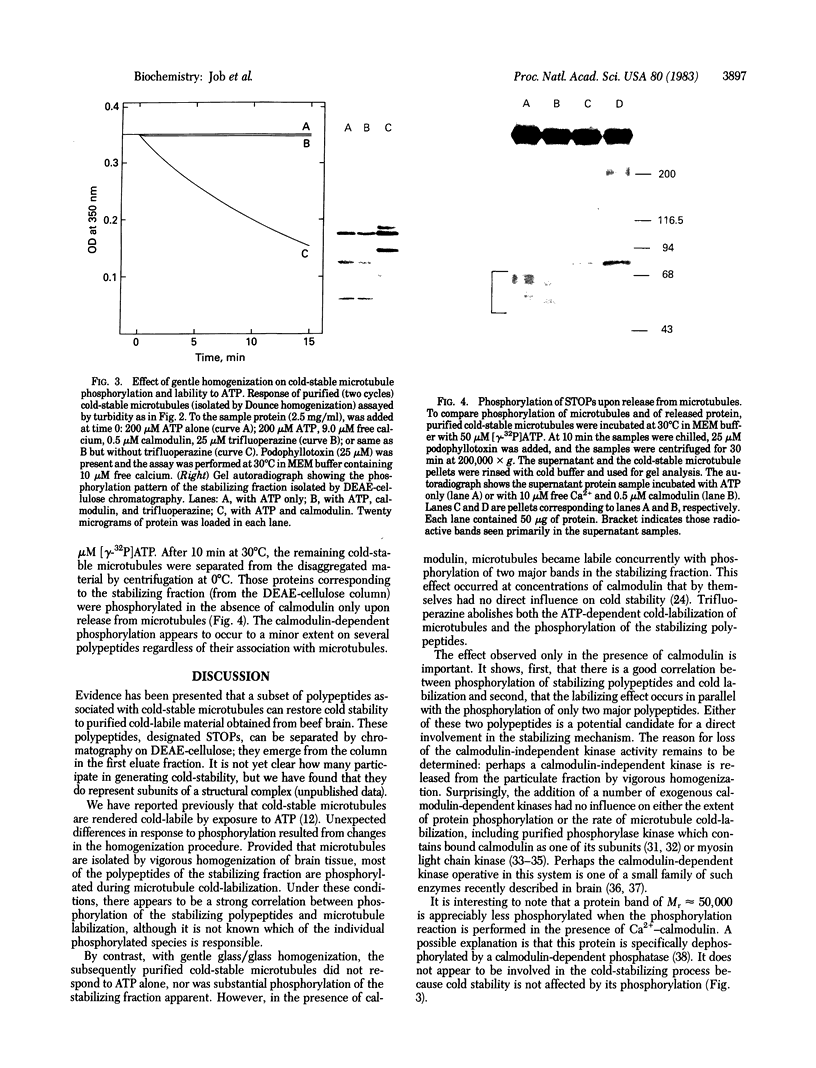
Cold-labile microtubule protein can be rendered cold-stable by addition of a fraction containing a small number of polypeptides that are derived from cold-stable microtubules. These polypeptides can be obtained from purified cold-stable microtubules by passage through a DEAE-cellulose (DE-52) ion exchange column from which they emerge in the first eluate fraction. The stabilizing activity of these proteins is abolished by phosphorylation catalyzed by two types of protein kinases, one dependent on calmodulin and the other independent of that regulatory protein. The calmodulin-dependent reaction appears to phosphorylate mainly two polypeptides, 56 and 72 kilodaltons; the reaction is blocked by trifluoperazine. The calmodulin-independent reaction appears to phosphorylate different cold-stable microtubule-associated proteins. That reaction is observed only in purified material obtained from vigorously homogenized brain tissue. Gently homogenization yields cold-stable microtubules that are responsive only to the calmodulin-dependent protein kinase. A distinguishing feature of the calmodulin-independent reaction is that it does not occur on polypeptides while they are bound to the microtubules.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asnes C. F., Wilson L. Isolation of bovine brain microtubule protein without glycerol: polymerization kinetics change during purification cycles. Anal Biochem. 1979 Sep 15;98(1):64–73. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90706-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergen L. G., Borisy G. G. Head-to-tail polymerization of microtubules in vitro. Electron microscope analysis of seeded assembly. J Cell Biol. 1980 Jan;84(1):141–150. doi: 10.1083/jcb.84.1.141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung W. Y. Calmodulin plays a pivotal role in cellular regulation. Science. 1980 Jan 4;207(4426):19–27. doi: 10.1126/science.6243188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P. The subunit structure of rabbit-skeletal-muscle phosphorylase kinase, and the molecular basis of its activation reactions. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Apr 2;34(1):1–14. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02721.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dabrowska R., Sherry J. M., Aromatorio D. K., Hartshorne D. J. Modulator protein as a component of the myosin light chain kinase from chicken gizzard. Biochemistry. 1978 Jan 24;17(2):253–258. doi: 10.1021/bi00595a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demaille J. G., Peters K. A., Fischer E. H. Isolation and properties of the rabbit skeletal muscle protein inhibitor of adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate dependent protein kinases. Biochemistry. 1977 Jul 12;16(14):3080–3086. doi: 10.1021/bi00633a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demaille J. G., Peters K. A., Strandjord T. P., Fischer E. H. Isolation and properties of the bovine brain protein inhibitor of adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinases. FEBS Lett. 1978 Feb 1;86(1):113–116. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80110-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass D. B., Krebs E. G. Comparison of the substrate specificity of adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate- and guanosine 3':5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinases. Kinetic studies using synthetic peptides corresponding to phosphorylation sites in histone H2B. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 10;254(19):9728–9738. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiratsuka T. A simple method for the separation of cardiac myosin light chains. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Oct 21;625(2):369–373. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(80)90301-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Job D., Fischer E. H., Margolis R. L. Rapid disassembly of cold-stable microtubules by calmodulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):4679–4682. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.4679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Job D., Rauch C. T., Fischer E. H., Margolis R. L. Recycling of cold-stable microtubules: evidence that cold stability is due to substoichiometric polymer blocks. Biochemistry. 1982 Feb 2;21(3):509–515. doi: 10.1021/bi00532a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KREBS E. G., LOVE D. S., BRATVOLD G. E., TRAYSER K. A., MEYER W. L., FISCHER E. H. PURIFICATION AND PROPERTIES OF RABBIT SKELETAL MUSCLE PHOSPHORYLASE B KINASE. Biochemistry. 1964 Aug;3:1022–1033. doi: 10.1021/bi00896a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy M. B., Greengard P. Two calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinases, which are highly concentrated in brain, phosphorylate protein I at distinct sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):1293–1297. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.1293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klee C. B., Crouch T. H., Richman P. G. Calmodulin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:489–515. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.002421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin R. M., Weiss B. Binding of trifluoperazine to the calcium-dependent activator of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase. Mol Pharmacol. 