Abstract
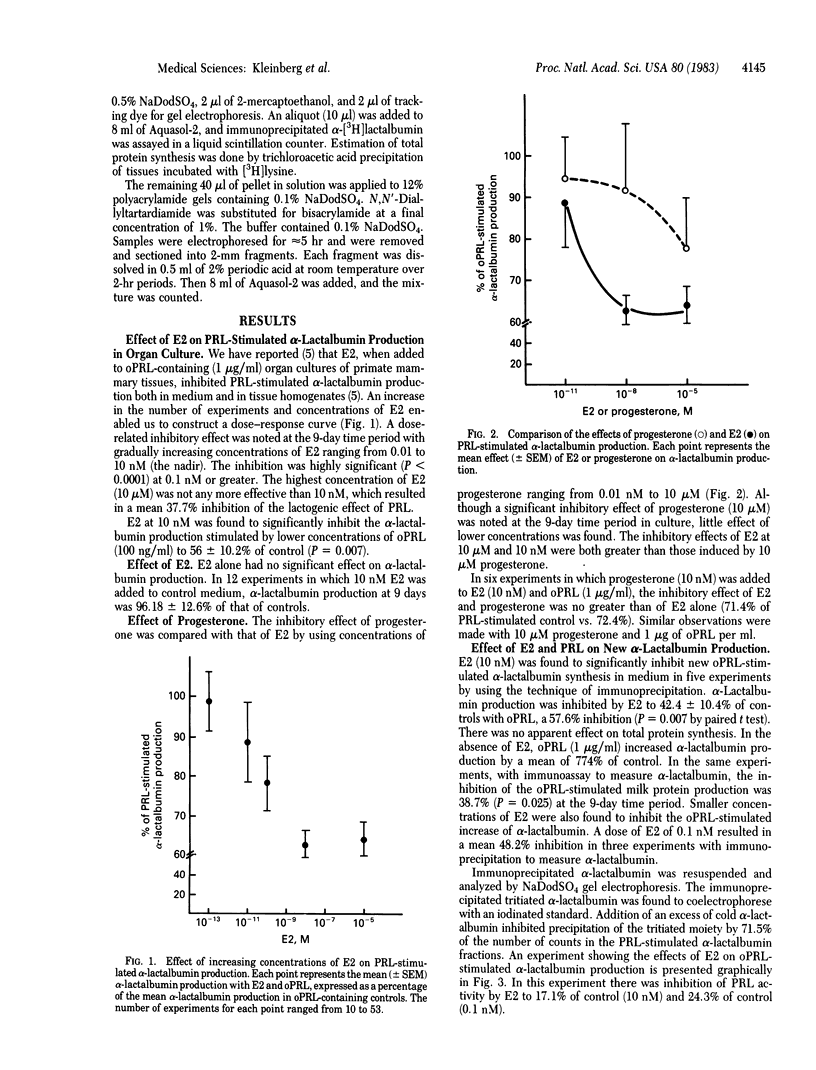
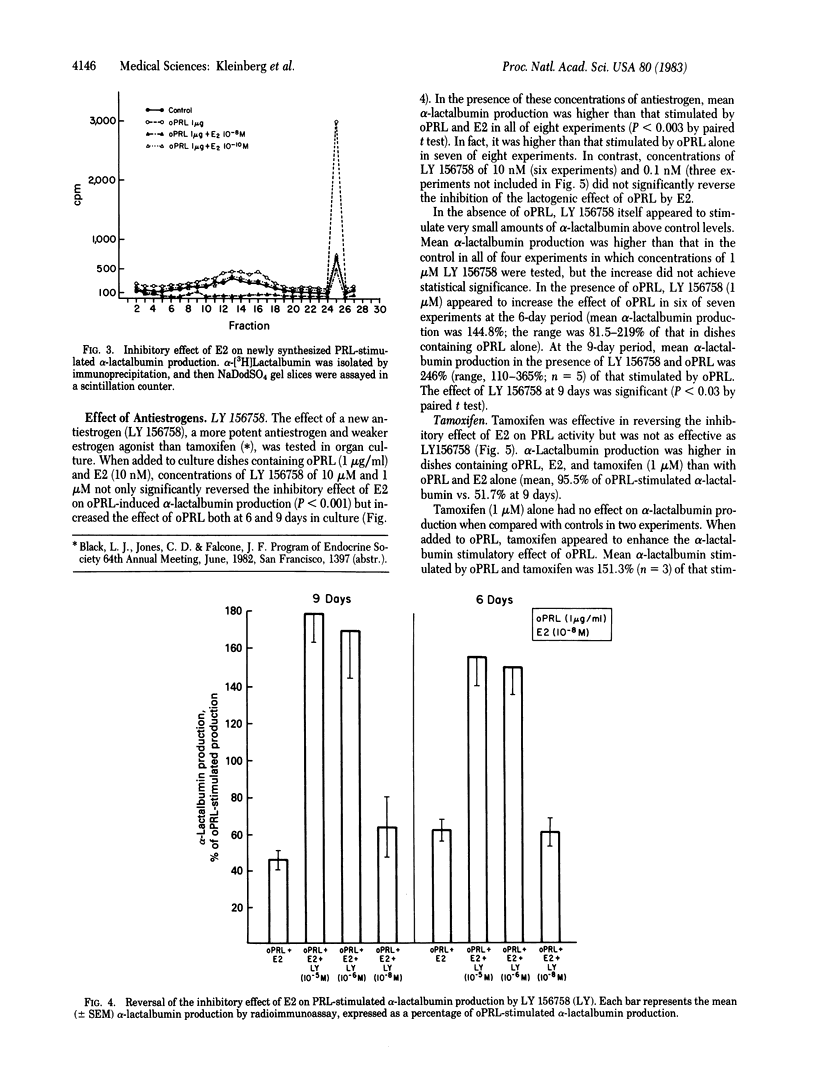
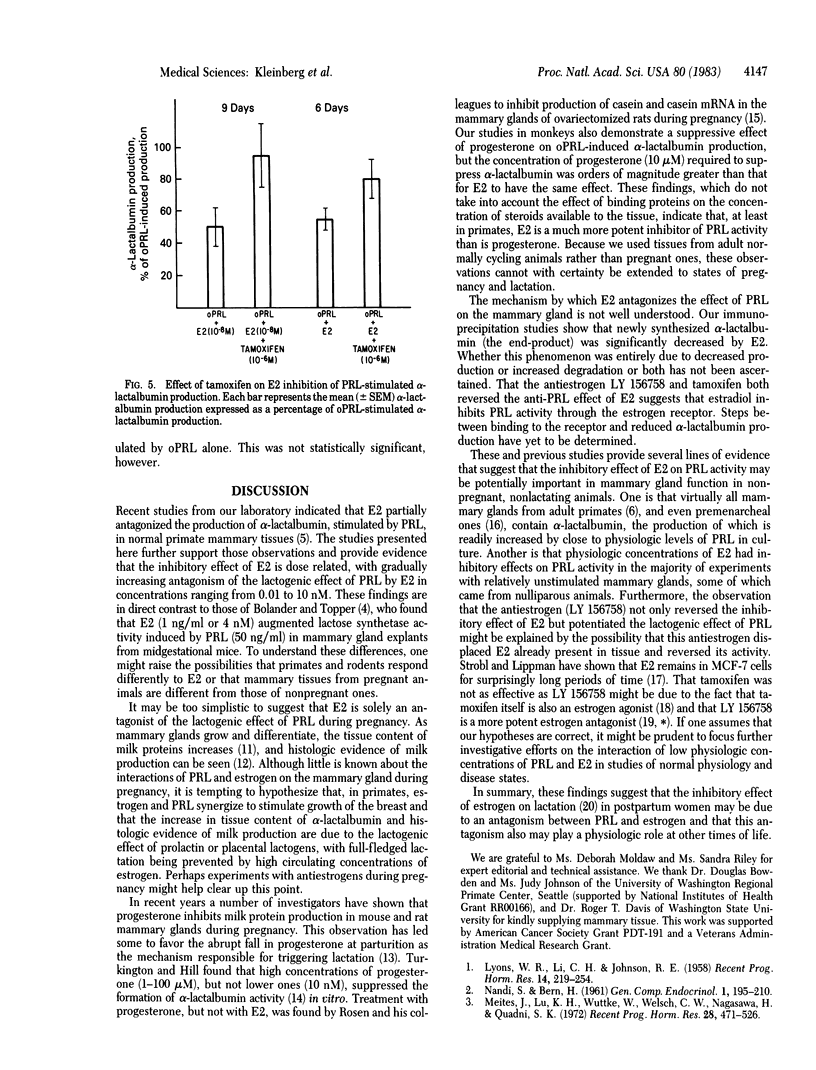
Increasing concentrations of estradiol (E2) ranging from 0.01 to 10 nM were found to inhibit partially but significantly the lactogenic effect of ovine prolactin (oPRL) on alpha-lactalbumin production in primate mammary tissues maintained in organ culture for 9 days. E2 at 10 nM inhibited by 38% (mean) PRL-stimulated alpha-lactalbumin production measured by radioimmunoassay. E2 antagonized the effect of oPRL by reducing new alpha-lactalbumin synthesis as determined by specific immunoprecipitation of alpha-lactalbumin and by analysis with NaDodSO4 gel electrophoresis. In immunoprecipitation studies, the mean inhibition of alpha-lactalbumin production was 57.6%. E2 in the absence of oPRL had no effect on alpha-lactalbumin production. In contrast to previous observations in rodents, progesterone was found to be a much weaker inhibitor of PRL-induced alpha-lactalbumin production than was E2 in primate breast tissues. Mean inhibition of oPRL-stimulated alpha-lactalbumin production was 32.3% with 10 microM progesterone and 8.3% with 10 nM. The inhibitory effect of E2 on oPRL-stimulated alpha-lactalbumin production was significantly reversed by both tamoxifen and a new antiestrogen, LY 156758. Although exact comparison of the effects of these two antiestrogens was not possible, it was apparent that LY 156758 was more potent in blocking the E2 inhibitory effect. In summary, these studies provide evidence that physiologic concentrations of estradiol partially block the lactogenic effect of PRL in primate mammary glands, suggesting a new role for estrogen in mammary physiology. The inhibitory effect of estrogen treatment on milk production in women after parturition may possibly be explained by this direct antagonism between E2 and PRL.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Black L. J., Goode R. L. Evidence for biological action of the antiestrogens LY117018 and tamoxifen by different mechanisms. Endocrinology. 