Abstract
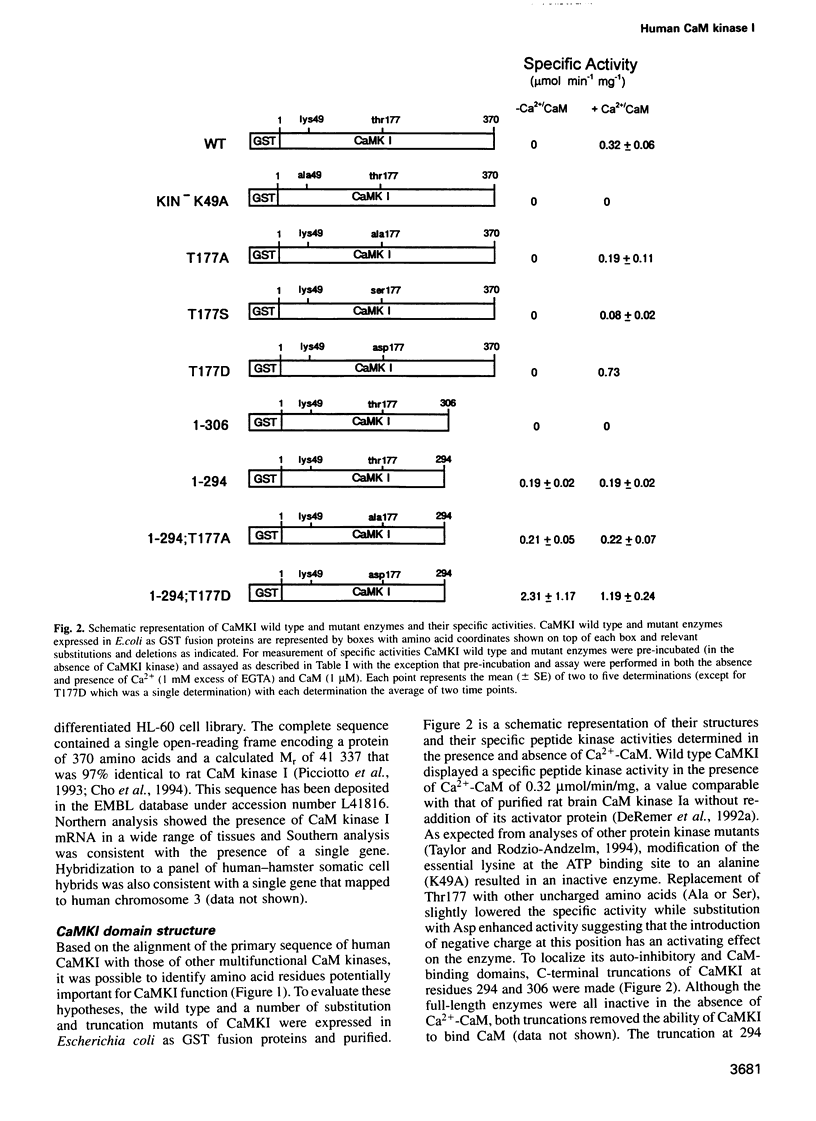
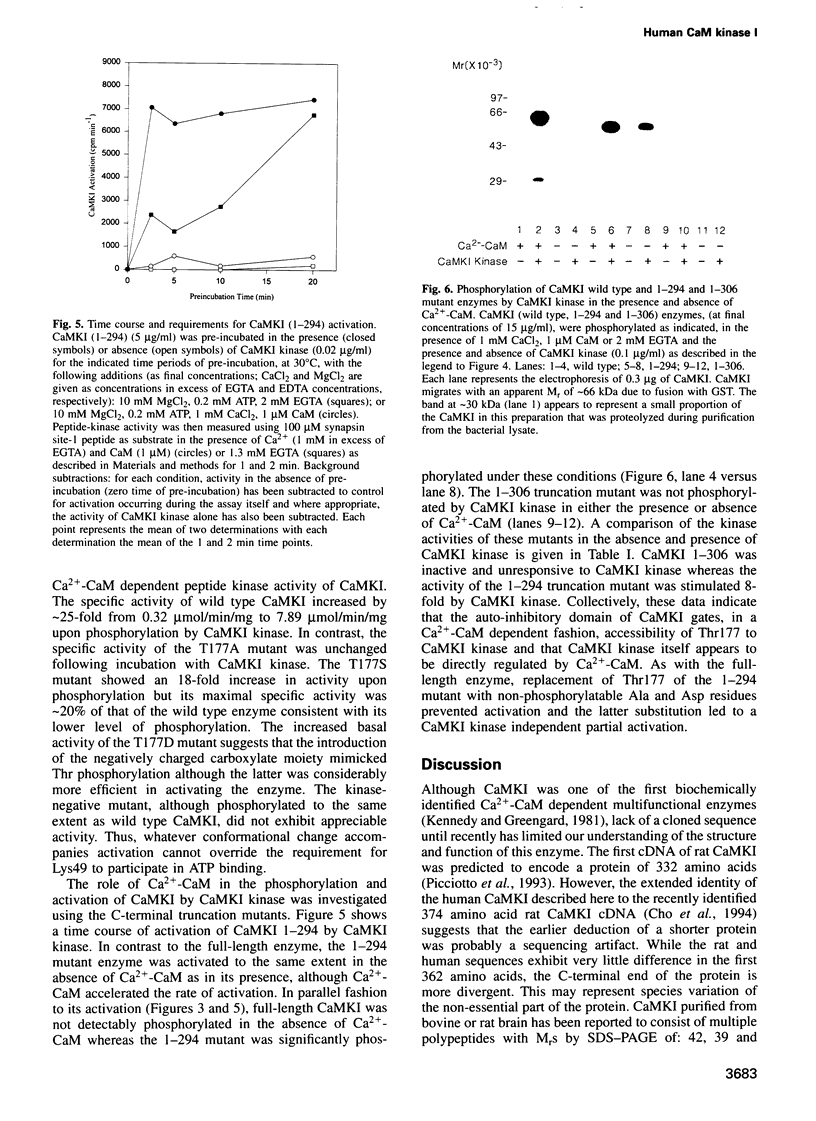
Human Ca(2+)-calmodulin (CaM) dependent protein kinase I (CaMKI) encodes a 370 amino acid protein with a calculated M(r) of 41,337. The 1.5 kb CaMKI mRNA is expressed in many different human tissues and is the product of a single gene located on human chromosome 3. CaMKI 1-306, was unable to bind Ca(2+)-CaM and was completely inactive thereby defining an essential component of the CaM-binding domain to residues C-terminal to 306. CaMKI 1-294 did not bind CaM but was fully active in the absence of Ca(2+)-CaM, indicating that residues 295-306 are sufficient to maintain CaMKI in an auto-inhibited state. CaMKI was phosphorylated on Thr177 and its activity enhanced approximately 25-fold by CaMKI kinase in a Ca(2+)-CaM dependent manner. Replacement of Thr177 with Ala or Asp prevented both phosphorylation and activation by CaMKI kinase and the latter replacement also led to partial activation in the absence of CaMKI kinase. Whereas CaMKI 1-306 was unresponsive to CaMKI kinase, the 1-294 mutant was phosphorylated and activated by CaMKI kinase in both the presence and absence of Ca(2+)-CaM although at a faster rate in its presence. These results indicate that the auto-inhibitory domain in CaMKI gates, in a Ca(2+)-CaM dependent fashion, accessibility of both substrates to the substrate binding cleft and CaMKI kinase to Thr177. Additionally, CaMKI kinase responds directly to Ca(2+)-CaM with increased activity.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brickey D. A., Bann J. G., Fong Y. L., Perrino L., Brennan R. G., Soderling T. R. Mutational analysis of the autoinhibitory domain of calmodulin kinase II. J Biol Chem. 1994 Nov 18;269(46):29047–29054. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cho F. S., Phillips K. S., Bogucki B., Weaver T. E. Characterization of a rat cDNA clone encoding calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase I. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1994 Oct 20;1224(1):156–160. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(94)90123-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colbran R. J., Fong Y. L., Schworer C. M., Soderling T. R. Regulatory interactions of the calmodulin-binding, inhibitory, and autophosphorylation domains of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 5;263(34):18145–18151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cruzalegui F. H., Kapiloff M. S., Morfin J. P., Kemp B. E., Rosenfeld M. G., Means A. R. Regulation of intrasteric inhibition of the multifunctional calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 15;89(24):12127–12131. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.24.12127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cruzalegui F. H., Means A. R. Biochemical characterization of the multifunctional Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase type IV expressed in insect cells. J Biol Chem. 1993 Dec 15;268(35):26171–26178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Bondt H. L., Rosenblatt J., Jancarik J., Jones H. D., Morgan D. O., Kim S. H. Crystal structure of cyclin-dependent kinase 2. Nature. 