Abstract
Most epithelial tissues retain stem/progenitor cells to maintain homeostasis of the adult tissues; however, the existence of a thymic epithelial cell (TEC) progenitor capable of maintaining homeostasis of the postnatal thymus remains unclear. Here, we show that a cell population expressing high levels of Meis1, a homeodomain transcription factor, is enriched in TECs with an immature cellular phenotype. These TECs selectively express genes involved in embryonic thymic organogenesis and epithelial stem cell maintenance, and also have the potential to proliferate and differentiate into mature TEC populations. Furthermore, postnatal inactivation of Meis1 in TECs caused disorganization of the thymic architecture, which ultimately leads to premature disappearance of the thymus. There was an age-associated reduction in the proportion of the TEC population expressing high levels of Meis1, which may also be related to thymic involution. These findings indicate that Meis1 is potentially involved in the maintenance of postnatal TECs with progenitor activity that is required for homeostasis of the postnatal thymus.
Introduction
The thymus is a primary lymphoid organ populated by several distinct epithelial and mesodermal cell lineages, including two thymic epithelial cell (TEC) subsets, cortical keratin 8 (K8)-positive TEC (cTEC) and medullary keratin 5 (K5)-positive TEC (mTEC), bone marrow-derived dendritic cells and macrophages, and endothelial cells. All of these cell types are required for proper intrathymic T cell proliferation, differentiation and selection [1], [2]. The epithelial component of the thymus is formed from the endoderm of the third pharyngeal pouch, which buds out into the underlying mesenchyme, a process that begins on day 10.5 of mouse embryonic development (E10.5). Epithelial cells initially cluster to form the thymic primordium, and then perithymic mesenchymal cells and lymphoid precursors migrate into this rudiment, initiating normal thymic development. Recently it has been demonstrated that embryonic TEC stem/progenitors arise as cells with cTEC markers, and then acquire mTEC markers [3]–[5]. TEC stem/progenitor cells have been formally identified by their capacity to differentiate into the full range of epithelial cells characteristic of a functional thymic microenvironment. Thus, a single K5+ K8+ epithelial cell from an E12 embryonic thymus can differentiate into both mTECs and cTECs when injected into a normal fetal thymic lobe [6]. Several transcription factors, including FoxN1 [7], [8], Hoxa3 [9], Pax1 [10], Pax9 [11], [12], Eya1 [13], Pbx1 [14] and p63 [15], [16], are important for thymic epithelial cell proliferation and differentiation, and altered expression or activity of any of them leads to severe defects in thymic organogenesis and development. Among them, p63 is of particular interest because this factor, especially one of its isoforms, ΔNp63, has been demonstrated to be selectively expressed in TEC stem/progenitor cells and required for their proliferation potential [15], [16].
In the postnatal thymus, the cortical and medullary architecture of the TEC microenvironment displays dynamic alterations in response to various physiological and pathological stimuli. The existence of TEC stem/progenitor cells that function to maintain the homeostasis of the postnatal thymic microenvironment has long been a matter of debate [17], [18]. Most epithelial tissues, including skin and intestine, that retain potential stem/progenitor cells are functionally maintained throughout the lifetime of the organism, whereas atrophy in the epithelial compartment of the thymus begins around puberty and progresses with age until, eventually, the functional microenvironment of this organ has been completely degraded in the aged organism [19]. However, like other epithelial tissues, the postnatal thymus appears to preserve an intrinsic ability to regenerate itself by responding to external stimuli, such as castration and cytokine administration [20], [21], suggesting the existence of stem/progenitor cells capable of maintaining homeostasis of the postnatal thymus. This idea is supported by the observation that postnatal reactivation of FoxN1 in single keratin 14 (K14)+ cells of FoxN1-deficient thymic cysts led to the development of small but functional thymic tissues with normally organized architecture [22]. In this regard, it has recently been demonstrated that Cbx4, a member of the Polycomb group family, is a critical regulator for both embryonic and postnatal TEC proliferation and functions [23], some of which are regulated by its interaction with p63, suggesting a possible link between embryonic and postnatal TEC stem/progenitor cells.
During a microarray search for transcription factors responsible for TEC regeneration, Meis1 (myeloid ecotropic viral integration site 1) was identified as one of the genes up-regulated in regenerating TECs following transient thymic atrophy induced by irradiation or dexamethasone treatment [24]. Meis1 encodes a homeodomain transcription factor of the TALE (three-amino-acid-loop extension) subfamily, and is homologous to the Drosophila Homothorax gene [25]. By interacting with Pbx, a member of another TALE homeodomain subfamily, Meis becomes intimately associated with certain Hox transcription factors and modulates the specificity and affinity of their DNA binding in several Hox-dependent developmental programs [26], including vertebrate hindbrain development and limb morphogenesis [27], [28]. Meis1 has also been reported to maintain the undifferentiated state and expansion of retinal progenitor cells [29], [30], olfactory epithelial cells [31] as well as embryonic hematopoietic stem cells [32], [33]. With respect to TEC differentiation, it is noteworthy that Hoxa3 and Pbx1, both of which are required for embryonic thymic organogenesis [9], [14], are functional and physical partners of Meis1.
In the present study, we used Meis1-EGFP reporter mice and tamoxifen-inducible epithelial-specific Meis1-conditional knockout mice to analyze the phenotype, function and molecular signature of Meis1-expressing TECs. We show here that postnatal thymic medulla contains two TEC populations with distinct Meis1 expression levels. The Meis1high TEC population represents immature TECs, as defined by cellular phenotypes, the expression patterns of genes involved in embryonic thymic organogenesis and epithelial stem cell maintenance, and progenitor-progeny analyses. Furthermore, Meis1 is required for maintenance of the postnatal thymus because its absence caused premature thymic disappearance and the proportion of the Meis1high TEC population decreases with age. Taken together, these findings demonstrate potential involvement of Meis1 in maintenance of the progenitor activity of postnatal TECs required for homeostasis of the postnatal thymus.
Results
Expression of Meis1 in the thymic microenvironment
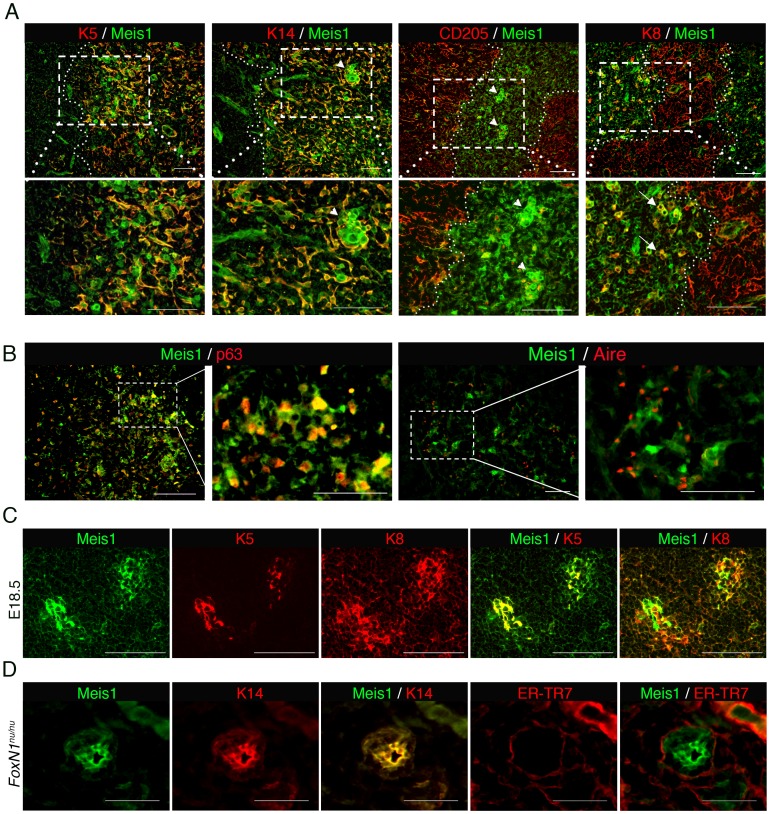
To understand the function of Meis1 in TEC differentiation, we first examined its expression in the thymus. In the postnatal thymus (at four weeks of age), Meis1 transcripts were selectively detectable in EpCAM+ TECs, particularly in MHC II+ UEA-1+ mTECs, but not in thymocytes, including the CD4+ or CD8+ single-positive (SP), CD4+CD8+ double-positive (DP) and CD4−CD8− double-negative (DN) subpopulations (Figure S1). Immunohistochemical analysis using an anti-Meis1 antibody revealed that Meis1+ cells were predominantly localized in the medulla and were very rare in the cortex, as defined by co-localized staining with K5 and K14, markers for mTECs, and by K8 and CD205, cTEC markers ( Figure 1A ). There were at least two distinguishable Meis1+ TECs in the medulla: round and relatively small cells expressing relatively high levels of Meis1 (Meis1high) and stellate cells with lower Meis1 expression (Meis1low) ( Figure 1A , indicated by arrowheads). Meis1low cells, forming the majority of Meis1+ cells in the medulla, were positive for K5 and K14, whereas some Meis1high cells were positive for K8, which is expressed in rare mTECs ( Figure 1A , indicated by arrows). Furthermore, p63, a transcription factor known to mark TEC stem/progenitor cells [15], [16], and Aire, a transcription factor expressed in mature mTECs [34], were differentially expressed in Meis1high and Meis1low cells, respectively ( Figure 1B ). Although Meis1 expression was not detectable in CD11c+ thymic dendritic cells, CD31+ vascular endothelial cells as well as ER-TR7-positive fibroblasts in the postnatal thymus were found to express Meis1 (Figure S2). In the thymus at embryonic day 18.5 (E18.5), Meis1 was highly expressed in TECs positive for both K5 and K8 ( Figure 1C ). We also examined the thymic rudiment present in nude mice that have a loss-of-function mutation in the FoxN1 gene. Their K14+ TECs, which have been shown to retain the capacity to regenerate complete thymic epithelial cell compartments [22], were found to express high levels of Meis1 ( Figure 1D ). These findings demonstrate that Meis1 is expressed at distinct levels in two populations of postnatal mTECs, and suggest that mTECs expressing high levels of Meis1 might include immature mTECs or TEC progenitors.
