Abstract
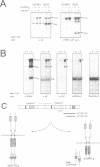
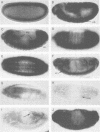
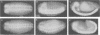
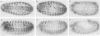
We report the cloning and primary structure of the Drosophila insulin receptor gene (inr), functional expression of the predicted polypeptide, and the isolation of mutations in the inr locus. Our data indicate that the structure and processing of the Drosophila insulin proreceptor are somewhat different from those of the mammalian insulin and IGF 1 receptor precursors. The INR proreceptor (M(r) 280 kDa) is processed proteolytically to generate an insulin-binding alpha subunit (M(r) 120 kDa) and a beta subunit (M(r) 170 kDa) with protein tyrosine kinase domain. The INR beta 170 subunit contains a novel domain at the carboxyterminal side of the tyrosine kinase, in the form of a 60 kDa extension which contains multiple potential tyrosine autophosphorylation sites. This 60 kDa C-terminal domain undergoes cell-specific proteolytic cleavage which leads to the generation of a total of four polypeptides (alpha 120, beta 170, beta 90 and a free 60 kDa C-terminus) from the inr gene. These subunits assemble into mature INR receptors with the structures alpha 2(beta 170)2 or alpha 2(beta 90)2. Mammalian insulin stimulates tyrosine phosphorylation of both types of beta subunits, which in turn allows the beta 170, but not the beta 90 subunit, to bind directly to p85 SH2 domains of PI-3 kinase. It is likely that the two different isoforms of INR have different signaling potentials. Finally, we show that loss of function mutations in the inr gene, induced by either a P-element insertion occurring within the predicted ORF, or by ethylmethane sulfonate treatment, render pleiotropic recessive phenotypes that lead to embryonic lethality. The activity of inr appears to be required in the embryonic epidermis and nervous system among others, since development of the cuticle, as well as the peripheral and central nervous systems are affected by inr mutations.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersen A. S., Kjeldsen T., Wiberg F. C., Vissing H., Schäffer L., Rasmussen J. S., De Meyts P., Møller N. P. Identification of determinants that confer ligand specificity on the insulin receptor. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 5;267(19):13681–13686. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azpiazu N., Frasch M. tinman and bagpipe: two homeo box genes that determine cell fates in the dorsal mesoderm of Drosophila. Genes Dev. 1993 Jul;7(7B):1325–1340. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.7b.1325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Backer J. M., Shoelson S. E., Weiss M. A., Hua Q. X., Cheatham R. B., Haring E., Cahill D. C., White M. F. The insulin receptor juxtamembrane region contains two independent tyrosine/beta-turn internalization signals. J Cell Biol. 1992 Aug;118(4):831–839. doi: 10.1083/jcb.118.4.831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batzer A. G., Rotin D., Ureña J. M., Skolnik E. Y., Schlessinger J. Hierarchy of binding sites for Grb2 and Shc on the epidermal growth factor receptor. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Aug;14(8):5192–5201. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.8.5192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benito M., Porras A., Nebreda A. R., Santos E. Differentiation of 3T3-L1 fibroblasts to adipocytes induced by transfection of ras oncogenes. Science. 1991 Aug 2;253(5019):565–568. doi: 10.1126/science.1857988. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggs W. H., 3rd, Zipursky S. L. Primary structure, expression, and signal-dependent tyrosine phosphorylation of a Drosophila homolog of extracellular signal-regulated kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 15;89(14):6295–6299. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.14.6295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bork P., Margolis B. A phosphotyrosine interaction domain. Cell. 1995 Mar 10;80(5):693–694. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90347-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bossing T., Technau G. M. The fate of the CNS midline progenitors in Drosophila as revealed by a new method for single cell labelling. Development. 1994 Jul;120(7):1895–1906. doi: 10.1242/dev.120.7.1895. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowtell D. D., Simon M. A., Rubin G. M. Nucleotide sequence and structure of the sevenless gene of Drosophila melanogaster. Genes Dev. 1988 Jun;2(6):620–634. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.6.620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunch T. A., Brower D. L. Drosophila PS2 integrin mediates RGD-dependent cell-matrix interactions. Development. 1992 Sep;116(1):239–247. doi: 10.1242/dev.116.1.239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunch T. A., Grinblat Y., Goldstein L. S. Characterization and use of the Drosophila metallothionein promoter in cultured Drosophila melanogaster cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Feb 11;16(3):1043–1061. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.3.1043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cadigan K. M., Grossniklaus U., Gehring W. J. Localized expression of sloppy paired protein maintains the polarity of Drosophila parasegments. Genes Dev. 1994 Apr 15;8(8):899–913. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.8.899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell G., Göring H., Lin T., Spana E., Andersson S., Doe C. Q., Tomlinson A. RK2, a glial-specific homeodomain protein required for embryonic nerve cord condensation and viability in Drosophila. Development. 