Abstract
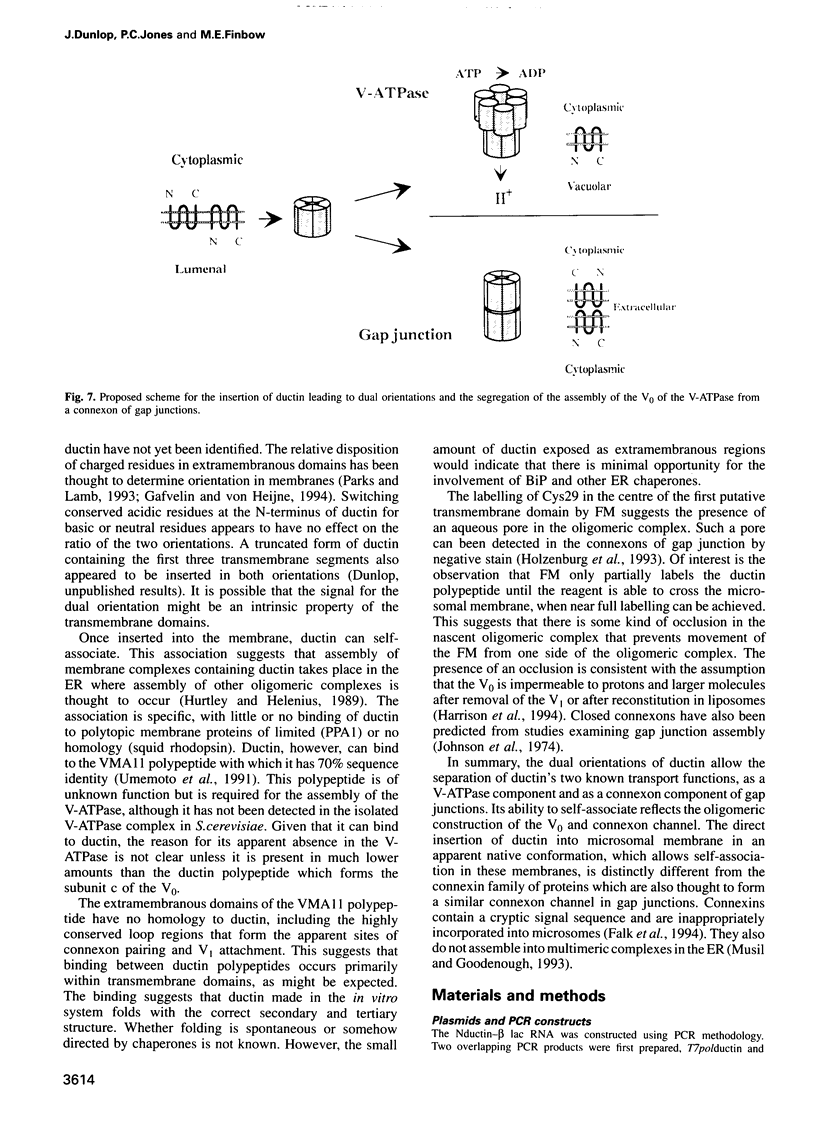
Ductin is a highly conserved and polytopic transmembrane protein which is the subunit c component of the vacuolar H(+)-ATPase (V-ATPase) and a component of a connexon channel of gap junctions. Previous studies have suggested that ductin in the V-ATPase has the opposite orientation of ductin in a connexon. Using an in vitro translation system coupled to microsomes derived from the endoplasmic reticulum, we show that ductin is co-translationally inserted into the membrane bilayer, suggesting a dependency on the signal recognition particle for synthesis. By attaching a C-terminal polypeptide derived from beta-lactamase and by using cysteine replacement coupled to chemical labelling, we show that ductin is inserted into the microsomal membrane in both orientations in similar proportions. In contrast, squid rhodopsin appears to be inserted in a single orientation. Changing conserved charged residues at the N-terminus of ductin does not affect the ratio of the two orientations. Once in the microsomal membrane, ductin assembles into an oligomeric complex which contains a pore accessible to a water-soluble probe, reminiscent of the ductin complex found in the V-ATPase and a connexon.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Apperson M., Jensen R. E., Suda K., Witte C., Yaffe M. P. A yeast protein, homologous to the proteolipid of the chromaffin granule proton-ATPase, is important for cell growth. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Apr 30;168(2):574–579. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)92359-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arai H., Terres G., Pink S., Forgac M. Topography and subunit stoichiometry of the coated vesicle proton pump. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 25;263(18):8796–8802. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falk M. M., Kumar N. M., Gilula N. B. Membrane insertion of gap junction connexins: polytopic channel forming membrane proteins. J Cell Biol. 1994 Oct;127(2):343–355. doi: 10.1083/jcb.127.2.343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finbow M. E., Eliopoulos E. E., Jackson P. J., Keen J. N., Meagher L., Thompson P., Jones P., Findlay J. B. Structure of a 16 kDa integral membrane protein that has identity to the putative proton channel of the vacuolar H(+)-ATPase. Protein Eng. 1992 Jan;5(1):7–15. doi: 10.1093/protein/5.1.7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finbow M. E., Goodwin S. F., Meagher L., Lane N. J., Keen J., Findlay J. B., Kaiser K. Evidence that the 16 kDa proteolipid (subunit c) of the vacuolar H(+)-ATPase and ductin from gap junctions are the same polypeptide in Drosophila and Manduca: molecular cloning of the Vha16k gene from Drosophila. J Cell Sci. 1994 Jul;107(Pt 7):1817–1824. doi: 10.1242/jcs.107.7.1817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finbow M. E., Harrison M., Jones P. Ductin--a proton pump component, a gap junction channel and a neurotransmitter release channel. Bioessays. 1995 Mar;17(3):247–255. doi: 10.1002/bies.950170311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finbow M. E., John S., Kam E., Apps D. K., Pitts J. D. Disposition and orientation of ductin (DCCD-reactive vacuolar H(+)-ATPase subunit) in mammalian membrane complexes. Exp Cell Res. 1993 Aug;207(2):261–270. doi: 10.1006/excr.1993.1192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finbow M. E., Pitts J. D. Is the gap junction channel--the connexon--made of connexin or ductin? J Cell Sci. 1993 Oct;106(Pt 2):463–471. doi: 10.1242/jcs.106.2.463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraga D., Fillingame R. H. Conserved polar loop region of Escherichia coli subunit c of the F1F0 H+-ATPase. Glutamine 42 is not absolutely essential, but substitutions alter binding and coupling of F1 to F0. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 25;264(12):6797–6803. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gafvelin G., von Heijne G. Topological "frustration" in multispanning E. coli inner membrane proteins. Cell. 1994 May 6;77(3):401–412. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90155-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girvin M. E., Fillingame R. H. Hairpin folding of subunit c of F1Fo ATP synthase: 1H distance measurements to nitroxide-derivatized aspartyl-61. Biochemistry. 1994 Jan 25;33(3):665–674. doi: 10.1021/bi00169a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girvin M. E., Fillingame R. H. Helical structure and folding of subunit c of F1F0 ATP synthase: 1H NMR resonance assignments and NOE analysis. Biochemistry. 1993 Nov 16;32(45):12167–12177. doi: 10.1021/bi00096a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein D. J., Finbow M. E., Andresson T., McLean P., Smith K., Bubb V., Schlegel R. Bovine papillomavirus E5 oncoprotein binds to the 16K component of vacuolar H(+)-ATPases. Nature. 1991 Jul 25;352(6333):347–349. doi: 10.1038/352347a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall M. D., Hoon M. A., Ryba N. J., Pottinger J. D., Keen J. N., Saibil H. R., Findlay J. B. Molecular cloning and primary structure of squid (Loligo forbesi) rhodopsin, a phospholipase C-directed G-protein-linked receptor. Biochem J. 1991 Feb 15;274(Pt 1):35–40. doi: 10.1042/bj2740035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison M. A., Jones P. C., Kim Y. I., Finbow M. E., Findlay J. B. Functional properties of a hybrid vacuolar H(+)-ATPase in Saccharomyces cells expressing the Nephrops 16-kDa proteolipid. Eur J Biochem. 1994 Apr 1;221(1):111–120. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1994.tb18719.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey W. R. Physiology of V-ATPases. J Exp Biol. 1992 Nov;172:1–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- High S., Dobberstein B. Mechanisms that determine the transmembrane disposition of proteins. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1992 Aug;4(4):581–586. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(92)90075-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holzenburg A., Jones P. C., Franklin T., Pali T., Heimburg T., Marsh D., Findlay J. B., Finbow M. E. Evidence for a common structure for a class of membrane channels. Eur J Biochem. 1993 Apr 1;213(1):21–30. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb17730.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurtley S. M., Helenius A. Protein oligomerization in the endoplasmic reticulum. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1989;5:277–307. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.05.110189.001425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R., Hammer M., Sheridan J., Revel J. P. Gap junction formation between reaggregated Novikoff hepatoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Nov;71(11):4536–4540. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.11.4536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones P. C., Harrison M. A., Kim Y. I., Finbow M. E., Findlay J. B. Structure and function of the proton-conducting sector of the vacuolar H(+)-ATPase. Biochem Soc Trans. 