Abstract
The control of self-renewal and differentiation of neural stem and progenitor cells is a crucial issue in stem cell and cancer biology. Drosophila type II neuroblast lineages are prone to developing impaired neuroblast homeostasis if the limited self-renewing potential of intermediate neural progenitors (INPs) is unrestrained. Here, we demonstrate that Drosophila SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling Brahma (Brm) complex functions cooperatively with another chromatin remodeling factor, Histone deacetylase 3 (HDAC3) to suppress the formation of ectopic type II neuroblasts. We show that multiple components of the Brm complex and HDAC3 physically associate with Earmuff (Erm), a type II-specific transcription factor that prevents dedifferentiation of INPs into neuroblasts. Consistently, the predicted Erm-binding motif is present in most of known binding loci of Brm. Furthermore, brm and hdac3 genetically interact with erm to prevent type II neuroblast overgrowth. Thus, the Brm-HDAC3-Erm repressor complex suppresses dedifferentiation of INPs back into type II neuroblasts.
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.01906.001
Research organism: D. melanogaster
eLife digest
Stem cells show great promise for repairing damaged tissue, and maybe even generating new organs, but stem cell therapies will only be successful if researchers can understand and control the behaviour of stem cells in the lab. Neural stem cells or ‘neuroblasts’ from the brains of larval fruit flies have become a popular model for studying these processes, and one type of neuroblast—known as a ‘type II’ neuroblast—is similar to mammalian neural stem cells in many ways.
When type II neuroblasts divide, they generate another neuroblast and a second cell called an intermediate neural progenitor (INP) cell. This progenitor cell then matures and undergoes a limited number of divisions to generate more INP cells and cells called ganglion mother cells. The process by which stem cells and INP cells become specific types of cells is known as differentiation. However, under certain circumstances, the INP cells can undergo the opposite process, which is called dedifferentiation, and become ‘ectopic neuroblasts’. This can give rise to tumors, so cells must employ a mechanism to prevent dedifferentiation. Researchers have known that a protein specifically expressed in INP cells called Earmuff is involved in this process, but many of the details have remained hidden.
Now, Koe et al. have discovered that a multi-protein complex containing Earmuff and a number of other proteins—Brahma and HDAC3—have important roles in preventing dedifferentiation. All three proteins are involved in different aspects of gene expression: Earmuff is a transcription factor that controls the process by which the genes in DNA are transcribed to make molecules of messenger RNA; Brahma and HDAC3 are both involved in a process called chromatin remodeling. The DNA inside cells is packaged into a compact structure known as chromatin, and chromatin remodeling involves partially unpacking this structure so that transcription factors and other proteins can have access to the DNA.
Koe et al. also showed that Earmuff, Brahma and HDAC3 combine to form a complex that prevents dedifferentiation. An immediate priority is to identify those genes whose expression is regulated by this complex in order to prevent dedifferentiation.
Introduction
The mechanism by which self-renewal and differentiation are balanced is a crucial issue in stem cell and cancer biology. The neural stem cells, or neuroblasts, of the Drosophila larval brain have emerged as a new model for studying stem cell self-renewal and tumorigenesis. In Drosophila larval central brains, there are at least two classes of neuroblast lineages (Bello et al., 2008; Boone and Doe, 2008; Bowman et al., 2008). A type I neuroblast that expresses both Deadpan (Dpn) and Asense (Ase) divides asymmetrically to generate a self-renewing neuroblast and a ganglion mother cell (GMC), which is committed to a differentiation pathway. In contrast, a type II neuroblast that expresses Dpn, but not Ase, divides asymmetrically to generate a neuroblast and a transient amplifying cell known as an intermediate neural progenitor (INP) (Bello et al., 2008; Boone and Doe, 2008; Bowman et al., 2008). Following maturation, the INP undergoes a limited number of asymmetric divisions to self-renew and to produce multiple GMCs (Weng et al., 2010). In both types of lineages, asymmetric division is dependent on apically localized proteins, including atypical protein kinase C (aPKC); basally localized proteins, such as Miranda and Numb; as well as several cell cycle regulators (Chang et al., 2012; Gonzalez, 2013). The failure of asymmetric division in either type of neuroblast can result in the hyperproliferation of these cells and the induction of brain tumors (Caussinus and Gonzalez, 2005; Wang et al., 2006, 2007, 2009, 2011; Lee et al., 2006a, 2006b; Cabernard and Doe, 2009; Chabu and Doe, 2009, 2011; Chang et al., 2010).
