Abstract
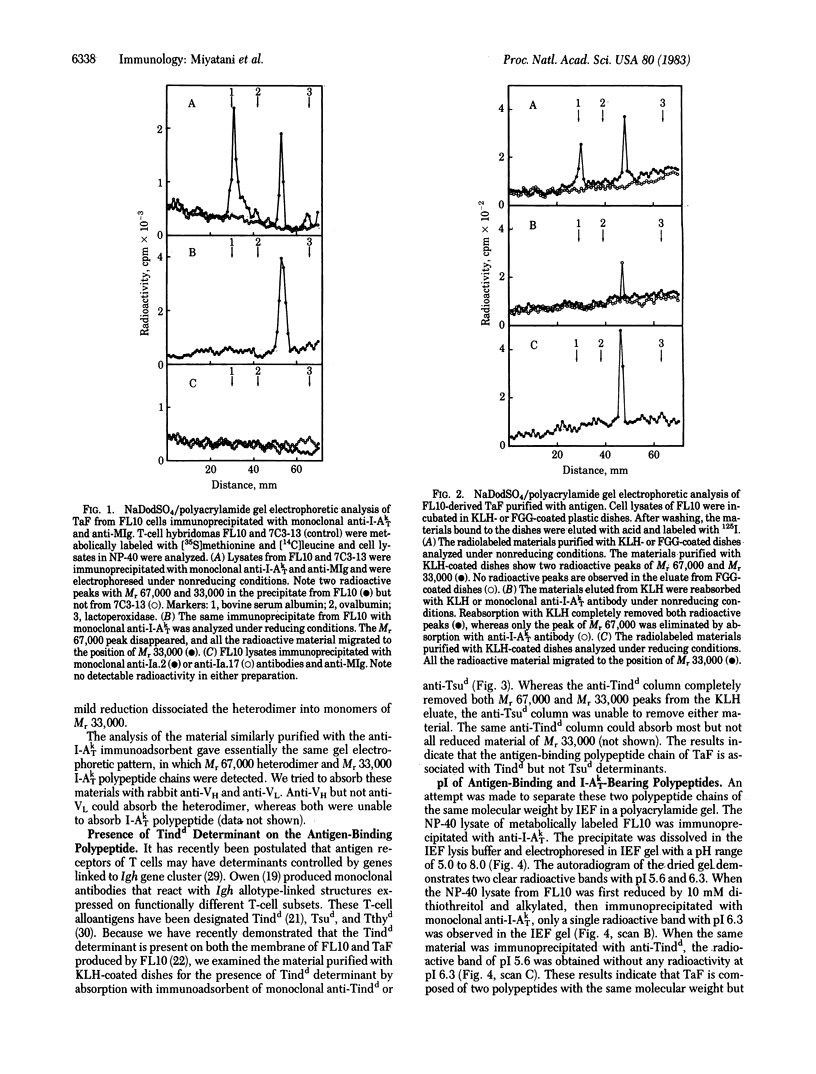
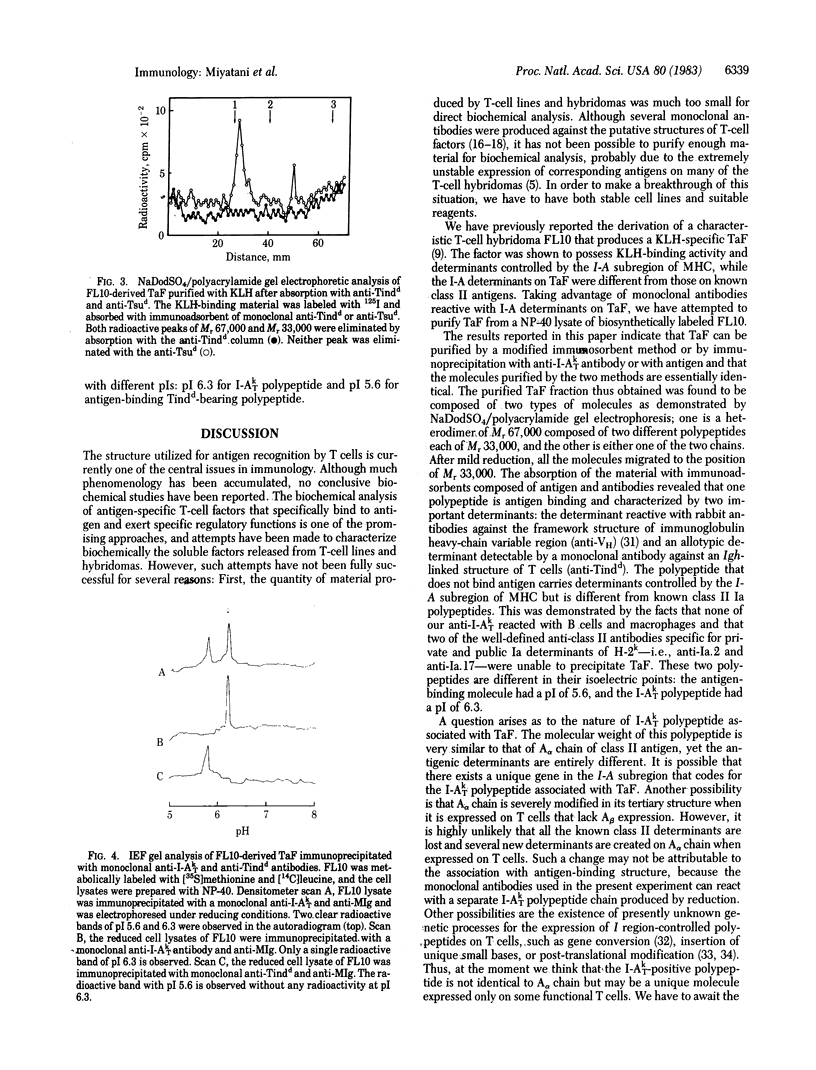
An antigen-specific T-cell factor (TaF) that specifically augments the antibody response was purified and biochemically analyzed by NaDodSO4/polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and isoelectric focusing. Biosynthetically labeled TaF was separated from the Nonidet P-40 extract of T-cell hybridoma FL10, which produces a keyhole limpet hemocyanin-specific TaF, by affinity chromatography either with antigen or with monoclonal anti-I-A antibodies. The material thus obtained was composed of two different types of molecules of molecular weights of 67,000 and 33,000 under nonreducing conditions. After reduction with dithiothreitol, all the molecules migrated to the position of molecular weight 33,000. The absorption studies with immunoadsorbents of antigen and antibodies revealed that the intact TaF is a heterodimer of two discrete polypeptide chains, one carrying a determinant detectable by a monoclonal anti-Tindd directed to an Igh-I -linked allotypic structure of T cells and being associated with the antigen-binding site and the other expressing a unique determinant controlled by the I-A subregion of murine H-2 major histocompatibility complex but being different from known class II polypeptide chains. The antigen-binding polypeptide has an isoelectric point of pH 5.6, and the I-A polypeptide has an isoelectric point of pH 6.3.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auchincloss H., Jr, Ozato K., Sachs D. H. Two distinct murine differentiation antigens determined by genes linked to the Ly-6 locus. J Immunol. 1981 Nov;127(5):1839–1843. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Axén R., Porath J., Ernback S. Chemical coupling of peptides and proteins to polysaccharides by means of cyanogen halides. Nature. 1967 Jun 24;214(5095):1302–1304. doi: 10.1038/2141302a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Neriah Y., Wuilmart C., Lonai P., Givol D. Preparation and characterization of anti-framework antibodies to the heavy chain variable region (VH) of mouse immunoglobulins. Eur J Immunol. 1978 Nov;8(11):797–801. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830081109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalchau R., Fabre J. W. Identification with a monoclonal antibody of a predominantly B lymphocyte-specific determinant of the human leukocyte common antigen. Evidence for structural and possible functional diversity of the human leukocyte common molecule. J Exp Med. 1981 Apr 1;153(4):753–765. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.4.753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eshhar Z., Apte R. N., Löwy I., Ben-Neriah Y., Givol D., Mozes E. T-cell hybridoma bearing heavy chain variable region determinants producing (T,G)-A--L-specific helper factor. Nature. 