Abstract
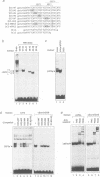
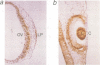
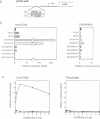
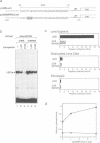
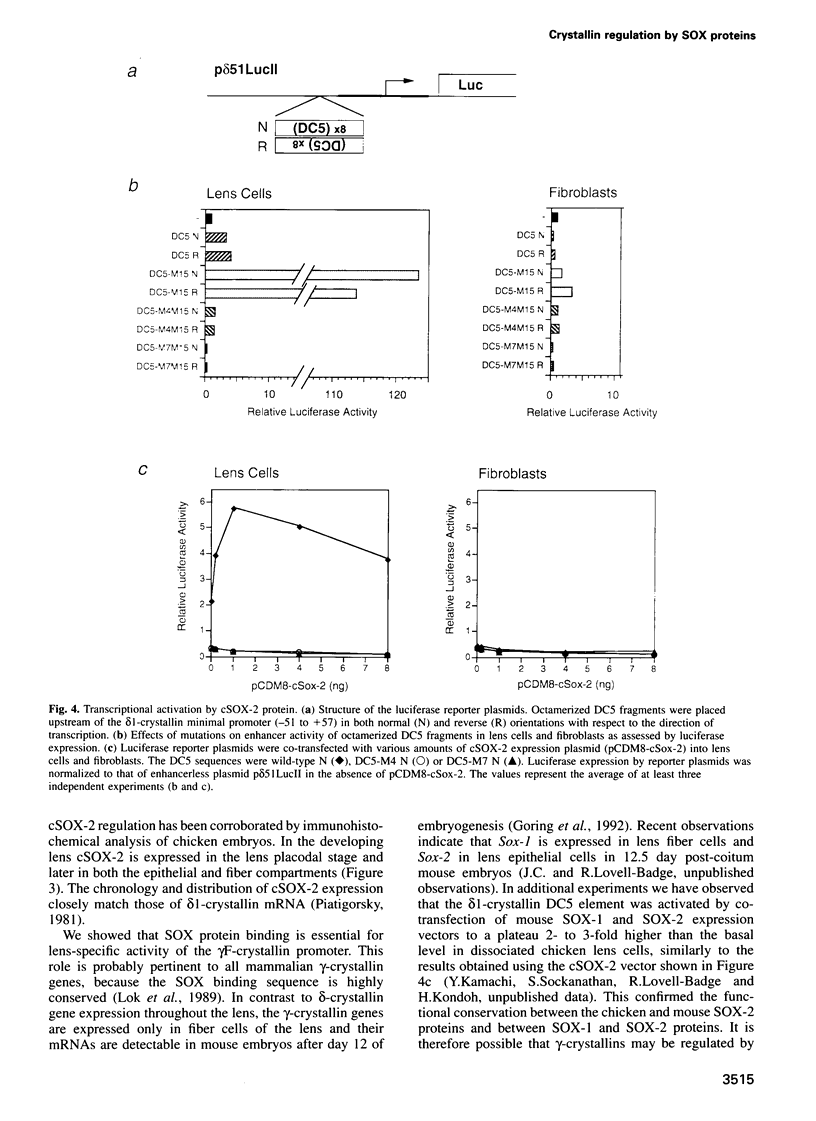
We have studied the mechanism of delta 1-crystallin gene activation, which occurs early in lens cell differentiation, and have previously shown that an essential element of the delta 1-crystallin enhancer is bound by a group of nuclear factors, delta EF2, among which delta EF2a is highly enriched in lens cells. In this report we show that the cDNA of delta EF2a codes for the chicken SOX-2 protein (cSOX-2), which is structurally related to the sex-determining factor SRY. Sox-2 is expressed at high levels in the early developing lens in both chicken and mouse embryos. Overexpression of delta EF2a/cSOX-2 increased delta 1-crystallin enhancer activity to a plateau in lens cells, but not in fibroblasts, consistent with the previously drawn conclusion that delta EF2a activates transcription only in concert with another factor present in the lens. This result supports the model that SOX proteins act as architectural components in the activating complex formed on an enhancer, as indicated for another HMG domain protein, lymphoid enhancer binding factor 1 (LEF-1). We also show that SOX protein binding is essential for lens-specific promoter activity of the mouse gamma F-crystallin gene. This work is the first to show delta- and gamma-crystallin genes as examples of direct regulatory targets of SOX proteins and provides evidence that diversified crystallin genes are regulated, at least partly, by a common mechanism.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Carlsson P., Waterman M. L., Jones K. A. The hLEF/TCF-1 alpha HMG protein contains a context-dependent transcriptional activation domain that induces the TCR alpha enhancer in T cells. Genes Dev. 1993 Dec;7(12A):2418–2430. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.12a.2418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chepelinsky A. B., King C. R., Zelenka P. S., Piatigorsky J. Lens-specific expression of the chloramphenicol acetyltransferase gene promoted by 5' flanking sequences of the murine alpha A-crystallin gene in explanted chicken lens epithelia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(8):2334–2338. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.8.2334. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denny P., Swift S., Brand N., Dabhade N., Barton P., Ashworth A. A conserved family of genes related to the testis determining gene, SRY. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jun 11;20(11):2887–2887. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.11.2887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denny P., Swift S., Connor F., Ashworth A. An SRY-related gene expressed during spermatogenesis in the mouse encodes a sequence-specific DNA-binding protein. EMBO J. 1992 Oct;11(10):3705–3712. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05455.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster J. W., Dominguez-Steglich M. A., Guioli S., Kwok C., Weller P. A., Stevanović M., Weissenbach J., Mansour S., Young I. D., Goodfellow P. N. Campomelic dysplasia and autosomal sex reversal caused by mutations in an SRY-related gene. Nature. 1994 Dec 8;372(6506):525–530. doi: 10.1038/372525a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
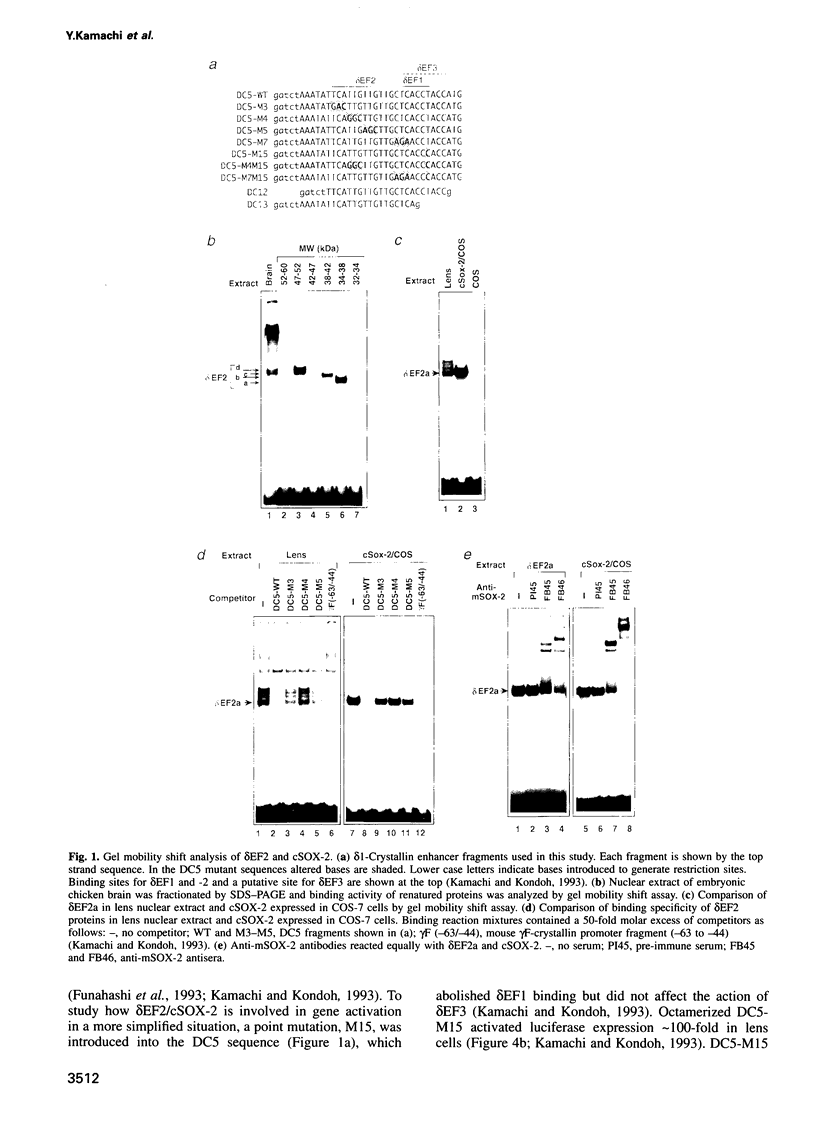
- Funahashi J., Kamachi Y., Goto K., Kondoh H. Identification of nuclear factor delta EF1 and its binding site essential for lens-specific activity of the delta 1-crystallin enhancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jul 11;19(13):3543–3547. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.13.3543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Funahashi J., Sekido R., Murai K., Kamachi Y., Kondoh H. Delta-crystallin enhancer binding protein delta EF1 is a zinc finger-homeodomain protein implicated in postgastrulation embryogenesis. Development. 1993 Oct;119(2):433–446. doi: 10.1242/dev.119.2.433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giese K., Cox J., Grosschedl R. The HMG domain of lymphoid enhancer factor 1 bends DNA and facilitates assembly of functional nucleoprotein structures. Cell. 1992 Apr 3;69(1):185–195. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90129-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giese K., Grosschedl R. LEF-1 contains an activation domain that stimulates transcription only in a specific context of factor-binding sites. EMBO J. 1993 Dec;12(12):4667–4676. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06155.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goring D. R., Breitman M. L., Tsui L. C. Temporal regulation of six crystallin transcripts during mouse lens development. Exp Eye Res. 1992 May;54(5):785–795. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(92)90034-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
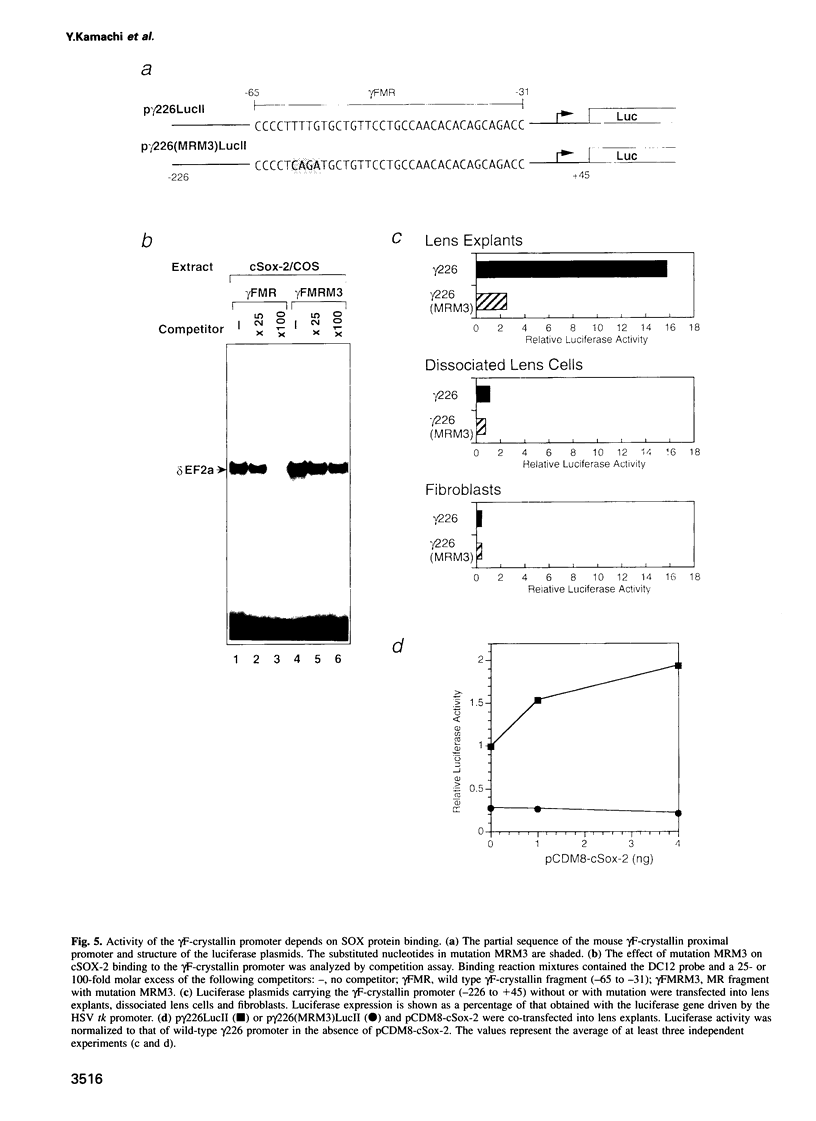