Figure 1. Expression of Meis1 in a small population of mTECs.
(A–B) Immunohistochemical analysis to localize Meis1-expressing cells in the postnatal thymus. Serial tissue sections of the thymus from 4-week-old wild-type mice were stained with the Meis1-specific antibody, in combination with anti-K5, K8, K14 or CD205 antibodies (A) and with anti-CD11c, CD31, p63, ER-TR7 or Aire antibodies (B). Broken lines indicate the cortico-medullary border. (C) Triple-color immunostaining of E18.5 thymus using anti-Meis1, K5 and K8 antibodies. (D) Triple-color immunostaining of the adult thymic rudiment from FoxN1 nu/nu mice using anti-Meis1, K14 and ER-TR7 antibodies. Images shown are representative of three independent experiments. Scale bars, 100 µm.
Epithelial-specific deletion of Meis1 causes thymic atrophy
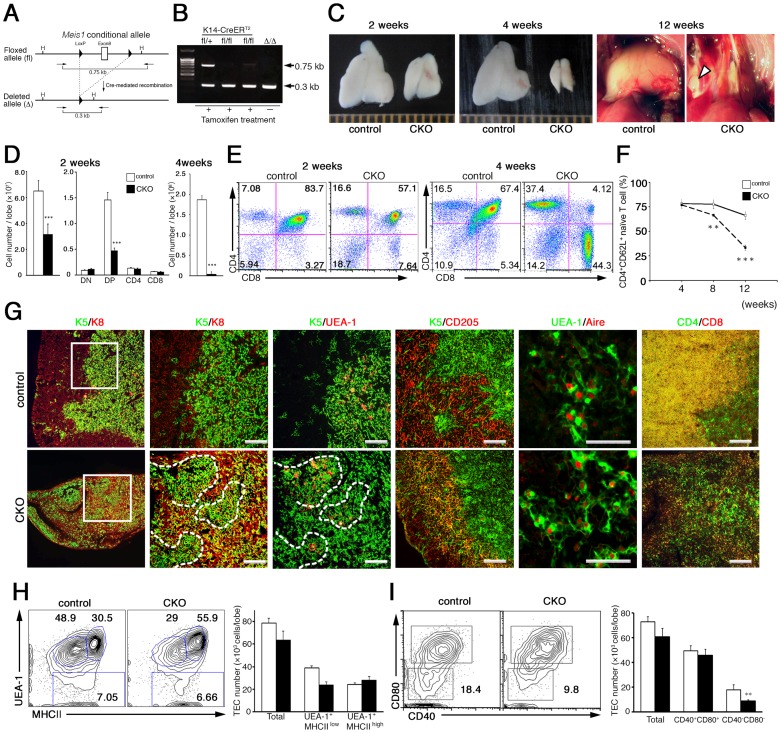
As the early embryonic lethality of germline deletion of the Meis1 gene precludes any study of postnatal maintenance of the thymus [32], [33], we generated mice harboring conditional alleles of Meis1 (Meis1fl), in which exon 8 of the Meis1 gene encoding the Meis1 homeodomain is flanked by loxP sites ( Figure 2A ). Given the high expression of Meis1 in immature mTECs, we chose to study the consequence of Meis1 ablation in these cells by crossing the Meis1fl conditional-knockout strain with the K14 gene promoter-driven tamoxifen-responsive K14-CreERT2 transgenic line, which effects highly efficient excision of loxP-flanked DNA in immature epithelial cells after induction with tamoxifen or 4-hydroxytamoxifen (4-OHT) [35]. Three intraperitoneal injections of tamoxifen into K14-CreERT2 Meis1fl/fl mice were sufficient to induce complete deletion of the floxed Meis1 locus in EpCAM+ CD205− TECs ( Figure 2B ).
Figure 2. Epithelial-specific deletion of Meis1 causes thymic atrophy.
(A) A diagram depicting the floxed Meis1 allele. LoxP sites (arrowheads) were inserted into intronic sites flanking exon 8 of the Meis1 gene. PCR primers for verifying the Cre-mediated deletion of the loxP-flanked fragment are indicated by arrows. (B) Confirmation of Meis1 deletion in K14-CreERT2 mice. DNAs from sorted EpCAM+ CD205− TECs from K14-CreERT2 Meis1 fl/fl and Meis1 fl/+ mice that were either treated (+) or untreated (−) with tamoxifen were subjected to PCR analysis using primer pairs shown in A. DNAs from Meis1 Δ/Δ mice were used as controls. (C) Gross appearance of thymus lobes from CKO and control mice 2 weeks (left) and 4 weeks (middle) post induction of Meis1 deletion. A macroscopic view of a mediastinum of CKO and control mice 12 weeks post induction of Meis1 deletion is also shown (right). The thymus lobes of control mice were positioned above the heart, whereas in the CKO the thymic lobes had completely disappeared. White arrowheads indicate ectopic lymph nodes. (D) Total cell numbers of total thymocytes (left) and subpopulations of thymocytes at different developmental stages (middle) from CKO (black bars) and control (white bars) mice 2 weeks post induction of Meis1 deletion. Numbers of total thymocytes (right) from CKO (black bars) and control (white bars) mice 4 weeks post induction of Meis1 deletion are also shown. Data are the mean and standard deviation of three independent experiments. ***, p<0.001. (E) Representative FACS profiles of thymocyte differentiation in CKO and control mice 2 weeks (left two panels) and 4 weeks (right two panels) post induction of Meis1 deletion. (F) The proportion of CD44− CD62L+ naïve CD4 T cells among total CD4 T cells in the peripheral blood of CKO (dotted line) and control (solid line) mice. Data are the mean and standard deviations of three independent experiments. **, p<0.01 and ***, p<0.001. (G) Immunohistochemical analysis of the thymus from CKO and control mice 4 weeks post induction of Meis1 deletion. Tissue sections were double stained with the indicated antibody combinations. Broken lines indicate cortico-medullary borders. Data are representative of 3 independent experiments. Scale bars, 100 µm. (H–I) Representative FACS profiles of TECs from K14-CreERT2 and control mice 4 days after tamoxifen treatment. Numbers indicate percentage of cells within the indicate gates. Bars show the cell number of the indicated EpCAM+ TECs from CKO (black) and control (white) mice. Shown are the mean and standard deviation from three independent experiments. **, p<0.01.
