Abstract
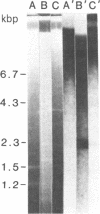
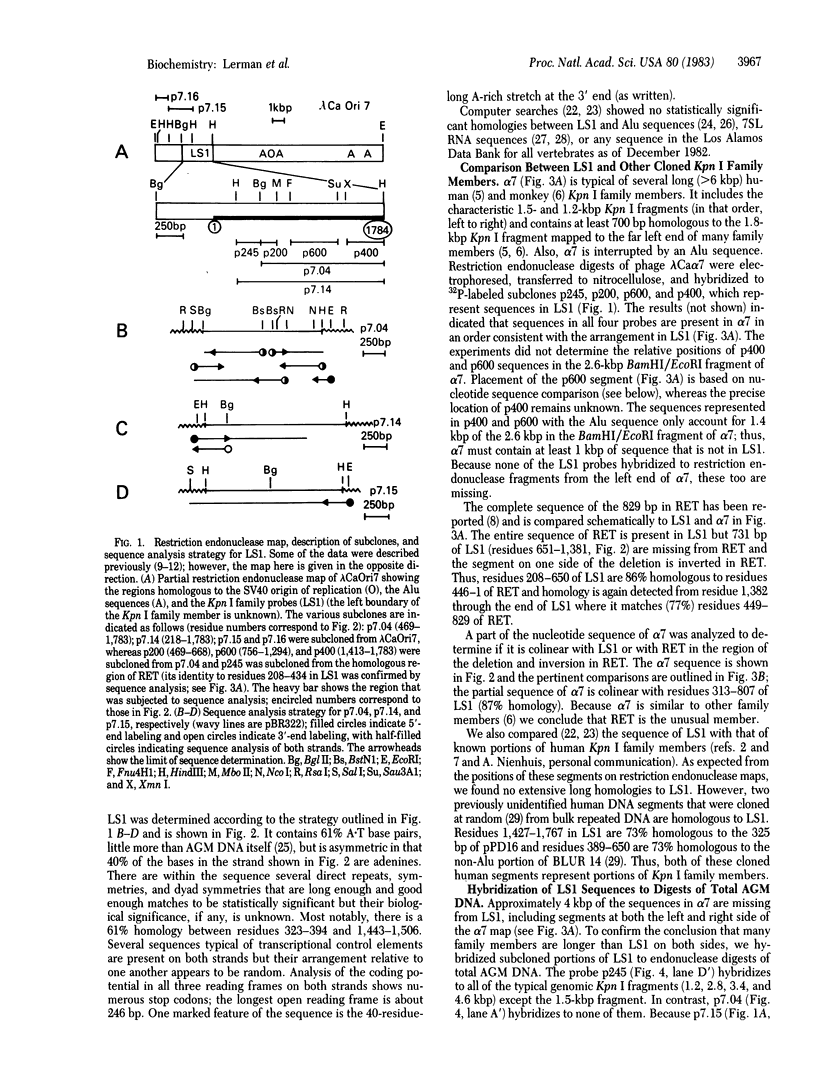
An approximately equal to 2-kilobase-pair-long member (Kpn I-LS1) of the African green monkey Kpn I family of repeated sequences has been cloned, subjected to sequence analysis, and compared to other family members which are over 6 kilobase pairs (Kpn I-alpha 7) and 829 base pairs (Kpn I-RET) long. Both Kpn I-LS1 and Kpn I-RET lack sequences found at the ends of the longer family member and their structures resemble those of processed genes. Kpm I-LS1 sequences are colinear with part of the long family member, Kpn I-alpha 7. However, although all sequences in Kpn I-RET are represented in Kpn I-LS1, the two are not colinear; Kpn I-RET is missing 731 base pairs found in Kpn I-LS1 and one segment flanking the deletion is inverted. The results demonstrate that Kpn I family members are not only of different lengths but may also contain scrambled arrangements of common sequences. Sequences in Kpn I-LS1 hybridize to RNA from monkey and human cells, indicating that some family members are transcribed.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams J. W., Kaufman R. E., Kretschmer P. J., Harrison M., Nienhuis A. W. A family of long reiterated DNA sequences, one copy of which is next to the human beta globin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Dec 20;8(24):6113–6128. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.24.6113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alt F. W., Baltimore D. Joining of immunoglobulin heavy chain gene segments: implications from a chromosome with evidence of three D-JH fusions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):4118–4122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.4118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deininger P. L., Jolly D. J., Rubin C. M., Friedmann T., Schmid C. W. Base sequence studies of 300 nucleotide renatured repeated human DNA clones. J Mol Biol. 1981 Sep 5;151(1):17–33. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90219-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denison R. A., Weiner A. M. Human U1 RNA pseudogenes may be generated by both DNA- and RNA-mediated mechanisms. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Jul;2(7):815–828. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.7.815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forget B. G., Tuan D., Biro P. A., Jagadeeswaran P. O., Weissman S. M. Structural features of the DNA flanking the human non-alpha globin genes: implications in the control of fetal hemoglobin switching. Trans Assoc Am Physicians. 1981;94:204–210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glisin V., Crkvenjakov R., Byus C. Ribonucleic acid isolated by cesium chloride centrifugation. Biochemistry. 1974 Jun 4;13(12):2633–2637. doi: 10.1021/bi00709a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg R., Lang R. B., Diamond M. S., Marcu K. B. A switch region inversion contributes to the aberrant rearrangement of a mu immunoglobulin heavy chain gene in MPC-11 cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Dec 11;10(23):7751–7761. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.23.7751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimaldi G., Queen C., Singer M. F. Interspersed repeated sequences in the African green monkey genome that are homologous to the human Alu family. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Nov 11;9(21):5553–5568. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.21.5553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimaldi G., Singer M. F. Members of the KpnI family of long interspersed repeated sequences join and interrupt alpha-satellite in the monkey genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jan 25;11(2):321–338. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.2.321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jagadeeswaran P., Forget B. G., Weissman S. M. Short interspersed repetitive DNA elements in eucaryotes: transposable DNA elements generated by reverse transcription of RNA pol III transcripts? Cell. 1981 Oct;26(2 Pt 2):141–142. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90296-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jelinek W. R., Schmid C. W. Repetitive sequences in eukaryotic DNA and their expression. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:813–844. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.004121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamp D., Kahmann R., Zipser D., Broker T. R., Chow L. T. Inversion of the G DNA segment of phage Mu controls phage infectivity. Nature. 1978 Feb 9;271(5645):577–580. doi: 10.1038/271577a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li W. Y., Reddy R., Henning D., Epstein P., Busch H. Nucleotide sequence of 7 S RNA. Homology to Alu DNA and La 4.5 S RNA. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 10;257(9):5136–5142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maio J. J. DNA strand reassociation and polyribonucleotide binding in the African green monkey, Cercopithecus aethiops. J Mol Biol. 1971 Mar 28;56(3):579–595. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90403-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Hardison R. C., Lacy E., Lauer J., O'Connell C., Quon D., Sim G. K., Efstratiadis A. The isolation of structural genes from libraries of eucaryotic DNA. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):687–701. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90036-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manley J. L., Colozzo M. T. Synthesis in vitro of an exceptionally long RNA transcript promoted by an AluI sequence. Nature. 1982 Nov 25;300(5890):376–379. doi: 10.1038/300376a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manuelidis L., Biro P. A. Genomic representation of the Hind II 1.9 kb repeated DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 May 25;10(10):3221–3239. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.10.3221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manuelidis L. Nucleotide sequence definition of a major human repeated DNA, the Hind III 1.9 kb family. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 May 25;10(10):3211–3219. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.10.3211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCutchan T. F., Singer M. F. DNA sequences similar to those around the simian virus 40 origin of replication are present in the monkey genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):95–99. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.95. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okayama H., Berg P. A cDNA cloning vector that permits expression of cDNA inserts in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Feb;3(2):280–289. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.2.280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Queen C. L., Korn L. J. Computer analysis of nucleic acids and proteins. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):595–609. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65062-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Queen C., Lord S. T., McCutchan T. F., Singer M. F. Three segments from the monkey genome that hybridize to simian virus 40 have common structural elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Dec;1(12):1061–1068. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.12.1061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saffer J. D., Lerman M. I. Unusual class of Alu sequences containing a potential Z-DNA segment. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 May;3(5):960–964. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.5.960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shafit-Zagardo B., Brown F. L., Maio J. J., Adams J. W. KpnI families of long, interspersed repetitive DNAs associated with the human beta-globin gene cluster. Gene. 1982 Dec;20(3):397–407. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90208-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shafit-Zagardo B., Maio J. J., Brown F. L. KpnI families of long, interspersed repetitive DNAs in human and other primate genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 May 25;10(10):3175–3193. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.10.3175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M., Zieg J., Silverman M., Mandel G., Doolittle R. Phase variation: evolution of a controlling element. Science. 1980 Sep 19;209(4463):1370–1374. doi: 10.1126/science.6251543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer M. F. Highly repeated sequences in mammalian genomes. Int Rev Cytol. 1982;76:67–112. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61789-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. R., Calvo J. M. Nucleotide sequence of the E coli gene coding for dihydrofolate reductase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 May 24;8(10):2255–2274. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.10.2255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thayer R. E. An improved method for detecting foreign DNA in plasmids of Escherichia coli. Anal Biochem. 1979 Sep 15;98(1):60–63. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90705-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullu E., Murphy S., Melli M. Human 7SL RNA consists of a 140 nucleotide middle-repetitive sequence inserted in an alu sequence. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):195–202. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90103-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Arsdell S. W., Denison R. A., Bernstein L. B., Weiner A. M., Manser T., Gesteland R. F. Direct repeats flank three small nuclear RNA pseudogenes in the human genome. Cell. 1981 Oct;26(1 Pt 1):11–17. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90028-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waalwijk C., Flavell R. A. MspI, an isoschizomer of hpaII which cleaves both unmethylated and methylated hpaII sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Sep;5(9):3231–3236. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.9.3231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wensink P. C., Tabata S., Pachl C. The clustered and scrambled arrangement of moderately repetitive elements in Drosophila DNA. Cell. 1979 Dec;18(4):1231–1246. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90235-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilbur W. J., Lipman D. J. Rapid similarity searches of nucleic acid and protein data banks. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(3):726–730. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.3.726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zasloff M., Santos T. Reiteration frequency mapping: analysis of repetitive sequence organization within cloned DNA fragments containing the human initiator methionine tRNA gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):5668–5672. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.5668. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]