Abstract
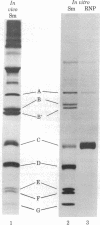
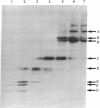
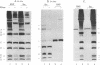
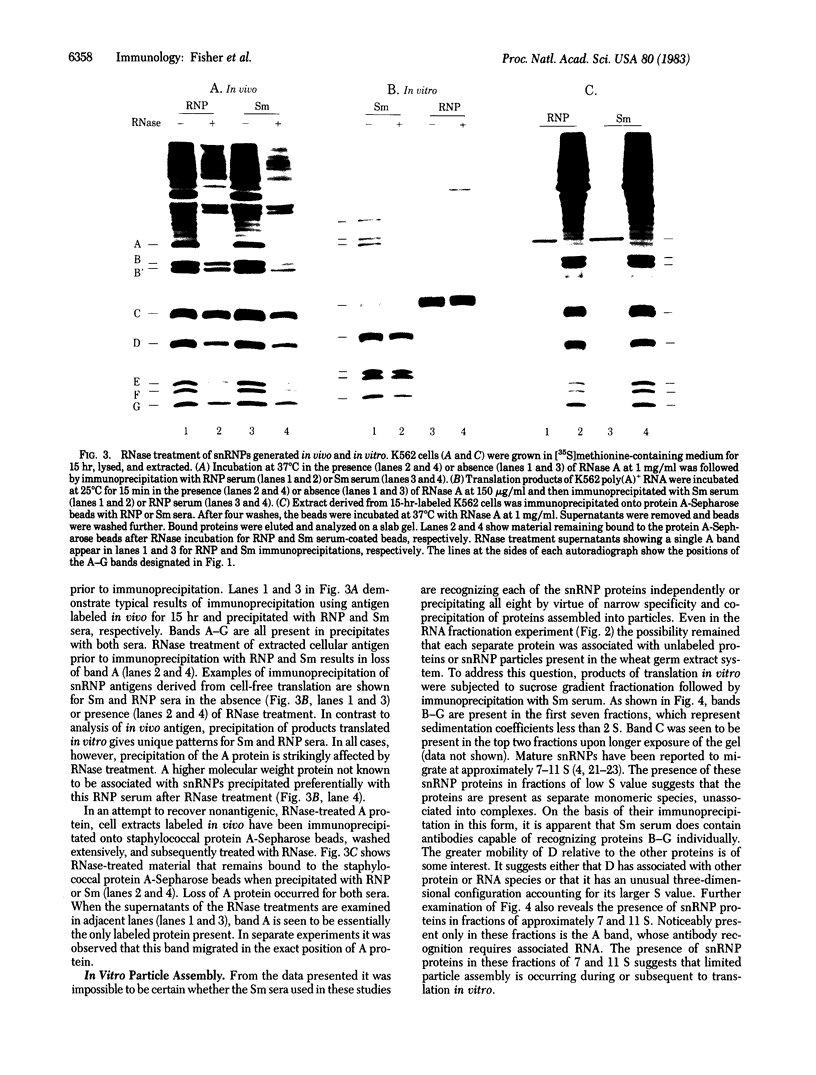
Cell-free translation of human poly(A)+ RNA was carried out to generate and analyze the protein constituents of small nuclear ribonucleoprotein (snRNP) particles. The snRNP proteins were identified by immunoprecipitation with sera from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Size fractionation of mRNA prior to translation revealed that these snBNP proteins are all encoded by separate messages. One of the proteins (the A protein, molecular weight 32,000) was seen to lose antigenicity upon RNase treatment either when extracted from cells or when generated in vitro. RNase treatment of immunoprecipitated snRNPs released the A protein in an electrophoretically pure form. Analysis of snRNPs translated in vitro revealed the presence of unassembled and assembled particles as determined by sucrose density gradient sedimentation. Post-translational assembly of snRNPs involving both RNA-protein binding (as revealed by A protein antigenicity) and associations of other snRNP proteins occurred in the in vitro system employed here. In addition, the presence of unassembled snRNP proteins permitted the determination of the precise antigen peptides recognized by Sm and RNP autoimmune sera. It was observed that Sm sera are capable of recognizing each of the eight snRNP proteins, whereas RNP sera recognize only two of the eight.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calvet J. P., Meyer L. M., Pederson T. Small nuclear RNA U2 is base-paired to heterogeneous nuclear RNA. Science. 1982 Jul 30;217(4558):456–458. doi: 10.1126/science.6178162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciejek E. M., Nordstrom J. L., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. Ribonucleic acid precursors are associated with the chick oviduct nuclear matrix. Biochemistry. 1982 Sep 28;21(20):4945–4953. doi: 10.1021/bi00263a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conner G. E., Nelson D., Wisniewolski R., Lahita R. G., Blobel G., Kunkel H. G. Protein antigens of the RNA-protein complexes detected by anti-SM and anti-RNP antibodies found in serum of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and related disorders. J Exp Med. 1982 Nov 1;156(5):1475–1485. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douvas A. S. Autoantibodies occurring in two different rheumatic diseases react with the same nuclear ribonucleoprotein particle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(17):5401–5405. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.17.5401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher P. A., Berrios M., Blobel G. Isolation and characterization of a proteinaceous subnuclear fraction composed of nuclear matrix, peripheral lamina, and nuclear pore complexes from embryos of Drosophila melanogaster. J Cell Biol. 1982 Mar;92(3):674–686. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.3.674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinterberger M., Pettersson I., Steitz J. A. Isolation of small nuclear ribonucleoproteins containing U1, U2, U4, U5, and U6 RNAs. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 25;258(4):2604–2613. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard E. F. Small nuclear RNA molecules in nuclear ribonucleoprotein complexes from mouse erythroleukemia cells. Biochemistry. 