We analyzed the thymic architecture of adult K14-CreERT2 Meis1fl/fl mice at 2, 4 and 12 weeks after the tamoxifen treatment (hereafter referred to as CKO) and compared it to that of similarly treated K14-CreERT2 Meis1fl/+ or Meis1fl/fl littermates (hereafter referred to as controls). Two weeks after the induction of Meis1 deletion, the size and total cell number of the thymus in the Meis1-CKO mice were about half of those in the controls ( Figures 2C and D ). The phenotype became more severe by four weeks post-induction (PI); Meis1-CKO mice harbored only a small thymic remnant and the total cell number was less than 1% of the control thymus ( Figures 2C and D ). Eventually, the thymus of the CKO mice completely disappeared by 12 weeks PI ( Figure 2C , right panels). Flow cytometric analysis revealed significant and selective reduction of the proportion and the absolute number of CD4+ CD8+ DP T cells in CKO mice at two weeks PI ( Figures 2D and E ). To understand the selective reduction in DP T cells upon Meis1 loss, we examined early T-cell progenitors and their differentiation through the DN stage. There were no significant alterations in the proportions and cell numbers of these immature T cells, including early T-cell progenitors (Fig. S3), suggesting that the arrival of bone marrow-derived early T-cell progenitors to the thymus as well as early T-cell development until the DN4 stage in the thymus is not affected by Meis1 loss in postnatal TECs. Furthermore, all the thymocyte populations were significantly diminished in the CKO at four weeks PI ( Figure 2D ), and the reduction in the proportion of CD4+ CD8+ DP T cells became more severe than was observed at two weeks ( Figure 2E ). The proportion of CD62L+ CD44− naïve CD4+ T cells in peripheral blood also gradually declined from 4 to 12 weeks PI ( Figure 2F ), indirectly implicating the defective function of the thymic microenvironment in supporting T-cell development.
Immunohistochemical analyses revealed that the architecture of the medulla and cortex was severely disorganized in the CKO mice after four weeks PI ( Figure 2G ). The K5+ medullary compartment in the CKO thymus was severely reduced in size, although it still retained UEA-1+ and Aire+ mature mTECs, suggesting that the mature mTEC compartment was not severely affected by Meis1 loss ( Figure 2G ). Furthermore, the K5+ K8+ as well as K5+ CD205+ TECs, but not K8+ TECs that are distributed in the cortex of control thymus, occupied the cortex compartment surrounding the medullary region of the CKO thymus ( Figure 2G ). Although the molecular mechanisms by which Meis1 loss in the K14+ mTEC compartment causes cTEC alterations remain unclear, the phenotypic alterations observed in the cTEC compartment might be accompanied by profound reductions in the cell number of CD4+ CD8+ DP cells that preferentially reside in the cortical compartment of the thymus. The appearance of K5+K8+ cells in the cortex was detectable at least at 2 weeks after Meis1 deletion, at which time point the level of CD4+ CD8+ DP cell proportion was already lower than that of control DP cell population (Figure S4). At 12 weeks PI, we occasionally observed two small thymus-like remnant tissues bilaterally in the thoracic cavity where the normal thymus had been located prior to the induction of Meis1 deletion ( Figure 2C , arrowheads). However, these structures turned out to be ectopic lymph nodes (LN) that contained no K5+ or K8+ epithelial cells but instead displayed the typical LN accumulation of B220+ B cells and CD3+ T cells (Figure S5).
To identify the initial target cell populations affected by Meis1 loss, we examined cellular changes in the TEC population by flow cytometry at the early phase of Meis1 deletion. Four days after the induction of Meis1 deletion, the numbers of EpCAM+ TECs in the CKO were comparable to those in control mice. However, the proportion and absolute number of immature mTECs (MHCIIlow UEA-1+ and CD40− CD80−) were profoundly reduced in the CKO mice. By contrast, Meis1 deletion only marginally affected the number of mature mTECs (MHCIIhigh UEA-1+ and CD40+ CD80+) as well as MHCIIdull UEA-1− cTECs ( Figures 2H and I ), suggesting the possibility that the initial loss of -immature mTECs induced by Meis1 deletion results in disorganization of the thymic microenvironment. Taken together, these findings demonstrate that Meis1 is functionally required for maintenance of the postnatal thymic microenvironment.
High levels of Meis1 expression mark immature TEC population in the postnatal thymus
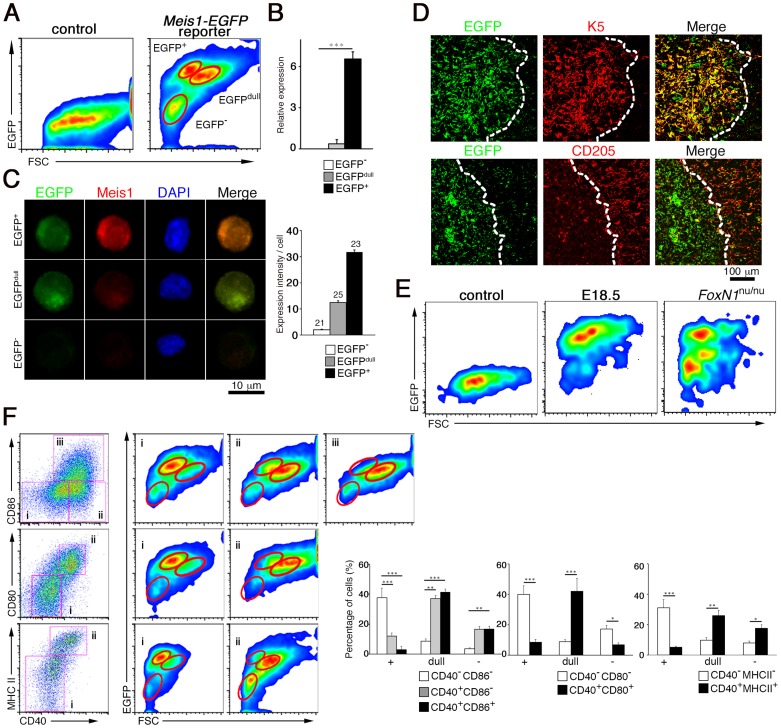
To understand how Meis1 functions to maintain the postnatal thymic microenvironment, we characterized TECs expressing Meis1 at the single cell level using Meis1-EGFP reporter mice [36]. These mice carry a bacterial artificial chromosome (BAC) transgene (RP23-306E8) corresponding to ∼80 kb upstream and ∼30 kb downstream of the mouse Meis1 gene, into which an EGFP cDNA was introduced just 5′ of the Meis1 translation start site, thus destroying any transgenic expression of Meis1 from the BAC. Meis1 expression was thus detectable in single cells by using EGFP fluorescence as a surrogate marker. Consistent with our RT-PCR results (Figure S1), EGFP expression was observed in EpCAM+ TECs but not in thymocytes (Figure S6). A more detailed analysis using a combination of EGFP fluorescence and forward scatter (FSC) showed that EpCAM+ TECs can be divided into three populations with different EGFP expression levels and cell sizes: EGFP+ FSClow, EGFPdull FSChigh and EGFP− FSClow ( Figure 3A ). When we compared endogenous Meis1 expression with EGFP fluorescence in these cell populations, Meis1 mRNA transcripts were significantly detectable only in the EGFP+ FSClow cells ( Figure 3B ), and the level of Meis1 protein expression, estimated from staining intensities, was approximately threefold higher in EGFP+ FSClow cells than in EGFPdull FSChigh cells ( Figure 3C ). These findings clearly indicate that EGFP+ FSClow cells are the TECs that have gone on to transcribe the Meis1 gene to generate high levels of Meis1 protein, while EGFPdull FSChigh cells appear to be EGFP+ FSClow descendants because they contain a substantial amount of Meis1 protein but have its gene transcription shut off. Immunohistochemical analyses also confirmed that the EGFP reporter was mainly expressed in the thymic medulla ( Figure 3D ). Furthermore, similar to endogenous Meis1 expression in the embryonic and FoxN1 nu/nu thymus ( Figures 1C and D ), both EGFP+ FSClow and EGFP− FSClow TECs were detectable in the thymus at E18.5 and in the thymic cysts of adult Meis1-EGFP reporter mice on the FoxN1 nu/nu background ( Figure 3E ). Thus, it is highly likely that EGFP+ FSClow, EGFPdull FSChigh and EGFP− FSClow cells correspond to endogenous Meis1high, Meis1low and Meis1− TECs observed by immunohistochemistry, respectively ( Figure 1A ; for simplicity hereafter referred to as EGFP+, EGFPdull and EGFP−).
Figure 3. The Meis1high TEC population represents immature TECs in the postnatal thymus.