The type II neuroblast lineage is highly analogous to the mammalian neural stem cell lineages, because both involve transient amplifying cells that are used to expand the progenitor cell population. It is prone to impaired neuroblast homeostasis, if the limited self-renewing potential of INPs is unrestrained. Brain tumor (Brat) and the Notch antagonist Numb function cooperatively to ensure that immature INPs undergo maturation and commit to the INP fate (Boone and Doe, 2008; Bowman et al., 2008). Notch signaling maintains neuroblast identity and its overactivation leads to dedifferentiation of INPs to ectopic neuroblasts (Wang et al., 2006; Bowman et al., 2008; Weng et al., 2010). A small number of transcription factors have been implicated in the control of INP identity and proliferative potential (Carney et al., 2012). Specifically expressed in INPs, a Zinc-finger transcription factor Earmuff (Erm) plays a critical role in maintaining the restricted developmental potential of the INPs (Weng et al., 2010). The Ets transcription factor Pointed (PntP1) is specifically expressed in type II neuroblasts and INPs and is both necessary and sufficient for the suppression of Ase in type II neuroblasts and the generation of INPs (Zhu et al., 2011). Prospero that is basally localized in mitotic type I neuroblast, but absent from type II neuroblasts, triggers cell cycle exit and GMC differentiation (Bello et al., 2006; Betschinger et al., 2006; Choksi et al., 2006; Lee et al., 2006c). However, the underlying mechanism by which Erm prevents dedifferentiation is poorly understood.
ATP-dependent chromatin-remodeling factors are critical for the expression of the eukaryotic genome. Four major classes of ATP-dependent chromatin remodeling complexes have been identified, including the extensively studied SWI/SNF complexes (Narlikar et al., 2002; Reisman et al., 2009). The mammalian SWI/SNF complex termed the Brahma (Brm or Brg1) complex regulates critical cellular processes such as differentiation and cell cycle arrest (Klochendler-Yeivin et al., 2002). Drosophila Brm complex acts similarly to control cell proliferation (Brumby et al., 2002) and differentiation (Marenda et al., 2003). A genome-wide RNAi study in Drosophila neuroblasts showed that the knockdown of genes encoding several core subunits of the SWI/SNF Brahma (Brm) remodeling complex may lead to neuroblast overproliferation (Neumuller et al., 2011). However, the precise role of the Brm remodeling complex during neuroblast self-renewal and the mechanism that underlying underlies this effect mechanism remain to be elucidated. Besides ATP-dependent chromatin remodeling complexes, the other major class of chromatin remodelers is histone modifiers. Histone deacetylases (HDACs) remove acetyl groups from the tails of core histones in the nucleosome and are often associated with transcriptional co-repressors (Dokmanovic et al., 2007). However, despite the critical role for histone modifiers in transcriptional regulation, it is unknown whether histone modifications play any role in Drosophila larval brain neuroblasts.
