Abstract
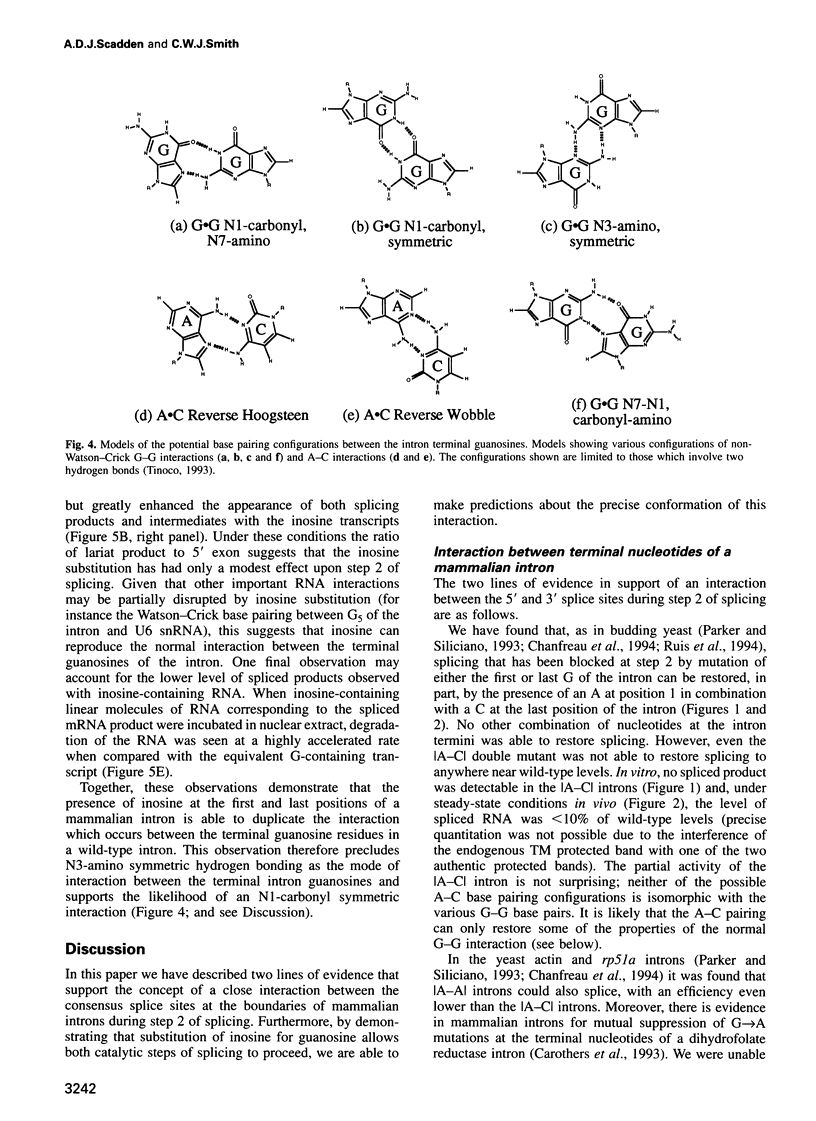
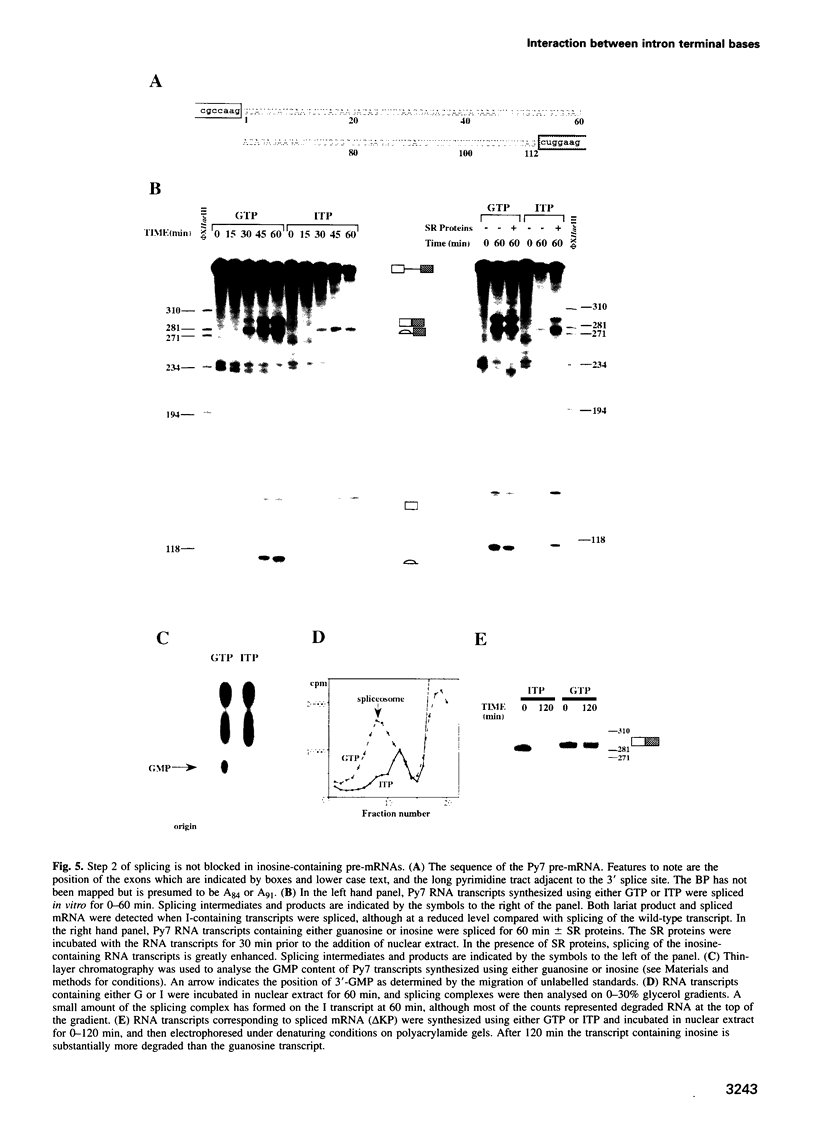
Nuclear pre-mRNA splicing has a fundamentally similar two-step mechanism to that employed by group II self-splicing introns. It is believed that nuclear pre-mRNA splicing involves a network of RNA-RNA interactions which form the catalytic core of the active spliceosome. We show here a non-Watson-Crick interaction between the first and last guanosine residues of a mammalian intron. As in Saccharomyces cerevisiae, substitution of the conserved guanosines at the 5' and 3' splice sites by A and C respectively, specifically suppresses step 2 splicing defects resulting from the individual mutations. No other combination of terminal nucleotides was able to restore splicing. We additionally provide independent evidence for an indirect interaction between other nucleotides of the consensus splice sites during step 2 of splicing. Substitution of the nucleotide in the +3 position of the 5' splice site affects competition between closely spaced AG dinucleotides at the 3' splice site, although the interaction is not via direct differential base pairing. Finally, we show that complete substitution of guanosine residues by inosine in a pre-mRNA has only a modest effect upon step 2 of splicing, although earlier spliceosome assembly steps are impaired. Predictions can thus be made about the precise configuration of the non-Watson-Crick interaction between the terminal residues.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abmayr S. M., Reed R., Maniatis T. Identification of a functional mammalian spliceosome containing unspliced pre-mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7216–7220. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aebi M., Hornig H., Padgett R. A., Reiser J., Weissmann C. Sequence requirements for splicing of higher eukaryotic nuclear pre-mRNA. Cell. 1986 Nov 21;47(4):555–565. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90620-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carothers A. M., Urlaub G., Grunberger D., Chasin L. A. Splicing mutants and their second-site suppressors at the dihydrofolate reductase locus in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Aug;13(8):5085–5098. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.8.5085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chanfreau G., Jacquier A. Interaction of intronic boundaries is required for the second splicing step efficiency of a group II intron. EMBO J. 1993 Dec 15;12(13):5173–5180. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06212.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chanfreau G., Legrain P., Dujon B., Jacquier A. Interaction between the first and last nucleotides of pre-mRNA introns is a determinant of 3' splice site selection in S. cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Jun 11;22(11):1981–1987. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.11.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cortes J. J., Sontheimer E. J., Seiwert S. D., Steitz J. A. Mutations in the conserved loop of human U5 snRNA generate use of novel cryptic 5' splice sites in vivo. EMBO J. 1993 Dec 15;12(13):5181–5189. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06213.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domdey H., Apostol B., Lin R. J., Newman A., Brody E., Abelson J. Lariat structures are in vivo intermediates in yeast pre-mRNA splicing. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):611–621. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90468-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M. R. Biochemical mechanisms of constitutive and regulated pre-mRNA splicing. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1991;7:559–599. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.07.110191.003015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M., Shatkin A. J. Sequences of two 5'-terminal ribosome-protected fragments from reovirus messenger RNAs. J Mol Biol. 1977 May 5;112(1):75–96. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80157-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madhani H. D., Guthrie C. Dynamic RNA-RNA interactions in the spliceosome. Annu Rev Genet. 1994;28:1–26. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.28.120194.000245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore M. J., Sharp P. A. Evidence for two active sites in the spliceosome provided by stereochemistry of pre-mRNA splicing. Nature. 1993 Sep 23;365(6444):364–368. doi: 10.1038/365364a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore M. J., Sharp P. A. Site-specific modification of pre-mRNA: the 2'-hydroxyl groups at the splice sites. Science. 1992 May 15;256(5059):992–997. doi: 10.1126/science.1589782. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullen M. P., Smith C. W., Patton J. G., Nadal-Ginard B. Alpha-tropomyosin mutually exclusive exon selection: competition between branchpoint/polypyrimidine tracts determines default exon choice. Genes Dev. 1991 Apr;5(4):642–655. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.4.642. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman A. J., Lin R. J., Cheng S. C., Abelson J. Molecular consequences of specific intron mutations on yeast mRNA splicing in vivo and in vitro. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):335–344. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80129-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman A. J., Norman C. U5 snRNA interacts with exon sequences at 5' and 3' splice sites. Cell. 1992 Feb 21;68(4):743–754. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90149-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman A. RNA splicing. Activity in the spliceosome. Curr Biol. 1994 May 1;4(5):462–464. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(00)00104-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsen T. W. RNA-RNA interactions in the spliceosome: unraveling the ties that bind. Cell. 1994 Jul 15;78(1):1–4. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90563-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padgett R. A., Podar M., Boulanger S. C., Perlman P. S. The stereochemical course of group II intron self-splicing. Science. 1994 Dec 9;266(5191):1685–1688. doi: 10.1126/science.7527587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker R., Siliciano P. G. Evidence for an essential non-Watson-Crick interaction between the first and last nucleotides of a nuclear pre-mRNA intron. Nature. 1993 Feb 18;361(6413):660–662. doi: 10.1038/361660a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peebles C. L., Perlman P. S., Mecklenburg K. L., Petrillo M. L., Tabor J. H., Jarrell K. A., Cheng H. L. A self-splicing RNA excises an intron lariat. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):213–223. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90755-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reich C. I., VanHoy R. W., Porter G. L., Wise J. A. Mutations at the 3' splice site can be suppressed by compensatory base changes in U1 snRNA in fission yeast. Cell. 1992 Jun 26;69(7):1159–1169. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90637-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruis B. L., Kivens W. J., Siliciano P. G. The interaction between the first and last intron nucleotides in the second step of pre-mRNA splicing is independent of other conserved intron nucleotides. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Dec 11;22(24):5190–5195. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.24.5190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro M. B., Senapathy P. RNA splice junctions of different classes of eukaryotes: sequence statistics and functional implications in gene expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Sep 11;15(17):7155–7174. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.17.7155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. W., Chu T. T., Nadal-Ginard B. Scanning and competition between AGs are involved in 3' splice site selection in mammalian introns. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Aug;13(8):4939–4952. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.8.4939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. W., Nadal-Ginard B. Mutually exclusive splicing of alpha-tropomyosin exons enforced by an unusual lariat branch point location: implications for constitutive splicing. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):749–758. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90678-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. W., Porro E. B., Patton J. G., Nadal-Ginard B. Scanning from an independently specified branch point defines the 3' splice site of mammalian introns. Nature. 1989 Nov 16;342(6247):243–247. doi: 10.1038/342243a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sontheimer E. J., Steitz J. A. The U5 and U6 small nuclear RNAs as active site components of the spliceosome. Science. 1993 Dec 24;262(5142):1989–1996. doi: 10.1126/science.8266094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staknis D., Reed R. SR proteins promote the first specific recognition of Pre-mRNA and are present together with the U1 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particle in a general splicing enhancer complex. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Nov;14(11):7670–7682. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.11.7670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner A. M. mRNA splicing and autocatalytic introns: distant cousins or the products of chemical determinism? Cell. 1993 Jan 29;72(2):161–164. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90654-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieringa B., Meyer F., Reiser J., Weissmann C. Unusual splice sites revealed by mutagenic inactivation of an authentic splice site of the rabbit beta-globin gene. Nature. 1983 Jan 6;301(5895):38–43. doi: 10.1038/301038a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yisraeli J. K., Melton D. A. Synthesis of long, capped transcripts in vitro by SP6 and T7 RNA polymerases. Methods Enzymol. 1989;180:42–50. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(89)80090-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zahler A. M., Lane W. S., Stolk J. A., Roth M. B. SR proteins: a conserved family of pre-mRNA splicing factors. Genes Dev. 1992 May;6(5):837–847. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.5.837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]