1993 Jun 17;363(6430):595–602. doi: 10.1038/363595a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeRemer M. F., Saeli R. J., Brautigan D. L., Edelman A. M. Ca(2+)-calmodulin-dependent protein kinases Ia and Ib from rat brain. II. Enzymatic characteristics and regulation of activities by phosphorylation and dephosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 5;267(19):13466–13471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeRemer M. F., Saeli R. J., Edelman A. M. Ca(2+)-calmodulin-dependent protein kinases Ia and Ib from rat brain I. Identification, purification, and structural comparisons. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 5;267(19):13460–13465. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Didsbury J. R., Snyderman R. Molecular cloning of a new human G protein. Evidence for two Gi alpha-like protein families. FEBS Lett. 1987 Jul 13;219(1):259–263. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)81228-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman A. M., Blumenthal D. K., Krebs E. G. Protein serine/threonine kinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:567–613. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fong Y. L., Soderling T. R. Studies on the regulatory domain of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II. Functional analyses of arginine 283 using synthetic inhibitory peptides and site-directed mutagenesis of the alpha subunit. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 5;265(19):11091–11097. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara T., Ohsako S., Yamauchi T. Studies on the regulatory domain of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II by expression of mutated cDNAs in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 5;266(25):16401–16408. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanks S. K., Quinn A. M. Protein kinase catalytic domain sequence database: identification of conserved features of primary structure and classification of family members. Methods Enzymol. 1991;200:38–62. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)00126-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson P. I., Kapiloff M. S., Lou L. L., Rosenfeld M. G., Schulman H. Expression of a multifunctional Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase and mutational analysis of its autoregulation. Neuron. 1989 Jul;3(1):59–70. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90115-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haribabu B., Snyderman R. Identification of additional members of human G-protein-coupled receptor kinase multigene family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Oct 15;90(20):9398–9402. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.20.9398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito M., Guerriero V., Jr, Chen X. M., Hartshorne D. J. Definition of the inhibitory domain of smooth muscle myosin light chain kinase by site-directed mutagenesis. Biochemistry. 1991 Apr 9;30(14):3498–3503. doi: 10.1021/bi00228a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito T., Yokokura H., Nairn A. C., Nimura Y., Hidaka H. Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase V and I may form a family of isoforms. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994 Jun 30;201(3):1561–1566. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.1882. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kameshita I., Fujisawa H. Autophosphorylation of calmodulin-dependent protein kinase IV from rat cerebral cortex. J Biochem. 1993 May;113(5):583–590. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a124087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy M. B., Greengard P. Two calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinases, which are highly concentrated in brain, phosphorylate protein I at distinct sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):1293–1297. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.1293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knighton D. R., Zheng J. H., Ten Eyck L. F., Ashford V. A., Xuong N. H., Taylor S. S., Sowadski J. M. Crystal structure of the catalytic subunit of cyclic adenosine monophosphate-dependent protein kinase. Science. 1991 Jul 26;253(5018):407–414. doi: 10.1126/science.1862342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. C., Edelman A. M. A protein activator of Ca(2+)-calmodulin-dependent protein kinase Ia. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 21;269(3):2158–2164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. C., Kwon Y. G., Lawrence D. S., Edelman A. M. A requirement of hydrophobic and basic amino acid residues for substrate recognition by Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase Ia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jul 5;91(14):6413–6417. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.14.6413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall C. J. Signal transduction. Hot lips and phosphorylation of protein kinases. Nature. 1994 Feb 24;367(6465):686–686. doi: 10.1038/367686a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meador W. E., Means A. R., Quiocho F. A. Modulation of calmodulin plasticity in molecular recognition on the basis of x-ray structures. Science. 1993 Dec 10;262(5140):1718–1721. doi: 10.1126/science.8259515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mochizuki H., Ito T., Hidaka H. Purification and characterization of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase V from rat cerebrum. J Biol Chem. 1993 Apr 25;268(12):9143–9147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nairn A. C., Greengard P. Purification and characterization of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase I from bovine brain. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 25;262(15):7273–7281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okuno S., Kitani T., Fujisawa H. Purification and characterization of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase IV kinase from rat brain. J Biochem. 1994 Oct;116(4):923–930. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a124617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orr J. W., Newton A. C. Requirement for negative charge on "activation loop" of protein kinase C. J Biol Chem. 1994 Nov 4;269(44):27715–27718. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne M. E., Fong Y. L., Ono T., Colbran R. J., Kemp B. E., Soderling T. R., Means A. R. Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II. Characterization of distinct calmodulin binding and inhibitory domains. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 25;263(15):7190–7195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson R. B., Woodgett J. R., Cohen P., Kemp B. E. Substrate specificity of a multifunctional calmodulin-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 25;260(27):14471–14476. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson G. L. A simplification of the protein assay method of Lowry et al. which is more generally applicable. Anal Biochem. 