In this study, we report the critical role of a central chromatin remodeler, the Brm complex in preventing the formation of ectopic neuroblasts in type II lineages. We show that another chromatin remodeling factor, HDAC3 functions cooperatively with the Brm complex to suppress the formation of ectopic type II neuroblasts. Interestingly, multiple components of the Brm complex and HDAC3 physically associate with Erm. brm and hdac3 interact genetically with erm to prevent type II neuroblast overgrowth. Thus, the Brm-HDAC3-Erm complex is a novel repressor complex that suppresses dedifferentiation of INPs back into type II neuroblasts.
Results
The Brm complex suppresses the formation of ectopic neuroblasts in type II neuroblast lineages
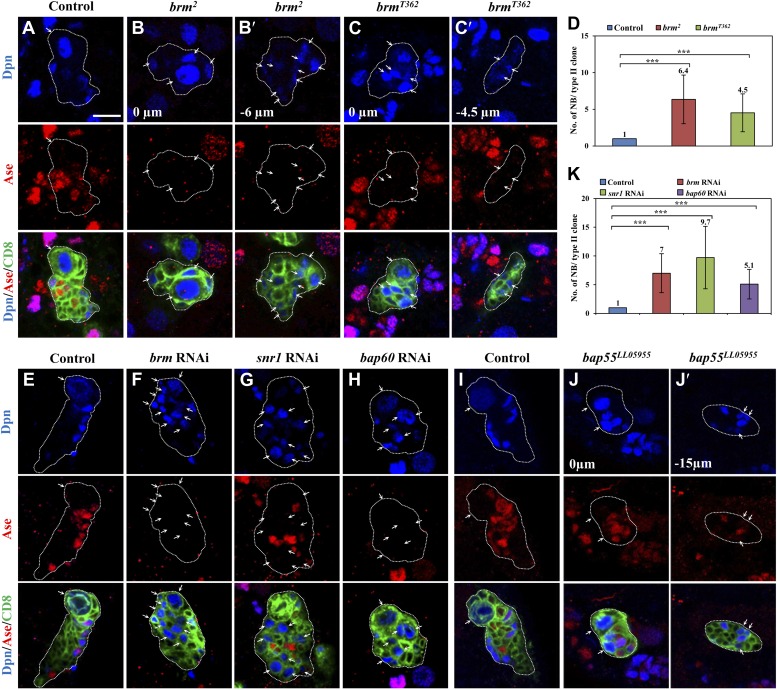
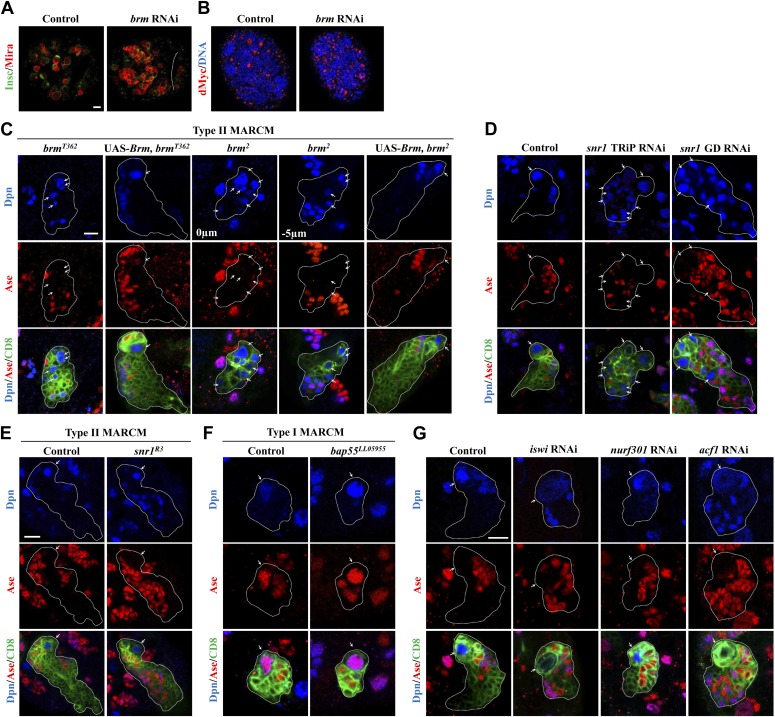
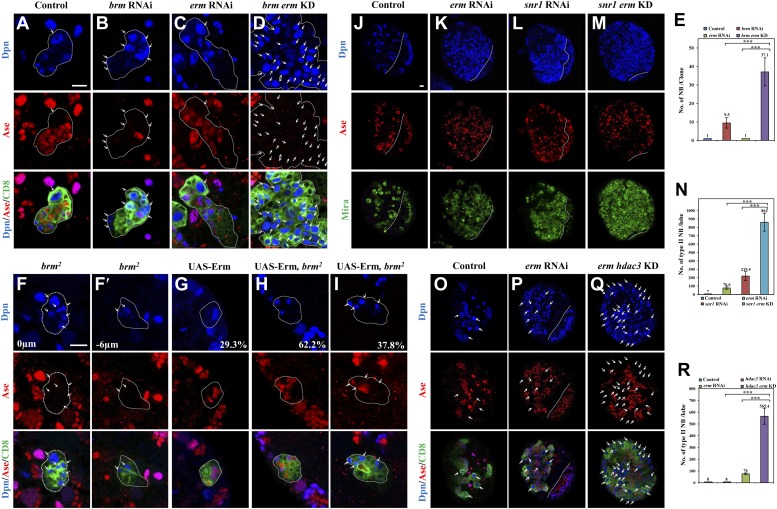
We independently identified brm from a RNA interference (RNAi) screen in which brm RNAi knockdown in larval brains resulted in an increase of Miranda-positive neuroblast-like cells in larval central brains (Figure 1—figure supplement 1A), showing a phenotype similar to one previously reported (Neumuller et al., 2011). Brm is a DNA-dependent ATPase and a major component of a multi-protein SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling complex, which controls gene expression by altering chromatin structure (Klochendler-Yeivin et al., 2002). The number of cells expressing the proto-oncogene dMyc was significantly increased upon brm RNAi knockdown (Figure 1—figure supplement 1B), consistent with the neuroblast overgrowth phenotype. To determine the function of Brm in different neuroblast lineages, we generated MARCM clones in two brm loss-of-function alleles. Type I wild-type (wt) clones always contained one neuroblast that is positive for both Dpn and Ase (data not shown). Similarly, only one neuroblast was present in both amorphic brm2 and hypomorphic brmT362 type I clones (data not shown), indicating that Brm has no significant effect on type I neuroblast numbers. Each wt type II MARCM clone also possessed only one neuroblast that was positive for Dpn, but negative for Ase (Figure 1A; n = 25). Unlike the wt control, 6.4 ± 3.3 and 4.5 ± 2.6 ectopic neuroblasts were observed in brm2 (Figure 1B,B′,D; 88.6%, n = 34) brmT362 (Figure 1C,C′,D; 75.9%, n = 58) type II clones, respectively. These phenotypes in brm alleles could be rescued by expressing a wild-type brm transgene (Figure 1—figure supplement 1C). Consistent with phenotypes in brm clones, knockdown of brm by RNAi using a type II neuroblast-specific neuroblast driver worniu (wor)-Gal4, ase-Gal80 (henceforth referred to as ‘type II driver’; ‘Materials and methods’) was sufficient to produce ectopic neuroblasts in 97.4% of type II neuroblast lineages (Figure 1F,K; 7 ± 3.4 neuroblasts/lineage, n = 38), while each control clone always has one neuroblast (Figure 1E,K; n = 80). We therefore conclude that Brm suppresses the formation of ectopic neuroblasts in type II neuroblast lineages.
