Abstract
The exocytotic release of potent hormones is a tightly controlled process. Its direct regulation without the involvement of second messengers would ensure rapid signal processing. In streptolysin O-permeabilized insulin-secreting cells, a preparation allowing dialysis of cytosolic macromolecules, activation of alpha 2-adrenergic receptors caused pertussis toxin-sensitive inhibition of calcium-induced exocytosis. This inhibition was mimicked very efficiently by the use of specific receptor-mimetic peptides, indicating the involvement of Gi and, to a lesser extent, of G(o). The regulation was exerted beyond the ATP-dependent step of exocytosis. In addition, low nanomolar amounts of pre-activated Gi/G(o) directly inhibited exocytosis. As transient overexpression of constitutively active mutants of G alpha i1, G alpha i2, G alpha i3 and G alpha o2 but not of G alpha o1 reproduced this regulation, the G alpha subunit alone is sufficient to induce inhibition. These results define exocytosis as an effector for heterotrimeric G-proteins and delineate the properties of the transduction pathway.
Full text
PDF
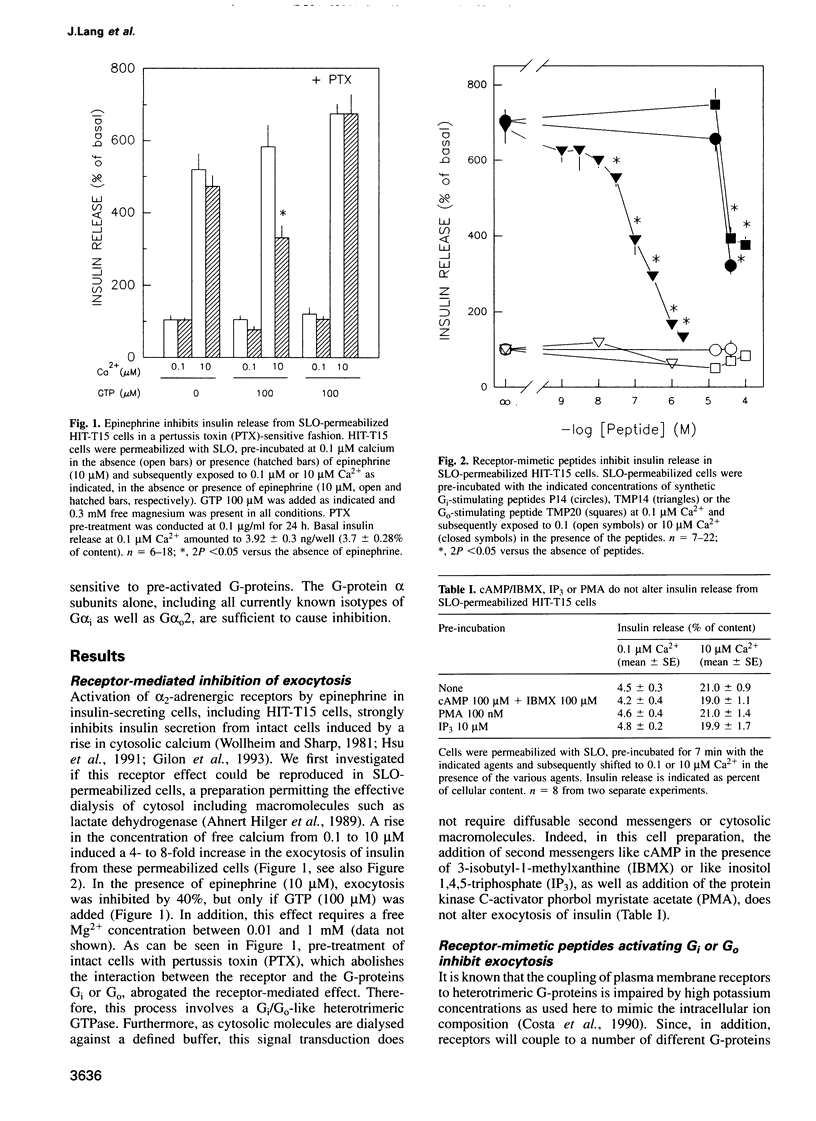
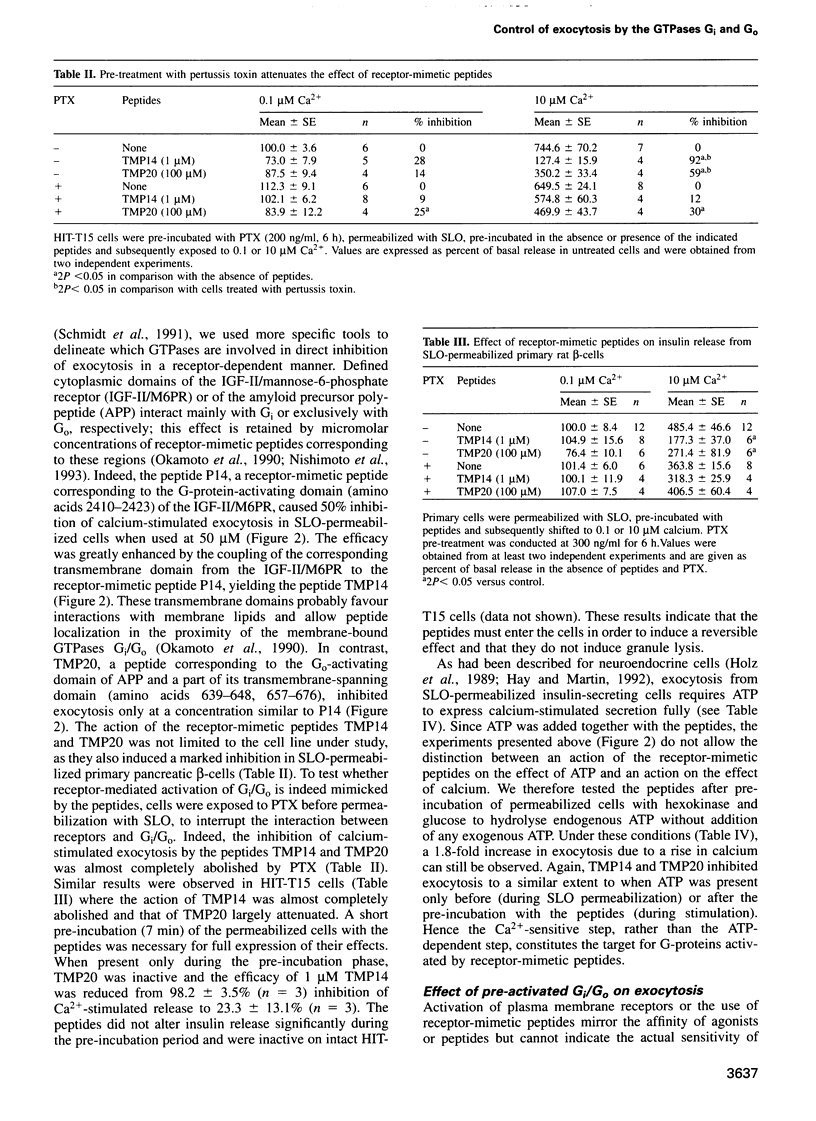
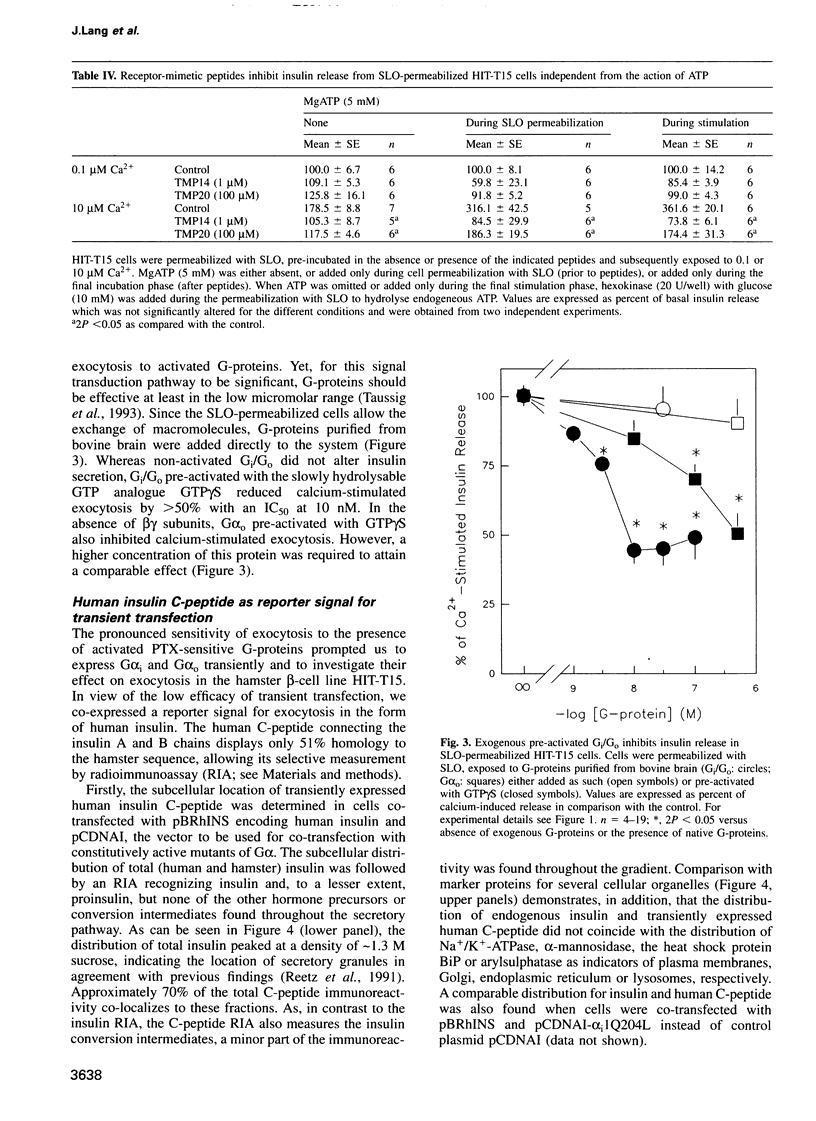
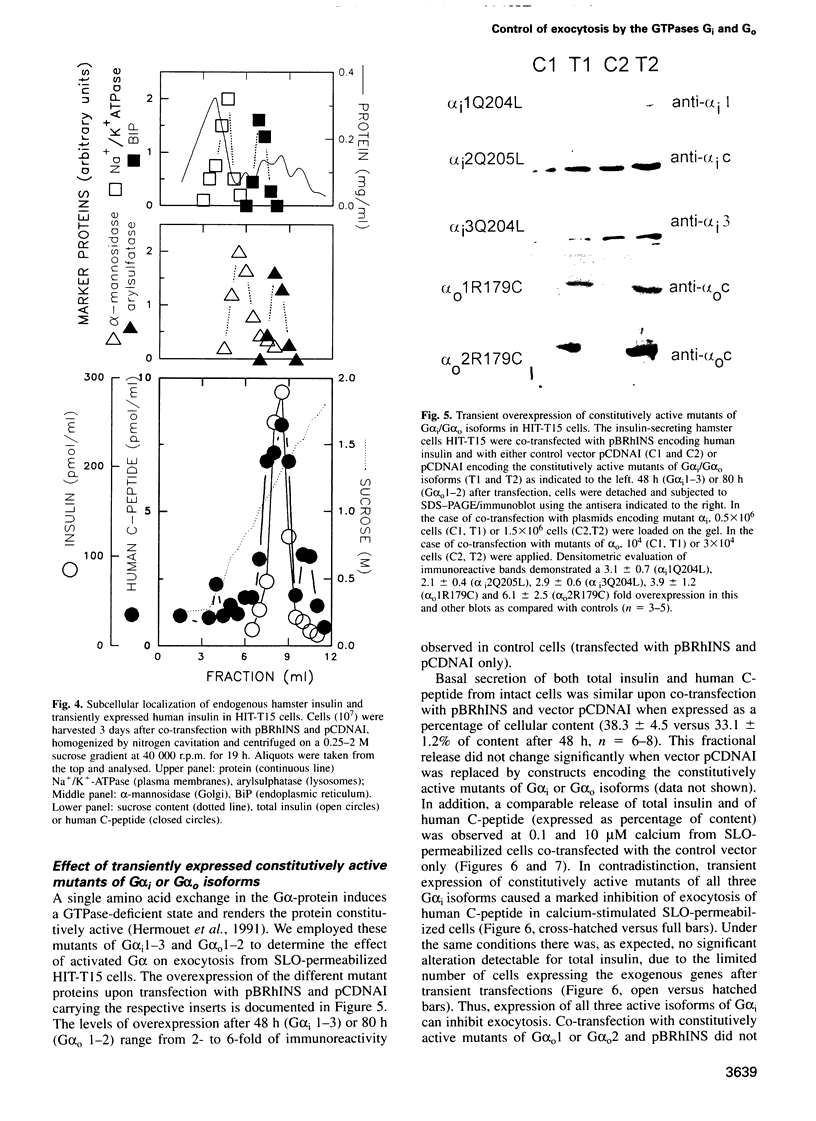
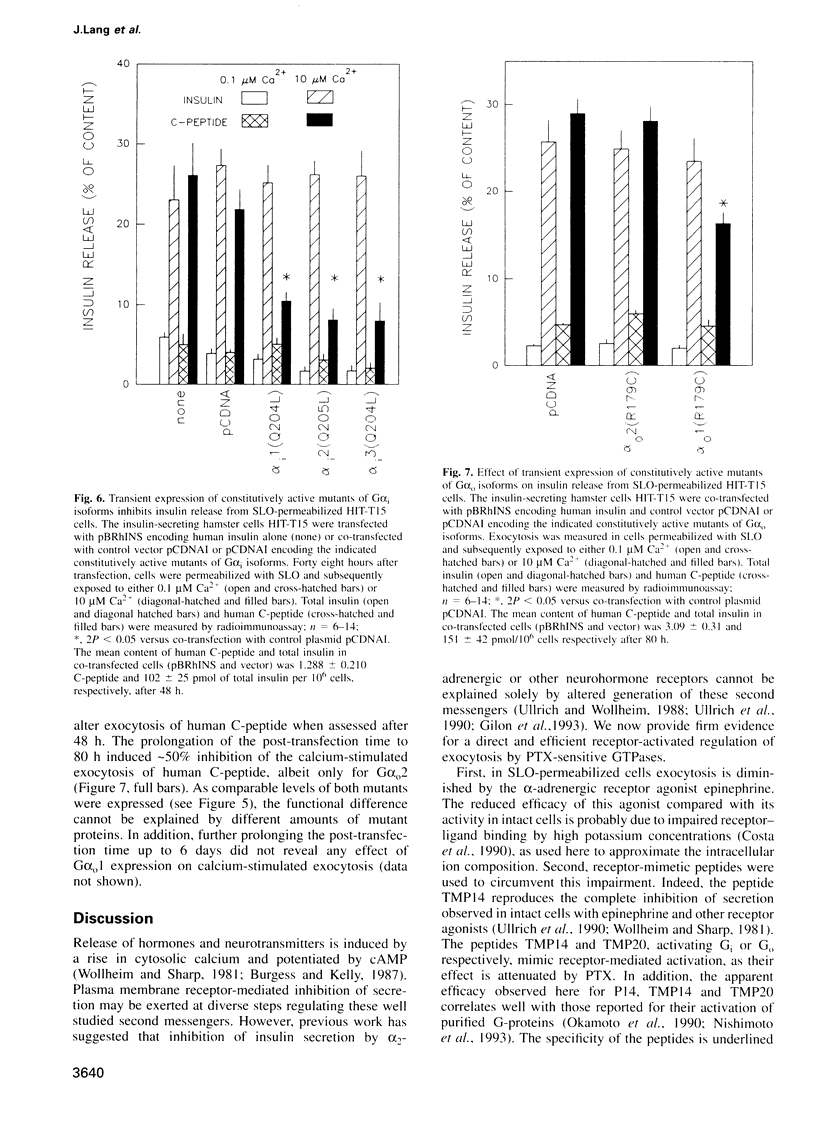




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahnert-Hilger G., Mach W., Föhr K. J., Gratzl M. Poration by alpha-toxin and streptolysin O: an approach to analyze intracellular processes. Methods Cell Biol. 1989;31:63–90. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)61602-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahnert-Hilger G., Schäfer T., Spicher K., Grund C., Schultz G., Wiedenmann B. Detection of G-protein heterotrimers on large dense core and small synaptic vesicles of neuroendocrine and neuronal cells. Eur J Cell Biol. 1994 Oct;65(1):26–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aridor M., Rajmilevich G., Beaven M. A., Sagi-Eisenberg R. Activation of exocytosis by the heterotrimeric G protein Gi3. Science. 1993 Dec 3;262(5139):1569–1572. doi: 10.1126/science.7504324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnbaumer L. Receptor-to-effector signaling through G proteins: roles for beta gamma dimers as well as alpha subunits. Cell. 1992 Dec 24;71(7):1069–1072. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(05)80056-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bomsel M., Mostov K. E. Possible role of both the alpha and beta gamma subunits of the heterotrimeric G protein, Gs, in transcytosis of the polymeric immunoglobulin receptor. J Biol Chem. 1993 Dec 5;268(34):25824–25835. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bomsel M., Mostov K. Role of heterotrimeric G proteins in membrane traffic. Mol Biol Cell. 1992 Dec;3(12):1317–1328. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.12.1317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess T. L., Kelly R. B. Constitutive and regulated secretion of proteins. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1987;3:243–293. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.03.110187.001331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colombo M. I., Mayorga L. S., Casey P. J., Stahl P. D. Evidence of a role for heterotrimeric GTP-binding proteins in endosome fusion. Science. 1992 Mar 27;255(5052):1695–1697. doi: 10.1126/science.1348148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colombo M. I., Mayorga L. S., Nishimoto I., Ross E. M., Stahl P. D. Gs regulation of endosome fusion suggests a role for signal transduction pathways in endocytosis. J Biol Chem. 1994 May 27;269(21):14919–14923. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa T., Lang J., Gless C., Herz A. Spontaneous association between opioid receptors and GTP-binding regulatory proteins in native membranes: specific regulation by antagonists and sodium ions. Mol Pharmacol. 1990 Mar;37(3):383–394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debuyser A., Drews G., Henquin J. C. Adrenaline inhibition of insulin release: role of cyclic AMP. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1991 Jul;78(3):179–186. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(91)90121-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson J. G., Kahn R. A., Lippincott-Schwartz J., Klausner R. D. Binding of ARF and beta-COP to Golgi membranes: possible regulation by a trimeric G protein. Science. 1991 Nov 22;254(5035):1197–1199. doi: 10.1126/science.1957170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferro-Novick S., Novick P. The role of GTP-binding proteins in transport along the exocytic pathway. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1993;9:575–599. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.09.110193.003043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer von Mollard G., Stahl B., Li C., Südhof T. C., Jahn R. Rab proteins in regulated exocytosis. Trends Biochem Sci. 1994 Apr;19(4):164–168. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(94)90278-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilon P., Shepherd R. M., Henquin J. C. Oscillations of secretion driven by oscillations of cytoplasmic Ca2+ as evidences in single pancreatic islets. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 25;268(30):22265–22268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomperts B. D. GE: a GTP-binding protein mediating exocytosis. Annu Rev Physiol. 1990;52:591–606. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.52.030190.003111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havel P. J., Taborsky G. J., Jr The contribution of the autonomic nervous system to changes of glucagon and insulin secretion during hypoglycemic stress. Endocr Rev. 1989 Aug;10(3):332–350. doi: 10.1210/edrv-10-3-332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay J. C., Martin T. F. Resolution of regulated secretion into sequential MgATP-dependent and calcium-dependent stages mediated by distinct cytosolic proteins. J Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;119(1):139–151. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.1.139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinemann C., von Rüden L., Chow R. H., Neher E. A two-step model of secretion control in neuroendocrine cells. Pflugers Arch. 1993 Jul;424(2):105–112. doi: 10.1007/BF00374600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermouet S., Merendino J. J., Jr, Gutkind J. S., Spiegel A. M. Activating and inactivating mutations of the alpha subunit of Gi2 protein have opposite effects on proliferation of NIH 3T3 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 1;88(23):10455–10459. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holz R. W., Bittner M. A., Peppers S. C., Senter R. A., Eberhard D. A. MgATP-independent and MgATP-dependent exocytosis. Evidence that MgATP primes adrenal chromaffin cells to undergo exocytosis. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 5;264(10):5412–5419. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holz R. W., Brondyk W. H., Senter R. A., Kuizon L., Macara I. G. Evidence for the involvement of Rab3A in Ca(2+)-dependent exocytosis from adrenal chromaffin cells. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 8;269(14):10229–10234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu W. H., Xiang H. D., Rajan A. S., Boyd A. E., 3rd Activation of alpha 2-adrenergic receptors decreases Ca2+ influx to inhibit insulin secretion in a hamster beta-cell line: an action mediated by a guanosine triphosphate-binding protein. Endocrinology. 1991 Feb;128(2):958–964. doi: 10.1210/endo-128-2-958. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikezu T., Okamoto T., Murayama Y., Okamoto T., Homma Y., Ogata E., Nishimoto I. Bidirectional regulation of c-fos promoter by an oncogenic gip2 mutant of G alpha i2. A novel implication of retinoblastoma gene product. J Biol Chem. 1994 Dec 16;269(50):31955–31961. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobsson G., Bean A. J., Scheller R. H., Juntti-Berggren L., Deeney J. T., Berggren P. O., Meister B. Identification of synaptic proteins and their isoform mRNAs in compartments of pancreatic endocrine cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Dec 20;91(26):12487–12491. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.26.12487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaziro Y., Itoh H., Kozasa T., Nakafuku M., Satoh T. Structure and function of signal-transducing GTP-binding proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:349–400. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang J., Boulay F., Li G., Wollheim C. B. Conserved transducer coupling but different effector linkage upon expression of the myeloid fMet-Leu-Phe receptor in insulin secreting cells. EMBO J. 1993 Jul;12(7):2671–2679. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05928.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang J. Purification and characterization of subforms of the guanine-nucleotide-binding proteins G alpha i and G alpha o. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Aug 15;183(3):687–692. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb21099.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leyte A., Barr F. A., Kehlenbach R. H., Huttner W. B. Multiple trimeric G-proteins on the trans-Golgi network exert stimulatory and inhibitory effects on secretory vesicle formation. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(13):4795–4804. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05585.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li G., Regazzi R., Balch W. E., Wollheim C. B. Stimulation of insulin release from permeabilized HIT-T15 cells by a synthetic peptide corresponding to the effector domain of the small GTP-binding protein rab3. FEBS Lett. 1993 Jul 26;327(2):145–149. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)80159-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson T., Arkhammar P., Rorsman P., Berggren P. O. Suppression of insulin release by galanin and somatostatin is mediated by a G-protein. An effect involving repolarization and reduction in cytoplasmic free Ca2+ concentration. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 15;264(2):973–980. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishimoto I., Okamoto T., Matsuura Y., Takahashi S., Okamoto T., Murayama Y., Ogata E. Alzheimer amyloid protein precursor complexes with brain GTP-binding protein G(o) Nature. 1993 Mar 4;362(6415):75–79. doi: 10.1038/362075a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor V., Augustine G. J., Betz H. Synaptic vesicle exocytosis: molecules and models. Cell. 1994 Mar 11;76(5):785–787. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90352-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto T., Katada T., Murayama Y., Ui M., Ogata E., Nishimoto I. A simple structure encodes G protein-activating function of the IGF-II/mannose 6-phosphate receptor. Cell. 1990 Aug 24;62(4):709–717. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90116-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prentki M., Janjic D., Wollheim C. B. Coordinated regulation of free Ca2+ by isolated organelles from a rat insulinoma. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):14054–14058. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reetz A., Solimena M., Matteoli M., Folli F., Takei K., De Camilli P. GABA and pancreatic beta-cells: colocalization of glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD) and GABA with synaptic-like microvesicles suggests their role in GABA storage and secretion. EMBO J. 1991 May;10(5):1275–1284. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08069.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman J. E. Mechanisms of intracellular protein transport. Nature. 1994 Nov 3;372(6501):55–63. doi: 10.1038/372055a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadoul K., Lang J., Montecucco C., Weller U., Regazzi R., Catsicas S., Wollheim C. B., Halban P. A. SNAP-25 is expressed in islets of Langerhans and is involved in insulin release. J Cell Biol. 1995 Mar;128(6):1019–1028. doi: 10.1083/jcb.128.6.1019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt A., Hescheler J., Offermanns S., Spicher K., Hinsch K. D., Klinz F. J., Codina J., Birnbaumer L., Gausepohl H., Frank R. Involvement of pertussis toxin-sensitive G-proteins in the hormonal inhibition of dihydropyridine-sensitive Ca2+ currents in an insulin-secreting cell line (RINm5F). J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 25;266(27):18025–18033. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seaquist E. R., Neal A. R., Shoger K. D., Walseth T. F., Robertson R. P. G-proteins and hormonal inhibition of insulin secretion from HIT-T15 cells and isolated rat islets. Diabetes. 1992 Nov;41(11):1390–1399. doi: 10.2337/diab.41.11.1390. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serafini T., Orci L., Amherdt M., Brunner M., Kahn R. A., Rothman J. E. ADP-ribosylation factor is a subunit of the coat of Golgi-derived COP-coated vesicles: a novel role for a GTP-binding protein. Cell. 1991 Oct 18;67(2):239–253. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90176-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storrie B., Madden E. A. Isolation of subcellular organelles. Methods Enzymol. 1990;182:203–225. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)82018-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stow J. L., de Almeida J. B., Narula N., Holtzman E. J., Ercolani L., Ausiello D. A. A heterotrimeric G protein, G alpha i-3, on Golgi membranes regulates the secretion of a heparan sulfate proteoglycan in LLC-PK1 epithelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1991 Sep;114(6):1113–1124. doi: 10.1083/jcb.114.6.1113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taussig R., Iñiguez-Lluhi J. A., Gilman A. G. Inhibition of adenylyl cyclase by Gi alpha. Science. 1993 Jul 9;261(5118):218–221. doi: 10.1126/science.8327893. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taussig R., Tang W. J., Hepler J. R., Gilman A. G. Distinct patterns of bidirectional regulation of mammalian adenylyl cyclases. J Biol Chem. 1994 Feb 25;269(8):6093–6100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toselli M., Lang J., Costa T., Lux H. D. Direct modulation of voltage-dependent calcium channels by muscarinic activation of a pertussis toxin-sensitive G-protein in hippocampal neurons. Pflugers Arch. 1989 Dec;415(3):255–261. doi: 10.1007/BF00370874. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukamoto T., Toyama R., Itoh H., Kozasa T., Matsuoka M., Kaziro Y. Structure of the human gene and two rat cDNAs encoding the alpha chain of GTP-binding regulatory protein Go: two different mRNAs are generated by alternative splicing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 15;88(8):2974–2978. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.8.2974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich S., Prentki M., Wollheim C. B. Somatostatin inhibition of Ca2(+)-induced insulin secretion in permeabilized HIT-T15 cells. Biochem J. 1990 Aug 15;270(1):273–276. doi: 10.1042/bj2700273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich S., Wollheim C. B. GTP-dependent inhibition of insulin secretion by epinephrine in permeabilized RINm5F cells. Lack of correlation between insulin secretion and cyclic AMP levels. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 25;263(18):8615–8620. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vitale N., Mukai H., Rouot B., Thiersé D., Aunis D., Bader M. F. Exocytosis in chromaffin cells. Possible involvement of the heterotrimeric GTP-binding protein G(o). J Biol Chem. 1993 Jul 15;268(20):14715–14723. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vitale N., Thiersé D., Aunis D., Bader M. F. Exocytosis in chromaffin cells: evidence for a MgATP-independent step that requires a pertussis toxin-sensitive GTP-binding protein. Biochem J. 1994 May 15;300(Pt 1):217–227. doi: 10.1042/bj3000217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wollheim C. B., Meda P., Halban P. A. Establishment and culture of insulin-secreting beta cell lines. Methods Enzymol. 1990;192:223–235. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)92072-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wollheim C. B., Meda P., Halban P. A. Isolation of pancreatic islets and primary culture of the intact microorgans or of dispersed islet cells. Methods Enzymol. 1990;192:188–223. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)92071-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wollheim C. B., Sharp G. W. Regulation of insulin release by calcium. Physiol Rev. 1981 Oct;61(4):914–973. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1981.61.4.914. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yatani A., Codina J., Brown A. M., Birnbaumer L. Direct activation of mammalian atrial muscarinic potassium channels by GTP regulatory protein Gk. Science. 1987 Jan 9;235(4785):207–211. doi: 10.1126/science.2432660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]