Abstract
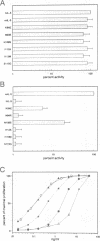
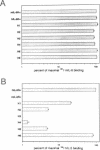
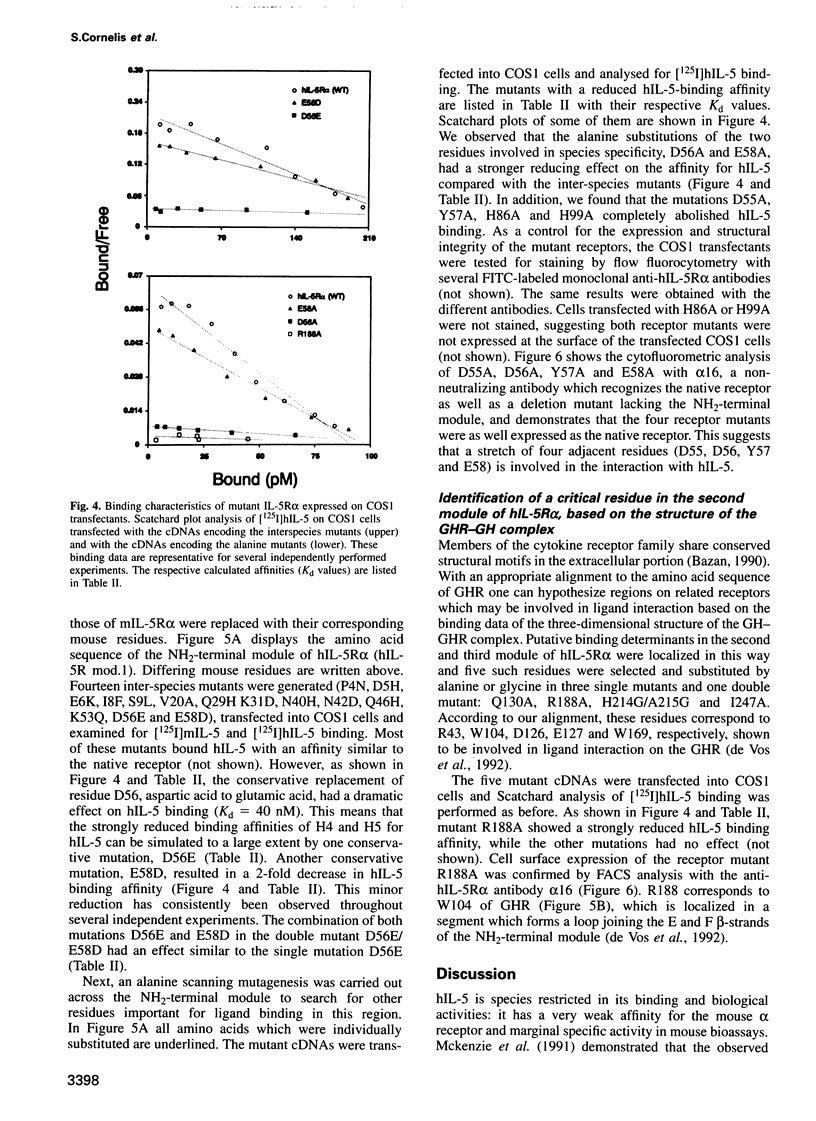
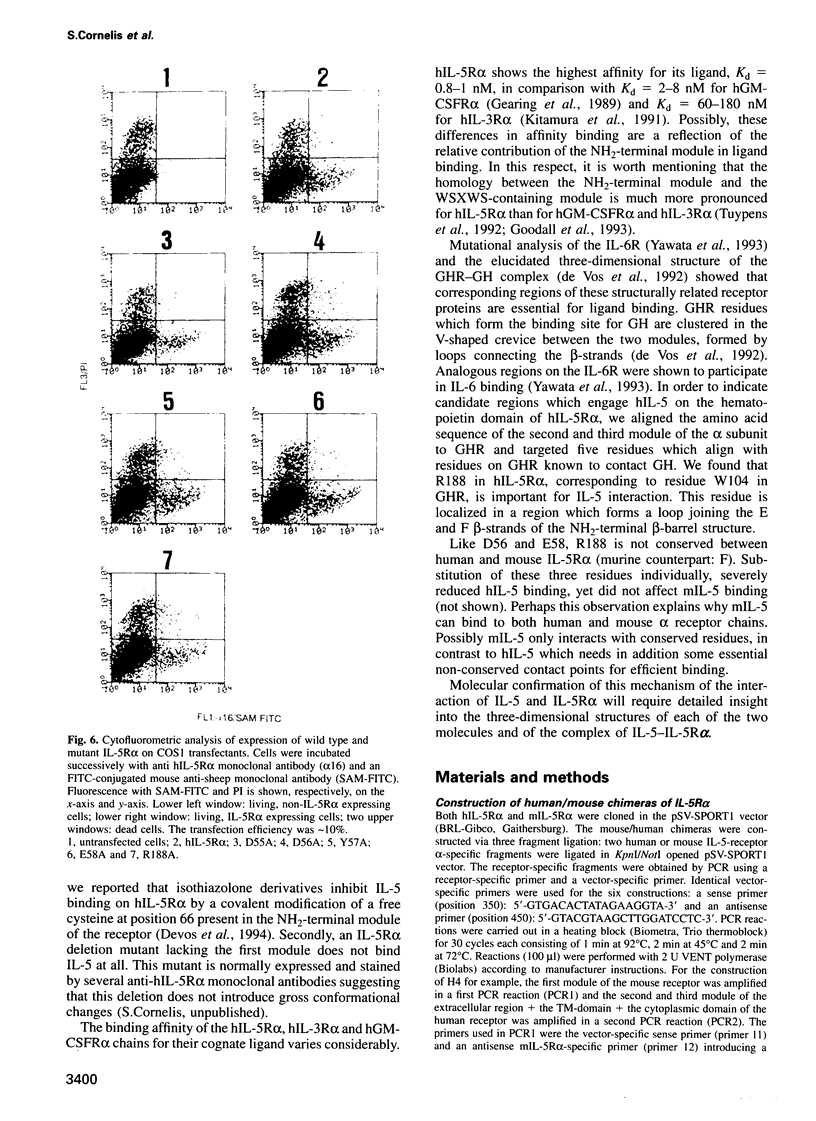
The receptor for interleukin-5 (IL-5) is composed of two different subunits. The IL-5 receptor alpha (IL-5R alpha) is required for ligand-specific binding while association with the beta-chain results in increased binding affinity. Murine IL-5 (mIL-5) has similar activity on human and murine cells, whereas human IL-5 (hIL-5) has marginal activity on murine cells. We found that the combined substitution of K84 and N108 on hIL-5 by their respective murine counterpart yields a molecule which is as potent as mIL-5 for growth stimulation of a murine cell line. Since the unidirectional species specificity is due only to the interaction with the IL-5R alpha subunit, we have used chimeric IL-5R alpha molecules to define regions of hIL-5R alpha involved in species-specific hIL-5 ligand binding. We found that this property is largely determined by the NH2-terminal module of hIL-5R alpha, and detailed analysis defined D56 and to a lesser extent E58 as important for binding. Moreover, two additional residues, D55 and Y57, were identified by alanine scanning mutagenesis within the same region. Based on the observed homology between the NH2-terminal module and the membrane proximal (WSXWS-containing) module of hIL-5R alpha we located this stretch of four amino acid residues (D55, D56, Y57 and E58) in the loop region that connects the C and D beta-strands on the proposed tertiary structure of the NH2-terminal module.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Clutterbuck E., Shields J. G., Gordon J., Smith S. H., Boyd A., Callard R. E., Campbell H. D., Young I. G., Sanderson C. J. Recombinant human interleukin 5 is an eosinophil differentiation factor but has no activity in standard human B cell growth factor assays. Eur J Immunol. 1987 Dec;17(12):1743–1750. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830171210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deng W. P., Nickoloff J. A. Site-directed mutagenesis of virtually any plasmid by eliminating a unique site. Anal Biochem. 1992 Jan;200(1):81–88. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(92)90280-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devos R., Guisez Y., Plaetinck G., Cornelis S., Tavernier J., van der Heyden J., Foley L. H., Scheffler J. E. Covalent modification of the interleukin-5 receptor by isothiazolones leads to inhibition of the binding of interleukin-5. Eur J Biochem. 1994 Oct 15;225(2):635–640. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1994.00635.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devos R., Plaetinck G., Van der Heyden J., Cornelis S., Vandekerckhove J., Fiers W., Tavernier J. Molecular basis of a high affinity murine interleukin-5 receptor. EMBO J. 1991 Aug;10(8):2133–2137. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07747.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gearing D. P., King J. A., Gough N. M., Nicola N. A. Expression cloning of a receptor for human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 1;8(12):3667–3676. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08541.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodall G. J., Bagley C. J., Vadas M. A., Lopez A. F. A model for the interaction of the GM-CSF, IL-3 and IL-5 receptors with their ligands. Growth Factors. 1993;8(2):87–97. doi: 10.3109/08977199309046929. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman D. M., Itoh N., Kitamura T., Schreurs J., Yonehara S., Yahara I., Arai K., Miyajima A. Cloning and expression of a gene encoding an interleukin 3 receptor-like protein: identification of another member of the cytokine receptor gene family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(14):5459–5463. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.14.5459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hara T., Miyajima A. Two distinct functional high affinity receptors for mouse interleukin-3 (IL-3). EMBO J. 1992 May;11(5):1875–1884. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05239.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashida K., Kitamura T., Gorman D. M., Arai K., Yokota T., Miyajima A. Molecular cloning of a second subunit of the receptor for human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF): reconstitution of a high-affinity GM-CSF receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):9655–9659. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.9655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura T., Sato N., Arai K., Miyajima A. Expression cloning of the human IL-3 receptor cDNA reveals a shared beta subunit for the human IL-3 and GM-CSF receptors. Cell. 1991 Sep 20;66(6):1165–1174. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90039-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez A. F., Vadas M. A., Woodcock J. M., Milton S. E., Lewis A., Elliott M. J., Gillis D., Ireland R., Olwell E., Park L. S. Interleukin-5, interleukin-3, and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor cross-compete for binding to cell surface receptors on human eosinophils. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 25;266(36):24741–24747. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenzie A. N., Barry S. C., Strath M., Sanderson C. J. Structure-function analysis of interleukin-5 utilizing mouse/human chimeric molecules. EMBO J. 1991 May;10(5):1193–1199. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08060.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPherson G. A. Analysis of radioligand binding experiments. A collection of computer programs for the IBM PC. J Pharmacol Methods. 1985 Nov;14(3):213–228. doi: 10.1016/0160-5402(85)90034-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milburn M. V., Hassell A. M., Lambert M. H., Jordan S. R., Proudfoot A. E., Graber P., Wells T. N. A novel dimer configuration revealed by the crystal structure at 2.4 A resolution of human interleukin-5. Nature. 