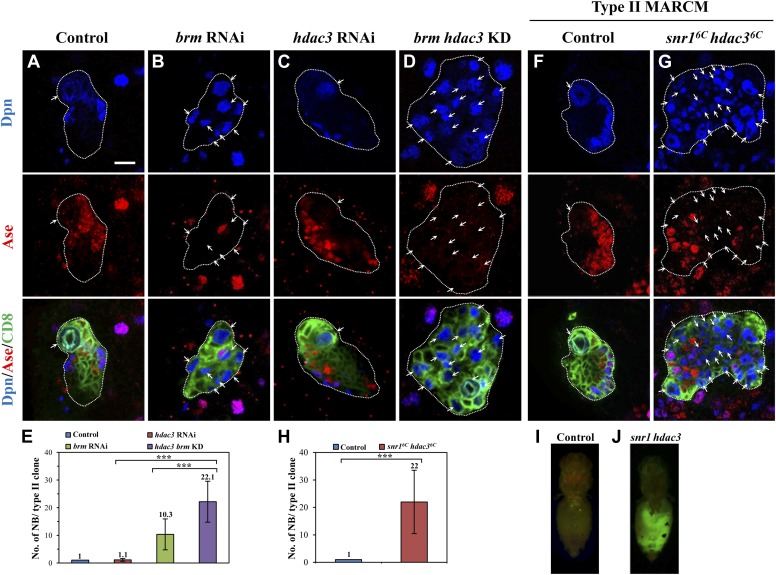
Figure 1. The Brm complex suppresses the formation of ectopic type II neuroblasts.
(A–C) Type II MARCM clones of control (the MARCM driver; D), brm2 (B, B′) and brmT362 (C, C′) were labeled with Dpn (blue), Ase (red) and CD8::GFP (green). (D) Quantification of neuroblast number per type II MARCM clone for A–C. (E–H) Type II neuroblast lineage from control (‘the type II driver’: wor-Gal4 ase-Gal80; E), brm knockdown (F), snr1 knockdown (108599 KK; G), and bap60 knockdown (H) were labeled with Dpn (blue), Ase (red) and CD8 (green). (I–J′) type II MARCM clone of control (I) and bap55LL05955 (J, J′) were labeled with Dpn (blue), Ase (red) and CD8 (green). (K) Quantification of neuroblast number per type II lineage for E–I. Arrows indicate neuroblasts. Clones are marked by CD8::GFP and indicated by white dotted line. Scale bars, 10 µm. *** indicates p<0.001.
Figure 1—figure supplement 1. Analysis of chromatin remodelers in larval brains.
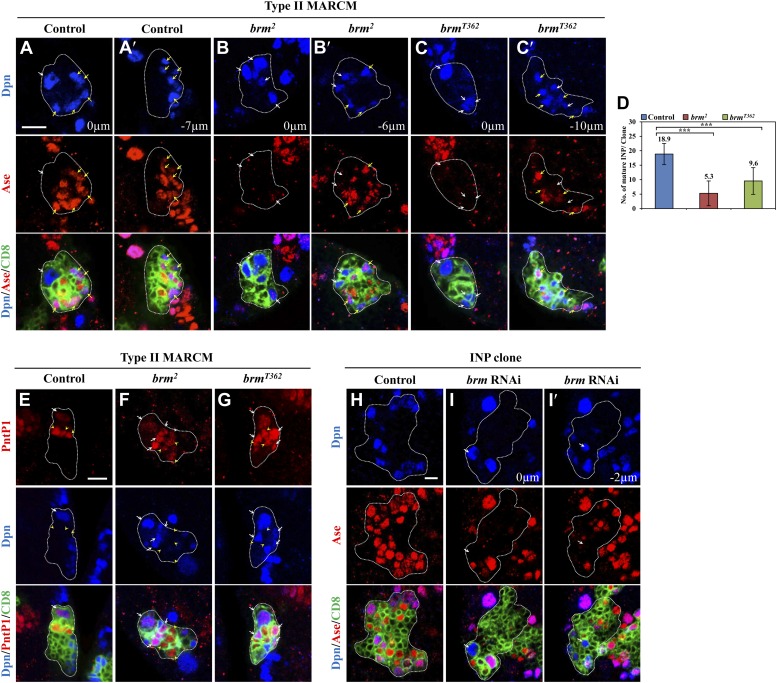
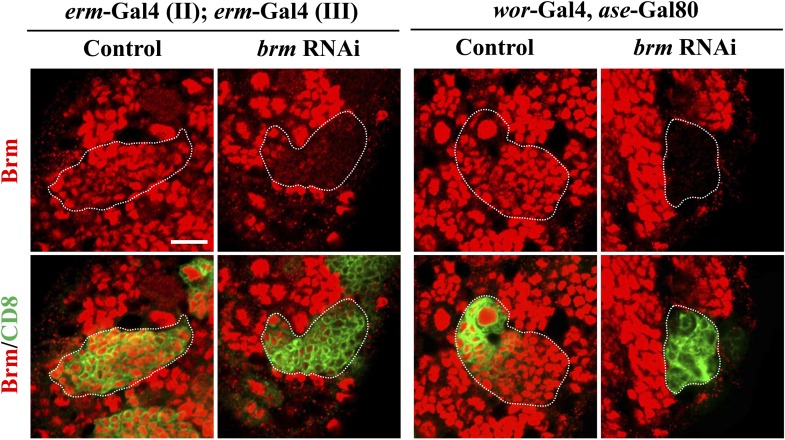
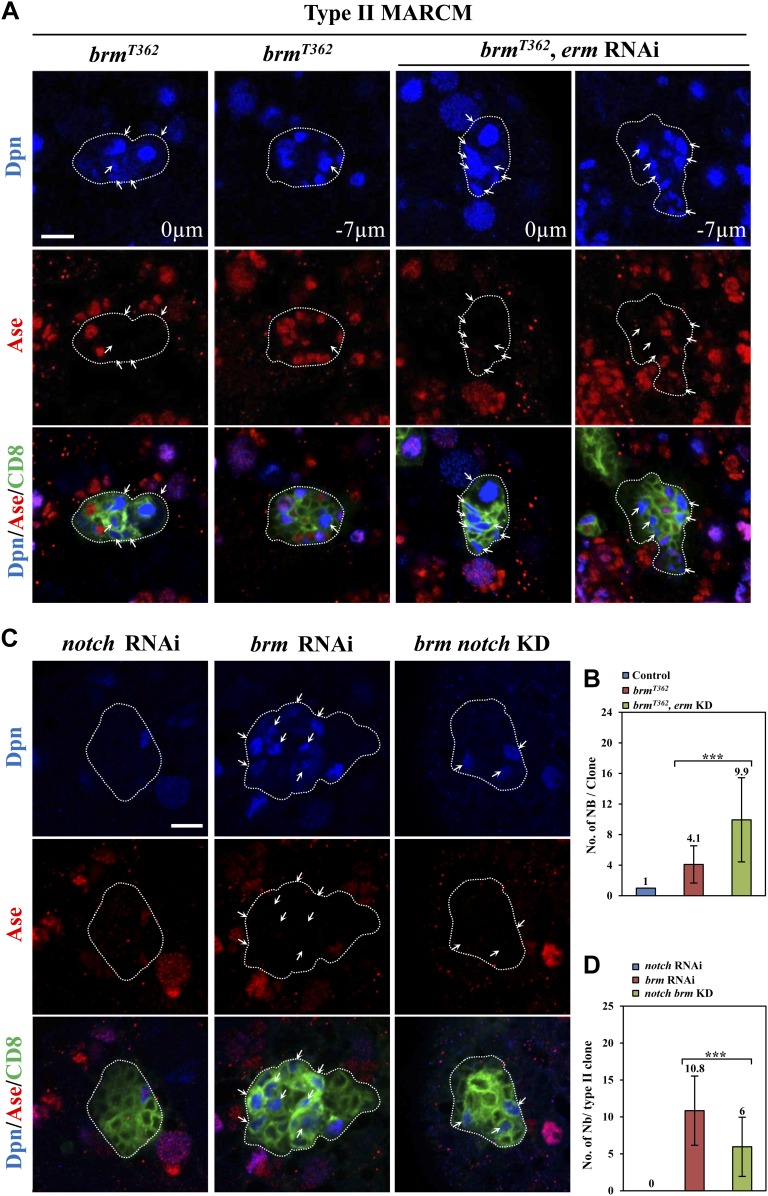