- Goring D. R., Bryce D. M., Tsui L. C., Breitman M. L., Liu Q. Developmental regulation and cell type-specific expression of the murine gamma F-crystallin gene is mediated through a lens-specific element containing the gamma F-1 binding site. Dev Dyn. 1993 Feb;196(2):143–152. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001960208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goto K., Okada T. S., Kondoh H. Functional cooperation of lens-specific and nonspecific elements in the delta 1-crystallin enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;10(3):958–964. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.3.958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosschedl R., Giese K., Pagel J. HMG domain proteins: architectural elements in the assembly of nucleoprotein structures. Trends Genet. 1994 Mar;10(3):94–100. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(94)90232-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubbay J., Collignon J., Koopman P., Capel B., Economou A., Münsterberg A., Vivian N., Goodfellow P., Lovell-Badge R. A gene mapping to the sex-determining region of the mouse Y chromosome is a member of a novel family of embryonically expressed genes. Nature. 1990 Jul 19;346(6281):245–250. doi: 10.1038/346245a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harley V. R., Lovell-Badge R., Goodfellow P. N. Definition of a consensus DNA binding site for SRY. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Apr 25;22(8):1500–1501. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.8.1500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi S., Goto K., Okada T. S., Kondoh H. Lens-specific enhancer in the third intron regulates expression of the chicken delta 1-crystallin gene. Genes Dev. 1987 Oct;1(8):818–828. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.8.818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamachi Y., Kondoh H. Overlapping positive and negative regulatory elements determine lens-specific activity of the delta 1-crystallin enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Sep;13(9):5206–5215. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.9.5206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamachi Y., Ogawa E., Asano M., Ishida S., Murakami Y., Satake M., Ito Y., Shigesada K. Purification of a mouse nuclear factor that binds to both the A and B cores of the polyomavirus enhancer. J Virol. 1990 Oct;64(10):4808–4819. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.10.4808-4819.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondoh H., Katoh K., Takahashi Y., Fujisawa H., Yokoyama M., Kimura S., Katsuki M., Saito M., Nomura T., Hiramoto Y. Specific expression of the chicken delta-crystallin gene in the lens and the pyramidal neurons of the piriform cortex in transgenic mice. Dev Biol. 1987 Mar;120(1):177–185. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(87)90116-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondoh H., Yasuda K., Okada T. S. Tissue-specific expression of a cloned chick delta-crystallin gene in mouse cells. Nature. 1983 Feb 3;301(5899):440–442. doi: 10.1038/301440a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. The scanning model for translation: an update. J Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;108(2):229–241. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.2.229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Q. R., Tini M., Tsui L. C., Breitman M. L. Interaction of a lens cell transcription factor with the proximal domain of the mouse gamma F-crystallin promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;11(3):1531–1537. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.3.1531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lok S., Stevens W., Breitman M. L., Tsui L. C. Multiple regulatory elements of the murine gamma 2-crystallin promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 May 11;17(9):3563–3582. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.9.3563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piatigorsky J. Lens differentiation in vertebrates. A review of cellular and molecular features. Differentiation. 1981;19(3):134–153. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1981.tb01141.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pontiggia A., Rimini R., Harley V. R., Goodfellow P. N., Lovell-Badge R., Bianchi M. E. Sex-reversing mutations affect the architecture of SRY-DNA complexes. EMBO J. 1994 Dec 15;13(24):6115–6124. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06958.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seed B. An LFA-3 cDNA encodes a phospholipid-linked membrane protein homologous to its receptor CD2. 1987 Oct 29-Nov 4Nature. 329(6142):840–842. doi: 10.1038/329840a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekido R., Murai K., Funahashi J., Kamachi Y., Fujisawa-Sehara A., Nabeshima Y., Kondoh H. The delta-crystallin enhancer-binding protein delta EF1 is a repressor of E2-box-mediated gene activation. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Sep;14(9):5692–5700. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.9.5692. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinclair A. H., Berta P., Palmer M. S., Hawkins J. R., Griffiths B. L., Smith M. J., Foster J. W., Frischauf A. M., Lovell-Badge R., Goodfellow P. N. A gene from the human sex-determining region encodes a protein with homology to a conserved DNA-binding motif. Nature. 