1994 Oct;120(10):2957–2966. doi: 10.1242/dev.120.10.2957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell K. S., Ogris E., Burke B., Su W., Auger K. R., Druker B. J., Schaffhausen B. S., Roberts T. M., Pallas D. C. Polyoma middle tumor antigen interacts with SHC protein via the NPTY (Asn-Pro-Thr-Tyr) motif in middle tumor antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jul 5;91(14):6344–6348. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.14.6344. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavener D. R., Ray S. C. Eukaryotic start and stop translation sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jun 25;19(12):3185–3192. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.12.3185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheatham B., Vlahos C. J., Cheatham L., Wang L., Blenis J., Kahn C. R. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activation is required for insulin stimulation of pp70 S6 kinase, DNA synthesis, and glucose transporter translocation. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Jul;14(7):4902–4911. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.7.4902. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu-LaGraff Q., Doe C. Q. Neuroblast specification and formation regulated by wingless in the Drosophila CNS. Science. 1993 Sep 17;261(5128):1594–1597. doi: 10.1126/science.8372355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung J., Grammer T. C., Lemon K. P., Kazlauskas A., Blenis J. PDGF- and insulin-dependent pp70S6k activation mediated by phosphatidylinositol-3-OH kinase. Nature. 1994 Jul 7;370(6484):71–75. doi: 10.1038/370071a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clifford R., Schüpbach T. Molecular analysis of the Drosophila EGF receptor homolog reveals that several genetically defined classes of alleles cluster in subdomains of the receptor protein. Genetics. 1994 Jun;137(2):531–550. doi: 10.1093/genetics/137.2.531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clifford R., Schüpbach T. The torpedo (DER) receptor tyrosine kinase is required at multiple times during Drosophila embryogenesis. Development. 1992 Jul;115(3):853–872. doi: 10.1242/dev.115.3.853. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Condron B. G., Zinn K. The grasshopper median neuroblast is a multipotent progenitor cell that generates glia and neurons in distinct temporal phases. J Neurosci. 1994 Oct;14(10):5766–5777. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.14-10-05766.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Meyts P. The structural basis of insulin and insulin-like growth factor-I receptor binding and negative co-operativity, and its relevance to mitogenic versus metabolic signalling. Diabetologia. 1994 Sep;37 (Suppl 2):S135–S148. doi: 10.1007/BF00400837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dohrmann C., Azpiazu N., Frasch M. A new Drosophila homeo box gene is expressed in mesodermal precursor cells of distinct muscles during embryogenesis. Genes Dev. 1990 Dec;4(12A):2098–2111. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.12a.2098. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doyle H. J., Bishop J. M. Torso, a receptor tyrosine kinase required for embryonic pattern formation, shares substrates with the sevenless and EGF-R pathways in Drosophila. Genes Dev. 1993 Apr;7(4):633–646. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.4.633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebina Y., Ellis L., Jarnagin K., Edery M., Graf L., Clauser E., Ou J. H., Masiarz F., Kan Y. W., Goldfine I. D. The human insulin receptor cDNA: the structural basis for hormone-activated transmembrane signalling. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):747–758. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90334-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabry M., Schaefer E., Ellis L., Kojro E., Fahrenholz F., Brandenburg D. Detection of a new hormone contact site within the insulin receptor ectodomain by the use of a novel photoreactive insulin. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 5;267(13):8950–8956. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez-Almonacid R., Rosen O. M. Structure and ligand specificity of the Drosophila melanogaster insulin receptor. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2718–2727. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2718. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fingar D. C., Birnbaum M. J. A role for Raf-1 in the divergent signaling pathways mediating insulin-stimulated glucose transport. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 1;269(13):10127–10132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fingar D. C., Hausdorff S. F., Blenis J., Birnbaum M. J. Dissociation of pp70 ribosomal protein S6 kinase from insulin-stimulated glucose transport in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 5;268(4):3005–3008. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman M. The spitz gene is required for photoreceptor determination in the Drosophila eye where it interacts with the EGF receptor. Mech Dev. 1994 Oct;48(1):25–33. doi: 10.1016/0925-4773(94)90003-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita S. C., Zipursky S. L., Benzer S., Ferrús A., Shotwell S. L. Monoclonal antibodies against the Drosophila nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7929–7933. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garofalo R. S., Rosen O. M. Tissue localization of Drosophila melanogaster insulin receptor transcripts during development. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1638–1647. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hausdorff S. F., Frangioni J. V., Birnbaum M. J. Role of p21ras in insulin-stimulated glucose transport in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1994 Aug 26;269(34):21391–21394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jan L. Y., Jan Y. N. Antibodies to horseradish peroxidase as specific neuronal markers in Drosophila and in grasshopper embryos. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(8):2700–2704. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.8.2700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jokerst R. S., Weeks J. R., Zehring W. A., Greenleaf A. L. Analysis of the gene encoding the largest subunit of RNA polymerase II in Drosophila. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 Jan;215(2):266–275. doi: 10.1007/BF00339727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn C. R. Banting Lecture. Insulin action, diabetogenes, and the cause of type II diabetes. Diabetes. 1994 Aug;43(8):1066–1084. doi: 10.2337/diab.43.8.1066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapeller R., Cantley L. C. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. Bioessays. 1994 Aug;16(8):565–576. doi: 10.1002/bies.950160810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karpen G. H., Spradling A. C. Analysis of subtelomeric heterochromatin in the Drosophila minichromosome Dp1187 by single P element insertional mutagenesis. Genetics. 1992 Nov;132(3):737–753. doi: 10.1093/genetics/132.3.737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller S. R., Lienhard G. E. Insulin signalling: the role of insulin receptor substrate 1. Trends Cell Biol. 1994 Apr;4(4):115–119. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(94)90065-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. J., von Kessler D. P., Parks S., Beachy P. A. Secretion and localized transcription suggest a role in positional signaling for products of the segmentation gene hedgehog. Cell. 1992 Oct 2;71(1):33–50. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90264-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemmon M. A., Schlessinger J. Regulation of signal transduction and signal diversity by receptor oligomerization. Trends Biochem Sci. 1994 Nov;19(11):459–463. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(94)90130-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Littleton J. T., Bellen H. J. Genetic and phenotypic analysis of thirteen essential genes in cytological interval 22F1-2; 23B1-2 reveals novel genes required for neural development in Drosophila. Genetics. 1994 Sep;138(1):111–123. doi: 10.1093/genetics/138.1.111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis B., Rhee S. G., Felder S., Mervic M., Lyall R., Levitzki A., Ullrich A., Zilberstein A., Schlessinger J. EGF induces tyrosine phosphorylation of phospholipase C-II: a potential mechanism for EGF receptor signaling. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1101–1107. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90047-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ming X. F., Burgering B. M., Wennström S., Claesson-Welsh L., Heldin C. H., Bos J. L., Kozma S. C., Thomas G. Activation of p70/p85 S6 kinase by a pathway independent of p21ras. Nature. 1994 Sep 29;371(6496):426–429. doi: 10.1038/371426a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount S. M., Burks C., Hertz G., Stormo G. D., White O., Fields C. Splicing signals in Drosophila: intron size, information content, and consensus sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Aug 25;20(16):4255–4262. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.16.4255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers M. G., Jr, Sun X. J., White M. F. The IRS-1 signaling system. Trends Biochem Sci. 1994 Jul;19(7):289–293. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(94)90007-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishida Y., Hata M., Nishizuka Y., Rutter W. J., Ebina Y. Cloning of a Drosophila cDNA encoding a polypeptide similar to the human insulin receptor precursor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Dec 15;141(2):474–481. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80197-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neill T. J., Craparo A., Gustafson T. A. Characterization of an interaction between insulin receptor substrate 1 and the insulin receptor by using the two-hybrid system. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Oct;14(10):6433–6442. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.10.6433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pawson T., Schlessingert J. SH2 and SH3 domains. Curr Biol. 1993 Jul 1;3(7):434–442. doi: 10.1016/0960-9822(93)90350-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petruzzelli L., Herrera R., Arenas-Garcia R., Fernandez R., Birnbaum M. J., Rosen O. M. Isolation of a Drosophila genomic sequence homologous to the kinase domain of the human insulin receptor and detection of the phosphorylated Drosophila receptor with an anti-peptide antibody. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4710–4714. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poole S. J., Kauvar L. M., Drees B., Kornberg T. The engrailed locus of Drosophila: structural analysis of an embryonic transcript. Cell. 1985 Jan;40(1):37–43. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90306-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porras A., Nebreda A. R., Benito M., Santos E. Activation of Ras by insulin in 3T3 L1 cells does not involve GTPase-activating protein phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 15;267(29):21124–21131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raz E., Schejter E. D., Shilo B. Z. Interallelic complementation among DER/flb alleles: implications for the mechanism of signal transduction by receptor-tyrosine kinases. Genetics. 1991 Sep;129(1):191–201. doi: 10.1093/genetics/129.1.191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raz E., Shilo B. Z. Dissection of the faint little ball (flb) phenotype: determination of the development of the Drosophila central nervous system by early interactions in the ectoderm. Development. 