Concomitantly with the formation of supernumerary neuroblasts, the number of mature INPs that are positive for Dpn and Ase were dramatically reduced in both brm2 (Figure 2B,B′,D; 5.3 ± 4.3/clone, n = 39) and brmT362 (Figure 2C,C′,D; 9.6 ± 4.6/clone, n = 56), compared with the control type II clones (Figure 2A,A′,D; 18.9 ± 3.7, n = 22). The number of Dpn− PntP1+ immature INPs and early mature INPs appeared to be normal or slightly increased in brm2 (Figure 2F; 8.4 ± 2.5, n = 26) and brmT362 (Figure 2G; 7.1 ± 2.1, n = 33) clones compared with the control (Figure 2E; 5.9 ± 1.1, n = 26). These results suggested that ectopic neuroblasts in brm− clones likely originate from INPs that fail to undergo maturation. To further determine whether INPs undergo dedifferentiation back into neuroblast, we used INP-specific RNAi to knock down brm in INPs by erm-Gal4, an INP-specific driver. In 42.5% of INP clones with brm knockdown, ectopic Dpn+ Ase− neuroblasts were observed (Figure 2I,I′; 1.2 ± 1.6 neuroblasts /INP clone, n = 40). In contrast, none of the INP clones from the driver control contained any neuroblasts (Figure 2H; 0 neuroblast/INP clone, n = 53). The relatively weak phenotype is likely due to incomplete knockdown of Brm, as shown by the reduced Brm staining in the INP clones (Figure 2—figure supplement 1). Thus, our data suggest that Brm functions in INPs to prevent INP dedifferentiation back into neuroblasts.
