Abstract
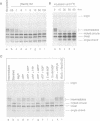
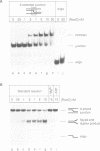
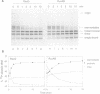
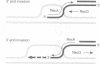
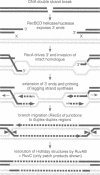
RecG protein is required for normal levels of recombination and DNA repair in Escherichia coli. This 76 kDa polypeptide is a junction-specific DNA helicase that acts post-synaptically to drive branch migration of Holliday junction intermediates made by RecA during the strand exchange stage of recombination. To gain further insight into the role of RecG, we studied its activity on three-strand intermediates formed by RecA between circular single-stranded and linear duplex DNAs. Once RecA is removed, RecG drives branch migration of these intermediates by a junction-targeted activity that depends on hydrolysis of ATP. RuvAB has a similar activity. However, when RecG is added to a RecA strand exchange reaction it severely reduces the accumulation of joint molecule intermediates by driving branch migration of junctions in the reverse direction to that catalysed by RecA strand exchange. In comparison, RuvAB has little effect on the reaction. We discuss how reverse branch migration by RecG, which acts counter of the 5'-->3' polarity of RecA binding and strand exchange, could serve to promote or abort the early stages of recombination, depending on the orientation of the single DNA strand initiating the exchange relative to the adjacent duplex region.
Full text
PDF



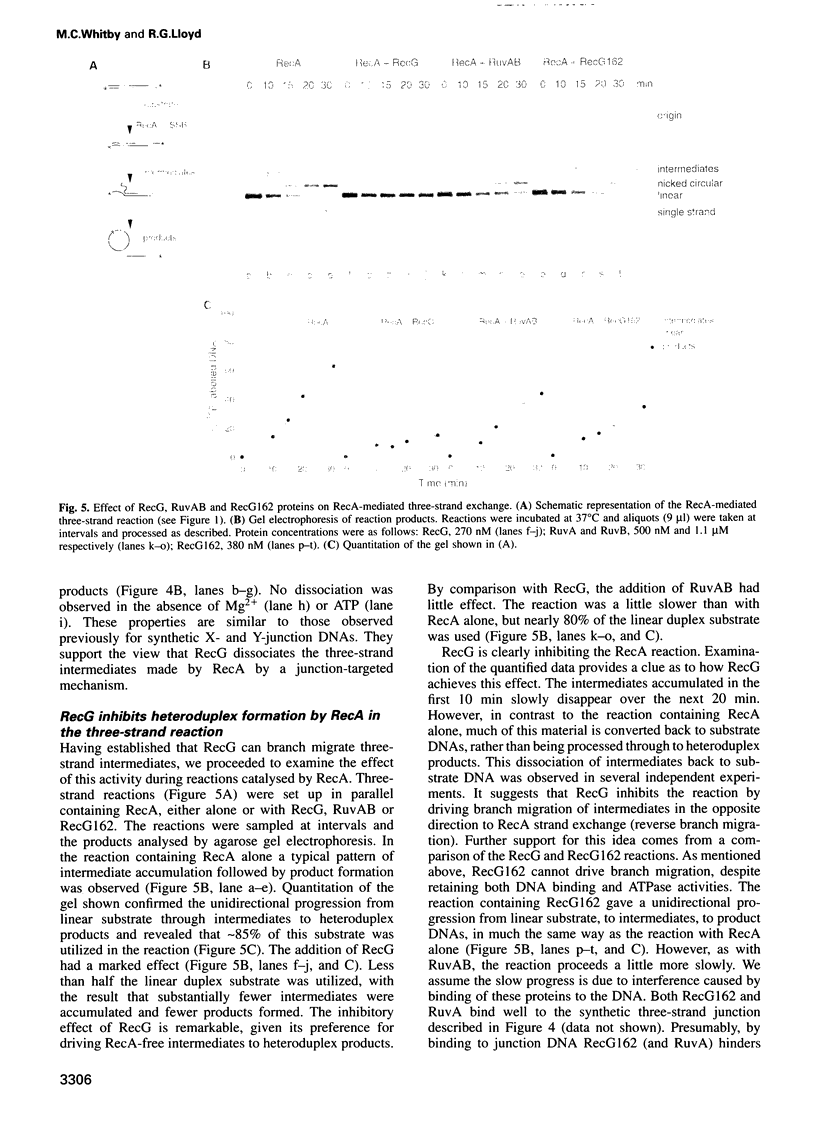
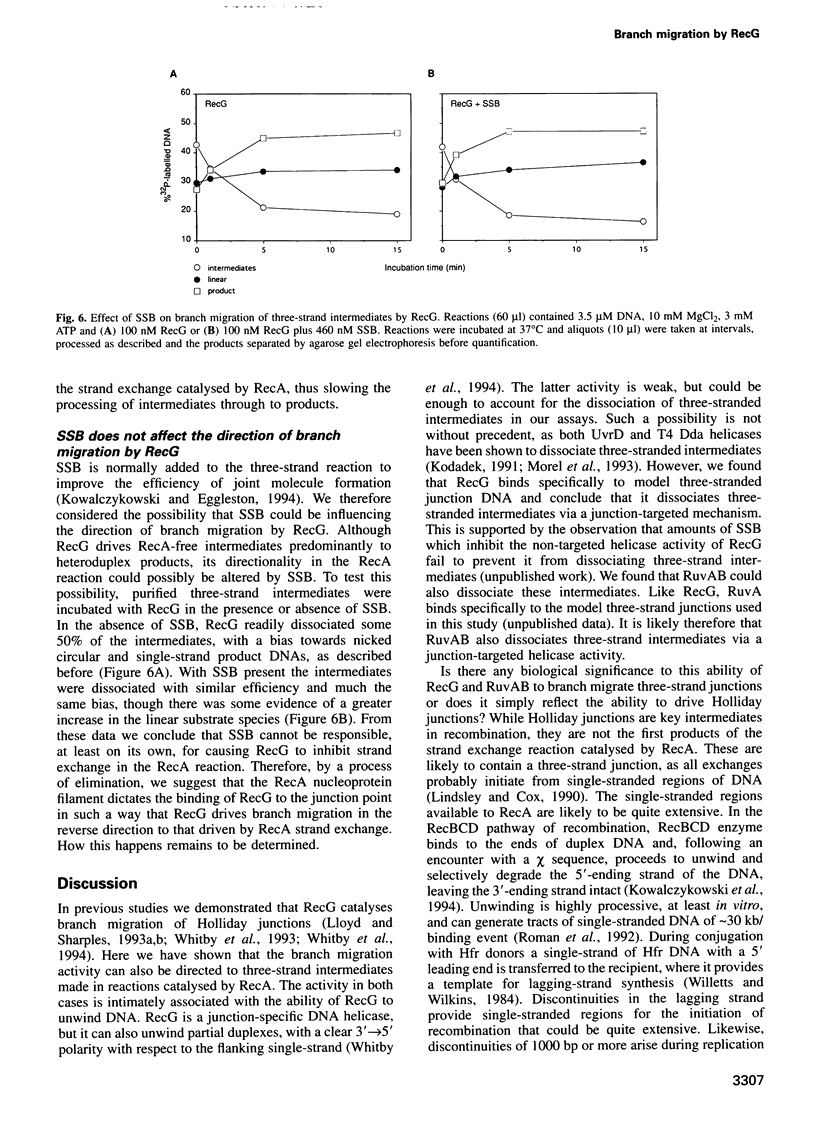

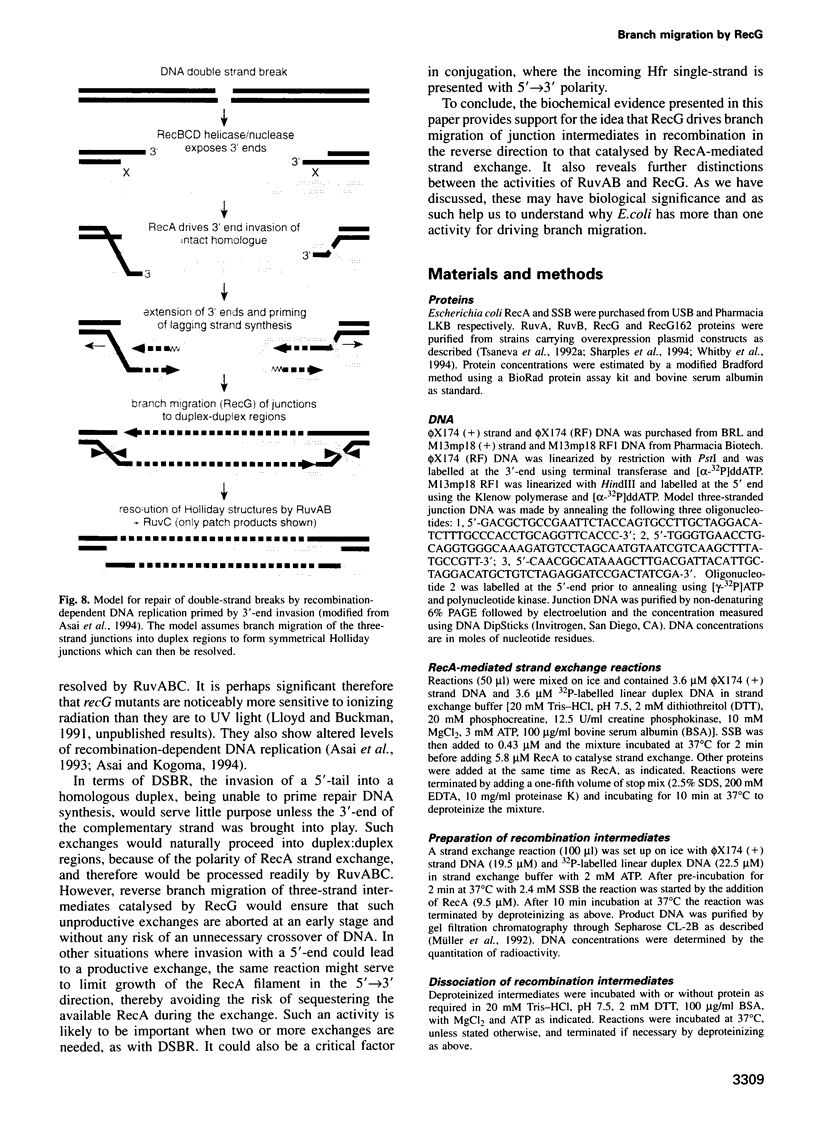

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asai T., Bates D. B., Kogoma T. DNA replication triggered by double-stranded breaks in E. coli: dependence on homologous recombination functions. Cell. 1994 Sep 23;78(6):1051–1061. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90279-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asai T., Kogoma T. Roles of ruvA, ruvC and recG gene functions in normal and DNA damage-inducible replication of the Escherichia coli chromosome. Genetics. 1994 Aug;137(4):895–902. doi: 10.1093/genetics/137.4.895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asai T., Sommer S., Bailone A., Kogoma T. Homologous recombination-dependent initiation of DNA replication from DNA damage-inducible origins in Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1993 Aug;12(8):3287–3295. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05998.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bianchi M., DasGupta C., Radding C. M. Synapsis and the formation of paranemic joints by E. coli RecA protein. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):931–939. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90550-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox M. M., Lehman I. R. recA protein of Escherichia coli promotes branch migration, a kinetically distinct phase of DNA strand exchange. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3433–3437. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard-Flanders P., West S. C., Stasiak A. Role of RecA protein spiral filaments in genetic recombination. Nature. 