(A) Representative FACS profiles showing EGFP expression in TECs from 4-week-old Meis1-EGFP reporter mice. EpCAM+ CD45− TECs were analyzed for EGFP fluorescence in combination with the forward scatter (FSC) profile. TECs from wild-type littermates were used as controls for background EGFP fluorescence. The TEC populations with distinct EGFP fluorescence intensities (EGFP+, EGFPdull and EGFP−) are marked by red circles. (B) The level of Meis1 mRNA transcripts in EGFP+, EGFPdull and EGFP− TECs. Data were normalized to ß-actin and the level of Meis1 transcript in the whole thymus was arbitrarily set to 1. Shown are the mean and standard deviations of three independent samples. (C) Representative image of sorted EGFP+, EGFPdull and EGFP− TECs stained with anti-EGFP (green) and anti-Meis1 (red) antibodies. Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI. Bar graphs represent signal intensities of Meis1 in sorted single EGFP+, EGFPdull and EGFP− TEC. Data were normalized to DAPI intensities and the level of each signal in EGFP− cells was arbitrarily set to 1. Numbers above the bars indicate the number of cells examined. (D) Immunohistochemical analysis of EGFP expression in the thymus from 4-week-old Meis1-EGFP reporter mice. Tissue sections were double stained with the indicated antibody combinations. Broken lines indicate cortico-medullary borders. (E) FACS profiles showing EGFP fluorescence in TECs from Meis1-EGFP reporter mice at E18.5 (middle) and on the FoxN1 nu/nu background (right). (F) FACS profiles showing the expression of EGFP with differentiation markers in TECs from 4-week-old Meis1-EGFP reporter mice. Cells were gated on CD45− EpCAM+ TECs and divided into developmental stages using the combination of cell surface markers CD40 with CD86 (upper panels), CD40 with CD80 (middle panels) or CD40 with MHC II (bottom panels). EGFP fluorescence in each gate is shown along with forward scatter profiles. Bar graphs shown on the right are the proportion of the indicated marker-positive cells among EGFP+, EGFPdull and EGFP− TECs. Data are the mean and standard deviation of three independent experiments.
To take advantage of the Meis1-EGFP reporter mice for characterization of Meis1-expressing cells, we further examined the phenotype of TECs with distinct Meis1 expression levels. As shown in Figure 3F , the majority of cells among the most immature TECs (CD40− CD86−) were EGFP+, whereas EGFPdull cells predominated in intermediate (CD40+ CD86−) and mature (CD40+ CD86+) TECs. A similar pattern of EGFP fluorescence was observed when we subdivided the TEC populations based on CD40 and CD80 or MHCII expression; CD40− CD80− and CD40− MHCII− immature TECs were enriched for the EGFP+ cells, while CD40+ CD80+ and CD40+ MHCII+ mature TECs were enriched for the EGFPdull cells ( Figure 3F ). The EGFP− cells did not show clear distribution patterns in terms of the TEC maturation stages. These results suggest that the EGFP+ cell population that selectively transcribes the Meis1 gene in the postnatal thymus corresponds to immature TECs that are the most sensitive to Meis1 deletion.
Gene expression patterns in TEC populations expressing different levels of Meis1
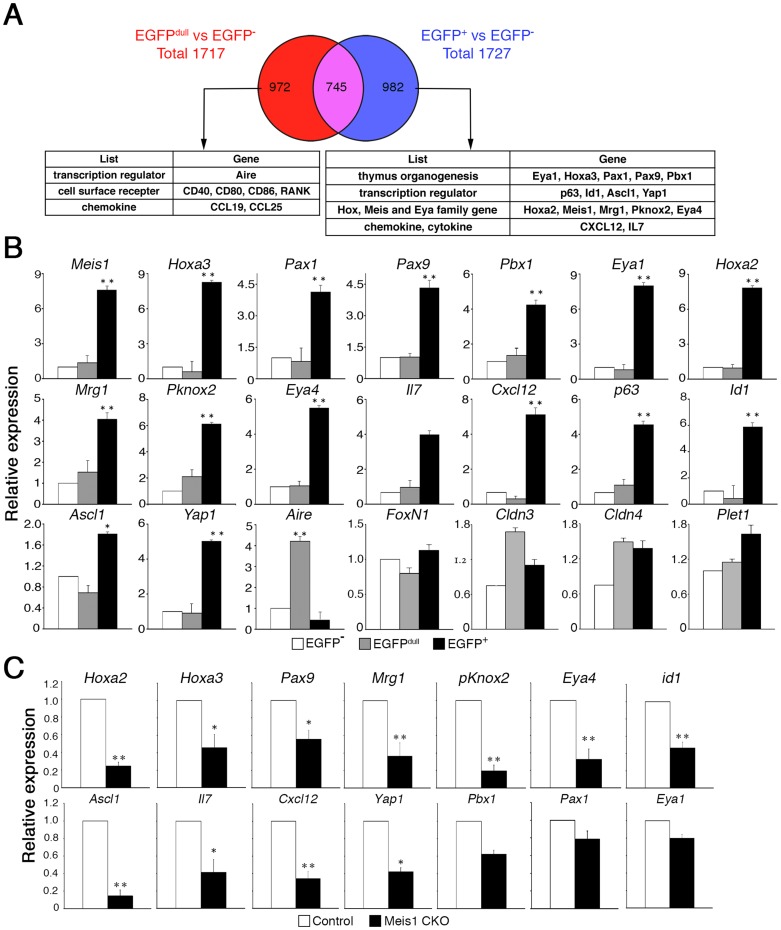
To obtain a better understanding of the nature of the differences in the TEC populations with distinct Meis1 expression levels, we performed comparative gene expression profiling by microarray analysis, and compared these data with the previously reported expression profiles of thymus stromal signature genes [37]. To define the thymus stromal signature genes differentially expressed in EGFP+ and EGFPdull TECs, we compared the genes differentially expressed 1.7-fold or more between EGFP+ and EGFP− TECs with the genes differentially expressed between EGFPdull and EGFP− TECs ( Figure 4A ; see Tables S1 and S2 for the full gene lists). We also validated the differential expression of a subset of these genes by quantitative PCR ( Figure 4B ). In addition to Meis1 itself, the genes differentially up-regulated in EGFP+ TECs included those involved in embryonic thymus organogenesis [9]–[14], such as Hoxa3, Pax1, Pax9, Pbx1 and Eya1, and in epithelial stem cell maintenance and differentiation [16], [38]–[40], such as p63, Id1, Ascl1 and Yap1 ( Figures 4A and B ). It is also worth noting that other Hox, Meis and Eya family genes (Hoxa2, Mrg1, Pknox2 and Eya4), previously unrecognized as potentially important in the development of TECs, were also up-regulated in EGFP+ cells. Furthermore, genes affecting TEC functions [41], [42], IL-7 and Cxcl12, were also up-regulated in EGFP+ cells. By contrast, the genes up-regulated in the EGFPdull TECs included Aire, a gene required for promiscuous gene expression in relatively mature mTECs [34], and genes encoding cell surface molecules expressed on mature TECs, such as CD40, CD80, CD86 and RANK (Tnfsf11a), a finding consistent with the mature phenotype of EGFPdull TECs ( Figure 3F ). Together, these findings demonstrated that EGFP+ TECs are a unique postnatal TEC population highly expressing key transcription factors essential for embryonic TEC differentiation and proliferation and also for the maintenance of epithelial stem/progenitor cells.
Figure 4. Expression profile of genes differentially enriched in Meis1low and Meis1high TECs.
(A) A Venn diagram showing the number of transcripts (gene probes) of up-regulated thymic stromal signature genes shared and distinct between EGFP+ and EGFPdull TECs sorted from the thymus of 4-week-old Meis1-EGFP reporter mice. The number of transcripts within each subpopulation is shown inside the Venn diagram. The full gene lists are shown in Table S1 and S2. Representative genes differentially expressed in EGFP+ and EGFPdull TECs relative to EGFP− TECs are also shown. (B) Gene expression levels between EGFP+, EGFPdull and EGFP− TECs were validated by quantitative RT-PCR. Histograms show the indicated transcripts in sorted TECs of EGFP+ (black bars), EGFPdull (gray bars) and EGFP− (white bars). Data were normalized to ß-actin expression and the level of each transcript in EGFP− cells was arbitrarily set to 1. Shown are the mean and standard deviation of at least three independent experiments. *p<0.05, and **p<0.01. (C) Alterations of gene expression in TECs induced by Meis1 loss were analyzed by quantitative RT-PCR. Histograms show the indicated transcripts in sorted TECs from K14-CreERT2 Meis1 fl/fl mice (white bars) and control mice (black bars) 4 days post tamoxifen treatment. Data were normalized to ß-actin expression and the level of each transcript in TECs from control mice was arbitrarily set to 1. Data are the mean and standard deviations of at least 3 independent experiments. *p<0.05 and **p<0.01.
To obtain further insight into the genetic effect of Meis1 loss on the EGFP+ TEC population, we examined alterations in the gene expression profiles of TECs from Meis1-CKO and controls at four days after tamoxifen treatment, and compared the genes that were down-regulated 1.7-fold or more by Meis1 deletion in TECs with the gene set differentially expressed in EGFP+ TECs (Table S3). Expression of some of the genes identified by microarray was also verified by quantitative PCR analysis ( Figure 4C ). Among genes up-regulated in EGFP+ TECs, most of the genes encoding transcription factors/co-activators, including Hoxa2, Hoxa3, Pax9, Mrg1, pKnox2, Eya4, Id1 and Ascl1, were down-regulated upon Meis1 deletion, although Pax1, Pbx1 and Eya1 expression levels were not significantly altered ( Figure 4C ). In addition, genes encoding IL-7 and Cxcl12 were significantly reduced in the Meis1-CKO TECs. These findings demonstrate that Meis1 is one of the components of transcription factor networks that are essential for the maintenance of postnatal thymic microenvironments that support T-cell differentiation.
