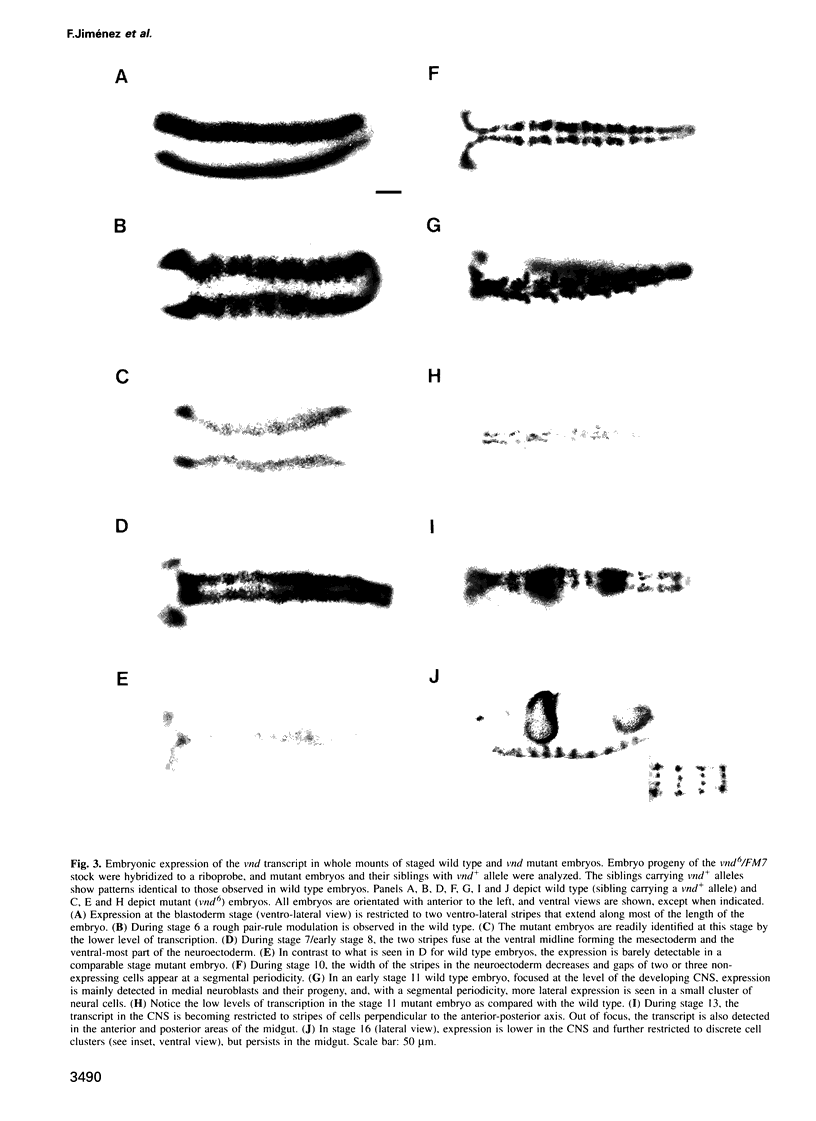
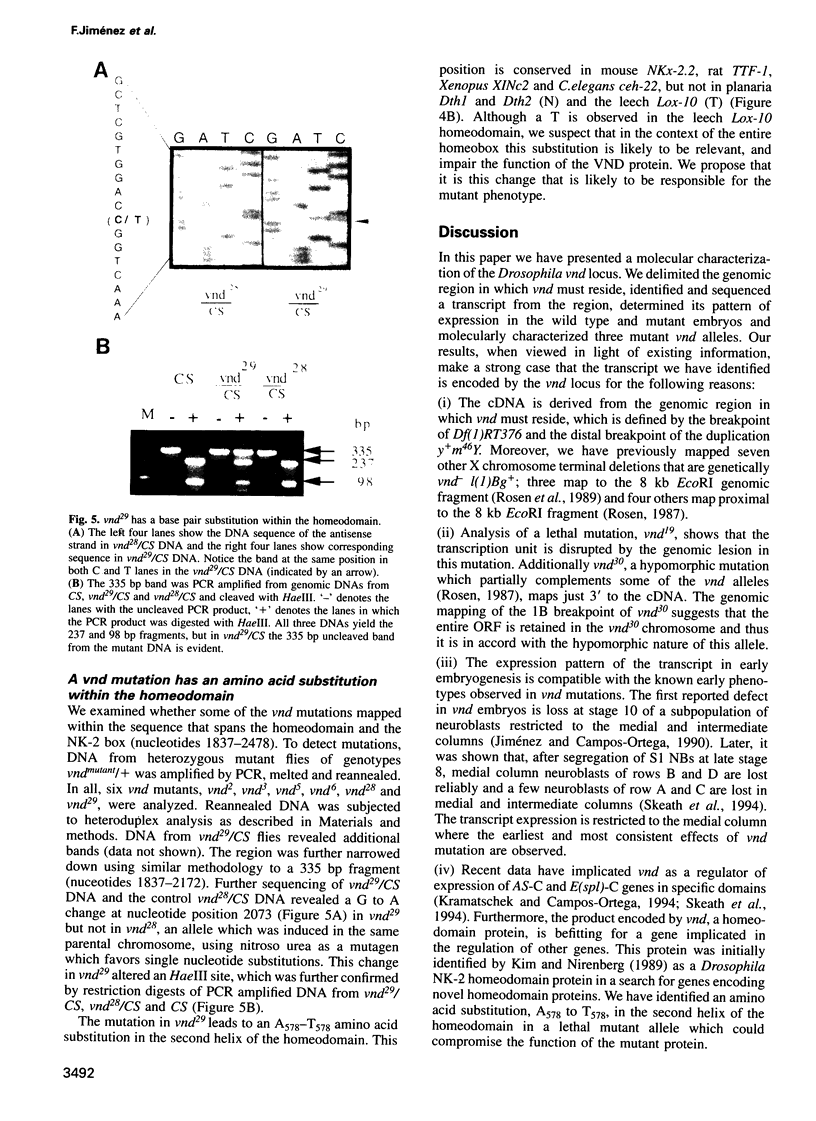
Abstract
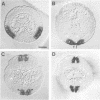
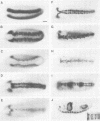
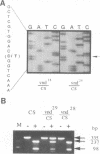
The development of the central nervous system in Drosophila is initiated by the segregation of neuroblasts, the neural progenitors, from the embryonic neuroectoderm. This process is guided by at least two classes of genes: the achaete-scute complex (AS-C) proneural genes and the neurogenic genes. It has been known for some time that loss-of-function mutations in the AS-C result in neural hypoplasia and the first observed defect is failure of segregation of a fraction of neuroblasts. Loss-of-function mutations at the ventral nervous system defective (vnd) locus are known to lead to similar phenotypic defects in early neurogenesis. More recently, the vnd locus has been implicated in the regulation of the proneural AS-C genes and the neurogenic genes of the Enhancer of split complex. In this paper we report the identification of a transcript associated with the vnd locus, the transcript distribution in embryogenesis, which is compatible with the nervous system mutant phenotypes described for this gene, and that the protein product is a member of the NK-2 homeodomain family. We discuss these findings within the framework of early Drosophila neurogenesis and the known phenotypes associated with the vnd locus.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cabrera C. V., Martinez-Arias A., Bate M. The expression of three members of the achaete-scute gene complex correlates with neuroblast segregation in Drosophila. Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):425–433. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90496-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campos A. R., Rosen D. R., Robinow S. N., White K. Molecular analysis of the locus elav in Drosophila melanogaster: a gene whose embryonic expression is neural specific. EMBO J. 1987 Feb;6(2):425–431. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04772.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campuzano S., Modolell J. Patterning of the Drosophila nervous system: the achaete-scute gene complex. Trends Genet. 1992 Jun;8(6):202–208. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(92)90234-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavener D. R. Comparison of the consensus sequence flanking translational start sites in Drosophila and vertebrates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Feb 25;15(4):1353–1361. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.4.1353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu-LaGraff Q., Doe C. Q. Neuroblast specification and formation regulated by wingless in the Drosophila CNS. Science. 1993 Sep 17;261(5128):1594–1597. doi: 10.1126/science.8372355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doe C. Q. Molecular markers for identified neuroblasts and ganglion mother cells in the Drosophila central nervous system. Development. 1992 Dec;116(4):855–863. doi: 10.1242/dev.116.4.855. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Fernàndez J., Baguñ J., Saló E. Planarian homeobox genes: cloning, sequence analysis, and expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):7338–7342. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.7338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghysen A., Dambly-Chaudiere C. Genesis of the Drosophila peripheral nervous system. Trends Genet. 1989 Aug;5(8):251–255. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(89)90097-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine K. D., Wieschaus E. Cell intercalation during Drosophila germband extension and its regulation by pair-rule segmentation genes. Development. 1994 Apr;120(4):827–841. doi: 10.1242/dev.120.4.827. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennings B., Preiss A., Delidakis C., Bray S. The Notch signalling pathway is required for Enhancer of split bHLH protein expression during neurogenesis in the Drosophila embryo. Development. 1994 Dec;120(12):3537–3548. doi: 10.1242/dev.120.12.3537. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiménez F., Campos-Ortega J. A. Defective neuroblast commitment in mutants of the achaete-scute complex and adjacent genes of D. melanogaster. Neuron. 1990 Jul;5(1):81–89. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90036-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiménez F., Campos-Ortega J. A. Genes in subdivision 1B of the Drosophila melanogaster X-chromosome and their influence on neural development. J Neurogenet. 1987 Jun;4(4):179–200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim Y., Nirenberg M. Drosophila NK-homeobox genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):7716–7720. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.7716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knust E., Schrons H., Grawe F., Campos-Ortega J. A. Seven genes of the Enhancer of split complex of Drosophila melanogaster encode helix-loop-helix proteins. Genetics. 