1984 May 17;309(5965):215–219. doi: 10.1038/309215a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh P., Camerini-Otero C. S., Camerini-Otero R. D. Pairing of homologous DNA sequences by proteins: evidence for three-stranded DNA. Genes Dev. 1990 Nov;4(11):1951–1963. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.11.1951. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iype L. E., Wood E. A., Inman R. B., Cox M. M. RuvA and RuvB proteins facilitate the bypass of heterologous DNA insertions during RecA protein-mediated DNA strand exchange. J Biol Chem. 1994 Oct 7;269(40):24967–24978. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jain S. K., Cox M. M., Inman R. B. On the role of ATP hydrolysis in RecA protein-mediated DNA strand exchange. III. Unidirectional branch migration and extensive hybrid DNA formation. J Biol Chem. 1994 Aug 12;269(32):20653–20661. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn R., Cunningham R. P., DasGupta C., Radding C. M. Polarity of heteroduplex formation promoted by Escherichia coli recA protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):4786–4790. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.4786. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn R., Radding C. M. Separation of the presynaptic and synaptic phases of homologous pairing promoted by recA protein. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 25;259(12):7495–7503. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kodadek T. Inhibition of protein-mediated homologous pairing by a DNA helicase. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 25;266(15):9712–9718. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowalczykowski S. C., Dixon D. A., Eggleston A. K., Lauder S. D., Rehrauer W. M. Biochemistry of homologous recombination in Escherichia coli. Microbiol Rev. 1994 Sep;58(3):401–465. doi: 10.1128/mr.58.3.401-465.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowalczykowski S. C., Eggleston A. K. Homologous pairing and DNA strand-exchange proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1994;63:991–1043. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.63.070194.005015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuzminov A., Schabtach E., Stahl F. W. Chi sites in combination with RecA protein increase the survival of linear DNA in Escherichia coli by inactivating exoV activity of RecBCD nuclease. EMBO J. 1994 Jun 15;13(12):2764–2776. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06570.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd R. G., Benson F. E., Shurvinton C. E. Effect of ruv mutations on recombination and DNA repair in Escherichia coli K12. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;194(1-2):303–309. doi: 10.1007/BF00383532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd R. G. Conjugational recombination in resolvase-deficient ruvC mutants of Escherichia coli K-12 depends on recG. J Bacteriol. 1991 Sep;173(17):5414–5418. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.17.5414-5418.