Differentiation potentials of the Meis1high TEC population
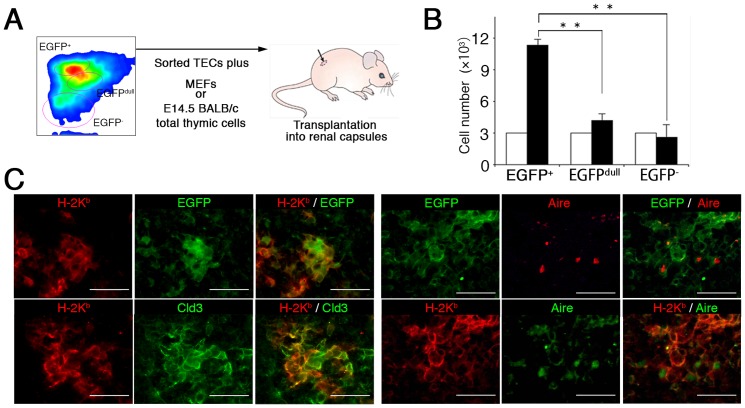
We further examined differentiation potentials of the Meis1high TEC population by using a cell transfer model that has been successfully applied for the generation of artificial lymph nodes [43]. TECs with distinct EGFP expression levels were sorted from adult Meis1-EGFP reporter mice (four weeks of age), and were incorporated into biocompatible cubic sponge-like collagenous scaffolds, which were then transplanted under the renal capsule of recipient mice ( Figure 5A ). Four weeks after the transplantation, the total number of EpCAM+ cells recovered from the grafted scaffold containing EGFP+ TECs increased about fourfold, whereas no cell expansion was observed in grafted scaffolds containing EGFPdull or EGFP− TECs ( Figure 5B ). Since the EGFP+ TECs themselves failed to generate the fully developed thymus-like epithelial organization with the medulla and cortex compartments in this transfer model (data not shown), we examined the differentiation capacity of postnatal EGFP+ TECs (H-2Kb) by incorporating them into an in vitro reaggregated E14.5 BALB/c (H-2Kd) thymus, which was transplanted under the renal capsule of recipient mice. Immunohistochemical analyses revealed that EGFP+ TEC-derived H-2Kb cells were detected in the thymic medulla as Claudin3+ as well as mature Aire+ TECs ( Figure 5C ), whereas the grafts embedded with EGFPdull cells or EGFP− cells contained no H-2Kb cells (data not shown), suggesting the differentiation potentials of postnatal immature TECs expressing high levels of Meis1 to mature TECs.
Figure 5. The Meis1high TEC population retains the progenitor activity.
(A) Experimental strategy for analysis of the progenitor potential of postnatal TECs with different Meis1 expression levels. TECs with distinct Meis1 expression levels (EGFP+, EGFPdull and EGFP−) were sorted from the thymus of 4-week-old Meis1-EGFP reporter mice; 3×103 cells from each fraction were mixed with 1×105 MEFs and absorbed into the scaffold. The resultant cell-embedded scaffold was implanted into the renal capsules of nude mice, and 4 weeks later the implanted scaffolds were analyzed. (B) Total numbers of CD45− EpCAM+ TECs from the renal implants. The input (open bars) and recovered (filled bars) cell numbers are shown. Data are the mean and standard deviation of three independent experiments. **, p<0.01. (C) Immunostaining of the reagregated E14.5 BALB/c thymus containing EGFPhigh TECs with the indicated antibody combinations. Scale bars, 100 µm.
Age-related aleration in the Meis1high TEC population
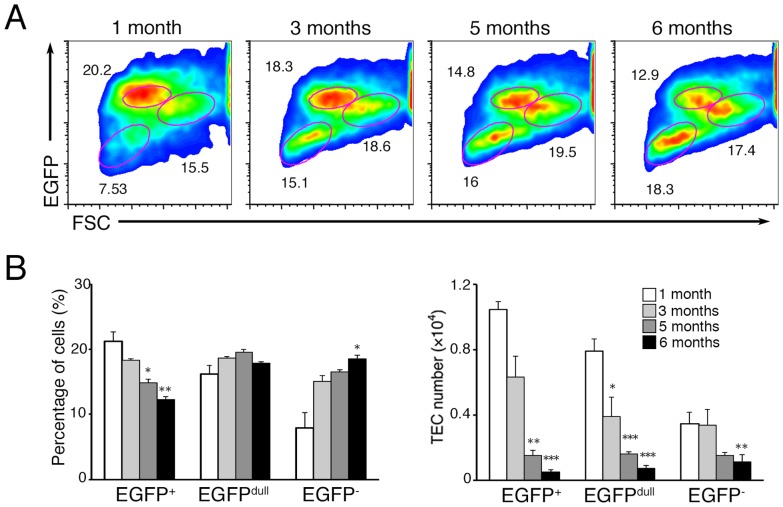
Given that the thymic architecture dynamically changes with age, we finally addressed the physiological relevance of Meis1 function in age-associated alterations in the thymic microenvironment. There was a gradual decrease in the proportion of EGFP+ cells beginning at ∼3 months of age and the reduction of these immature EGFP+ TECs was clearly apparent at 5 and 6 months of age ( Figures 6A and B ), indicating an age-associated reduction in an immature Meis1high TEC population in the postnatal thymus. This reduction in immature Meis1high TECs may result in age-associated exhaustion of progenitor cells capable of maintaining homeostasis of the postnatal thymus.
Figure 6. Age-associated reduction in the Meis1high TECs.
(A) Representative FACS profiles showing the expression of Meis1 by CD45− EpCAM+ TECs with age. TECs from mice of the indicated ages were analyzed for expression of EGFP by flow cytometry. Data are representative of three independent experiments. (B) The percentage and total cell numbers of EGFP+, EGFPdull and EGFP− TECs in mice of different ages; 1 month (white bars), 3 months (light gray bars), 5 months (dark gray bars) and 6 months (black bars). Bars represent the mean and standard deviations of the percentage (left) and cell numbers (right) of each TEC population from four independent experiments. Significance relative to 1-month-old mice; ***, p<0.001; **, p<0.01; *, p<0.05.
Discussion
In the present study, we demonstrate that expression of Meis1 in TECs is required for maintenance of the postnatal thymic microenvironment, as the postnatal loss of Meis1 in the K14+ TEC compartment causes not only a reduction in the size of the medulla but also formation of a disorganized cortex, eventually leading to complete disappearance of the thymus.
Our analyses of endogenous Meis1 and reporter gene expression in the thymus have shown that Meis1 is expressed in subpopulations of mTECs, and this heterogeneity in Meis1 expression levels marks distinct mTEC populations with respect to their differentiation and maturation stages. The Meis1high TEC population (EGFP+), corresponding to the cells going on to transcribe the Meis1 gene, represents immature TECs (CD40− MHCII− CD80− and CD86−) with up-regulated expression of genes encoding transcription factors/co-activators that are essential for embryonic thymus organogenesis, such as Hoxa3, Pax1, Pax9, Pbx1 and Eya1. In contrast, the Meis1low TEC population (EGFPdull), corresponding to the cells in which Meis1 gene transcription has already been shut down, represents mature TECs with a CD40+ MHCII+ CD80+ CD86+ phenotype and high expression of Aire, a finding that is consistent with a previous observation that TECs expressing Aire are postmitotic terminally differentiated mTECs [44]. Furthermore, Meis1high TECs were found to proliferate and to differentiate into mature TECs when ectopically transplanted under the renal capsule of nude mice. These findings suggest that the Meis1high TEC population in the postnatal thymus may include a postnatal TEC progenitor. In this regard, it has recently been demonstrated that postnatal TEC clones cultured under particular conditions in vitro and displaying a medullary phenotype (K5+, K14+) with enriched expression of p63 have the capacity to reconstitute a thymic microenvironment under the kidney capsule of nude mice [45]. Furthermore, these cultured TEC clones were shown to exhibit high expression of key transcription factors/co-activators involved in thymus organogenesis, such as Eya1, Six1, Pax1, Pax9 and Hoxa3, most of which are also enriched in the Meis1high TEC population described here. Thus, observed similarities in gene expression profiles of the Meis1high TEC population with the reported cultured TEC clones with stem cell activity further reinforce the idea that the Meis1high TEC population contains postnatal TEC progenitors.