1990 Jul 19;346(6281):240–244. doi: 10.1038/346240a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi Y., Hanaoka K., Goto K., Kondoh H. Lens-specific activity of the chicken delta 1-crystallin enhancer in the mouse. Int J Dev Biol. 1994 Jun;38(2):365–368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi Y., Hanaoka K., Hayasaka M., Katoh K., Kato Y., Okada T. S., Kondoh H. Embryonic stem cell-mediated transfer and correct regulation of the chicken delta-crystallin gene in developing mouse embryos. Development. 1988 Feb;102(2):259–269. doi: 10.1242/dev.102.2.259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tjian R., Maniatis T. Transcriptional activation: a complex puzzle with few easy pieces. Cell. 1994 Apr 8;77(1):5–8. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90227-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner T., Wirth J., Meyer J., Zabel B., Held M., Zimmer J., Pasantes J., Bricarelli F. D., Keutel J., Hustert E. Autosomal sex reversal and campomelic dysplasia are caused by mutations in and around the SRY-related gene SOX9. Cell. 1994 Dec 16;79(6):1111–1120. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90041-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitfield L. S., Lovell-Badge R., Goodfellow P. N. Rapid sequence evolution of the mammalian sex-determining gene SRY. Nature. 1993 Aug 19;364(6439):713–715. doi: 10.1038/364713a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wistow G. J., Piatigorsky J. Lens crystallins: the evolution and expression of proteins for a highly specialized tissue. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:479–504. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.002403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright E. M., Snopek B., Koopman P. Seven new members of the Sox gene family expressed during mouse development. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Feb 11;21(3):744–744. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.3.744. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Wetering M., Oosterwegel M., Dooijes D., Clevers H. Identification and cloning of TCF-1, a T lymphocyte-specific transcription factor containing a sequence-specific HMG box. EMBO J. 1991 Jan;10(1):123–132. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07928.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Wetering M., Oosterwegel M., van Norren K., Clevers H. Sox-4, an Sry-like HMG box protein, is a transcriptional activator in lymphocytes. EMBO J. 1993 Oct;12(10):3847–3854. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06063.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]