1978 Aug 8;17(16):3228–3236. doi: 10.1021/bi00609a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner M. R., Steitz J. A. Antibodies to small nuclear RNAs complexed with proteins are produced by patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5495–5499. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lizardi P. M., Engelberg A. Rapid isolation of RNA using proteinase K and sodium perchlorate. Anal Biochem. 1979 Sep 15;98(1):116–122. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90714-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matter L., Schopfer K., Wilhelm J. A., Nyffenegger T., Parisot R. F., De Robertis E. M. Molecular characterization of ribonucleoprotein antigens bound by antinuclear antibodies. A diagnostic evaluation. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Nov;25(11):1278–1283. doi: 10.1002/art.1780251102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattioli M., Reichlin M. Characterization of a soluble nuclear ribonucleoprotein antigen reactive with SLE sera. J Immunol. 1971 Nov;107(5):1281–1290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount S. M., Steitz J. A. Sequence of U1 RNA from Drosophila melanogaster: implications for U1 secondary structure and possible involvement in splicing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6351–6368. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers J., Wall R. A mechanism for RNA splicing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):1877–1879. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.1877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp G. C., Irvin W. S., May C. M., Holman H. R., McDuffie F. C., Hess E. V., Schmid F. R. Association of antibodies to ribonucleoprotein and Sm antigens with mixed connective-tissue disease, systematic lupus erythematosus and other rheumatic diseases. N Engl J Med. 1976 Nov 18;295(21):1149–1154. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197611182952101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp G. C., Irvin W. S., Tan E. M., Gould R. G., Holman H. R. Mixed connective tissue disease--an apparently distinct rheumatic disease syndrome associated with a specific antibody to an extractable nuclear antigen (ENA). Am J Med. 1972 Feb;52(2):148–159. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(72)90064-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. M., Kunkel H. G. Characteristics of a soluble nuclear antigen precipitating with sera of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol. 1966 Mar;96(3):464–471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White P. J., Hoch S. O. Definition of the antigenic polypeptides in the Sm and RNP ribonucleoprotein complexes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Sep 16;102(1):365–371. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)91530-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieben E. D., Madore S. J., Pederson T. Protein binding sites are conserved in U1 small nuclear RNA from insects and mammals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1217–1220. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieben E. D., Madore S. J., Pederson T. U1 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein studied by in vitro assembly. J Cell Biol. 1983 Jun;96(6):1751–1755. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.6.1751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeller R., Nyffenegger T., De Robertis E. M. Nucleocytoplasmic distribution of snRNPs and stockpiled snRNA-binding proteins during oogenesis and early development in Xenopus laevis. Cell. 1983 Feb;32(2):425–434. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90462-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]