Figure 2. The Brm complex suppresses INP dedifferentiation into type II neuroblasts.
(A–C′) Type II MARCM clones of control (the MARCM driver; A, A′), brm2 (B, B′) and brmT362 (C, C′) were labeled with Dpn (blue), Ase (red) and CD8::GFP (green). (D) Quantifications of INP number per type II clone for A–C′. *** indicates p<0.001. (E–G) Type II MARCM clones of control (E), brm2 (F) and brmT362 (G) were labeled with Dpn (blue), PntP1 (red) and CD8::GFP (green). (H–I′) INP clones of a control (driver: erm-Gal4 [II]; erm-Gal4 [III]; (H) and brm RNAi under erm-Gal4 (II); erm-Gal4 (III) with UAS-Dcr2 UAS-CD8-GFP (I, I′) were labeled with Dpn (blue), Ase (red) and CD8 (green). White arrows indicate neuroblasts, yellow arrows indicate Dpn+ Ase+ mature INPs and yellow arrowheads indicate Dpn− PntP1+ INPs. Clones are marked by CD8::GFP and indicated by white dotted line. Scale bars, 10 µm (A–G) and 5 µm (H–I′).
Figure 2—figure supplement 1. Partial knock down of brm in INP clones.
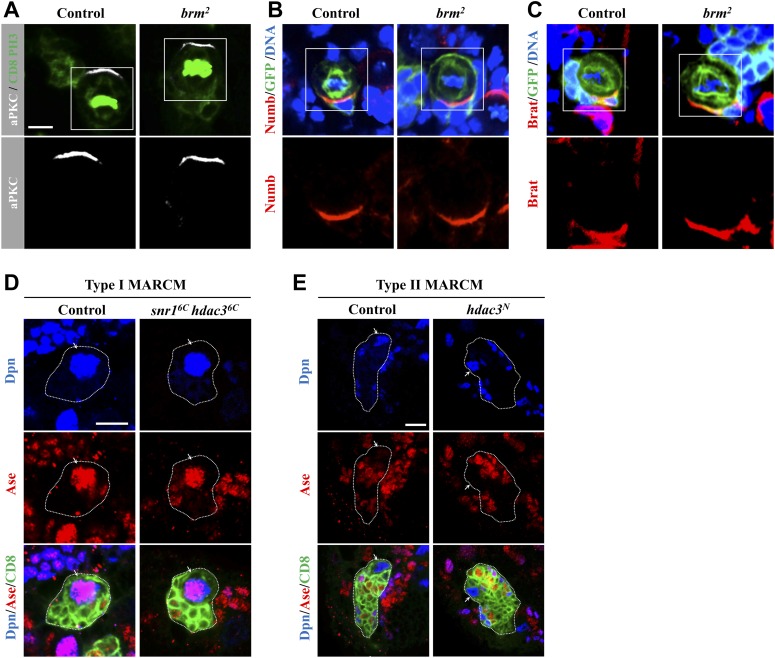
To assess whether Brm was affecting apico-basal cell polarity, we examined the localization of aPKC, Numb and Brat, which are asymmetrically localized in wild-type neuroblasts in prometaphase/metaphase. brm2 MARCM clones did not show any defects in the localization of these markers (Figure 3—figure supplement 1A–C), suggesting that Brm is not important for the apical-basal polarity regulation in neuroblasts.
We then assessed the function of other core subunits of the Brm remodeling complex using RNAi knockdown in larval brains. Knock down either of the three core components snr1 (Figure 1G,K, 9.5 ± 5.5 neuroblasts/lineage, 64.5%, n = 34), bap60 (Figure 1H,K, 5.1 ± 2.8 neuroblasts/lineage, 87.0%, n = 52), and moira (data not shown; also reported in Neumuller et al. (2011)) resulted in prominent phenotypes with ectopic Dpn+ Ase− neuroblasts in type II neuroblast lineages. Two additional snr1 RNAi lines under the control of the type II driver also displayed excess type II neuroblasts (Figure 1—figure supplement 1D). Furthermore, bap55LL5955 MARCM clones also showed ectopic neuroblasts in type II (Figure 1J,J′, 2.3 ± 1.7 neuroblasts/clone; 30.5%, n = 57), but not type I neuroblast lineages (Figure 1—figure supplement 1F; n = 20). The number of Dpn+ Ase+ mature INPs in bap55LL5955 was significantly reduced (13.8 ± 4.1; n = 49) compared with the control (18.9 ± 3.7, n = 22), while the number of Dpn− PntP1+ immature and early mature INPs (4.2 ± 1.9, n = 26) was similar to the control (5.9 ± 1.1, n = 26). In various mutants and RNAi lines described above, we also observed an increased number of Dpn+ PntP1+ cells (data not shown), which serves as an independent set of marker for type II neuroblasts. This data further supports that loss-of-function of the Brm complex caused the phenotype of ectopic type II neuroblasts. We conclude that core components of the Brm remodeling complex are required to suppress ectopic neuroblast formation in type II neuroblast lineages.
