Abstract
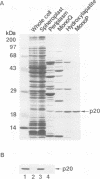
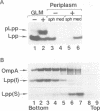
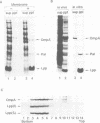
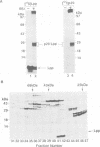
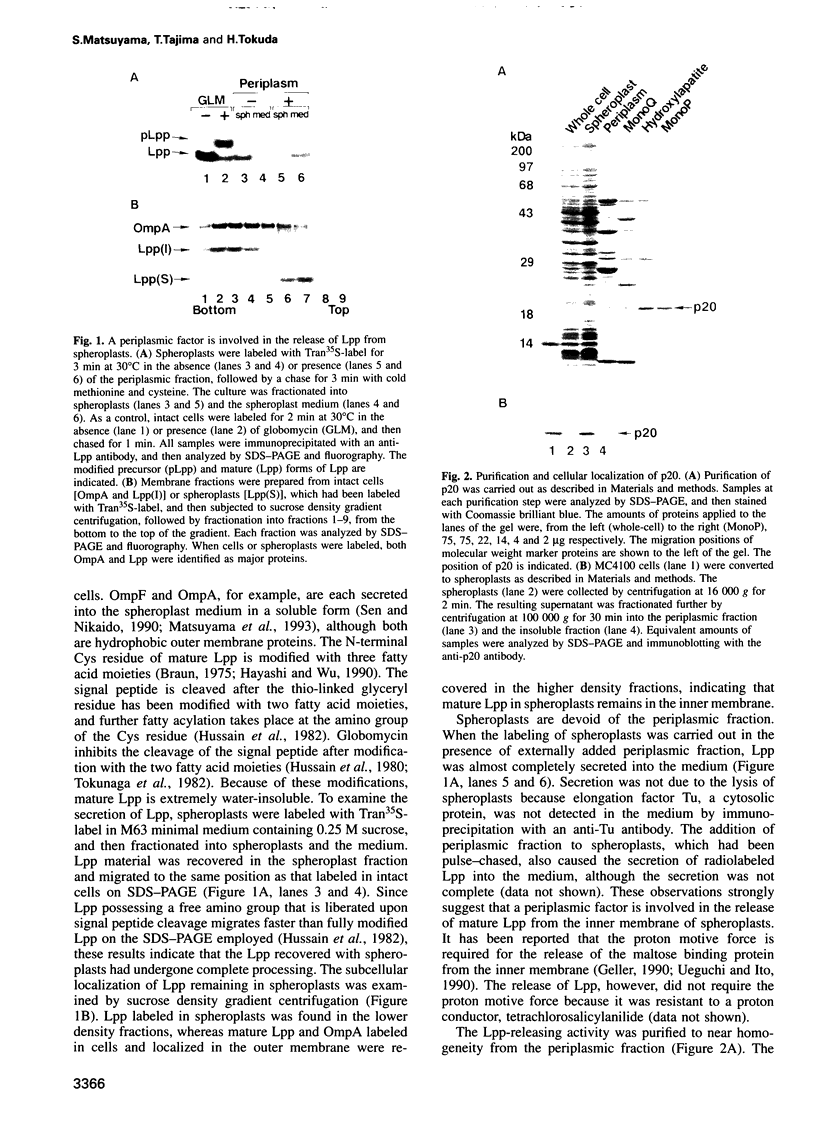
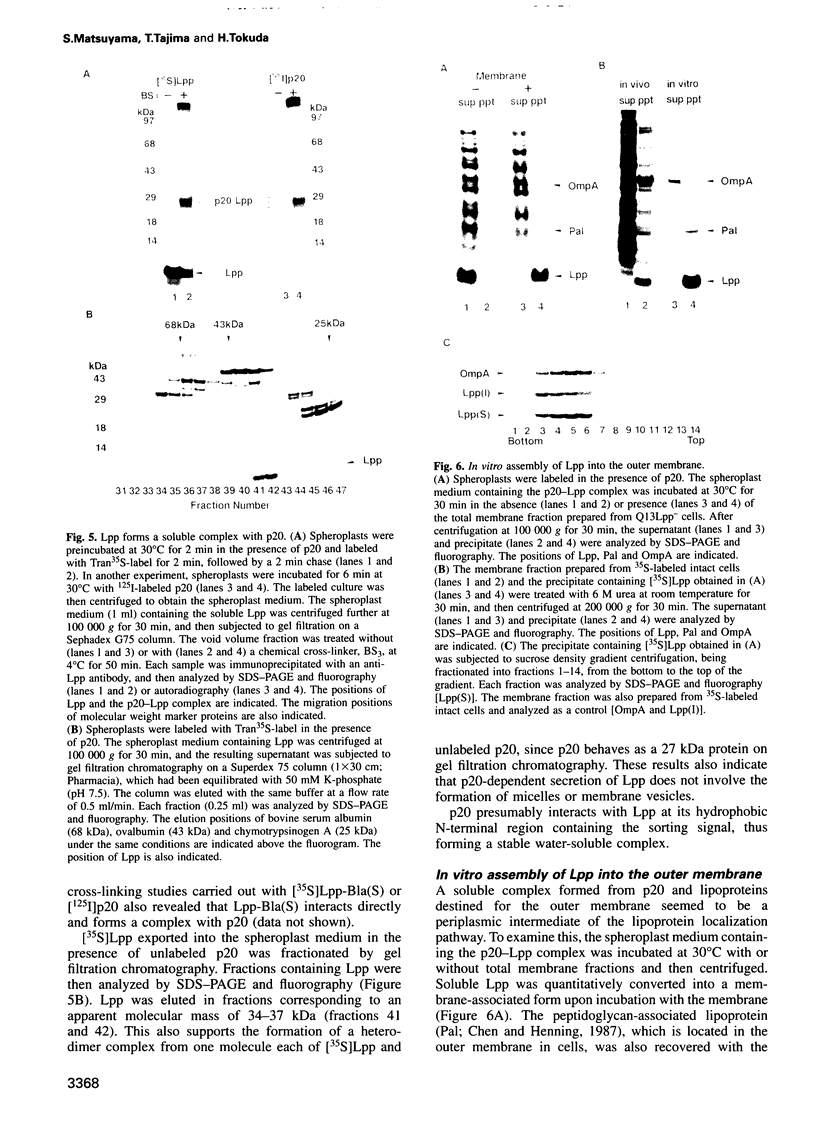
Lipoproteins are localized in the outer or inner membrane of Escherichia coli, depending on the species of amino acid located next to the N-terminal fatty acylated Cys. The major outer membrane lipoprotein (Lpp) expressed in spheroplasts was, however, retained in the inner membrane as a mature form. A novel protein that is essential for the release of Lpp from the inner membrane was discovered in the periplasm and purified. The partial amino acid sequence of this 20 kDa protein (p20) was determined and used to clone a gene for p20. Sequencing of the gene revealed that p20 is synthesized as a precursor with a signal sequence. p20 formed a soluble complex only with outer membrane-directed lipoproteins such as Lpp, indicating that p20 plays a critical role in the sorting of lipoproteins. Lpp released from the inner membrane in the presence of p20 was specifically assembled into the outer membrane in vitro. These results indicate that p20 is a periplasmic carrier protein involved in the translocation of lipoproteins from the inner to the outer membrane.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akimaru J., Matsuyama S., Tokuda H., Mizushima S. Reconstitution of a protein translocation system containing purified SecY, SecE, and SecA from Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 1;88(15):6545–6549. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.15.6545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bieker K. L., Phillips G. J., Silhavy T. J. The sec and prl genes of Escherichia coli. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1990 Jun;22(3):291–310. doi: 10.1007/BF00763169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun V. Covalent lipoprotein from the outer membrane of Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Oct 31;415(3):335–377. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(75)90013-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brundage L., Hendrick J. P., Schiebel E., Driessen A. J., Wickner W. The purified E. coli integral membrane protein SecY/E is sufficient for reconstitution of SecA-dependent precursor protein translocation. Cell. 1990 Aug 24;62(4):649–657. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90111-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabelli R. J., Chen L., Tai P. C., Oliver D. B. SecA protein is required for secretory protein translocation into E. coli membrane vesicles. Cell. 1988 Nov 18;55(4):683–692. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90227-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casadaban M. J. Transposition and fusion of the lac genes to selected promoters in Escherichia coli using bacteriophage lambda and Mu. J Mol Biol. 1976 Jul 5;104(3):541–555. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90119-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen R., Henning U. Nucleotide sequence of the gene for the peptidoglycan-associated lipoprotein of Escherichia coli K12. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Feb 16;163(1):73–77. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb10738.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi D. S., Yamada H., Mizuno T., Mizushima S. Trimeric structure and localization of the major lipoprotein in the cell surface of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 5;261(19):8953–8957. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emr S. D., Hanley-Way S., Silhavy T. J. Suppressor mutations that restore export of a protein with a defective signal sequence. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):79–88. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90272-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardel C., Johnson K., Jacq A., Beckwith J. The secD locus of E.coli codes for two membrane proteins required for protein export. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3209–3216. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07519.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geller B. L. Electrochemical potential releases a membrane-bound secretion intermediate of maltose-binding protein in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1990 Sep;172(9):4870–4876. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.9.4870-4876.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghrayeb J., Inouye M. Nine amino acid residues at the NH2-terminal of lipoprotein are sufficient for its modification, processing, and localization in the outer membrane of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 10;259(1):463–467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glomset J. A., Gelb M. H., Farnsworth C. C. Prenyl proteins in eukaryotic cells: a new type of membrane anchor. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Apr;15(4):139–142. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90213-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halegoua S., Inouye M. Translocation and assembly of outer membrance proteins of Escherichia coli. Selective accumulation of precursors and novel assembly intermediates caused by phenethyl alcohol. J Mol Biol. 1979 May 5;130(1):39–61. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90551-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock J. F., Paterson H., Marshall C. J. A polybasic domain or palmitoylation is required in addition to the CAAX motif to localize p21ras to the plasma membrane. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):133–139. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90294-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi S., Wu H. C. Accumulation of prolipoprotein in Escherichia coli mutants defective in protein secretion. J Bacteriol. 1985 Mar;161(3):949–954. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.3.949-954.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi S., Wu H. C. Lipoproteins in bacteria. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1990 Jun;22(3):451–471. doi: 10.1007/BF00763177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hussain M., Ichihara S., Mizushima S. Accumulation of glyceride-containing precursor of the outer membrane lipoprotein in the cytoplasmic membrane of Escherichia coli treated with globomycin. J Biol Chem. 1980 Apr 25;255(8):3707–3712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hussain M., Ichihara S., Mizushima S. Mechanism of signal peptide cleavage in the biosynthesis of the major lipoprotein of the Escherichia coli outer membrane. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 10;257(9):5177–5182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Innis M. A., Tokunaga M., Williams M. E., Loranger J. M., Chang S. Y., Chang S., Wu H. C. Nucleotide sequence of the Escherichia coli prolipoprotein signal peptidase (lsp) gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(12):3708–3712. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.12.3708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito K., Wittekind M., Nomura M., Shiba K., Yura T., Miura A., Nashimoto H. A temperature-sensitive mutant of E. coli exhibiting slow processing of exported proteins. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):789–797. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90065-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson J. H., Cochrane C. G., Bourne J. R., Solski P. A., Buss J. E., Der C. J. Farnesol modification of Kirsten-ras exon 4B protein is essential for transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(8):3042–3046. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.8.3042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawasaki H., Matsuyama S., Sasaki S., Akita M., Mizushima S. SecA protein is directly involved in protein secretion in Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett. 1989 Jan 2;242(2):431–434. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80516-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lill R., Cunningham K., Brundage L. A., Ito K., Oliver D., Wickner W. SecA protein hydrolyzes ATP and is an essential component of the protein translocation ATPase of Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):961–966. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03458.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuyama S., Fujita Y., Mizushima S. SecD is involved in the release of translocated secretory proteins from the cytoplasmic membrane of Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1993 Jan;12(1):265–270. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05652.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuyama S., Fujita Y., Sagara K., Mizushima S. Overproduction, purification and characterization of SecD and SecF, integral membrane components of the protein translocation machinery of Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Jul 13;1122(1):77–84. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(92)90130-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizushima S. Post-translational modification and processing of outer membrane prolipoproteins in Escherichia coli. Mol Cell Biochem. 1984;60(1):5–15. doi: 10.1007/BF00226297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishiyama K., Hanada M., Tokuda H. Disruption of the gene encoding p12 (SecG) reveals the direct involvement and important function of SecG in the protein translocation of Escherichia coli at low temperature. EMBO J. 1994 Jul 15;13(14):3272–3277. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06628.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishiyama K., Mizushima S., Tokuda H. A novel membrane protein involved in protein translocation across the cytoplasmic membrane of Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1993 Sep;12(9):3409–3415. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06015.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver D. B., Beckwith J. E. coli mutant pleiotropically defective in the export of secreted proteins. Cell. 1981 Sep;25(3):765–772. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90184-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn M. J., Munson R. Separation of the inner (cytoplasmic) and outer membranes of Gram-negative bacteria. Methods Enzymol. 1974;31:642–653. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)31070-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pogliano J. A., Beckwith J. SecD and SecF facilitate protein export in Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1994 Feb 1;13(3):554–561. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06293.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pryer N. K., Wuestehube L. J., Schekman R. Vesicle-mediated protein sorting. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:471–516. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.002351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugsley A. P. The complete general secretory pathway in gram-negative bacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1993 Mar;57(1):50–108. doi: 10.1128/mr.57.1.50-108.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiner A. M. Isolation and mapping of polynucleotide phosphorylase mutants of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1969 Mar;97(3):1431–1436. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.3.1431-1436.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riggs P. D., Derman A. I., Beckwith J. A mutation affecting the regulation of a secA-lacZ fusion defines a new sec gene. Genetics. 