With regard to the function of Meis1 in postnatal TEC progenitor activity, p63 is of particular interest among the transcription factors potentially regulating TEC progenitors because it is preferentially expressed in TEC stem/progenitor cells to regulate their potential to self-renew [16]. Although p63 is enriched in the Meis1high immature TEC population (Figures 1B and 4B) and expression of both Meis1 and p63 is independent of the activity of FoxN1, p63-deficient thymic phenotypes were apparently different from those in Meis1 deficiency. The loss of p63 in TECs selectively caused a proliferation defect in TECs, but did not disturb TEC differentiation, as both K5+ mTECs and K8+ cTECs were normally distributed in the p63-deficient thymus [15], [16]. Furthermore, p63-deficient mice displayed severe reductions in the absolute numbers of thymocytes without a disturbance in the relative proportion of CD4+ CD8+ DP as well as CD4+ and CD8+ SP thymocytes. Thus, p63 appears to exhibit selective control of the proliferation potentials of TEC stem/progenitors, but not their maturation and functions supporting T-cell differentiation in the thymus. In sharp contrast, postnatal Meis1 loss in TECs caused not only maturation defects in thymocyte differentiation, particularly at the CD4+ CD8+ DP stage, but also the disorganization of TEC compartments, which is characterized by the early loss of immature TECs and also by the appearance of K5+K8+CD205+ atypical TECs in the cortex. In this regard, one intriguing TEC phenotype that may link the phenotypic difference between Meis1 and p63 deficiency is that caused by deficiency in Cbx4, a Polycomb protein that directly interacts and potentially functions in conjunction with p63 [23]. The Cbx4-deficient mice displayed the hypoplastic, but morphologically intact, thymic microenvironment in the perinatal period, which highly resembles that observed in p63 deficiency [23]. However, similar to the Meis1-deficient phenotypes describe in the present report, loss of Cbx4 in the TEC compartment resulted in the appearance of K5+K8+ double-positive TECs in the postnatal thymus, which was also accompanied by the preferential reduction of CD4+CD8+ DP thymocytes, although such phenotypic alterations in TECs as well as in thymocyte development were not observed in the neonatal and embryonic thymus of the Cbx4 deficient mice [23]. Although it remains to be clarified whether Cbx4 functions in conjunction with p63 in the postnatal thymus, Meis1, like Cbx4, may have roles in the maintenance of the TEC functions supporting T-cell differentiation in the postnatal thymus. Further investigation of the functional interplay between Meis1 and p63/Cbx4 is clearly warranted to resolve this issue.
Aging causes thymic involution, but the genetic pathways that control this process are poorly understood. It has been reported that TECs from aged mice had reduced proliferative capacity and a higher rate of apoptosis [46]. Postnatal TEC division predominantly occurs in the mTEC population [47], and reduction in the proportion of dividing TECs with age causes the changes in stromal composition that characterize the involuted thymus. In this regard, we observed that the proportion of the immature Meis1high TEC population is reduced with age. This age-associated reduction in immature Meis1high cells potentially containing postnatal TEC progenitors seems to be one of the potential mechanisms involved in age-associated thymic involution. In this regard, p63, in association with FoxN1, has also recently been revealed to participate in age-related thymic involution [48]. Further studies on the function of Meis1 in TECs, in relation to the p63-FoxN1 regulatory axis, could provide an avenue for clarifying the molecular mechanism underlying age-associated thymic atrophy.
In conclusion, we provide evidence that, in the postnatal thymus, the high expression of Meis1 marks an immature TEC population with potential progenitor activities, and that Meis1 is required for homeostatic maintenance of the postnatal thymus. Further dissection of the function of Meis1 in the transcription factor networks regulating maintenance of the postnatal thymic microenvironment, particularly in association with p63 and Cbx4, should shed light on the role of epithelial stem/progenitor cells in the homeostasis and regenerative capability of the postnatal thymus, and may lead to the development of novel therapeutic strategies to regenerate thymic functions in pathological conditions.
Materials and Methods
Ethics Statement
All animal experiments were carried out under the ethical guidance of Tokyo University of Science, and protocols were reviewed and approved by the Tokyo University of Science Animal Care and Use Committee.
Mice
Details in the generation of mice carrying floxed allele of the Meis1 gene (Meis1fl/fl) will be described elsewhere. In brief, the targeting vector containing a 0.9-kb genomic fragment immediately upstream of the loxP-flanked 0.5-kb fragment containing exon 8 of the Meis1 gene and a 6.5-kb DNA fragment immediately downstream of the gene was electroporated into E14 ES cells, and drug-resistant colonies were screened for homologous recombination. Targeted clones were injected into C57BL/6 blastocysts and the resultant chimeric mice were bred to produce progeny having germ line transmission of the mutated allele. By crossing with EIIa-Cre transgenic mice [49], the loxP-flanked neomycin-resistant gene cassette was removed from the allele. The resultant mice were backcrossed at least 8 times onto the C57BL/6 background and then were crossed with K14-CreERT2 transgenic mice on a pure C57BL/6 background [35]. EIIa-Cre and K14-CreERT2 mice on a C57BL/6 background were obtained from The Jackson Laboratory and Dr. Pierre Chambon, respectively. Meis1-EGFP BAC-transgenic reporter mice, generated by the GENSAT BAC transgenic project [36], were obtained from the Mutant Mouse Regional Resource Center and were backcrossed at least 5 times onto the C57BL/6 background. BALB/c nude mice were purchased from CLEA Japan. To induce Meis1 deletion, 3-week-old K14-CreERT2 Meis1fl/fl and K14-CreERT2 Meis1f//+ mice were injected intraperitoneally on 3 consecutive days with 1 mg of tamoxifen (Final concentration 20 mg/ml, Sigma-Aldrich, St Louis, MO) that was prepared following the manufacturer's instructions by completely dissolving Tamoxifen into 200 µl of 100% ethanol at 55°C, adding 1800 µl of warmed sunflower oil, and mixing them well by vortexing. Primer sequences and PCR conditions for genotyping are available upon request.
TEC preparation
Thymic fragments were stirred gently in RPMI-1640 (Wako Pure Chemical Industries) medium for 15 min at 4°C to remove free thymocytes and then transferred to fresh medium containing 1.25 mg/ml collagenase/dispase with 0.01 mg/ml DNase I (Roche Diagnostics, Basel, Switzerland), and incubated for 15 min at 37°C and subjected to vigorous pipetting. The last three steps were repeated twice, discarding the supernatant each time, and incubation was continued until tissue digestion was complete. Released cells were filtered to remove clumps. For enrichment of the TEC populations, an immunomagnetic separation technique was performed using anti-CD45 coated beads and anti-Ter119 coated beads (Miltenyi Biotec) to deplete hematopoietic cells and erythroblasts. Purified TECs were sorted with a FACSArea™II or FACSvantage (BD Bioscience, San Diego, CA).
Flow cytometry analysis
Single cell suspensions from the indicated organ were stained with a combination of FITC-, PE-, -APC, -APC-Cy7 and biotin-conjugated antibodies, followed by streptavidin-PE, -APC, -PE-Cy7, -and PerCP-Cy5.5 (eBioscience, San Diego, CA). The conjugated and unconjugated antibodies specific to the following antigens were purchased from BD Biosciences and eBioscience: TCRσß (H57-597), CD3e (145-2C11), CD4 (L3T4), CD8a (53-6.72), B220 (RA3-6B2), CD62L (MEL-14), CD44 (IM-7), CD45 (104), CD40 (HM40-3), CD80 (16-10A1), CD86 (GL1), MHC II (M5/114.15.2), CD205 (DEC205), TER119, CD16/CD32 (2.4G2). A biotin-labeled anti-EpCAM (G8.8) antibody was kindly provided from Dr. H. Kawamoto. Thymocytes and TECs were blocked by anti-CD16/32 antibody before staining and incubated with the antibodies for 20 min at 4°C. Data were collected on a FACSCalibur or FACSCanto™II flow cytometers (BD Bioscience) and analyzed using FlowJo software (TreeStar, Ashland, OR). FACSArea™II or FACSvantage (BD Bioscience) was used for cell sorting.