1992 Oct;132(2):505–518. doi: 10.1093/genetics/132.2.505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramatschek B., Campos-Ortega J. A. Neuroectodermal transcription of the Drosophila neurogenic genes E(spl) and HLH-m5 is regulated by proneural genes. Development. 1994 Apr;120(4):815–826. doi: 10.1242/dev.120.4.815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lints T. J., Parsons L. M., Hartley L., Lyons I., Harvey R. P. Nkx-2.5: a novel murine homeobox gene expressed in early heart progenitor cells and their myogenic descendants. Development. 1993 Oct;119(2):419–431. doi: 10.1242/dev.119.2.419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin-Morris L. E., White K. The Drosophila transcript encoded by the beta-amyloid protein precursor-like gene is restricted to the nervous system. Development. 1990 Sep;110(1):185–195. doi: 10.1242/dev.110.1.185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martín-Bermudo M. D., Carmena A., Jiménez F. Neurogenic genes control gene expression at the transcriptional level in early neurogenesis and in mesectoderm specification. Development. 1995 Jan;121(1):219–224. doi: 10.1242/dev.121.1.219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martín-Bermudo M. D., Martínez C., Rodríguez A., Jiménez F. Distribution and function of the lethal of scute gene product during early neurogenesis in Drosophila. Development. 1991 Oct;113(2):445–454. doi: 10.1242/dev.113.2.445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nardelli-Haefliger D., Shankland M. Lox10, a member of the NK-2 homeobox gene class, is expressed in a segmental pattern in the endoderm and in the cephalic nervous system of the leech Helobdella. Development. 1993 Jul;118(3):877–892. doi: 10.1242/dev.118.3.877. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okkema P. G., Fire A. The Caenorhabditis elegans NK-2 class homeoprotein CEH-22 is involved in combinatorial activation of gene expression in pharyngeal muscle. Development. 1994 Aug;120(8):2175–2186. doi: 10.1242/dev.120.8.2175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price M., Lazzaro D., Pohl T., Mattei M. G., Rüther U., Olivo J. C., Duboule D., Di Lauro R. Regional expression of the homeobox gene Nkx-2.2 in the developing mammalian forebrain. Neuron. 1992 Feb;8(2):241–255. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90291-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romani S., Campuzano S., Modolell J. The achaete-scute complex is expressed in neurogenic regions of Drosophila embryos. EMBO J. 1987 Jul;6(7):2085–2092. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02474.