Next, we ascertained whether other chromatin remodeling complexes such as Nucleosome remodeling factor (NURF) and ACF complex (ATP-utilizing chromatin assembly and remodeling factor), play any role during neuroblast self-renewal. RNAi knockdown of nurf301 or ACF complex components iswi and acf1 (Figure 1—figure supplement 1G) in the type II neuroblast lineages did not result in any obvious neuroblast overgrowth. These data suggest that they may not be important for type II neuroblast lineages or their RNAi targeting was insufficient to induce an effect.
HDAC3 acts cooperatively with the Brm complex to suppress the formation of ectopic type II neuroblasts
To assess the involvement of histone modifications in type II neuroblast lineages, we screened a collection of 43 histone modifiers (Table 1; Kirilly et al., 2011) by RNAi under the control of a type II-specific driver but failed to identify any RNAi lines with ectopic neuroblasts. We reasoned that histone modifiers may act cooperatively with the Brm complex in type II neuroblast lineages and the phenotype may be masked due to the presence of the functional Brm complex. We therefore re-screened the same collection of potential histone modifiers in a brm RNAi background and showed that the simultaneous knockdown of both brm and hdac3 under the control of the type II driver resulted in a more severe phenotype of ectopic neuroblasts (Figure 3D,E; 22.1 ± 7.4 neuroblasts/clone, n = 21) compared with brm RNAi (Figure 3B,E; 10.3 ± 5.6 neuroblasts/clone, n = 30) or hdac3 RNAi knockdown alone (Figure 3C,E; 1.1 ± 0.5 neuroblasts/clone, n = 85). This finding suggests that HDAC3 functions cooperatively with Brm to regulate type II neuroblast lineages. Next, we took advantage of an existing deletion mutant snr16c hdac36c, which removes the entire snr1 coding region and the C-terminal region of hdac3. Type II neuroblast MARCM clones from snr16c hdac36c homozygotes possessed a large number of ectopic neuroblasts (Figure 3G,H, 22 ± 11.5 neuroblasts/clone, 83.0%, n = 22). The number of mature Dpn+ Ase+ INPs in each snr16c hdac36c type II neuroblast clone was modestly reduced to 15.6 ± 4.4 (n = 22) compared with 20.3 ± 3/clone (n = 20) in control, while the number of Dpn− PntP1+ immature and early mature INPs (6.3 ± 3/clone, n = 21) are slightly greater compared with the control clones (4.1 ± 0.9, n = 21). In contrast, type I neuroblast clones of this double mutant appeared normal, as there was only one neuroblast per clone (Figure 3—figure supplement 1D, n = 17). Similar to hdac3 RNAi (Figure 3C), neither type I nor type II neuroblast mutant clones of a loss-of-function hdac3N allele had ectopic neuroblasts (Figure 3—figure supplement 1E and data not shown). Despite that ectopic neuroblasts were observed in multiple snr1 RNAi lines (Figure 1—figure supplement 1D), snr1R3 MARCM clones did not show obvious ectopic type II neuroblasts (Figure 1—figure supplement 1E). Because Snr1 protein was speculated to have extended perdurance in somatic clones of its null allele (Marenda et al., 2004), the lack of phenotype in snr1R3 is likely due to protein perdurance in the neuroblast clones. Our data suggest that HDAC3 acts cooperatively with the Brm complex to suppress the formation of ectopic type II neuroblasts. To ascertain whether snr16c hdac36c causes tumorigenesis, larval brain tissues carrying snr16c hdac36c MARCM clones were transplanted into the abdomen of wild-type hosts. A significant portion of the mutant tissue (Figure 3J; 21%, n = 14) proliferated massively and formed malignant tumors, whilst control clones did not proliferate after the implantation (Figure 3I; n = 25). In subsequent rounds of transplantation, 70% (T1, n = 10) and 80% (T2, n = 5) of the snr16c hdac36c mutant brain tissues developed tumors, suggesting that snr16c hdac36c can induce malignant tumor-like growth after allograft culture.
Table 1.
