Abstract
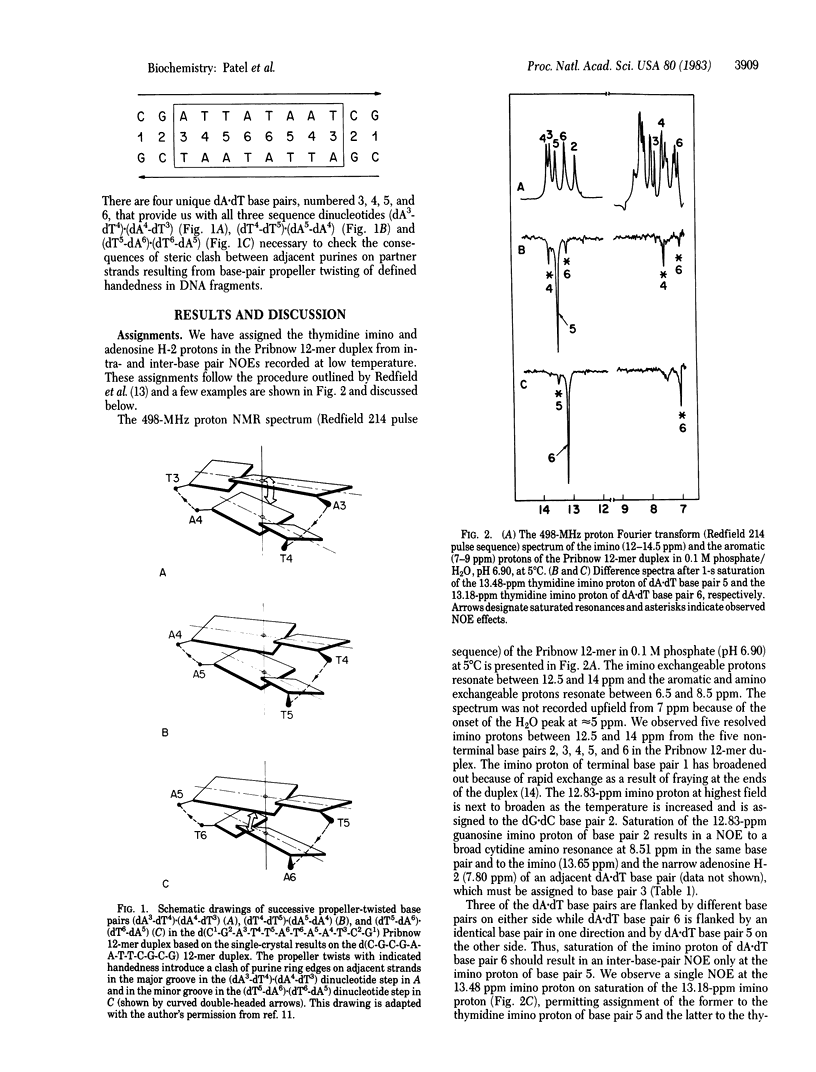
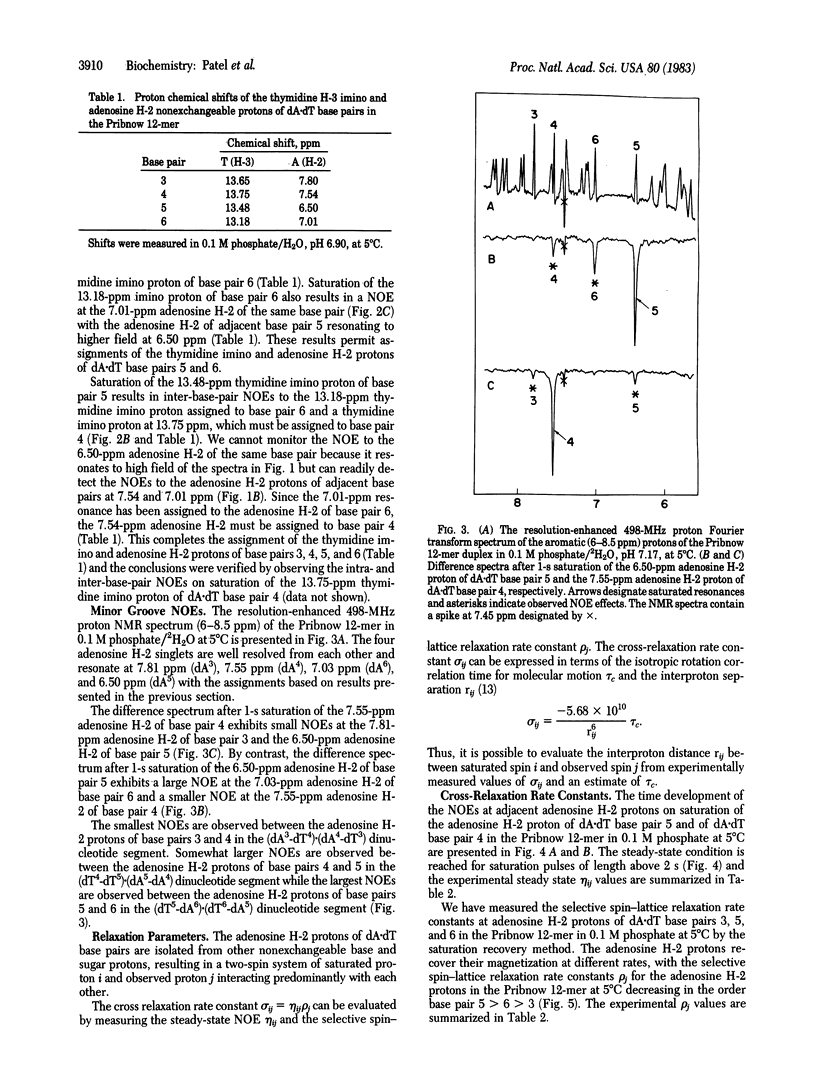
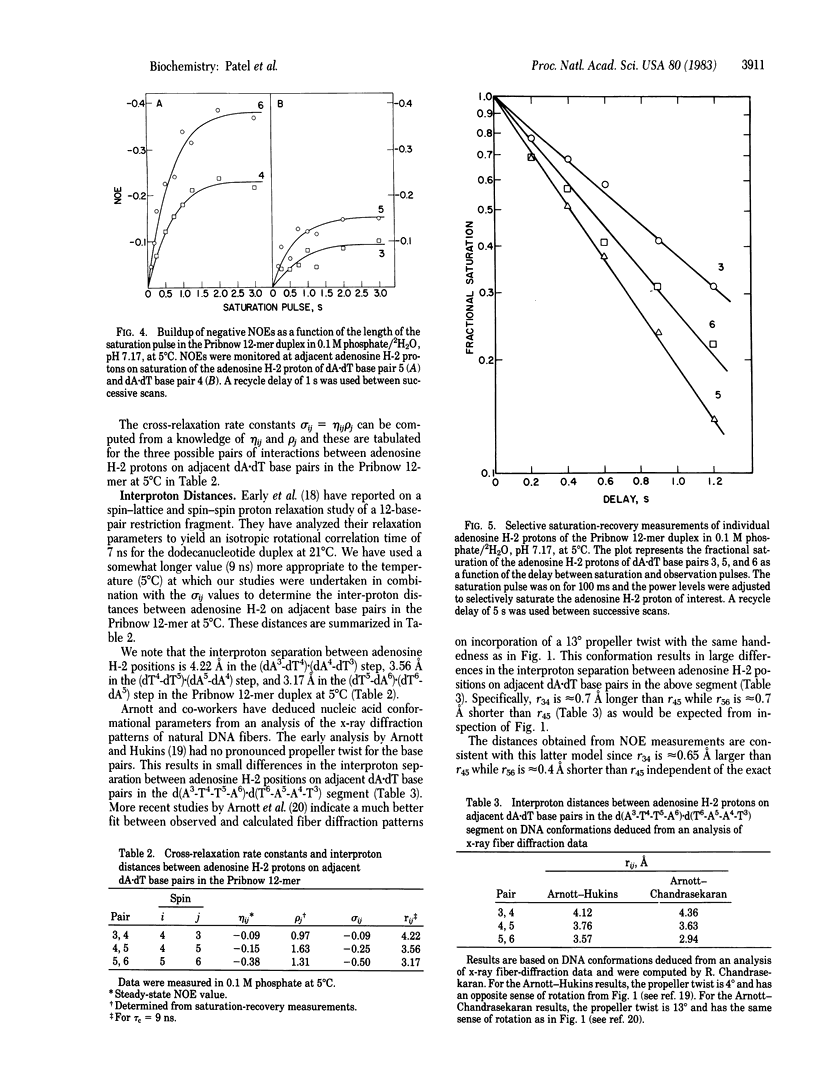
Single-crystal x-ray studies of d(C-G-C-G-A-A-T-T-C-G-C-G) exhibit base-pair propeller twisting [Dickerson, R. E. & Drew, H. R. (1981) J. Mol. Biol. 149, 761-786] that results in close contacts between adjacent purines in the minor groove in pyrimidine (3'-5')-purine steps and in the major groove in purine (3'-5')-pyrimidine steps [Calladine, C. R. (1982) J. Mol. Biol. 161, 343-362]. These observations require an approximately 3.4 A separation between the minor groove edges of adenosines on adjacent base pairs for the dA-dA step but predict a smaller separation for the dT-dA step and a larger separation for the dA-dT step in a D(A-T-T-A).d(T-A-A-T) fragment. We have confirmed these predictions from steady-state nuclear Overhauser effect measurements between assigned minor groove adenosine H-2 protons on adjacent base pairs in the proton NMR spectrum of the d(C1-G2-A3-T4-T5-A6-T6-A5-A4-T3-C2-G1) self-complementary dodecanucleotide duplex (henceforth called the Pribnow 12-mer) in solution. The measured cross-relaxation rates (product of steady-state nuclear Overhauser effect and selective spin- lattice relaxation rates) translate to interproton separations between adjacent adenosine H-2 protons of 4.22 A in the (dA3-dT4).(dA4-dT3) step, of 3.56 A in the (dT4-dT5).dA5-dA4) step, and of 3.17 A in the (dT5-dA6).(dT6-dA5) step for the Pribnow 12-mer duplex with an isotropic rotational correlation time of 9 ns at 5 degrees C. These proton NMR results show that the sequence-dependent base-pair stacking resulting from base-pair propeller twisting of defined handedness for right-handed DNA in the solid state is maintained in aqueous solution.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnott S., Chandrasekaran R., Hall I. H., Puigjaner L. C., Walker J. K., Wang M. DNA secondary structures: helices, wrinkles, and junctions. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;47(Pt 1):53–65. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.047.01.