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd R. G., Sharples G. J. Dissociation of synthetic Holliday junctions by E. coli RecG protein. EMBO J. 1993 Jan;12(1):17–22. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05627.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd R. G., Sharples G. J. Processing of recombination intermediates by the RecG and RuvAB proteins of Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Apr 25;21(8):1719–1725. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.8.1719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandal T. N., Mahdi A. A., Sharples G. J., Lloyd R. G. Resolution of Holliday intermediates in recombination and DNA repair: indirect suppression of ruvA, ruvB, and ruvC mutations. J Bacteriol. 1993 Jul;175(14):4325–4334. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.14.4325-4334.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menetski J. P., Bear D. G., Kowalczykowski S. C. Stable DNA heteroduplex formation catalyzed by the Escherichia coli RecA protein in the absence of ATP hydrolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(1):21–25. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.1.21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morel P., Hejna J. A., Ehrlich S. D., Cassuto E. Antipairing and strand transferase activities of E. coli helicase II (UvrD). Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Jul 11;21(14):3205–3209. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.14.3205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller B., Burdett I., West S. C. Unusual stability of recombination intermediates made by Escherichia coli RecA protein. EMBO J. 1992 Jul;11(7):2685–2693. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05334.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa T., Yu X., Shinohara A., Egelman E. H. Similarity of the yeast RAD51 filament to the bacterial RecA filament. Science. 1993 Mar 26;259(5103):1896–1899. doi: 10.1126/science.8456314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otsuji N., Iyehara H., Hideshima Y. Isolation and characterization of an Escherichia coli ruv mutant which forms nonseptate filaments after low doses of ultraviolet light irradiation. J Bacteriol. 1974 Feb;117(2):337–344. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.2.337-344.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons C. A., Tsaneva I., Lloyd R. G., West S. C. Interaction of Escherichia coli RuvA and RuvB proteins with synthetic Holliday junctions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 15;89(12):5452–5456. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.12.5452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons C. A., West S. C. Formation of a RuvAB-Holliday junction complex in vitro. J Mol Biol. 1993 Jul 20;232(2):397–405. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radding C. M. Helical interactions in homologous pairing and strand exchange driven by RecA protein. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 25;266(9):5355–5358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao B. J., Dutreix M., Radding C. M. Stable three-stranded DNA made by RecA protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 15;88(8):2984–2988. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.8.2984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roman L. J., Eggleston A. K., Kowalczykowski S. C. Processivity of the DNA helicase activity of Escherichia coli recBCD enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 25;267(6):4207–4214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryder L., Whitby M. C., Lloyd R. G. Mutation of recF, recJ, recO, recQ, or recR improves Hfr recombination in resolvase-deficient ruv recG strains of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1994 Mar;176(6):1570–1577. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.6.1570-1577.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah R., Bennett R. J., West S. C. Genetic recombination in E. coli: RuvC protein cleaves Holliday junctions at resolution hotspots in vitro. Cell. 1994 Dec 2;79(5):853–864. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90074-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaner S. L., Flory J., Radding C. M. The distribution of Escherichia coli recA protein bound to duplex DNA with single-stranded ends. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 5;262(19):9220–9230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaner S. L., Radding C. M. Translocation of Escherichia coli recA protein from a single-stranded tail to contiguous duplex DNA. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 5;262(19):9211–9219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharples G. J., Whitby M. C., Ryder L., Lloyd R. G. A mutation in helicase motif III of E. coli RecG protein abolishes branch migration of Holliday junctions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Feb 11;22(3):308–313. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.3.308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinohara A., Ogawa H., Matsuda Y., Ushio N., Ikeo K., Ogawa T. Cloning of human, mouse and fission yeast recombination genes homologous to RAD51 and recA. Nat Genet. 1993 Jul;4(3):239–243. doi: 10.1038/ng0793-239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinohara A., Ogawa H., Ogawa T. Rad51 protein involved in repair and recombination in S. cerevisiae is a RecA-like protein. Cell. 1992 May 1;69(3):457–470. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90447-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. R. Conjugational recombination in E. coli: myths and mechanisms. Cell. 1991 Jan 11;64(1):19–27. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90205-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stasiak A., Tsaneva I. R., West S. C., Benson C. J., Yu X., Egelman E. H. The Escherichia coli RuvB branch migration protein forms double hexameric rings around DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Aug 2;91(16):7618–7622. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.16.7618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun H., Treco D., Szostak J. W. Extensive 3'-overhanging, single-stranded DNA associated with the meiosis-specific double-strand breaks at the ARG4 recombination initiation site. Cell. 1991 Mar 22;64(6):1155–1161. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90270-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsaneva I. R., Illing G., Lloyd R. G., West S. C. Purification and properties of the RuvA and RuvB proteins of Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1992 Oct;235(1):1–10. doi: 10.1007/BF00286175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsaneva I. R., Müller B., West S. C. ATP-dependent branch migration of Holliday junctions promoted by the RuvA and RuvB proteins of E. coli. Cell. 1992 Jun 26;69(7):1171–1180. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90638-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsaneva I. R., Müller B., West S. C. RuvA and RuvB proteins of Escherichia coli exhibit DNA helicase activity in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Feb 15;90(4):1315–1319. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.4.1315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsaneva I. R., West S. C. Targeted versus non-targeted DNA helicase activity of the RuvA and RuvB proteins of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1994 Oct 21;269(42):26552–26558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umlauf S. W., Cox M. M., Inman R. B. Triple-helical DNA pairing intermediates formed by recA protein. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 5;265(28):16898–16912. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West S. C., Cassuto E., Howard-Flanders P. Heteroduplex formation by recA protein: polarity of strand exchanges. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6149–6153. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West S. C. Enzymes and molecular mechanisms of genetic recombination. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:603–640. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.003131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West S. C. The processing of recombination intermediates: mechanistic insights from studies of bacterial proteins. Cell. 1994 Jan 14;76(1):9–15. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90168-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitby M. C., Ryder L., Lloyd R. G. Reverse branch migration of Holliday junctions by RecG protein: a new mechanism for resolution of intermediates in recombination and DNA repair. Cell. 1993 Oct 22;75(2):341–350. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)80075-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitby M. C., Vincent S. D., Lloyd R. G. Branch migration of Holliday junctions: identification of RecG protein as a junction specific DNA helicase. EMBO J. 1994 Nov 1;13(21):5220–5228. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06853.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willetts N., Wilkins B. Processing of plasmid DNA during bacterial conjugation. Microbiol Rev. 1984 Mar;48(1):24–41. doi: 10.1128/mr.48.1.24-41.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]