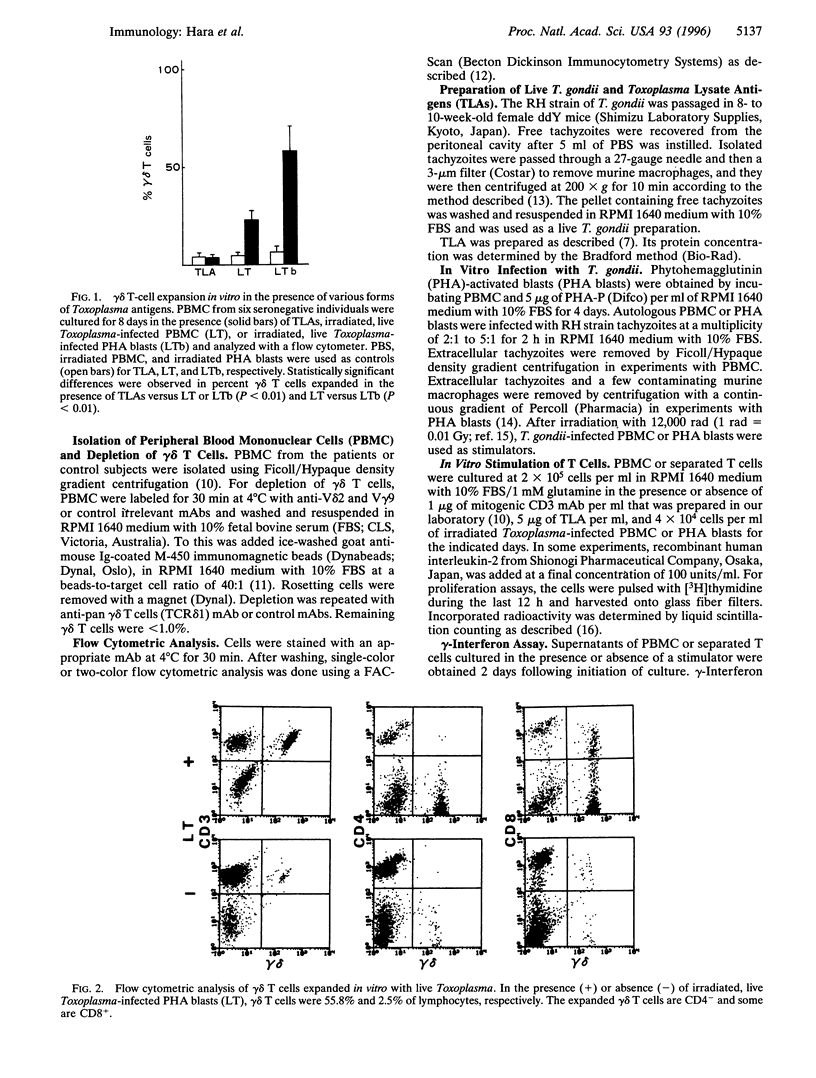
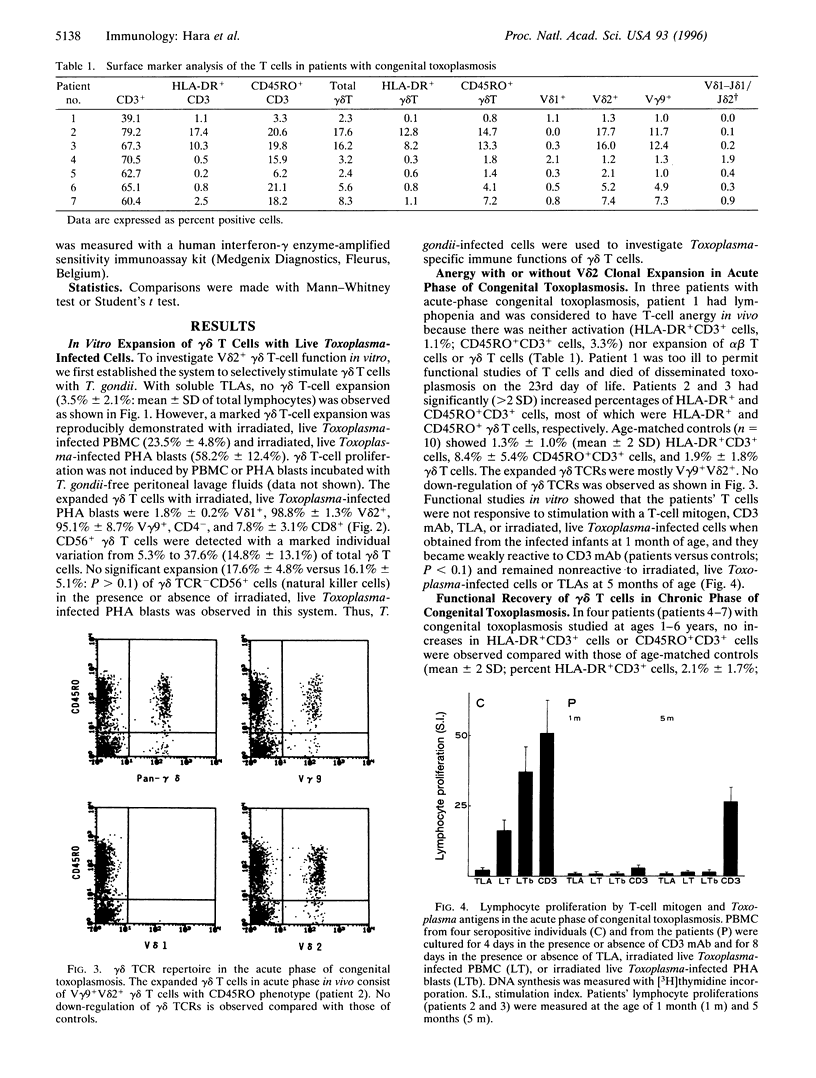
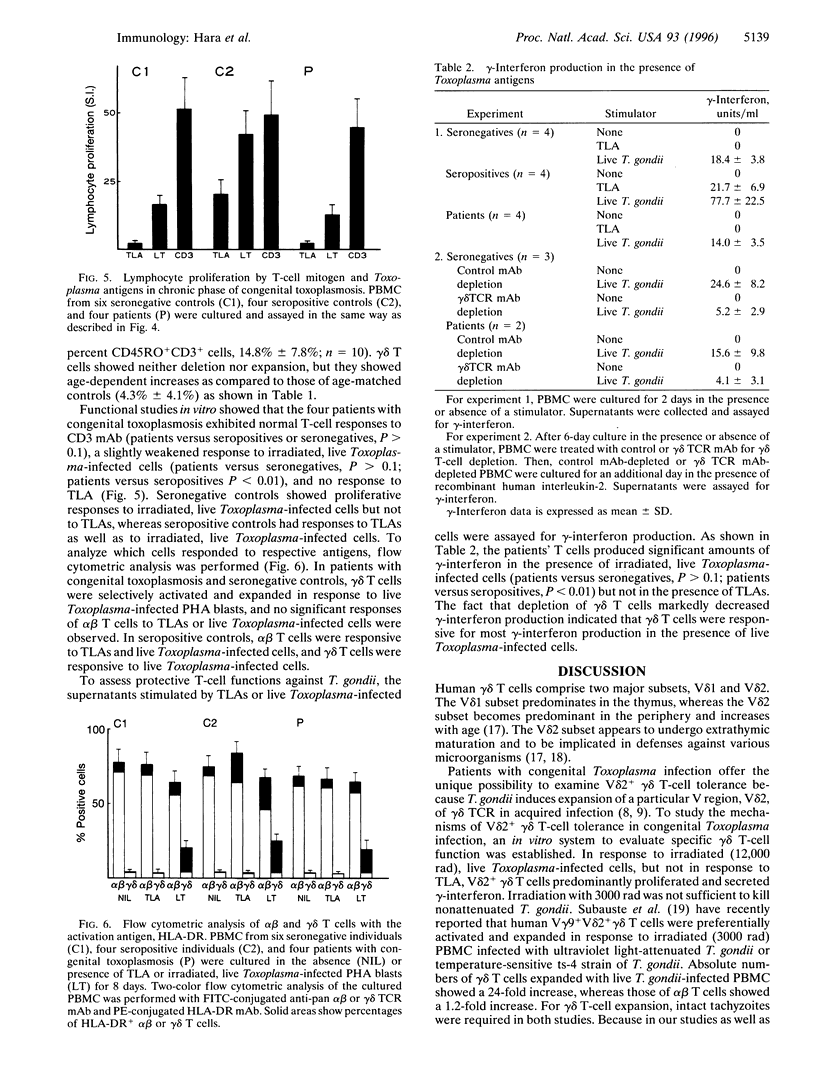
Abstract
Little is known about the mechanisms involved in human gammadelta T-cell tolerance to self or to foreign antigens. Patients with congenital toxoplasmosis offer a unique opportunity to examine Vdelta2+ gammadelta T-cell tolerance. Analysis of gammadelta T cells in patients with congenital toxoplasmosis revealed evidence for anergy of these cells with or without clonal Vdelta2+ gammadelta T-cell expansion in the acute phase of the Toxoplasma infection. T cells in general were unresponsive and did not proliferate upon exposure to mitogens or to Toxoplasma lysate antigens or in response to live Toxoplasma-infected cells when the congenitally infected infants were 1 month of age, and they exhibited selective anergy to Toxoplasma lysate antigens and live Toxoplasma-infected cells when the infants were aged 5 months. During the chronic phase of congenital toxoplasmosis in the patients who were more than I year of age, the repertoires of the gammadelta T-cell receptors were found to be within normal ranges. In addition, in the chronic phase, the gammadelta T cells proliferated and secreted gamma-interferon in response to exposure to live Toxoplasmia-infected cells. By contrast, alphabeta T cells remained anergic. Vdelta2+ gammadelta T cells have been considered to undergo extrathymic maturation and thus to be subject to development of peripheral tolerance. Our findings indicate that Vdelta2+ gammadelta T-cell tolerance was lost in these infected infants earlier than alphabeta T-cell tolerance. These findings suggest that gammadelta T cells play a role in protection against Toxoplasma gondii in the chronic phase when congenitally infected children are more than 1 year of age, especially in those in whom alphabeta T cells continue to exhibit deficits in specific immune responses to Toxoplasma antigens.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson S. E., Jr, Krahenbuhl J. L., Remington J. S. Longitudinal studies of lymphocyte response to Toxoplasma antigen in humans infected with T. gondii. J Clin Lab Immunol. 1979 Nov;2(4):293–297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett T. A., Delvy M. L., Kennedy D. M., Lefrancois L., Matis L. A., Dent A. L., Hedrick S. M., Bluestone J. A. Mechanism of self-tolerance of gamma/delta T cells in epithelial tissue. J Exp Med. 1992 Jan 1;175(1):65–70. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.1.65. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett T. A., Tatsumi Y., Bluestone J. A. Tolerance of T cell receptor gamma/delta cells in the intestine. J Exp Med. 1993 Jun 1;177(6):1755–1762. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.6.1755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaman M. H., Wong S. Y., Remington J. S. Cytokines, Toxoplasma and intracellular parasitism. Immunol Rev. 1992 Jun;127:97–117. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1992.tb01410.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonneville M., Ishida I., Itohara S., Verbeek S., Berns A., Kanagawa O., Haas W., Tonegawa S. Self-tolerance to transgenic gamma delta T cells by intrathymic inactivation. Nature. 1990 Mar 8;344(6262):163–165. doi: 10.1038/344163a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan J., Siegel J. P., Luft B. J. Demonstration of T-cell dysfunction during acute toxoplasma infection. Cell Immunol. 1986 Apr 1;98(2):422–433. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(86)90301-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chao C. C., Gekker G., Hu S., Peterson P. K. Human microglial cell defense against Toxoplasma gondii. The role of cytokines. J Immunol. 1994 Feb 1;152(3):1246–1252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curiel T. J., Krug E. C., Purner M. B., Poignard P., Berens R. L. Cloned human CD4+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes specific for Toxoplasma gondii lyse tachyzoite-infected target cells. J Immunol. 1993 Aug 15;151(4):2024–2031. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Paoli P., Basaglia G., Gennari D., Crovatto M., Modolo M. L., Santini G. Phenotypic profile and functional characteristics of human gamma and delta T cells during acute toxoplasmosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Mar;30(3):729–731. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.3.729-731.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dent A. L., Matis L. A., Hooshmand F., Widacki S. M., Bluestone J. A., Hedrick S. M. Self-reactive gamma delta T cells are eliminated in the thymus. Nature. 1990 Feb 22;343(6260):714–719. doi: 10.1038/343714a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geenen V., Kroemer G. Multiple ways to cellular immune tolerance. Immunol Today. 1993 Dec;14(12):573–575. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(93)90195-Q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gmelig-Meyling F., Waldmann T. A. Separation of human blood monocytes and lymphocytes on a continuous Percoll gradient. J Immunol Methods. 