1993 May 13;363(6425):172–176. doi: 10.1038/363172a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murata Y., Takaki S., Migita M., Kikuchi Y., Tominaga A., Takatsu K. Molecular cloning and expression of the human interleukin 5 receptor. J Exp Med. 1992 Feb 1;175(2):341–351. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.2.341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park L. S., Martin U., Sorensen R., Luhr S., Morrissey P. J., Cosman D., Larsen A. Cloning of the low-affinity murine granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor receptor and reconstitution of a high-affinity receptor complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 15;89(10):4295–4299. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.10.4295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plaetinck G., Van der Heyden J., Tavernier J., Faché I., Tuypens T., Fischkoff S., Fiers W., Devos R. Characterization of interleukin 5 receptors on eosinophilic sublines from human promyelocytic leukemia (HL-60) cells. J Exp Med. 1990 Sep 1;172(3):683–691. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.3.683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rolink A. G., Melchers F., Palacios R. Monoclonal antibodies reactive with the mouse interleukin 5 receptor. J Exp Med. 1989 May 1;169(5):1693–1701. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.5.1693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakamaki K., Miyajima I., Kitamura T., Miyajima A. Critical cytoplasmic domains of the common beta subunit of the human GM-CSF, IL-3 and IL-5 receptors for growth signal transduction and tyrosine phosphorylation. EMBO J. 1992 Oct;11(10):3541–3549. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05437.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson C. J. Interleukin-5, eosinophils, and disease. Blood. 1992 Jun 15;79(12):3101–3109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato N., Sakamaki K., Terada N., Arai K., Miyajima A. Signal transduction by the high-affinity GM-CSF receptor: two distinct cytoplasmic regions of the common beta subunit responsible for different signaling. EMBO J. 1993 Nov;12(11):4181–4189. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06102.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takaki S., Mita S., Kitamura T., Yonehara S., Yamaguchi N., Tominaga A., Miyajima A., Takatsu K. Identification of the second subunit of the murine interleukin-5 receptor: interleukin-3 receptor-like protein, AIC2B is a component of the high affinity interleukin-5 receptor. EMBO J. 1991 Oct;10(10):2833–2838. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07832.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takaki S., Murata Y., Kitamura T., Miyajima A., Tominaga A., Takatsu K. Reconstitution of the functional receptors for murine and human interleukin 5. J Exp Med. 1993 Jun 1;177(6):1523–1529. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.6.1523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takaki S., Tominaga A., Hitoshi Y., Mita S., Sonoda E., Yamaguchi N., Takatsu K. Molecular cloning and expression of the murine interleukin-5 receptor. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(13):4367–4374. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07886.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takatsu K., Tominaga A., Harada N., Mita S., Matsumoto M., Takahashi T., Kikuchi Y., Yamaguchi N. T cell-replacing factor (TRF)/interleukin 5 (IL-5): molecular and functional properties. Immunol Rev. 1988 Feb;102:107–135. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1988.tb00743.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tavernier J., Devos R., Cornelis S., Tuypens T., Van der Heyden J., Fiers W., Plaetinck G. A human high affinity interleukin-5 receptor (IL5R) is composed of an IL5-specific alpha chain and a beta chain shared with the receptor for GM-CSF. Cell. 1991 Sep 20;66(6):1175–1184. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90040-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tavernier J., Devos R., Van der Heyden J., Hauquier G., Bauden R., Fache I., Kawashima E., Vandekerckhove J., Contreras R., Fiers W. Expression of human and murine interleukin-5 in eukaryotic systems. DNA. 1989 Sep;8(7):491–501. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1989.8.491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tavernier J., Tuypens T., Plaetinck G., Verhee A., Fiers W., Devos R. Molecular basis of the membrane-anchored and two soluble isoforms of the human interleukin 5 receptor alpha subunit. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 1;89(15):7041–7045. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.15.7041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuypens T., Plaetinck G., Baker E., Sutherland G., Brusselle G., Fiers W., Devos R., Tavernier J. Organization and chromosomal localization of the human interleukin 5 receptor alpha-chain gene. Eur Cytokine Netw. 1992 Sep-Oct;3(5):451–459. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker C., Virchow J. C., Jr, Bruijnzeel P. L., Blaser K. T cell subsets and their soluble products regulate eosinophilia in allergic and nonallergic asthma. J Immunol. 1991 Mar 15;146(6):1829–1835. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss M., Yokoyama C., Shikama Y., Naugle C., Druker B., Sieff C. A. Human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor receptor signal transduction requires the proximal cytoplasmic domains of the alpha and beta subunits. Blood. 1993 Dec 1;82(11):3298–3306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yawata H., Yasukawa K., Natsuka S., Murakami M., Yamasaki K., Hibi M., Taga T., Kishimoto T. Structure-function analysis of human IL-6 receptor: dissociation of amino acid residues required for IL-6-binding and for IL-6 signal transduction through gp130. EMBO J. 1993 Apr;12(4):1705–1712. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05815.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vos A. M., Ultsch M., Kossiakoff A. A. Human growth hormone and extracellular domain of its receptor: crystal structure of the complex. Science. 1992 Jan 17;255(5042):306–312. doi: 10.1126/science.1549776. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]