1981 Sep;109(3):987–989. doi: 10.1210/endo-109-3-987. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolander F. F., Jr, Topper Y. J. Stimulation of lactose synthetase activity and casein synthesis in mouse mammary explants by estradiol. Endocrinology. 1980 Feb;106(2):490–495. doi: 10.1210/endo-106-2-490. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler S. W. Rapid isolation of antigens from cells with a staphylococcal protein A-antibody adsorbent: parameters of the interaction of antibody-antigen complexes with protein A. J Immunol. 1975 Dec;115(6):1617–1624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinberg D. L., Frantz A. G. Human prolactin: measurement in plasma by in vitro bioassay. J Clin Invest. 1971 Aug;50(8):1557–1568. doi: 10.1172/JCI106643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinberg D. L. Human alpha-lactalbumin: measurement in serum and in breast cancer organ cultures by radioimmunoassay. Science. 1975 Oct 17;190(4211):276–278. doi: 10.1126/science.1179206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinberg D. L., Todd J., Babitsky G., Greising J. Estradiol inhibits prolactin induced alpha-lactalbumin production in normal primate mammary tissue in vitro. Endocrinology. 1982 Jan;110(1):279–281. doi: 10.1210/endo-110-1-279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinberg D. L., Todd J., Groves M. L. Studies on human alpha-lactalbumin: radioimmunoassay measurements in normal human breast and breast cancer. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1977 Dec;45(6):1238–1250. doi: 10.1210/jcem-45-6-1238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinberg D. L., Todd J., Niemann W. Evidence that prolactin stimulates alpha-lactalbumin production in mannary tissues from premenarcheal rhesus monkeys. Endocrinology. 1979 Jun;104(6):1569–1573. doi: 10.1210/endo-104-6-1569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinberg D. L., Todd J., Niemann W. Prolactin stimulation of alpha-lactalbumin in normal primate mammary gland. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1978 Aug;47(2):435–441. doi: 10.1210/jcem-47-2-435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn N. J. Progesterone withdrawal as the lactogenic trigger in the rat. J Endocrinol. 1969 May;44(1):39–54. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0440039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LYONS W. R., LI C. H., JOHNSON R. E. The hormonal control of mammary growth and lactation. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1958;14:219–254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meites J., Lu K. H., Wuttke W., Welsch C. W., Nagasawa H., Quadri S. K. Recent studies on functions and control of prolactin secretion in rats. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1972;28:471–526. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NANDI S., BERN H. A. The hormones responsible for lactogenesis in BALB/cCrgl mice. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 1961 Sep;1:195–210. doi: 10.1016/0016-6480(61)90029-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen J. M., O'Neal D. L., McHugh J. E., Comstock J. P. Progesterone-mediated inhibition of casein mRNA and polysomal casein synthesis in the rat mammary gland during pregnancy. Biochemistry. 1978 Jan 24;17(2):290–297. doi: 10.1021/bi00595a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strobl J. S., Lippman M. E. Prolonged retention of estradiol by human breast cancer cells in tissue culture. Cancer Res. 1979 Sep;39(9):3319–3327. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Topper Y. J. Multiple hormone interactions in the development of mammary gland in vitro. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1970;26:287–308. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571126-5.50011-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turkington R. W., Hill R. L. Lactose synthetase: progesterone inhibition of the induction of alpha-lactalbumin. Science. 1969 Mar 28;163(3874):1458–1460. doi: 10.1126/science.163.3874.1458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