1980;33(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90077-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas W., Pereira P., Tonegawa S. Gamma/delta cells. Annu Rev Immunol. 1993;11:637–685. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.11.040193.003225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hara T., Fu S. M., Hansen J. A. Human T cell activation. II. A new activation pathway used by a major T cell population via a disulfide-bonded dimer of a 44 kilodalton polypeptide (9.3 antigen). J Exp Med. 1985 Jun 1;161(6):1513–1524. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hara T., Fu S. M. Human T cell activation. I. Monocyte-independent activation and proliferation induced by anti-T3 monoclonal antibodies in the presence of tumor promoter 12-o-tetradecanoyl phorbol-13 acetate. J Exp Med. 1985 Apr 1;161(4):641–656. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.4.641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hara T., Mizuno Y., Nagata M., Okabe Y., Taniguchi S., Harada M., Niho Y., Oshimi K., Ohga S., Yoshikai Y. Human gamma delta T-cell receptor-positive cell-mediated inhibition of erythropoiesis in vitro in a patient with type I autoimmune polyglandular syndrome and pure red blood cell aplasia. Blood. 1990 Feb 15;75(4):941–950. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hara T., Mizuno Y., Takaki K., Takada H., Akeda H., Aoki T., Nagata M., Ueda K., Matsuzaki G., Yoshikai Y. Predominant activation and expansion of V gamma 9-bearing gamma delta T cells in vivo as well as in vitro in Salmonella infection. J Clin Invest. 1992 Jul;90(1):204–210. doi: 10.1172/JCI115837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLeod R., Mack D. G., Boyer K., Mets M., Roizen N., Swisher C., Patel D., Beckmann E., Vitullo D., Johnson D. Phenotypes and functions of lymphocytes in congenital toxoplasmosis. J Lab Clin Med. 1990 Nov;116(5):623–635. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michie C., Harvey D. Can expression of CD45RO, a T-cell surface molecule, be used to detect congenital infection? Lancet. 1994 May 21;343(8908):1259–1260. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(94)92153-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohashi P. S., Oehen S., Buerki K., Pircher H., Ohashi C. T., Odermatt B., Malissen B., Zinkernagel R. M., Hengartner H. Ablation of "tolerance" and induction of diabetes by virus infection in viral antigen transgenic mice. Cell. 1991 Apr 19;65(2):305–317. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90164-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pircher H., Bürki K., Lang R., Hengartner H., Zinkernagel R. M. Tolerance induction in double specific T-cell receptor transgenic mice varies with antigen. Nature. 1989 Nov 30;342(6249):559–561. doi: 10.1038/342559a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rocha B., Tanchot C., Von Boehmer H. Clonal anergy blocks in vivo growth of mature T cells and can be reversed in the absence of antigen. J Exp Med. 1993 May 1;177(5):1517–1521. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.5.1517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rocha B., von Boehmer H. Peripheral selection of the T cell repertoire. Science. 1991 Mar 8;251(4998):1225–1228. doi: 10.1126/science.1900951. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Röcken M., Urban J. F., Shevach E. M. Infection breaks T-cell tolerance. Nature. 1992 Sep 3;359(6390):79–82. doi: 10.1038/359079a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scalise F., Gerli R., Castellucci G., Spinozzi F., Fabietti G. M., Crupi S., Sensi L., Britta R., Vaccaro R., Bertotto A. Lymphocytes bearing the gamma delta T-cell receptor in acute toxoplasmosis. Immunology. 1992 Aug;76(4):668–670. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steel C., Guinea A., McCarthy J. S., Ottesen E. A. Long-term effect of prenatal exposure to maternal microfilaraemia on immune responsiveness to filarial parasite antigens. Lancet. 1994 Apr 9;343(8902):890–893. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(94)90009-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subauste C. S., Chung J. Y., Do D., Koniaris A. H., Hunter C. A., Montoya J. G., Porcelli S., Remington J. S. Preferential activation and expansion of human peripheral blood gamma delta T cells in response to Toxoplasma gondii in vitro and their cytokine production and cytotoxic activity against T. gondii-infected cells. J Clin Invest. 1995 Jul;96(1):610–619. doi: 10.1172/JCI118076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vartdal F., Kvalheim G., Lea T. E., Bosnes V., Gaudernack G., Ugelstad J., Albrechtsen D. Depletion of T lymphocytes from human bone marrow. Use of magnetic monosized polymer microspheres coated with T-lymphocyte-specific monoclonal antibodies. Transplantation. 1987 Mar;43(3):366–371. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb S., Morris C., Sprent J. Extrathymic tolerance of mature T cells: clonal elimination as a consequence of immunity. Cell. 1990 Dec 21;63(6):1249–1256. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90420-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



