Abstract
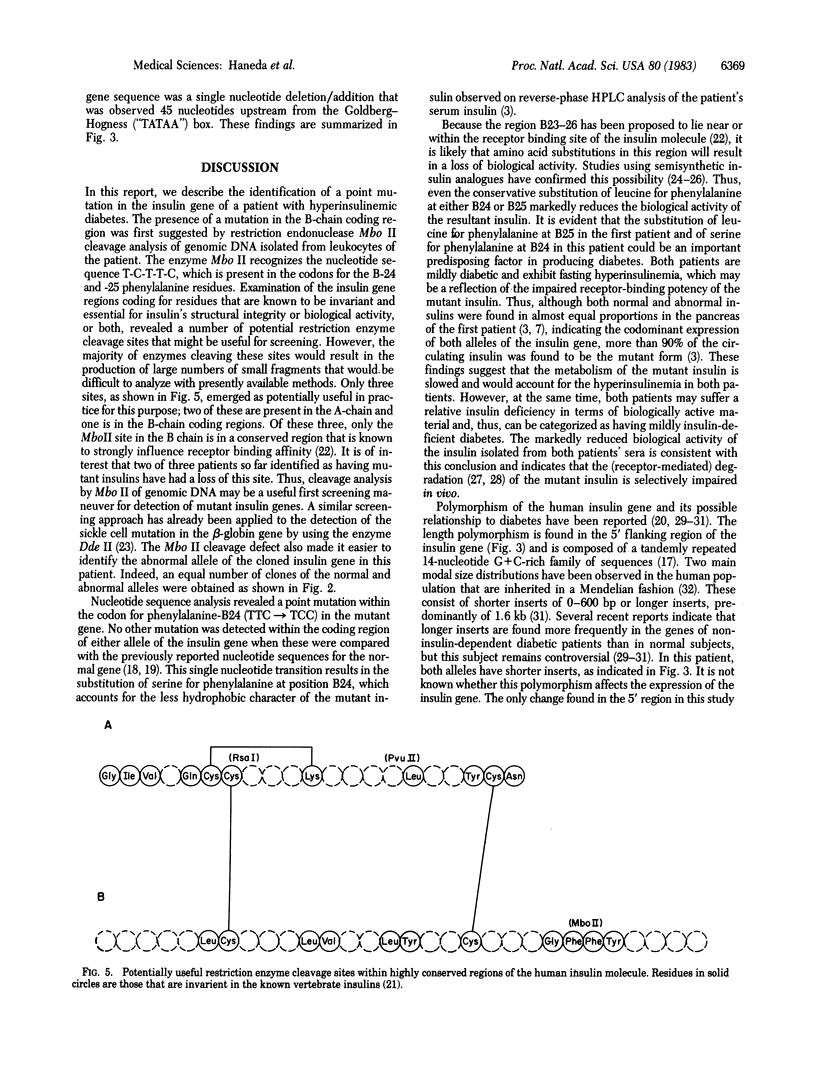
Both alleles of the insulin gene of a patient with mild diabetes [maturity-onset-diabetes-of-the-young (MODY)-type syndrome] associated with hyperinsulinemia have been cloned, and the sequences have been determined. One allele contained a mutation (single nucleotide transition) in the coding sequence for the B chain at position 24 (TTC leads to TCC), resulting in the loss of a restriction enzyme (Mbo II) cleavage site in the gene. This mutation results in the substitution of serine for phenylalanine in a critically important region of the insulin molecule that is intimately involved in receptor binding. Both insulin alleles were of the alpha type and, aside from a single nucleotide deletion in the 5' region of the normal allele, their sequences were identical to those previously determined.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Assoian R. K., Thomas N. E., Kaiser E. T., Tager H. S. [LeuB24]insulin and [AlaB24]insulin: altered structures and cellular processing of B24-substituted insulin analogs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(17):5147–5151. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.17.5147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell G. I., Karam J. H., Rutter W. J. Polymorphic DNA region adjacent to the 5' end of the human insulin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5759–5763. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell G. I., Pictet R. L., Rutter W. J., Cordell B., Tischer E., Goodman H. M. Sequence of the human insulin gene. Nature. 1980 Mar 6;284(5751):26–32. doi: 10.1038/284026a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell G. I., Selby M. J., Rutter W. J. The highly polymorphic region near the human insulin gene is composed of simple tandemly repeating sequences. Nature. 1982 Jan 7;295(5844):31–35. doi: 10.1038/295031a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blattner F. R., Blechl A. E., Denniston-Thompson K., Faber H. E., Richards J. E., Slightom J. L., Tucker P. W., Smithies O. Cloning human fetal gamma globin and mouse alpha-type globin DNA: preparation and screening of shotgun collections. Science. 1978 Dec 22;202(4374):1279–1284. doi: 10.1126/science.725603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fajans S. S., Cloutier M. C., Crowther R. L. The Banting Memorial Lecture 1978. Clinical and etiologic heterogeneity of idiopathic diabetes mellitus. Diabetes. 1978 Nov;27(11):1112–1125. doi: 10.2337/diab.27.11.1112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabbay K. H., Bergenstal R. M., Wolff J., Mako M. E., Rubenstein A. H. Familial hyperproinsulinemia: partial characterization of circulating proinsulin-like material. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2881–2885. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geever R. F., Wilson L. B., Nallaseth F. S., Milner P. F., Bittner M., Wilson J. T. Direct identification of sickle cell anemia by blot hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):5081–5085. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.5081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Given B. D., Mako M. E., Tager H. S., Baldwin D., Markese J., Rubenstein A. H., Olefsky J., Kobayashi M., Kolterman O., Poucher R. Diabetes due to secretion of an abnormal insulin. N Engl J Med. 1980 Jan 17;302(3):129–135. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198001173020301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohn B. In vitro packaging of lambda and cosmid DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:299–309. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68021-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keefer L. M., Piron M. A., De Meyts P., Gattner H. G., Diaconescu C., Saunders D., Brandenburg D. Impaired negative cooperativity of the semisynthetic analogues human [LeuB24]- and [LeuB25]-insulins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Jun 16;100(3):1229–1236. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)91955-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi M., Ohgaku S., Iwasaki M., Maegawa H., Shigeta Y., Inouye K. Characterization of [LeuB-24]- and [LeuB-25]-insulin analogues. Receptor binding and biological activity. Biochem J. 1982 Sep 15;206(3):597–603. doi: 10.1042/bj2060597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwok S. C., Chan S. J., Rubenstein A. H., Poucher R., Steiner D. F. Loss of a restriction endonuclease cleavage site in the gene of a structurally abnormal human insulin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Feb 12;98(3):844–849. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)91188-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwok S. C., Chan S. J., Steiner D. F. Cloning and nucleotide sequence analysis of the dog insulin gene. Coded amino acid sequence of canine preproinsulin predicts an additional C-peptide fragment. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 25;258(4):2357–2363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwok S. C., Steiner D. F., Rubenstein A. H., Tager H. S. Identification of a point mutation in the human insulin gene giving rise to a structurally abnormal insulin (insulin Chicago). Diabetes. 1983 Sep;32(9):872–875. doi: 10.2337/diab.32.9.872. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Hardison R. C., Lacy E., Lauer J., O'Connell C., Quon D., Sim G. K., Efstratiadis A. The isolation of structural genes from libraries of eucaryotic DNA. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):687–701. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90036-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olefsky J. M., Saekow M., Tager H., Rubenstein A. H. Characterization of a mutant human insulin species. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 10;255(13):6098–6105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owerbach D., Nerup J. Restriction fragment length polymorphism of the insulin gene in diabetes mellitus. Diabetes. 1982 Mar;31(3):275–277. doi: 10.2337/diab.31.3.275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owerbach D., Poulsen S., Billesbølle P., Nerup J. DNA insertion sequences near the insulin gene affect glucose regulation. Lancet. 1982 Apr 17;1(8277):880–883. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)92152-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pullen R. A., Lindsay D. G., Wood S. P., Tickle I. J., Blundell T. L., Wollmer A., Krail G., Brandenburg D., Zahn H., Gliemann J. Receptor-binding region of insulin. Nature. 1976 Feb 5;259(5542):369–373. doi: 10.1038/259369a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pyke D. A. Diabetes: the genetic connections. Diabetologia. 1979 Dec;17(6):333–343. doi: 10.1007/BF01236266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins D. C., Blix P. M., Rubenstein A. H., Kanazawa Y., Kosaka K., Tager H. S. A human proinsulin variant at arginine 65. Nature. 1981 Jun 25;291(5817):679–681. doi: 10.1038/291679a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotter J. I., Rimoin D. L. Heterogeneity in diabetes mellitus--update, 1978. Evidence for further genetic heterogeneity within juvenile-onset insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Diabetes. 1978 May;27(5):599–605. doi: 10.2337/diab.27.5.599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotwein P. S., Chirgwin J., Province M., Knowler W. C., Pettitt D. J., Cordell B., Goodman H. M., Permutt M. A. Polymorphism in the 5' flanking region of the human insulin gene: a genetic marker for non-insulin-dependent diabetes. N Engl J Med. 1983 Jan 13;308(2):65–71. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198301133080202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotwein P., Chyn R., Chirgwin J., Cordell B., Goodman H. M., Permut M. A. Polymorphism in the 5'-flanking region of the human insulin gene and its possible relation to type 2 diabetes. Science. 1981 Sep 4;213(4512):1117–1120. doi: 10.1126/science.6267694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoelson S., Haneda M., Blix P., Nanjo A., Sanke T., Inouye K., Steiner D., Rubenstein A., Tager H. Three mutant insulins in man. Nature. 1983 Apr 7;302(5908):540–543. doi: 10.1038/302540a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tager H., Given B., Baldwin D., Mako M., Markese J., Rubenstein A., Olefsky J., Kobayashi M., Kolterman O., Poucher R. A structurally abnormal insulin causing human diabetes. Nature. 1979 Sep 13;281(5727):122–125. doi: 10.1038/281122a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tattersall R. B., Fajans S. S. A difference between the inheritance of classical juvenile-onset and maturity-onset type diabetes of young people. Diabetes. 1975 Jan;24(1):44–53. doi: 10.2337/diab.24.1.44. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terris S., Steiner D. F. Binding and degradation of 125I-insulin by rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1975 Nov 10;250(21):8389–8398. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terris S., Steiner D. F. Retention and degradation of 125I-insulin by perfused livers from diabetic rats. J Clin Invest. 1976 Apr;57(4):885–896. doi: 10.1172/JCI108365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Dull T. J., Gray A., Brosius J., Sures I. Genetic variation in the human insulin gene. Science. 1980 Aug 1;209(4456):612–615. doi: 10.1126/science.6248962. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]