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnott S., Hukins D. W. Optimised parameters for A-DNA and B-DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Jun 28;47(6):1504–1509. doi: 10.1016/0006-291X(72)90243-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calladine C. R. Mechanics of sequence-dependent stacking of bases in B-DNA. J Mol Biol. 1982 Oct 25;161(2):343–352. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90157-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickerson R. E., Drew H. R. Structure of a B-DNA dodecamer. II. Influence of base sequence on helix structure. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jul 15;149(4):761–786. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90357-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Early T. A., Kearns D. R., Hillen W., Wells R. D. A 300 MHz and 600 MHz proton NMR study of a 12 base pair restriction fragment: investigation of structure by relaxation measurements. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Dec 11;8(23):5795–5812. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.23.5795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grant R. C., Kodama M., Wells R. D. Enzymatic and physical studies on (dI-dC) n -(dI-dC) n and (dG-dC) n -(dG-dC) n . Biochemistry. 1972 Feb 29;11(5):805–815. doi: 10.1021/bi00755a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogan M., Dattagupta N., Crothers D. M. Transient electric dichroism of rod-like DNA molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):195–199. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klug A., Jack A., Viswamitra M. A., Kennard O., Shakked Z., Steitz T. A. A hypothesis on a specific sequence-dependent conformation of DNA and its relation to the binding of the lac-repressor protein. J Mol Biol. 1979 Jul 15;131(4):669–680. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90196-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitt M. How many base-pairs per turn does DNA have in solution and in chromatin? Some theoretical calculations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Feb;75(2):640–644. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.2.640. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomonossoff G. P., Butler P. J., Klug A. Sequence-dependent variation in the conformation of DNA. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jul 15;149(4):745–760. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90356-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel D. J. Antibiotic-DNA interactions: intermolecular nuclear Overhauser effects in the netropsin-d(C-G-C-G-A-A-T-T-C-G-C-G) complex in solution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6424–6428. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel D. J., Canuel L. L., Pohl F. M. "Alternating B-DNA" conformation for the oligo(dG-dC) duplex in high-salt solution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2508–2511. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel D. J., Kozlowski S. A., Ikuta S., Itakura K., Bhatt R., Hare D. R. NMR studies of DNA conformation and dynamics in solution. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;47(Pt 1):197–206. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.047.01.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel D. J., Kozlowski S. A., Nordheim A., Rich A. Right-handed and left-handed DNA: studies of B- and Z-DNA by using proton nuclear Overhauser effect and P NMR. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(5):1413–1417. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.5.1413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel D. J., Pardi A., Itakura K. DNA conformation, dynamics, and interactions in solution. Science. 1982 May 7;216(4546):581–590. doi: 10.1126/science.6280281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheffler I. E., Elson E. L., Baldwin R. L. Helix formation by dAT oligomers. I. Hairpin and straight-chain helices. J Mol Biol. 1968 Sep 28;36(3):291–304. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90156-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATSON J. D., CRICK F. H. Molecular structure of nucleic acids; a structure for deoxyribose nucleic acid. Nature. 1953 Apr 25;171(4356):737–738. doi: 10.1038/171737a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang A. H., Quigley G. J., Kolpak F. J., Crawford J. L., van Boom J. H., van der Marel G., Rich A. Molecular structure of a left-handed double helical DNA fragment at atomic resolution. Nature. 1979 Dec 13;282(5740):680–686. doi: 10.1038/282680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



