Abstract
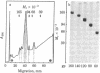
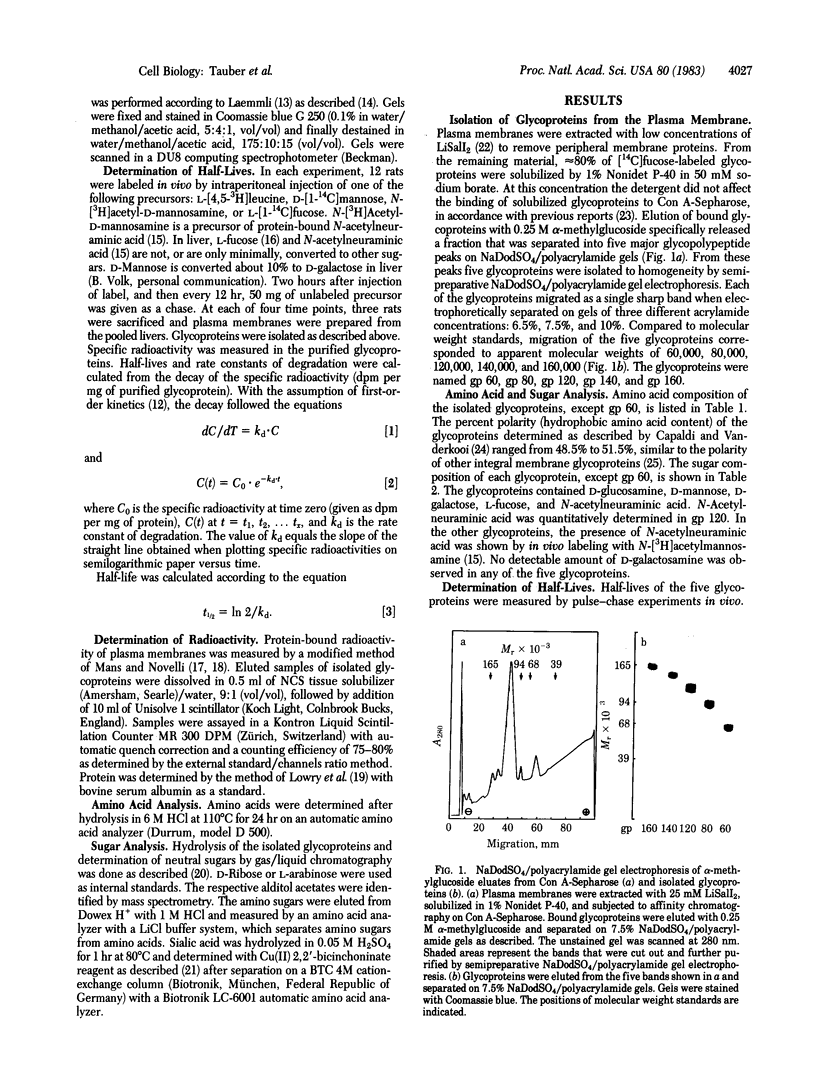
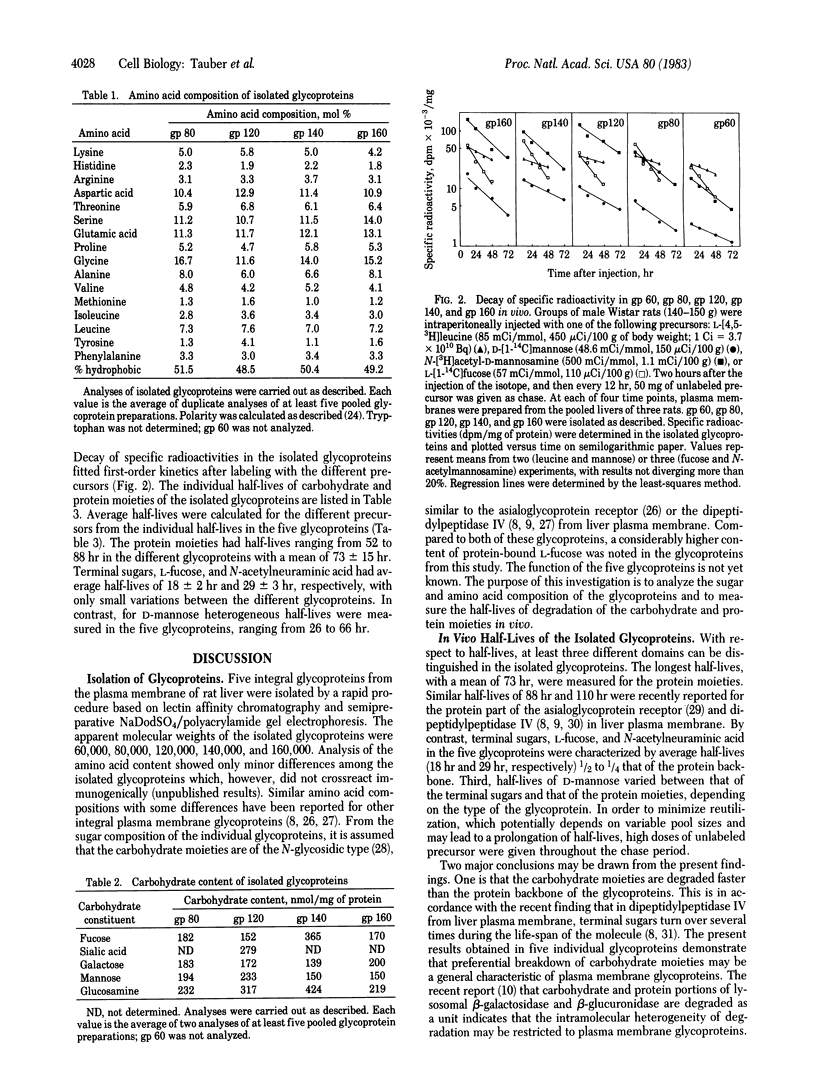
Five integral plasma membrane glycoproteins (60, 80, 120, 140, and 160 kilodaltons) were isolated to homogeneity from rat liver by a four-step procedure: (i) extraction of plasma membranes with lithium diiodosalicylate, (ii) solubilization of glycoproteins with Nonidet P-40, (iii) affinity chromatography on concanavalin A-Sepharose, and (iv) semipreparative NaDodSO4/polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. The glycoproteins contained 48.5--51.5% hydrophobic amino acids. Carbohydrate moieties contained N-acetyl-D-glucosamine, D-mannose, D-galactose, L-fucose, and N-acetylneuraminic acid. N-Acetyl-D-galactosamine was not detectable. Half-lives of degradation of the carbohydrate and protein moieties of the five glycoproteins were measured by pulse-chase experiments in vivo. Protein moieties had half-lives ranging from 52 to 88 hr in the five glycoproteins, with a mean of 73 +/- 15 hr. Terminal sugars, L-fucose, and N-acetylneuraminic acid had significantly shorter half-lives, averaging 18 +/- 2 hr and 29 +/- 3 hr, respectively. The half-life of D-mannose varied between that of the terminal sugars and that of the protein moiety, depending on the type of the glycoprotein. The data show that the carbohydrate moieties are degraded faster than the protein portion of the glycoproteins. As this finding was obtained in each of the five glycoproteins, intramolecular heterogeneity of breakdown may be a general characteristic of plasma membrane glycoproteins in liver.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashwell G., Harford J. Carbohydrate-specific receptors of the liver. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:531–554. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.002531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer C. H., Lukaschek R., Reutter W. G. Studies on the golgi apparatus. Cumulative inhibition of protein and glycoprotein secretion by D-galactosamine. Biochem J. 1974 Aug;142(2):221–230. doi: 10.1042/bj1420221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bekesi J. G., Winzler R. J. The metabolism of plasma glycoproteins. Studies on the incorporation of L-fucose-1-14-C into tissue and serum in the normal rat. J Biol Chem. 1967 Sep 10;242(17):3873–3879. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosmann H. B., Spataro A. C., Myers M. W. Serum and host liver activities of glycosidases and sialyltransferases in animals bearing transplantable tumors. Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol. 1975 Nov;12(3):499–512. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell K. P., MacLennan D. H. Purification and characterization of the 53,000-dalton glycoprotein from the sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 10;256(9):4626–4632. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capaldi R. A., Vanderkooi G. The low polarity of many membrane proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Apr;69(4):930–932. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.4.930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elovson J. Biogenesis of plasma membrane glycoproteins. Purification and properties of two rat liver plasma membrane glycoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jun 25;255(12):5807–5815. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elovson J. Biogenesis of plasma membrane glycoproteins. Tracer kinetic study of two rat liver plasma membrane glycoproteins in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jun 25;255(12):5816–5825. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harms E., Reutter W. Half-life of N-acetylneuraminic acid in plasma membranes of rat liver and Morris hepatoma 7777. Cancer Res. 1974 Dec;34(12):3165–3172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawasaki T., Ashwell G. Carbohydrate structure of glycopeptides isolated from an hepatic membrane-binding protein specific for asialoglycoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1976 Sep 10;251(17):5292–5299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornfeld R., Kornfeld S. Comparative aspects of glycoprotein structure. Annu Rev Biochem. 1976;45:217–237. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.45.070176.001245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreisel W., Heussner R., Volk B., Büchsel R., Reutter W., Gerok W. Identification of the 110000 Mr glycoprotein isolated from rat liver plasma membrane as dipeptidylaminopeptidase IV. FEBS Lett. 1982 Oct 4;147(1):85–88. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)81016-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreisel W., Volk B. A., Büchsel R., Reutter W. Different half-lives of the carbohydrate and protein moieties of a 110,000-dalton glycoprotein isolated from plasma membranes of rat liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):1828–1831. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.1828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehnhardt W. F., Winzler R. J. Determination of neutral sugars in glycoproteins by gas-liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr. 1968 May 7;34(4):471–479. doi: 10.1016/0021-9673(68)80091-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotan R., Beattie G., Hubbell W., Nicolson G. L. Activities of lectins and their immobilized derivatives in detergent solutions. Implications on the use of lectin affinity chromatography for the purification of membrane glycoproteins. Biochemistry. 