Abstract
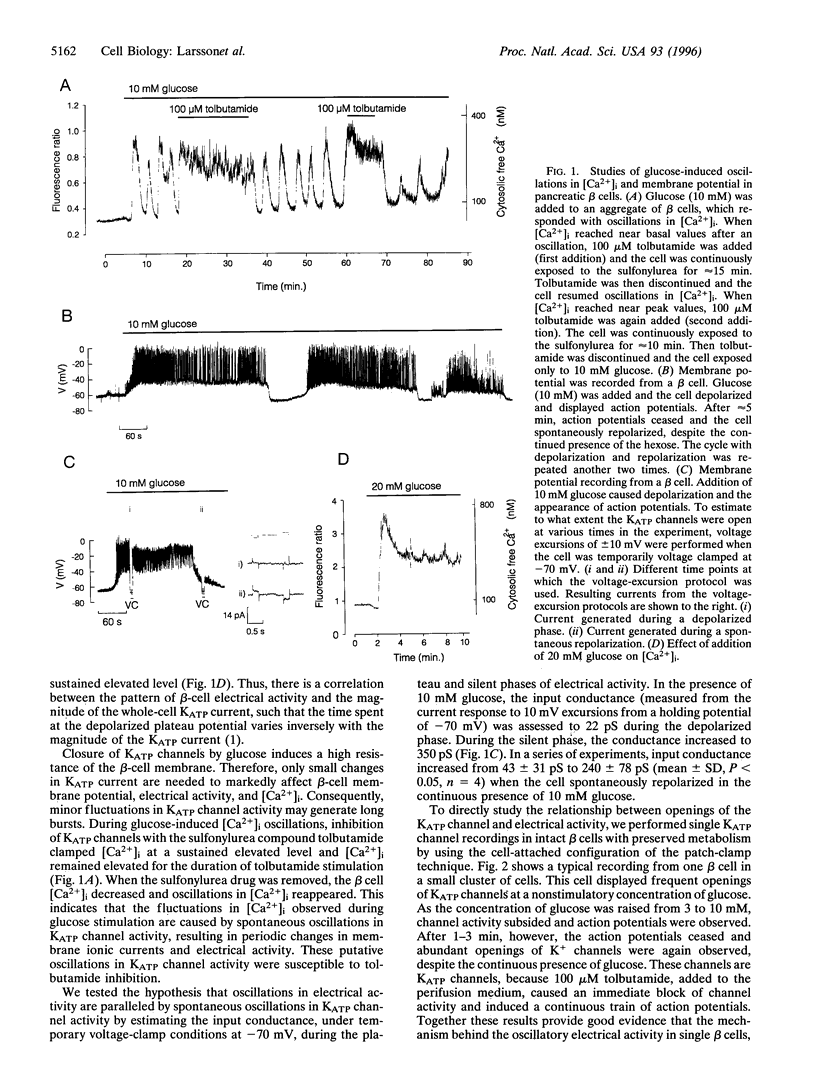
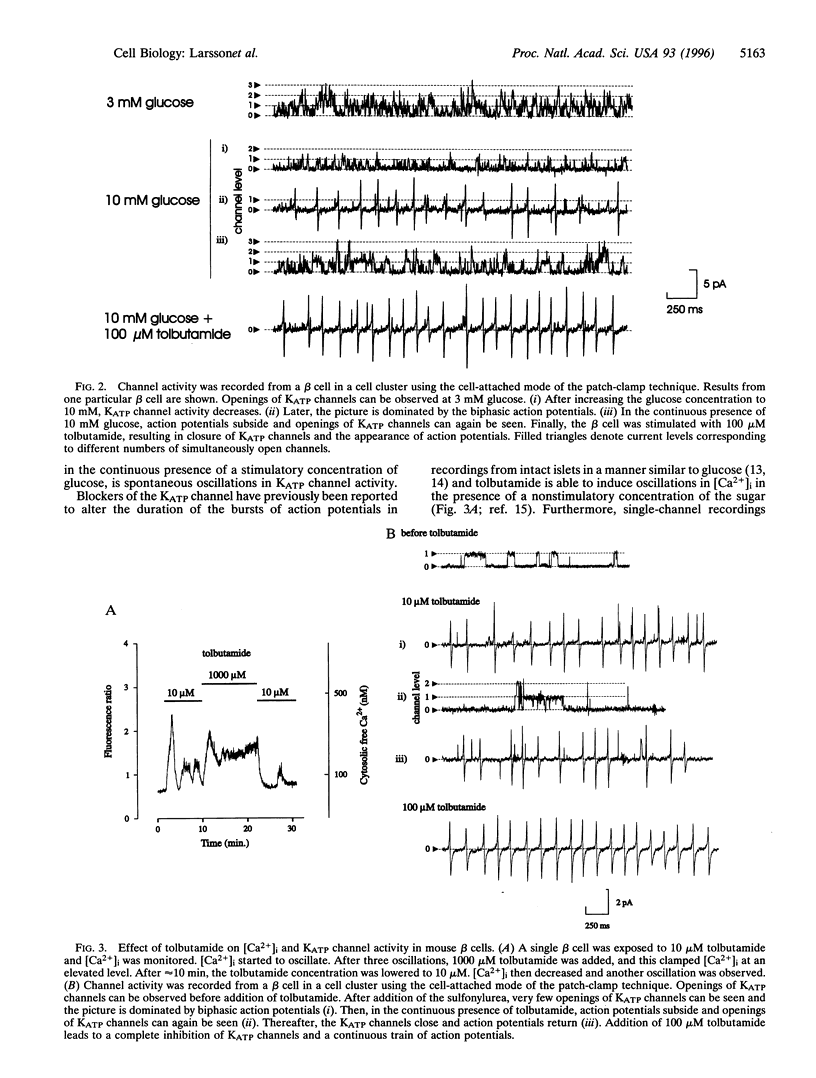
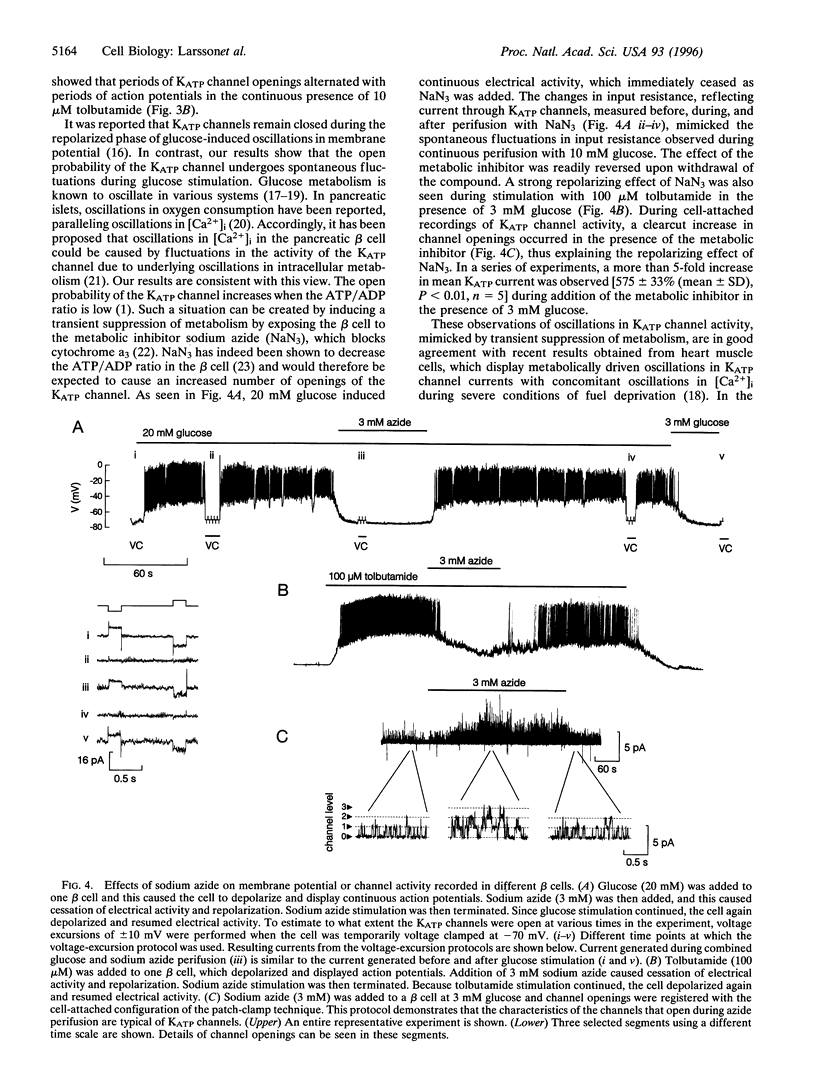
Pancreatic beta cells exhibit oscillations in electrical activity, cytoplasmic free Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+](i)), and insulin release upon glucose stimulation. The mechanism by which these oscillations are generated is not known. Here we demonstrate fluctuations in the activity of the ATP-dependent K+ channels (K(ATP) channels) in single beta cells subject to glucose stimulation or to stimulation with low concentrations of tolbutamide. During stimulation with glucose or low concentrations of tolbutamide, K(ATP) channel activity decreased and action potentials ensued. After 2-3 min, despite continuous stimulation, action potentials subsided and openings of K(ATP) channels could again be observed. Transient suppression of metabolism by azide in glucose-stimulated beta cells caused reversible termination of electrical activity, mimicking the spontaneous changes observed with continuous glucose stimulation. Thus, oscillations in K(ATP) channel activity during continuous glucose stimulation result in oscillations in electrical activity and [Ca2+](i).
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrés V., Schultz V., Tornheim K. Oscillatory synthesis of glucose 1,6-bisphosphate and frequency modulation of glycolytic oscillations in skeletal muscle extracts. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 15;265(35):21441–21447. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arkhammar P., Nilsson T., Rorsman P., Berggren P. O. Inhibition of ATP-regulated K+ channels precedes depolarization-induced increase in cytoplasmic free Ca2+ concentration in pancreatic beta-cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 25;262(12):5448–5454. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashcroft F. M., Ashcroft S. J., Harrison D. E. Properties of single potassium channels modulated by glucose in rat pancreatic beta-cells. J Physiol. 1988 Jun;400:501–527. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashcroft F. M., Rorsman P. Electrophysiology of the pancreatic beta-cell. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1989;54(2):87–143. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(89)90013-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BETZ A., CHANCE B. PHASE RELATIONSHIP OF GLYCOLYTIC INTERMEDIATES IN YEAST CELLS WITH OSCILLATORY METABOLIC CONTROL. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1965 Mar;109:585–594. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(65)90404-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berggren P. O., Larsson O. Ca2+ and pancreatic B-cell function. Biochem Soc Trans. 1994 Feb;22(1):12–18. doi: 10.1042/bst0220012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bokvist K., Ammälä C., Ashcroft F. M., Berggren P. O., Larsson O., Rorsman P. Separate processes mediate nucleotide-induced inhibition and stimulation of the ATP-regulated K(+)-channels in mouse pancreatic beta-cells. Proc Biol Sci. 1991 Feb 22;243(1307):139–144. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1991.0022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook D. L., Ikeuchi M. Tolbutamide as mimic of glucose on beta-cell electrical activity. ATP-sensitive K+ channels as common pathway for both stimuli. Diabetes. 1989 Apr;38(4):416–421. doi: 10.2337/diab.38.4.416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corkey B. E., Tornheim K., Deeney J. T., Glennon M. C., Parker J. C., Matschinsky F. M., Ruderman N. B., Prentki M. Linked oscillations of free Ca2+ and the ATP/ADP ratio in permeabilized RINm5F insulinoma cells supplemented with a glycolyzing cell-free muscle extract. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 25;263(9):4254–4258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies N. W. Modulation of ATP-sensitive K+ channels in skeletal muscle by intracellular protons. Nature. 1990 Jan 25;343(6256):375–377. doi: 10.1038/343375a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean P. M., Matthews E. K. Electrical activity in pancreatic islet cells. Nature. 