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen D. R., Martin-Morris L., Luo L. Q., White K. A Drosophila gene encoding a protein resembling the human beta-amyloid protein precursor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2478–2482. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Gómez M., Ghysen A. The expression and role of a proneural gene, achaete, in the development of the larval nervous system of Drosophila. EMBO J. 1993 Mar;12(3):1121–1130. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05753.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saha M. S., Michel R. B., Gulding K. M., Grainger R. M. A Xenopus homebox gene defines dorsal-ventral domains in the developing brain. Development. 1993 May;118(1):193–202. doi: 10.1242/dev.118.1.193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skeath J. B., Carroll S. B. Regulation of proneural gene expression and cell fate during neuroblast segregation in the Drosophila embryo. Development. 1992 Apr;114(4):939–946. doi: 10.1242/dev.114.4.939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skeath J. B., Panganiban G., Selegue J., Carroll S. B. Gene regulation in two dimensions: the proneural achaete and scute genes are controlled by combinations of axis-patterning genes through a common intergenic control region. Genes Dev. 1992 Dec;6(12B):2606–2619. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.12b.2606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tautz D., Pfeifle C. A non-radioactive in situ hybridization method for the localization of specific RNAs in Drosophila embryos reveals translational control of the segmentation gene hunchback. Chromosoma. 1989 Aug;98(2):81–85. doi: 10.1007/BF00291041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsao D. H., Gruschus J. M., Wang L. H., Nirenberg M., Ferretti J. A. Elongation of helix III of the NK-2 homeodomain upon binding to DNA: a secondary structure study by NMR. Biochemistry. 1994 Dec 20;33(50):15053–15060. doi: 10.1021/bi00254a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
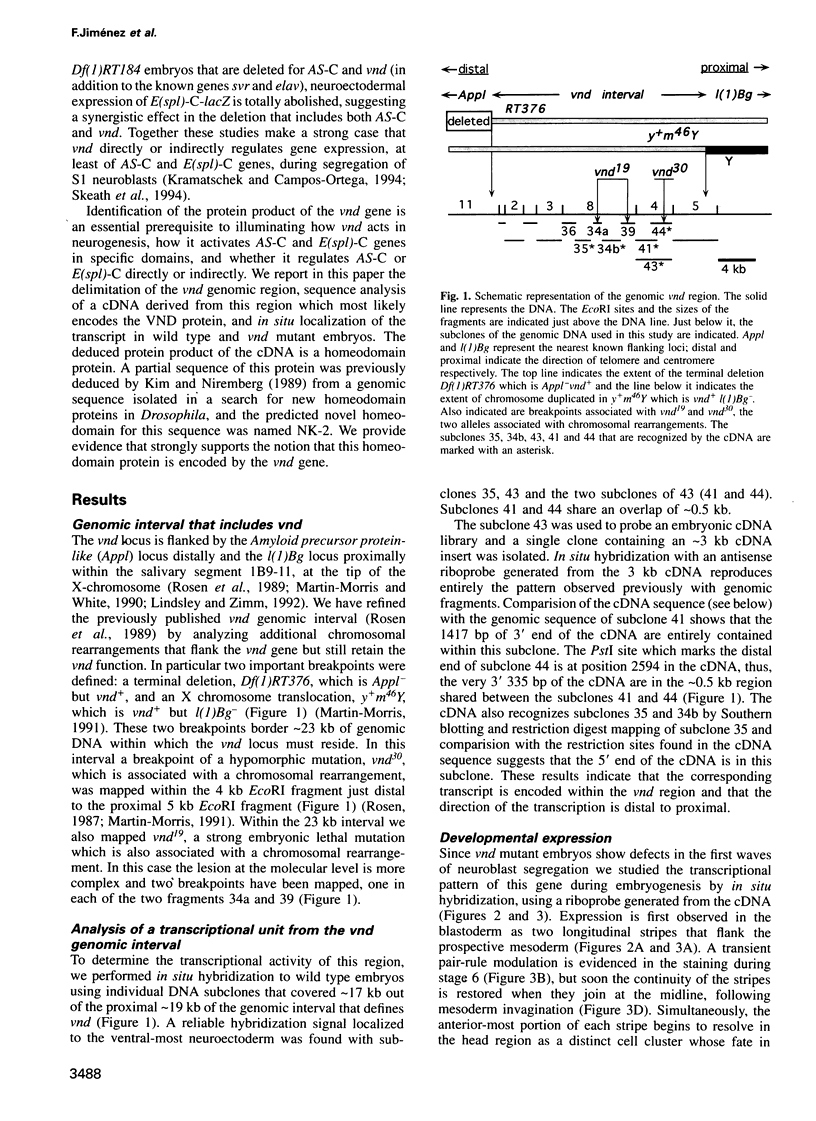
- White K., DeCelles N. L., Enlow T. C. Genetic and developmental analysis of the locus vnd in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 1983 Jul;104(3):433–448. doi: 10.1093/genetics/104.3.433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White K. Defective neural development in Drosophila melanogaster embryos deficient for the tip of the X chromosome. Dev Biol. 1980 Dec;80(2):332–344. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(80)90409-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]