1977 May 3;16(9):1787–1794. doi: 10.1021/bi00628a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFeeters R. F. A manual method for reducing sugar determinations with 2,2'-bicinchoninate reagent. Anal Biochem. 1980 Apr;103(2):302–306. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90614-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olden K., Parent J. B., White S. L. Carbohydrate moieties of glycoproteins. A re-evaluation of their function. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 May 12;650(4):209–232. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(82)90017-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfleger R. C., Anderson N. G., Snyder F. Lipid class and fatty acid composition of rat liver plasma membranes isolated by zonal centrifugation. Biochemistry. 1968 Aug;7(8):2826–2833. doi: 10.1021/bi00848a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schengrund C. L., Jensen D. S., Rosenberg A. Localization of sialidase in the plasma membrane of rat liver cells. J Biol Chem. 1972 May 10;247(9):2742–2746. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverstein S. C., Steinman R. M., Cohn Z. A. Endocytosis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:669–722. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.003321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skudlarek M. D., Swank R. T. Turnover of two lysosomal enzymes in macrophages. J Biol Chem. 1981 Oct 10;256(19):10137–10144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steck T. L., Yu J. Selective solubilization of proteins from red blood cell membranes by protein perturbants. J Supramol Struct. 1973;1(3):220–232. doi: 10.1002/jss.400010307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanabe T., Pricer W. E., Jr, Ashwell G. Subcellular membrane topology and turnover of a rat hepatic binding protein specific for asialoglycoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1979 Feb 25;254(4):1038–1043. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tauber R., Reutter W. Protein degradation in the plasma membrane of regenerating liver and Morris hepatomas. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Feb 1;83(1):37–45. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12065.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tauber R., Reutter W. Turnover of plasma membrane proteins and glycoproteins in normal and regenerating liver and Morris hepatoma 7777. Eur J Cell Biol. 1981 Dec;26(1):35–42. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tulsiani D. R., Hubbard S. C., Robbins P. W., Touster O. alpha-D-Mannosidases of rat liver Golgi membranes. Mannosidase II is the GlcNAcMAN5-cleaving enzyme in glycoprotein biosynthesis and mannosidases Ia and IB are the enzymes converting Man9 precursors to Man5 intermediates. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 10;257(7):3660–3668. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]