1968 Jul 27;219(5152):389–390. doi: 10.1038/219389a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Detimary P., Gilon P., Nenquin M., Henquin J. C. Two sites of glucose control of insulin release with distinct dependence on the energy state in pancreatic B-cells. Biochem J. 1994 Feb 1;297(Pt 3):455–461. doi: 10.1042/bj2970455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dryselius S., Lund P. E., Gylfe E., Hellman B. Variations in ATP-sensitive K+ channel activity provide evidence for inherent metabolic oscillations in pancreatic beta-cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994 Nov 30;205(1):880–885. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.2746. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunne M. J., Findlay I., Petersen O. H. Effects of pyridine nucleotides on the gating of ATP-sensitive potassium channels in insulin-secreting cells. J Membr Biol. 1988 Jun;102(3):205–216. doi: 10.1007/BF01925714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilon P., Shepherd R. M., Henquin J. C. Oscillations of secretion driven by oscillations of cytoplasmic Ca2+ as evidences in single pancreatic islets. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 25;268(30):22265–22268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grapengiesser E., Gylfe E., Hellman B. Sulfonylurea mimics the effect of glucose in inducing large amplitude oscillations of cytoplasmic Ca2+ in pancreatic beta-cells. Mol Pharmacol. 1990 Mar;37(3):461–467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellman B. The significance of calcium for glucose stimulation of insulin release. Endocrinology. 1975 Aug;97(2):392–398. doi: 10.1210/endo-97-2-392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henquin J. C. ATP-sensitive K+ channels may control glucose-induced electrical activity in pancreatic B-cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Oct 31;156(2):769–775. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80910-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Islam M. S., Berggren P. O., Larsson O. Sulfhydryl oxidation induces rapid and reversible closure of the ATP-regulated K+ channel in the pancreatic beta-cell. FEBS Lett. 1993 Mar 15;319(1-2):128–132. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)80051-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kindmark H., Köhler M., Efendić S., Rorsman P., Larsson O., Berggren P. O. Protein kinase C activity affects glucose-induced oscillations in cytoplasmic free Ca2+ in the pancreatic B-cell. FEBS Lett. 1992 May 25;303(1):85–90. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80483-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang D. A., Matthews D. R., Burnett M., Turner R. C. Brief, irregular oscillations of basal plasma insulin and glucose concentrations in diabetic man. Diabetes. 1981 May;30(5):435–439. doi: 10.2337/diab.30.5.435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longo E. A., Tornheim K., Deeney J. T., Varnum B. A., Tillotson D., Prentki M., Corkey B. E. Oscillations in cytosolic free Ca2+, oxygen consumption, and insulin secretion in glucose-stimulated rat pancreatic islets. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 15;266(14):9314–9319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misler S., Gee W. M., Gillis K. D., Scharp D. W., Falke L. C. Metabolite-regulated ATP-sensitive K+ channel in human pancreatic islet cells. Diabetes. 1989 Apr;38(4):422–427. doi: 10.2337/diab.38.4.422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson T., Arkhammar P., Hallberg A., Hellman B., Berggren P. O. Characterization of the inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-induced Ca2+ release in pancreatic beta-cells. Biochem J. 1987 Dec 1;248(2):329–336. doi: 10.1042/bj2480329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Rourke B., Ramza B. M., Marban E. Oscillations of membrane current and excitability driven by metabolic oscillations in heart cells. Science. 1994 Aug 12;265(5174):962–966. doi: 10.1126/science.8052856. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santos R. M., Rosario L. M., Nadal A., Garcia-Sancho J., Soria B., Valdeolmillos M. Widespread synchronous [Ca2+]i oscillations due to bursting electrical activity in single pancreatic islets. Pflugers Arch. 1991 May;418(4):417–422. doi: 10.1007/BF00550880. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. A., Ashcroft F. M., Rorsman P. Simultaneous recordings of glucose dependent electrical activity and ATP-regulated K(+)-currents in isolated mouse pancreatic beta-cells. FEBS Lett. 1990 Feb 12;261(1):187–190. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80667-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



