Abstract
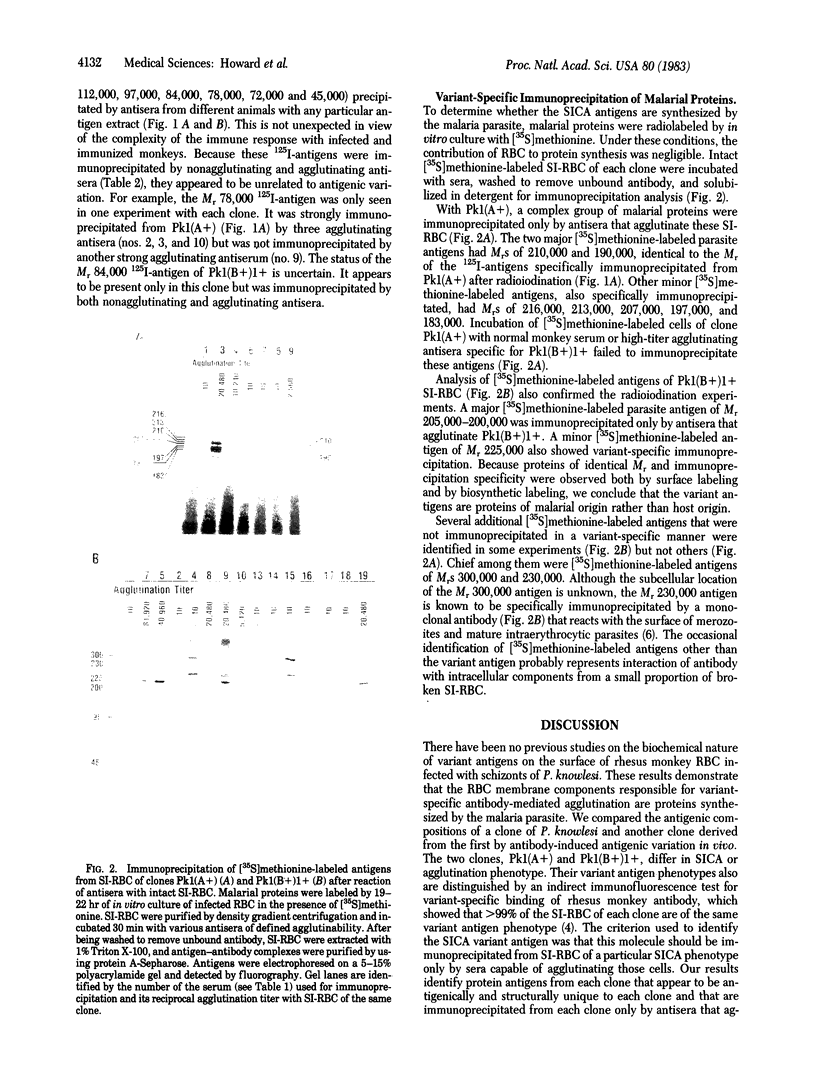
Erythrocytes infected with mature asexual stages of Plasmodium knowlesi express a new surface antigen such that rhesus monkey antisera specifically agglutinate these cells. Cloned parasites can express different antigenic variants of this antigen. The variant antigen has been identified by comparison of the surface membrane antigens of a clone and of an antigenic variant of that clone of different agglutination phenotype. After lactoperoxidase labeling, 125I-labeled proteins of Mrs 210,000 and 190,000 with one clone and of Mrs 205,000 with the antigenic variant were only immunoprecipitated by antisera containing homologous anti-variant antibody. Antigens of the same Mr from each clone were labeled by [35S]methionine incorporation during parasite growth and also specifically immunoprecipitated only by agglutinating antisera. Therefore, the variant antigens are malarial proteins rather than modified host proteins.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barnwell J. W., Howard R. J., Miller L. H. Altered expression of Plasmodium knowlesi variant antigen on the erythrocyte membrane in splenectomized rhesus monkeys. J Immunol. 1982 Jan;128(1):224–226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnwell J. W., Howard R. J., Miller L. H. Influence of the spleen on the expression of surface antigens on parasitized erythrocytes. Ciba Found Symp. 1983;94:117–136. doi: 10.1002/9780470715444.ch8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown K. N., Brown I. N. Immunity to malaria: antigenic variation in chronic infections of Plasmodium knowlesi. Nature. 1965 Dec 25;208(5017):1286–1288. doi: 10.1038/2081286a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown K. N., Brown I. N., Trigg P. I., Phillips R. S., Hills L. A. Immunity to malaria. II. Serological response of monkeys sensitized by drug-suppressed infection or by dead parasitized cells in Freund's complete adjuvant. Exp Parasitol. 1970 Oct;28(2):318–338. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(70)90102-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein N., Miller L. H., Kaushel D. C., Udeinya I. J., Rener J., Howard R. J., Asofsky R., Aikawa M., Hess R. L. Monoclonal antibodies against a specific surface determinant on malarial (Plasmodium knowlesi) merozoites block erythrocyte invasion. J Immunol. 1981 Jul;127(1):212–217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard R. J., Barnwell J. W., Kao V., Daniel W. A., Aley S. B. Radioiodination of new protein antigens on the surface of Plasmodium knowlesi schizont-infected erythrocytes. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1982 Dec;6(6):343–367. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(82)90024-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K., Favre M. Maturation of the head of bacteriophage T4. I. DNA packaging events. J Mol Biol. 1973 Nov 15;80(4):575–599. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90198-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips D. R., Morrison M. Exposed protein on the intact human erythrocyte. Biochemistry. 1971 May 11;10(10):1766–1771. doi: 10.1021/bi00786a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanstrom R., Shank P. R. X-Ray Intensifying Screens Greatly Enhance the Detection by Autoradiography of the Radioactive Isotopes 32P and 125I. Anal Biochem. 1978 May;86(1):184–192. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90333-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]