Immunofluorescence analysis
Frozen thymus lobes embedded in OCT compound (Sakura Finetek) were cut into 6 µm sections and stained with hematoxylin and eosin. For multicolor analysis, frozen sections were fixed 4% paraformaldehyde or 100% cold acetone. Sections were incubated with primary antibodies diluted in blocking buffer overnight at 4°C. The following primary antibodies were used: rabbit anti-Meis1 (Abcam), rabbit anti-keratin 5 (Covance Research, Berkeley, CA, USA), rabbit anti-keratin 14 (Covance), rabbit anti-EGFP (Molecular Probes, Invitrogen), mouse anti-keratin 8 (PROGEN), mouse anti-CD4 (eBioscience), mouse anti-CD8 (eBioscience), rat anti-CD31 (eBioscience), rat anti-ER-TR7 (Abcam), biotinylated UEA-1 (Vector Laboratories), biotinylated anti-mouse CD11c (eBioscience), goat anti-Aire (D-17; sc-17986, Santa Cruz, CA, USA), biotinylated anti-mouse CD205 (eBioscience) and rabbit anti-p63 (Santa Cruz Biotechnology). Secondary antibodies were Alexa Fluor 488 conjugated anti-rabbit antibody (Molecular Probes), Alexa Fluor 633-conjugated anti-mouse (Molecular Probes), Alexa Fluor 555 conjugated anti-rat (Molecular Probes) or Alexa Fluor 555 conjugated streptavidin (Molecular Probes). Anti-rabbit Keratin5 and Keratin14 antibodies were also directly labeled with Alexa Fluor 555 using a Zenon Antibody Labeling Kit according to the manufacturer's instructions (Molecular Probes). Nuclei were counterstained with Prolong Gold antifade reagent with DAPI (Molecular Probes). The FACS-sorted cells were spun onto glass slides with a cytospin centrifuge, and immunostained with anti-Meis1 and EGFP antibodies. For quantification of staining intensities, average intensities of the Meis1, EGFP and DAPI signals in the cells were measured with MetaMorph software (Molecular Device). The Meis1 and EGFP signals in the cells were normalized to the DAPI signal. Images were analyzed with a BIOREVO BZ-9000 microscope (KEYENCE).
Transplantation
TECs were obtained from the thymus of 4-week-old Meis1-EGFP reporter mice by sorting on the basis of EGFP expression levels. Each of TEC populations (3×103 cells) was mixed with MEFs (1×105 cells) and then suspended in 10 µl of PBS. The cell suspension was then placed onto a piece of the collagen sponge (CS-35; KOKEN), which was squeezed several times to absorb cells into the scaffold. The matrix-embedded cells were maintained on ice and kept moist throughout this procedure and immediately implanted into the renal subcapsular spaces of nude mice. For thymic reaggregation, each of TEC populations (3×103 cells) was reaggregated with total enzyme-digested cells from E14.5 BALB/c thymic lobe (3×105 cells) in vitro on membrane filters (Whatman), cultured for 24 hours, and then transplanted into the renal subcapsular spaces of nude mice. Four weeks after transplantation, the grafts were collected for immunohistochemical and flow cytometric analyses.
Microarray analysis
RNA was isolated using the Qiagen RNeasy micro kit (Qiagen) from TECs with distinct Meis1 expression levels (EGFPhigh, EGFPint and EGFP−) sorted from 4-week-old Meis1-EGFP reporter mice (pools of 6 mice; 2 pools per sample) or TECs from tamoxifen-treated K14-CreER Meis1 fl/fl and sham-treated K14-CreER Meis1 fl/+ mice (pools of 6 mice; 2 pools per genotype). Ten ng of total RNA was amplified using the WT-Ovation™ Pico RNA Amplification system (NuGEN Technologies, Inc.) and labeled using the Genomic Enzymatic Labeling Kit (Aligent Technologies). Labeled probes were hybridized on 4×44 K Whole Mouse Genome Oligo Microarrays (Aligent) and scanned with an Aligent Microarray Scanner. Microarray signals and background information were retrieved using Feature Extraction Software (v.9.5.3.1). All data analyses were performed using the GeneSpring software GX11.0.2 (Aligent). Genes with a raw P-value<0.01 and a fold-change greater than 1.7-fold were defined as differentially expressed. Array data will be available at Gene Expression Omnibus (accession number; GSE30826).
RT-PCR analysis
Total RNA from sorted TECs was prepared and reverse transcribed using SuperScript VILO cDNA Synthesis system (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA). The cDNA was PCR-amplified, electrophoresed, and visualized with ethidium bromide. For quantitative analysis, real-time RT-PCR was performed with EXPRESS SYBR GreenER (Invitrogen) and ABI 7500 Fast thermocycler (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA). Amplified signals were confirmed to be single bands over gel electrophoresis, and normalized to ß-actin. Primer sequences and PCR were listed in Table S4.
Statistical analysis
Statistical significance was calculated with the unpaired two-tailed Student's t-test.
Supporting Information
RT-PCR analysis of the endogenous Meis1 expression in the thymus.
(TIF)
Expression of Meis1 in thymic microenvironment other than TECs.
(TIF)
Flow cytometric analysis of CD4− CD8− double-negative thymocyte differentiation two weeks after Meis1 deletion.
(TIF)
Immunohistochemical analysis of TECs two weeks after Meis1 deletion.
(TIF)
Lymph node-like tissues ectopically developed upon Meis1 loss. Immunohistochemistry (left panels) and representative FACS profiles (right panels) of lymphoid-like remnants in CKO mice and the thymus from control mice 12 weeks post induction of Meis1 deletion. Tissue sections were double stained with the indicated antibody combinations. Scale bars, 100 µm.
(TIF)
Flow cytometric analysis of Meis1 expression in the thymus by using Meis1-EGFP reporter mice.
(TIF)
Thymic stromal signature genes differentially expressed in Meis1high TECs compared with Meis1− TECs.
(XLS)
Thymic stromal signature genes differentially expressed in Meis1low TECs compared with Meis1− TECs.
(XLS)
Thymic stromal signature genes preferentially expressed in Meis1high TECs that were down-regulated upon Meis1 deletion.
(XLS)
List of PCR primer sequences.
(XLS)
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Drs. Daniel Metzger and Pierre Chambon for providing mice, and Dr. Peter D. Burrows for critical reading of the manuscript. This work is dedicated to the memory of Dr. Tomio Tada, the founding Director of the Division of Development and Aging in RIBS.
Funding Statement
This work has been supported by Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (21380183, 23658246, 25111513 to R. G.) from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology of Japan. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
References
- 1. Hollander G, Gill J, Zuklys S, Iwanami N, Liu C, et al. (2006) Cellular and molecular events during early thymus development. Immunological Reviews 209: 28–46. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Nowell CS, Farley AM, Blackburn CC (2007) Thymus organogenesis and development of the thymic stroma. Methods Mol Biol 380: 125–162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Baik S, Jenkinson EJ, Lane PJ, Anderson G, Jenkinson WE (2013) Generation of both cortical and Aire(+) medullary thymic epithelial compartments from CD205(+) progenitors. Eur J Immunol 43: 589–594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Ohigashi I, Zuklys S, Sakata M, Mayer CE, Zhanybekova S, et al. (2013) Aire-expressing thymic medullary epithelial cells originate from beta5t-expressing progenitor cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110: 9885–9890. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Peterson P, Laan M (2013) Bipotency of thymic epithelial progenitors comes in sequence. Eur J Immunol 43: 580–583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Rossi SW, Jenkinson WE, Anderson G, Jenkinson EJ (2006) Clonal analysis reveals a common progenitor for thymic cortical and medullary epithelium. Nature 441: 988–991. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Nehls M, Pfeifer D, Schorpp M, Hedrich H, Boehm T (1994) New member of the winged-helix protein family disrupted in mouse and rat nude mutations. Nature 372: 103–107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Blackburn CC, Augustine CL, Li R, Harvey RP, Malin MA, et al. (1996) The nu gene acts cell-autonomously and is required for differentiation of thymic epithelial progenitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 93: 5742–5746. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Manley NR, Capecchi MR (1998) Hox group 3 paralogs regulate the development and migration of the thymus, thyroid, and parathyroid glands. Developmental Biology 195: 1–15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Wallin J, Eibel H, Neubuser A, Wilting J, Koseki H, et al. (1996) Pax1 is expressed during development of the thymus epithelium and is required for normal T-cell maturation. Development 122: 23–30. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Peters H, Neubuser A, Kratochwil K, Balling R (1998) Pax9-deficient mice lack pharyngeal pouch derivatives and teeth and exhibit craniofacial and limb abnormalities. Genes & Development 12: 2735–2747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Hetzer-Egger C, Schorpp M, Haas-Assenbaum A, Balling R, Peters H, et al. (2002) Thymopoiesis requires Pax9 function in thymic epithelial cells. Eur J Immunol 32: 1175–1181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Xu PX, Zheng W, Laclef C, Maire P, Maas RL, et al. (2002) Eya1 is required for the morphogenesis of mammalian thymus, parathyroid and thyroid. Development 129: 3033–3044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Manley NR, Selleri L, Brendolan A, Gordon J, Cleary ML (2004) Abnormalities of caudal pharyngeal pouch development in Pbx1 knockout mice mimic loss of Hox3 paralogs. Developmental Biology 276: 301–312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Candi E, Rufini A, Terrinoni A, Giamboi-Miraglia A, Lena AM, et al. (2007) DeltaNp63 regulates thymic development through enhanced expression of FgfR2 and Jag2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104: 11999–12004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Senoo M, Pinto F, Crum CP, McKeon F (2007) p63 is essential for the proliferative potential of stem cells in stratified epithelia. Cell 129: 523–536. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Swann JB, Boehm T (2007) Back to the beginning - the quest for thymic epithelial stem cells. European Journal of Immunology 37: 2364–2366. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Anderson G, Jenkinson EJ, Rodewald HR (2009) A roadmap for thymic epithelial cell development. Eur J Immunol 39: 1694–1699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Taub DD, Longo DL (2005) Insights into thymic aging and regeneration. Immunol Rev 205: 72–93. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Heng TS, Goldberg GL, Gray DH, Sutherland JS, Chidgey AP, et al. (2005) Effects of castration on thymocyte development in two different models of thymic involution. J Immunol 175: 2982–2993. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Rossi SW, Jeker LT, Ueno T, Kuse S, Keller MP, et al. (2007) Keratinocyte growth factor (KGF) enhances postnatal T-cell development via enhancements in proliferation and function of thymic epithelial cells. Blood 109: 3803–3811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Bleul CC, Corbeaux T, Reuter A, Fisch P, Monting JS, et al. (2006) Formation of a functional thymus initiated by a postnatal epithelial progenitor cell. Nature 441: 992–996. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Liu B, Liu YF, Du YR, Mardaryev AN, Yang W, et al. (2013) Cbx4 regulates the proliferation of thymic epithelial cells and thymus function. Development 140: 780–788. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Popa I, Zubkova I, Medvedovic M, Romantseva T, Mostowski H, et al. (2007) Regeneration of the adult thymus is preceded by the expansion of K5(+)K8(+) epithelial cell progenitors and by increased expression of Trp63, cMyc and Tcf3 transcription factors in the thymic stroma. International Immunology 19: 1249–1260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Noro B, Culi J, Mckay DJ, Zhang W, Mann RS (2006) Distinct functions of homeodomain-containing and homeodomain-less isoforms encoded by homothorax. Genes & Development 20: 1636–1650. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Mann RS, Affolter M (1998) Hox proteins meet more partners. Current Opinion in Genetics & Development 8: 423–429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Maeda R, Mood K, Jones TL, Aruga J, Buchberg AM, et al. (2001) Xmeis1, a protooncogene involved in specifying neural crest cell fate in Xenopus embryos. Oncogene 20: 1329–1342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Capdevila J, Tsukui T, Esteban CR, Zappavigna V, Belmonte JCI (1999) Control of vertebrate limb outgrowth by the proximal factor Meis2 and distal antagonism of BMPs by Gremlin. Molecular Cell 4: 839–849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Heine P, Dohle E, Bumsted-O'Brien K, Engelkamp D, Schulte D (2008) Evidence for an evolutionary conserved role of homothorax/Meis1/2 during vertebrate retina development. Development 135: 805–811. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Bessa J, Tavares MJ, Santos J, Kikuta H, Laplante M, et al. (2008) meis1 regulates cyclin D1 and c-myc expression, and controls the proliferation of the multipotent cells in the early developing zebrafish eye. Development 135: 799–803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Tucker ES, Lehtinen MK, Maynard T, Zirlinger M, Dulac C, et al. (2010) Proliferative and transcriptional identity of distinct classes of neural precursors in the mammalian olfactory epithelium. Development 137: 2471–2481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Hisa T, Spence SE, Rachel RA, Fujita M, Nakamura T, et al. (2004) Hematopoietic, angiogenic and eye defects in Meis1 mutant animals. Embo J 23: 450–459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Azcoitia V, Aracil M, Martinez AC, Torres M (2005) The homeodomain protein Meis1 is essential for definitive hematopoiesis and vascular patterning in the mouse embryo. Dev Biol 280: 307–320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Anderson MS, Venanzi ES, Klein L, Chen Z, Berzins SP, et al. (2002) Projection of an immunological self shadow within the thymus by the aire protein. Science 298: 1395–1401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Indra AK, Li M, Brocard J, Warot X, Bornert JM, et al. (2000) Targeted somatic mutagenesis in mouse epidermis. Horm Res 54: 296–300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Gong SC, Zheng C, Doughty ML, Losos K, Didkovsky N, et al. (2003) A gene expression atlas of the central nervous system based on bacterial artificial chromosomes. Nature 425: 917–925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Griffith AV, Fallahi M, Nakase H, Gosink M, Young B, et al. (2009) Spatial mapping of thymic stromal microenvironments reveals unique features influencing T lymphoid differentiation. Immunity 31: 999–1009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Camargo FD, Gokhale S, Johnnidis JB, Fu D, Bell GW, et al. (2007) YAP1 increases organ size and expands undifferentiated progenitor cells. Curr Biol 17: 2054–2060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Nam HS, Benezra R (2009) High levels of Id1 expression define B1 type adult neural stem cells. Cell Stem Cell 5: 515–526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Torii M, Matsuzaki F, Osumi N, Kaibuchi K, Nakamura S, et al. (1999) Transcription factors Mash-1 and Prox-1 delineate early steps in differentiation of neural stem cells in the developing central nervous system. Development 126: 443–456. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Janas ML, Varano G, Gudmundsson K, Noda M, Nagasawa T, et al. (2010) Thymic development beyond beta-selection requires phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activation by CXCR4. J Exp Med 207: 247–261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. Shitara S, Hara T, Liang B, Wagatsuma K, Zuklys S, et al. (2013) IL-7 produced by thymic epithelial cells plays a major role in the development of thymocytes and TCRgammadelta+ intraepithelial lymphocytes. J Immunol 190: 6173–6179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43. Suematsu S, Watanabe T (2004) Generation of a synthetic lymphoid tissue-like organoid in mice. Nature Biotechnology 22: 1539–1545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44. Gray D, Abramson J, Benoist C, Mathis D (2007) Proliferative arrest and rapid turnover of thymic epithelial cells expressing Aire. J Exp Med 204: 2521–2528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45. Bonfanti P, Claudinot S, Amici AW, Farley A, Blackburn CC, et al. (2010) Microenvironmental reprogramming of thymic epithelial cells to skin multipotent stem cells. Nature 466: 978–982. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46. Gui JG, Zhu XK, Dohkan JI, Cheng LL, Barnes PF, et al. (2007) The aged thymus shows normal recruitment of lymphohematopoietic progenitors but has defects in thymic epithelial cells. International Immunology 19: 1201–1211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47. Yang SJ, Ahn SJ, Park CS, Holmes KL, Westrup J, et al. (2006) The quantitative assessment of MHC II on thymic epithelium: implications in cortical thymocyte development. International Immunology 18: 729–739. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48. Burnley P, Rahman M, Wang H, Zhang Z, Sun X, et al. (2013) Role of the p63-FoxN1 regulatory axis in thymic epithelial cell homeostasis during aging. Cell Death Dis 4: e932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49. Lakso M, Pichel JG, Gorman JR, Sauer B, Okamoto Y, et al. (1996) Efficient in vivo manipulation of mouse genomic sequences at the zygote stage. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 93: 5860–5865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
RT-PCR analysis of the endogenous Meis1 expression in the thymus.
(TIF)
Expression of Meis1 in thymic microenvironment other than TECs.
(TIF)
Flow cytometric analysis of CD4− CD8− double-negative thymocyte differentiation two weeks after Meis1 deletion.
(TIF)
Immunohistochemical analysis of TECs two weeks after Meis1 deletion.
(TIF)
Lymph node-like tissues ectopically developed upon Meis1 loss. Immunohistochemistry (left panels) and representative FACS profiles (right panels) of lymphoid-like remnants in CKO mice and the thymus from control mice 12 weeks post induction of Meis1 deletion. Tissue sections were double stained with the indicated antibody combinations. Scale bars, 100 µm.
(TIF)
Flow cytometric analysis of Meis1 expression in the thymus by using Meis1-EGFP reporter mice.
(TIF)
Thymic stromal signature genes differentially expressed in Meis1high TECs compared with Meis1− TECs.
(XLS)
Thymic stromal signature genes differentially expressed in Meis1low TECs compared with Meis1− TECs.
(XLS)
Thymic stromal signature genes preferentially expressed in Meis1high TECs that were down-regulated upon Meis1 deletion.
(XLS)
List of PCR primer sequences.
(XLS)