1994 Aug;22(3):805–809. doi: 10.1042/bst0220805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar N. M., Gilula N. B. Molecular biology and genetics of gap junction channels. Semin Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;3(1):3–16. doi: 10.1016/s1043-4682(10)80003-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leitch B., Finbow M. E. The gap junction-like form of a vacuolar proton channel component appears not to be an artifact of isolation: an immunocytochemical localization study. Exp Cell Res. 1990 Oct;190(2):218–226. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(90)90189-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel M., Moriyama Y., Hulmes J. D., Pan Y. C., Nelson H., Nelson N. cDNA sequence encoding the 16-kDa proteolipid of chromaffin granules implies gene duplication in the evolution of H+-ATPases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5521–5524. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miao G. H., Hong Z., Verma D. P. Topology and phosphorylation of soybean nodulin-26, an intrinsic protein of the peribacteroid membrane. J Cell Biol. 1992 Jul;118(2):481–490. doi: 10.1083/jcb.118.2.481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musil L. S., Goodenough D. A. Multisubunit assembly of an integral plasma membrane channel protein, gap junction connexin43, occurs after exit from the ER. Cell. 1993 Sep 24;74(6):1065–1077. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90728-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noumi T., Beltrán C., Nelson H., Nelson N. Mutational analysis of yeast vacuolar H(+)-ATPase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 1;88(5):1938–1942. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.5.1938. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parks G. D., Lamb R. A. Role of NH2-terminal positively charged residues in establishing membrane protein topology. J Biol Chem. 1993 Sep 5;268(25):19101–19109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryba N. J., Hoon M. A., Findlay J. B., Saibil H. R., Wilkinson J. R., Heimburg T., Marsh D. Rhodopsin mobility, structure, and lipid-protein interaction in squid photoreceptor membranes. Biochemistry. 1993 Apr 6;32(13):3298–3305. doi: 10.1021/bi00064a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skach W. R., Shi L. B., Calayag M. C., Frigeri A., Lingappa V. R., Verkman A. S. Biogenesis and transmembrane topology of the CHIP28 water channel at the endoplasmic reticulum. J Cell Biol. 1994 May;125(4):803–815. doi: 10.1083/jcb.125.4.803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tam L. Y., Loo T. W., Clarke D. M., Reithmeier R. A. Identification of an internal topogenic signal sequence in human Band 3, the erythrocyte anion exchanger. J Biol Chem. 1994 Dec 23;269(51):32542–32550. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umemoto N., Ohya Y., Anraku Y. VMA11, a novel gene that encodes a putative proteolipid, is indispensable for expression of yeast vacuolar membrane H(+)-ATPase activity. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 25;266(36):24526–24532. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter P., Gilmore R., Blobel G. Protein translocation across the endoplasmic reticulum. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):5–8. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90520-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolin S. L., Walter P. Signal recognition particle mediates a transient elongation arrest of preprolactin in reticulocyte lysate. J Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;109(6 Pt 1):2617–2622. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.6.2617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]