Abstract
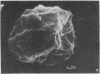
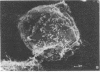
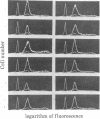
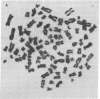
We have selected a thioguanine-resistant lymphoblastoid cell line (LTR228) that forms human-human hybrids with high efficiency. Fusions with peripheral B cells consistently yield one colony per 10(5) cells plated. To produce antitetanus monoclonal antibodies, we withdrew blood from persons who had recently received booster injections of tetanus toxoid. T cells were separated from peripheral mononuclear cells by 2-aminoethylisothiouronium bromide-induced rosette formation, given 1,500 rads (1 rad = 0.01 gray), and cultured in a 1:1 ratio with nonrosetting cells. After 3 days of pokeweed mitogen stimulation, heterokaryons were produced by a plate-fusion technique and cultured in Iscove's Dulbecco's minimal essential medium for 24 hr prior to hybrid selection. Colonies appeared after 10-14 days in hypoxanthine/azaserine supplemented medium. A direct binding enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay with specific tetanus toxoid inhibition identified positive wells. The hybridomas were cloned twice in soft agarose and by limiting dilution. The subcloned hybridomas double every 26 hr (vs. every 16 hr for LTR228) and produce 1-5 micrograms of specific IgG, kappa antibody per 10(6) cells per ml per 24 hr. All subclones (almost 200) continue to secrete antibody after 11 months of continuous culture. Twelve representative subclones have near tetraploid amounts of DNA. From hybridomas grown in 5-liter spinner flasks, milligram quantities of the IgG, kappa antibody were purified by staphylococcus protein A affinity chromatography. Specific antibody from hybridoma cultures protected mice injected with 1,000 times the LD50 of tetanus toxin. Our cell line and associated techniques should permit the production of therapeutically important human monoclonal antibodies.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bengtsson B. O., Nabholz M., Kennett R., Bodmer W. F., Povey S., Swallow D. Human intraspecific somatic cell hybrids: a genetic and karyotypic analysis of crosses between lymphocytes and D98/AH-2. Somatic Cell Genet. 1975 Jan;1(1):41–64. doi: 10.1007/BF01538731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brahe C., Serra A. A simple method for fusing human lymphocytes with rodent cells in monolayer by polyethylene glycol. Somatic Cell Genet. 1981 Jan;7(1):109–115. doi: 10.1007/BF01544752. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler J. L., Lane H. C., Fauci A. S. Delineation of optimal conditions for producing mouse-human heterohybridomas from human peripheral blood B cells of immunized subjects. J Immunol. 1983 Jan;130(1):165–168. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiorazzi N., Wasserman R. L., Kunkel H. G. Use of Epstein-Barr virus-transformed B cell lines for the generation of immunoglobulin-producing human B cell hybridomas. J Exp Med. 1982 Sep 1;156(3):930–935. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.3.930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croce C. M., Linnenbach A., Hall W., Steplewski Z., Koprowski H. Production of human hybridomas secreting antibodies to measles virus. Nature. 1980 Dec 4;288(5790):488–489. doi: 10.1038/288488a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E., Perlmann P. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Quantitative assay of immunoglobulin G. Immunochemistry. 1971 Sep;8(9):871–874. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(71)90454-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gronowicz E., Coutinho A., Melchers F. A plaque assay for all cells secreting Ig of a given type or class. Eur J Immunol. 1976 Aug;6(8):588–590. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830060812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozbor D., Dexter D., Roder J. C. A comparative analysis of the phenotypic characteristics of available fusion partners for the construction of human hybridomas. Hybridoma. 1983;2(1):7–16. doi: 10.1089/hyb.1983.2.7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozbor D., Lagarde A. E., Roder J. C. Human hybridomas constructed with antigen-specific Epstein-Barr virus-transformed cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6651–6655. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozbor D., Roder J. C., Chang T. H., Steplewski Z., Koprowski H. Human anti-tetanus toxoid monoclonal antibody secreted by EBV-transformed human B cells fused with murine myeloma. Hybridoma. 1982;1(3):323–328. doi: 10.1089/hyb.1.1982.1.323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozbor D., Roder J. C. Requirements for the establishment of high-titered human monoclonal antibodies against tetanus toxoid using the Epstein-Barr virus technique. J Immunol. 1981 Oct;127(4):1275–1280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity. Nature. 1975 Aug 7;256(5517):495–497. doi: 10.1038/256495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane H. C., Shelhamer J. H., Mostowski H. S., Fauci A. S. Human monoclonal anti-keyhole limpet hemocyanin antibody-secreting hybridoma produced from peripheral blood B lymphocytes of a keyhole limpet hemocyanin-immune individual. J Exp Med. 1982 Jan 1;155(1):333–338. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.1.333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy J. A., Virolainen M., Defendi V. Human lymphoblastoid lines from lymph node and spleen. Cancer. 1968 Sep;22(3):517–524. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(196809)22:3<517::aid-cncr2820220305>3.0.co;2-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madsen M., Johnsen H. E. A methodological study of E-rosette formation using AET-treated sheep red blood cells. J Immunol Methods. 1979 May 10;27(1):61–74. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(79)90239-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsson L., Kaplan H. S. Human-human hybridomas producing monoclonal antibodies of predefined antigenic specificity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5429–5431. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoenfeld Y., Rauch J., Massicotte H., Datta S. K., André-Schwartz J., Stollar B. D., Schwartz R. S. Polyspecificity of monoclonal lupus autoantibodies produced by human-human hybridomas. N Engl J Med. 1983 Feb 24;308(8):414–420. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198302243080802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sikora K., Alderson T., Phillips J., Watson J. V. Human hybridomas from malignant gliomas. Lancet. 1982 Jan 2;1(8262):11–14. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)92556-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanbridge E. J., Der C. J., Doersen C. J., Nishimi R. Y., Peehl D. M., Weissman B. E., Wilkinson J. E. Human cell hybrids: analysis of transformation and tumorigenicity. Science. 1982 Jan 15;215(4530):252–259. doi: 10.1126/science.7053574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stashenko P., Nadler L. M., Hardy R., Schlossman S. F. Characterization of a human B lymphocyte-specific antigen. J Immunol. 1980 Oct;125(4):1678–1685. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinitz M., Klein G., Koskimies S., Makel O. EB virus-induced B lymphocyte cell lines producing specific antibody. Nature. 1977 Sep 29;269(5627):420–422. doi: 10.1038/269420a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor I. W., Milthorpe B. K. An evaluation of DNA fluorochromes, staining techniques, and analysis for flow cytometry. I. Unperturbed cell populations. J Histochem Cytochem. 1980 Nov;28(11):1224–1232. doi: 10.1177/28.11.6159392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
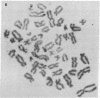
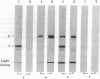
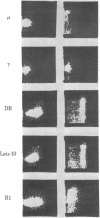
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]