1977 Jul;13(4):690–697. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis R. L., Rauch C. T. Characterization of rat brain crude extract microtubule assembly: correlation of cold stability with the phosphorylation state of a microtubule-associated 64K protein. Biochemistry. 1981 Jul 21;20(15):4451–4458. doi: 10.1021/bi00518a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis R. L., Wilson L. Microtubule treadmills--possible molecular machinery. Nature. 1981 Oct 29;293(5835):705–711. doi: 10.1038/293705a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis R. L., Wilson L. Opposite end assembly and disassembly of microtubules at steady state in vitro. Cell. 1978 Jan;13(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90132-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis R. L., Wilson L. Regulation of the microtubule steady state in vitro by ATP. Cell. 1979 Nov;18(3):673–679. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90122-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrie W. T., Smillie L. B., Perry S. V. A phosphorylated light-chain component of myosin. Biochem J. 1972 Jul;128(3):105P–106P. doi: 10.1042/bj1280105p. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters K. A., Demaille J. G., Fischer E. H. Adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate dependent protein kinase from bovine heart. Characterization of the catalytic subunit. Biochemistry. 1977 Dec 27;16(26):5691–5697. doi: 10.1021/bi00645a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pirollet F., Job D., Fischer E. H., Margolis R. L. Purification and characterization of sheep brain cold-stable microtubules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(6):1560–1564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.6.1560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheir-Neiss G., Lai M. H., Morris N. R. Identification of a gene for beta-tubulin in Aspergillus nidulans. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):639–647. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90032-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shenolikar S., Cohen P. T., Cohen P., Nairn A. C., Perry S. V. The role of calmodulin in the structure and regulation of phosphorylase kinase from rabbit skeletal muscle. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Oct 15;100(2):329–337. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb04175.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder J. A., McIntosh J. R. Biochemistry and physiology of microtubules. Annu Rev Biochem. 1976;45:699–720. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.45.070176.003411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobue K., Fujita M., Muramoto Y., Kakiuchi S. The calmodulin-binding protein in microtubules is tau factor. FEBS Lett. 1981 Sep 14;132(1):137–140. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80447-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinhardt R., Zucker R., Schatten G. Intracellular calcium release at fertilization in the sea urchin egg. Dev Biol. 1977 Jul 1;58(1):185–196. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(77)90084-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart A. A., Ingebritsen T. S., Manalan A., Klee C. B., Cohen P. Discovery of a Ca2+- and calmodulin-dependent protein phosphatase: probable identity with calcineurin (CaM-BP80). FEBS Lett. 1982 Jan 11;137(1):80–84. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80319-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincenzi F. F. Calmodulin pharmacology. Cell Calcium. 1981 Aug;2(4):387–409. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(81)90027-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watterson D. M., Harrelson W. G., Jr, Keller P. M., Sharief F., Vanaman T. C. Structural similarities between the Ca2+-dependent regulatory proteins of 3':5'-cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase and actomyosin ATPase. J Biol Chem. 1976 Aug 10;251(15):4501–4513. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb B. C., Wilson L. Cold-stable microtubules from brain. Biochemistry. 1980 Apr 29;19(9):1993–2001. doi: 10.1021/bi00550a041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weingarten M. D., Lockwood A. H., Hwo S. Y., Kirschner M. W. A protein factor essential for microtubule assembly. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 May;72(5):1858–1862. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.5.1858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh M. J., Dedman J. R., Brinkley B. R., Means A. R. Tubulin and calmodulin. Effects of microtubule and microfilament inhibitors on localization in the mitotic apparatus. J Cell Biol. 1979 Jun;81(3):624–634. doi: 10.1083/jcb.81.3.624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yagi K., Yazawa M., Kakiuchi S., Ohshima M., Uenishi K. Identification of an activator protein for myosin light chain kinase as the Ca2+-dependent modulator protein. J Biol Chem. 1978 Mar 10;253(5):1338–1340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamauchi T., Fujisawa H. Evidence for three distinct forms of calmodulin-dependent protein kinases from rat brain. FEBS Lett. 1980 Jul 28;116(2):141–144. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80628-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]