1980 Jul 17;286(5770):270–272. doi: 10.1038/286270a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fresno M., McVay-Boudreau L., Nabel G., Cantor H. Antigen-specific T lymphocyte clones. II. Purification and biological characterization of an antigen-specific suppressive protein synthesized by cloned T cells. J Exp Med. 1981 May 1;153(5):1260–1274. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.5.1260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiramatsu K., Miyatani S., Kim M., Yamada S., Okumura K., Tada T. Unique T cell Ia antigen expressed on a hybrid cell line producing antigen-specific augmenting T cell factor. J Immunol. 1981 Sep;127(3):1118–1122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiramatsu K., Ochi A., Miyatani S., Segawa A., Tada T. Monoclonal antibodies against unique I-region gene products expressed only on mature functional T cells. Nature. 1982 Apr 15;296(5858):666–668. doi: 10.1038/296666a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanno M., Kobayashi S., Tokuhisa T., Takei I., Shinohara N., Taniguchi M. Monoclonal antibodies that recognize the product controlled by a gene in the I-J subregion of the mouse H-2 complex. J Exp Med. 1981 Nov 1;154(5):1290–1304. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.5.1290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapp J. A., Araneo B. A., Clevinger B. L. Suppression of antibody and T cell proliferative responses to L-glutamic acid60-L-alanine30-L-tyrosine10 by a specific monoclonal T cell factor. J Exp Med. 1980 Jul 1;152(1):235–240. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.1.235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krupen K., Araneo B. A., Brink L., Kapp J. A., Stein S., Wieder K. J., Webb D. R. Purification and characterization of a monoclonal T-cell suppressor factor specific for poly(LGlu60LAla30LTyr10). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):1254–1258. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.1254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lonai P., Bitton S., Savelkoul H. F., Puri J., Hämmerling G. J. Two separate genes regulate self-Ia and carrier recognition in H-2-restricted helper factors secreted by hybridoma cells. J Exp Med. 1981 Dec 1;154(6):1910–1921. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.6.1910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lonai P., Puri J., Hämmerling G. H-2-restricted antigen binding by a hybridoma clone that produces antigen-specific helper factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):549–553. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minami M., Okuda K., Furusawa S., Benacerraf B., Dorf M. E. Analysis of T cell hybridomas. I. Characterization of H-2 and Igh-restricted monoclonal suppressor factors. J Exp Med. 1981 Nov 1;154(5):1390–1402. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.5.1390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima P. B., Ochi A., Owen F. L., Tada T. Presence of IgT-C and I-A subregion-encoded determinants on distinct chains of monoclonal antigen-specific augmenting factor derived from a T cell hybridoma. J Exp Med. 1983 Jun 1;157(6):2110–2120. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.6.2110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okuda K., Minami M., Ju S. T., Dorf M. E. Functional association of idiotypic and I-J determinants on the antigen receptor of suppressor T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4557–4561. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen F. L. Products of the IgT-C region of chromosome 12 are maturational markers for T cells. Sequence of appearance in immunocompetent T cells parallels ontogenetic appearance of Tthyd, Tindd, and Tsud. J Exp Med. 1982 Sep 1;156(3):703–718. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.3.703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen F. L., Riblet R., Taylor B. A. The T suppressor cell alloantigen Tsud maps near immunoglobulin allotype genes and may be an heavy chain constant-region marker on a T cell receptor. J Exp Med. 1981 Apr 1;153(4):801–810. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.4.801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen F. L., Spurll G. M., Panageas E. Tthyd, a new thymocyte alloantigen linked to Igh-1. Implications for a switch mechanism for T cell antigen receptors. J Exp Med. 1982 Jan 1;155(1):52–60. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.1.52. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spurll G. M., Owen F. L. A family of T-cell alloantigens linked to Igh-1. Nature. 1981 Oct 29;293(5835):742–745. doi: 10.1038/293742a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tada T., Okumura K. The role of antigen-specific T cell factors in the immune response. Adv Immunol. 1979;28:1–87. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60799-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tada T., Taniguchi M., David C. S. Properties of the antigen-specific suppressive T-cell factor in the regulation of antibody response of the mouse. IV. Special subregion assignment of the gene(s) that codes for the suppressive T-cell factor in the H-2 histocompatibility complex. J Exp Med. 1976 Sep 1;144(3):713–725. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.3.713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takemori T., Tada T. Properties of antigen-specific suppressive T-cell factor in the regulation of antibody response of the mouse. I. In vivo activity and immunochemical characterization. J Exp Med. 1975 Nov 1;142(5):1241–1253. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.5.1241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi M., Miller J. F. Enrichment of specific suppressor T cells and characterization of their surface markers. J Exp Med. 1977 Nov 1;146(5):1450–1454. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.5.1450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi M., Miller J. F. Specific suppressive factors produced by hybridomas derived from the fusion of enriched suppressor T cells and a T lymphoma cell line. J Exp Med. 1978 Aug 1;148(2):373–382. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.2.373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi M., Saito T., Tada T. Antigen-specific suppressive factor produced by a transplantable I-J bearing T-cell hybridoma. Nature. 1979 Apr 5;278(5704):555–558. doi: 10.1038/278555a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi M., Saito T., Takei I., Tokuhisa T. Presence of interchain disulfide bonds between two gene products that compose the secreted form of an antigen-specific suppressor factor. J Exp Med. 1981 Jun 1;153(6):1672–1677. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.6.1672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi M., Takei I., Tada T. Functional and molecular organisation of an antigen-specific suppressor factor from a T-cell hybridoma. Nature. 1980 Jan 10;283(5743):227–228. doi: 10.1038/283227a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi M., Tokuhisa T., Kanno M., Yaoita Y., Shimizu A., Honjo T. Reconstitution of antigen-specific suppressor activity with translation products of mRNA. Nature. 1982 Jul 8;298(5870):172–174. doi: 10.1038/298172a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokuhisa T., Taniguchi M., Okumura K., Tada T. An antigen-specific I region gene product that augments the antibody response. J Immunol. 1978 Feb;120(2):414–421. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokuhisa T., Taniguchi M. Two distinct allotypic determinants on the antigen-specific suppressor and enhancing T cell factors that are encoded by genes linked to the immunoglobulin heavy chain locus. J Exp Med. 1982 Jan 1;155(1):126–139. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.1.126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waltenbaugh C. Regulation of immune responses by I-J gene products. I. Production and characterization of anti-I-J monoclonal antibodies. J Exp Med. 1981 Nov 1;154(5):1570–1583. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.5.1570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss E. H., Mellor A., Golden L., Fahrner K., Simpson E., Hurst J., Flavell R. A. The structure of a mutant H-2 gene suggests that the generation of polymorphism in H-2 genes may occur by gene conversion-like events. Nature. 1983 Feb 24;301(5902):671–674. doi: 10.1038/301671a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieder K. J., Araneo B. A., Kapp J. A., Webb D. R. Cell-free translation of a biologically active, antigen-specific suppressor T cell factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jun;79(11):3599–3603. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.11.3599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamauchi K., Murphy D., Cantor H., Gershon R. K. Analysis of antigen-specific, Ig-restricted cell-free material made by I-J+ Ly-1 cells (Ly-1 TsiF) that induces Ly-2+ cells to express suppressive activity. Eur J Immunol. 1981 Nov;11(11):905–912. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830111110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