1977 Dec;83(2):346–356. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picciotto M. R., Cohn J. A., Bertuzzi G., Greengard P., Nairn A. C. Phosphorylation of the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 25;267(18):12742–12752. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picciotto M. R., Czernik A. J., Nairn A. C. Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase I. cDNA cloning and identification of autophosphorylation site. J Biol Chem. 1993 Dec 15;268(35):26512–26521. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polymeropoulos M. H., Xiao H., Glodek A., Gorski M., Adams M. D., Moreno R. F., Fitzgerald M. G., Venter J. C., Merril C. R. Chromosomal assignment of 46 brain cDNAs. Genomics. 1992 Mar;12(3):492–496. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90439-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheng M., Thompson M. A., Greenberg M. E. CREB: a Ca(2+)-regulated transcription factor phosphorylated by calmodulin-dependent kinases. Science. 1991 Jun 7;252(5011):1427–1430. doi: 10.1126/science.1646483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. B., Johnson K. S. Single-step purification of polypeptides expressed in Escherichia coli as fusions with glutathione S-transferase. Gene. 1988 Jul 15;67(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stokoe D., Caudwell B., Cohen P. T., Cohen P. The substrate specificity and structure of mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase-activated protein kinase-2. Biochem J. 1993 Dec 15;296(Pt 3):843–849. doi: 10.1042/bj2960843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugita R., Mochizuki H., Ito T., Yokokura H., Kobayashi R., Hidaka H. Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase kinase cascade. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994 Aug 30;203(1):694–701. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.2238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor S. S., Radzio-Andzelm E. Three protein kinase structures define a common motif. Structure. 1994 May 15;2(5):345–355. doi: 10.1016/s0969-2126(00)00036-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokumitsu H., Brickey D. A., Glod J., Hidaka H., Sikela J., Soderling T. R. Activation mechanisms for Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase IV. Identification of a brain CaM-kinase IV kinase. J Biol Chem. 1994 Nov 18;269(46):28640–28647. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldmann R., Hanson P. I., Schulman H. Multifunctional Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase made Ca2+ independent for functional studies. Biochemistry. 1990 Feb 20;29(7):1679–1684. doi: 10.1021/bi00459a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waxham M. N., Aronowski J., Westgate S. A., Kelly P. T. Mutagenesis of Thr-286 in monomeric Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II eliminates Ca2+/calmodulin-independent activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(4):1273–1277. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.4.1273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang F., Strand A., Robbins D., Cobb M. H., Goldsmith E. J. Atomic structure of the MAP kinase ERK2 at 2.3 A resolution. Nature. 1994 Feb 24;367(6465):704–711. doi: 10.1038/367704a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]