1988 Apr;118(4):571–579. doi: 10.1093/genetics/118.4.571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schatz P. J., Beckwith J. Genetic analysis of protein export in Escherichia coli. Annu Rev Genet. 1990;24:215–248. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.24.120190.001243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schatz P. J., Riggs P. D., Jacq A., Fath M. J., Beckwith J. The secE gene encodes an integral membrane protein required for protein export in Escherichia coli. Genes Dev. 1989 Jul;3(7):1035–1044. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.7.1035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen K., Nikaido H. In vitro trimerization of OmpF porin secreted by spheroplasts of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(2):743–747. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.2.743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugai M., Wu H. C. Export of the outer membrane lipoprotein is defective in secD, secE, and secF mutants of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1992 Apr;174(8):2511–2516. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.8.2511-2516.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokuda H., Akimaru J., Matsuyama S., Nishiyama K., Mizushima S. Purification of SecE and reconstitution of SecE-dependent protein translocation activity. FEBS Lett. 1991 Feb 25;279(2):233–236. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80156-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokuda H. Biochemical characterization of the presecretory protein translocation machinery of Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett. 1994 Jun 6;346(1):65–68. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)00317-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokunaga M., Tokunaga H., Wu H. C. Post-translational modification and processing of Escherichia coli prolipoprotein in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(7):2255–2259. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.7.2255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueguchi C., Ito K. Escherichia coli sec mutants accumulate a processed immature form of maltose-binding protein (MBP), a late-phase intermediate in MBP export. J Bacteriol. 1990 Oct;172(10):5643–5649. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.10.5643-5649.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe T., Hayashi S., Wu H. C. Synthesis and export of the outer membrane lipoprotein in Escherichia coli mutants defective in generalized protein export. J Bacteriol. 1988 Sep;170(9):4001–4007. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.9.4001-4007.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickner W., Driessen A. J., Hartl F. U. The enzymology of protein translocation across the Escherichia coli plasma membrane. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:101–124. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.000533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi K., Yu F., Inouye M. A single amino acid determinant of the membrane localization of lipoproteins in E. coli. Cell. 1988 May 6;53(3):423–432. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90162-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamane K., Ichihara S., Mizushima S. In vitro translocation of protein across Escherichia coli membrane vesicles requires both the proton motive force and ATP. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 15;262(5):2358–2362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu F., Yamada H., Daishima K., Mizushima S. Nucleotide sequence of the lspA gene, the structural gene for lipoprotein signal peptidase of Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett. 1984 Jul 23;173(1):264–268. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)81060-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]