1992 Jan;114(1):113–123. doi: 10.1242/dev.114.1.113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson L. J., Razzack Z. F., Lawrence J. C., Jr, James D. E. Mitogen-activated protein kinase activation is not sufficient for stimulation of glucose transport or glycogen synthase in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1993 Dec 15;268(35):26422–26427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schumacher R., Mosthaf L., Schlessinger J., Brandenburg D., Ullrich A. Insulin and insulin-like growth factor-1 binding specificity is determined by distinct regions of their cognate receptors. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 15;266(29):19288–19295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schäffer L. A model for insulin binding to the insulin receptor. Eur J Biochem. 1994 May 1;221(3):1127–1132. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1994.tb18833.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skolnik E. Y., Lee C. H., Batzer A., Vicentini L. M., Zhou M., Daly R., Myers M. J., Jr, Backer J. M., Ullrich A., White M. F. The SH2/SH3 domain-containing protein GRB2 interacts with tyrosine-phosphorylated IRS1 and Shc: implications for insulin control of ras signalling. EMBO J. 1993 May;12(5):1929–1936. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05842.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. B., Johnson K. S. Single-step purification of polypeptides expressed in Escherichia coli as fusions with glutathione S-transferase. Gene. 1988 Jul 15;67(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun X. J., Rothenberg P., Kahn C. R., Backer J. M., Araki E., Wilden P. A., Cahill D. A., Goldstein B. J., White M. F. Structure of the insulin receptor substrate IRS-1 defines a unique signal transduction protein. Nature. 1991 Jul 4;352(6330):73–77. doi: 10.1038/352073a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tio M., Ma C., Moses K. spitz, a Drosophila homolog of transforming growth factor-alpha, is required in the founding photoreceptor cells of the compound eye facets. Mech Dev. 1994 Oct;48(1):13–23. doi: 10.1016/0925-4773(94)90002-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Udolph G., Prokop A., Bossing T., Technau G. M. A common precursor for glia and neurons in the embryonic CNS of Drosophila gives rise to segment-specific lineage variants. Development. 1993 Jul;118(3):765–775. doi: 10.1242/dev.118.3.765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Bell J. R., Chen E. Y., Herrera R., Petruzzelli L. M., Dull T. J., Gray A., Coussens L., Liao Y. C., Tsubokawa M. Human insulin receptor and its relationship to the tyrosine kinase family of oncogenes. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):756–761. doi: 10.1038/313756a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Gray A., Tam A. W., Yang-Feng T., Tsubokawa M., Collins C., Henzel W., Le Bon T., Kathuria S., Chen E. Insulin-like growth factor I receptor primary structure: comparison with insulin receptor suggests structural determinants that define functional specificity. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2503–2512. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04528.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White M. F., Kahn C. R. The insulin signaling system. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 7;269(1):1–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White M. F., Livingston J. N., Backer J. M., Lauris V., Dull T. J., Ullrich A., Kahn C. R. Mutation of the insulin receptor at tyrosine 960 inhibits signal transmission but does not affect its tyrosine kinase activity. Cell. 1988 Aug 26;54(5):641–649. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80008-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White M. F., Maron R., Kahn C. R. Insulin rapidly stimulates tyrosine phosphorylation of a Mr-185,000 protein in intact cells. Nature. 1985 Nov 14;318(6042):183–186. doi: 10.1038/318183a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilden P. A., Siddle K., Haring E., Backer J. M., White M. F., Kahn C. R. The role of insulin receptor kinase domain autophosphorylation in receptor-mediated activities. Analysis with insulin and anti-receptor antibodies. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 5;267(19):13719–13727. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi T., Fernandez R., Roth R. A. Comparison of the signaling abilities of the Drosophila and human insulin receptors in mammalian cells. Biochemistry. 1995 Apr 18;34(15):4962–4968. doi: 10.1021/bi00015a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yonezawa K., Ando A., Kaburagi Y., Yamamoto-Honda R., Kitamura T., Hara K., Nakafuku M., Okabayashi Y., Kadowaki T., Kaziro Y. Signal transduction pathways from insulin receptors to Ras. Analysis by mutant insulin receptors. J Biol Chem. 1994 Feb 11;269(6):4634–4640. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang B., Roth R. A. A region of the insulin receptor important for ligand binding (residues 450-601) is recognized by patients' autoimmune antibodies and inhibitory monoclonal antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 1;88(21):9858–9862. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.21.9858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zipursky S. L., Rubin G. M. Determination of neuronal cell fate: lessons from the R7 neuron of Drosophila. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1994;17:373–397. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.17.030194.002105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. A new method for predicting signal sequence cleavage sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jun 11;14(11):4683–4690. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.11.4683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]