Histone modifiers and their RNAi lines
| S/No. | Gene name | Full name | CG # | Main function | VDRC RNAi lines |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | enok | Enoki mmushroom | CG11290 | HAT | KK108400, GD37527 |
| 2 | nej | Nejire/CBP | CG15319 | HAT | KK105115 |
| 3 | CG1894 | CG1894 | HAT | GD41575, GD41574 | |
| 4 | CG2051 | CG2051 | HAT | GD33458 | |
| 5 | Mof | Males absent on the first | CG3025 | HAT | KK105370 |
| 6 | Rpb4 | Rpb4 | CG33520 | HAT | GD21985, GD23308 |
| 7 | Pcaf | Gcn | CG4107 | HAT | KK108943, GD21786 |
| 8 | YL-1 | YL-1 | CG4621 | HAT | GD21903 |
| 9 | Chm | Chameau | CG5229 | HAT | KK105542 |
| 10 | Dik | Diskette | CG7098 | HAT | GD46320 |
| 11 | lid | Little imaginal discs | CG9088 | HAT | GD42203, KK103830 |
| 12 | Ada2b | CG9638 | HAT | GD24076 | |
| 13 | Sirt7 | CG11305 | HDAC | GD18043, GD18045 | |
| 14 | HDAC4 | CG1770 | HDAC | GD20522 | |
| 15 | HDAC3 | CG2128 | HDAC | KK107073 | |
| 16 | HDACX | CG31119 | HDAC | KK108098 | |
| 17 | Sirt4 | CG3187 | HDAC | GD40295, KK110639 | |
| 18 | Sirt2 | CG5085 | HDAC | KK103790 | |
| 19 | Sir2 | CG5216 | HDAC | GD23199, KK108241, KK105502 | |
| 20 | Bin1 | Bicoid interacting protein | CG6046 | HDAC | KK105352, GD15710 |
| 21 | Sirt6 | CG6284 | HDAC | GD22483 | |
| 22 | Gug | Grunge | CG6964 | HDAC | GD13687 |
| 23 | Rpd3 | HDAC1 | CG7471 | HDAC | GD46929, GD30600, GD46929 |
| 24 | Sin3a | CG8815 | HDAC | KK105852 | |
| 25 | Rtf1 | CG10955 | Methyl transferase | KK110392 | |
| 26 | Vig2 | CG11844 | Methyl transferase | KK107081, GD17245 | |
| 27 | egg | eggless | CG12196 | Methyl transferase | KK101677, GD33730 |
| 28 | esc | extra sexcombs | CG14941 | Methyl transferase | GD5690, GD5692 |
| 29 | set2 | CG1716 | Methyl transferase | GD30707 | |
| 30 | g9a | CG2995 | Methyl transferase | GD25474 | |
| 31 | pr-set7 | CG3307 | Methyl transferase | KK105422 | |
| 32 | trr | trithorax-related | CG3848 | Methyl transferase | GD10749, KK110276 |
| 33 | CG40351 | CG40351 | Methyl transferase | GD40683, GD10833, GD45267 | |
| 34 | CG4565 | CG4565 | Methyl transferase | GD5665 | |
| 35 | mes-4 | CG4976 | Methyl transferase | GD10836 | |
| 36 | Art4 | Arginine methyl transferase 4 | CG5358 | Methyl transferase | KK107009 |
| 37 | Su(var)3–9 | auppressor of variegation 3–9 | CG6476 | Methyl transferase | GD39377 |
| 38 | Art1 | Arginine methyl transferase 11 | CG6554 | Methyl transferase | GD40388, KK110391 |
| 39 | ash2 | absent, small or homeotic discs 2 | CG6677 | Methyl transferase | KK100718 |
| 40 | LKR | Lysine ketoglutarate reductase | CG7144 | Methyl transferase | GD51346 |
| 41 | Su(z)12 | Suppressor of Zeste 205 | CG8013 | Methyl transferase | GD42422, GD42423 |
| 42 | Su(var)205 | Suppressor of variegation 205 | CG8409 | Methyl transferase | KK107477 |
| 43 | Ash1 | Absent, small or homeotic discs 1 | CG8887 | Methyl transferase | GD28928 |
Figure 3. HDAC3 acts cooperatively with the Brm complex to suppress the formation of ectopic type II neuroblasts.
(A–D) The driver control (A), brm RNAi (B), hdac3 RNAi (C), brm hdac3 double knockdown (D) under the type II driver were labeled with Dpn, Ase, and CD8. (E) Quantification of neuroblast number per type II MARCM clone in A–D. (F–G) Type II MARCM clones from the driver control (F) and snr16c hdac36c (G) homozygous MARCM clones were labeled with Dpn, Ase and CD8. Arrows indicate neuroblasts. (H) Quantification of neuroblast number per type II MARCM clone in F–G. *** indicates p<0.001. (I–J) Clones are marked by CD8::GFP and indicated by white dotted line. Larval brain tissues from the wild-type MARCM clones (I) and snr16c hdac36c MARCM clones (J) were implanted into the abdomen of wild-type hosts. Scale bar, 10 µm.
Figure 3—figure supplement 1. Brm is not important for the apical-basal polarity of neuroblasts.
The Brm remodeling complex physically associates with Erm and HDAC3
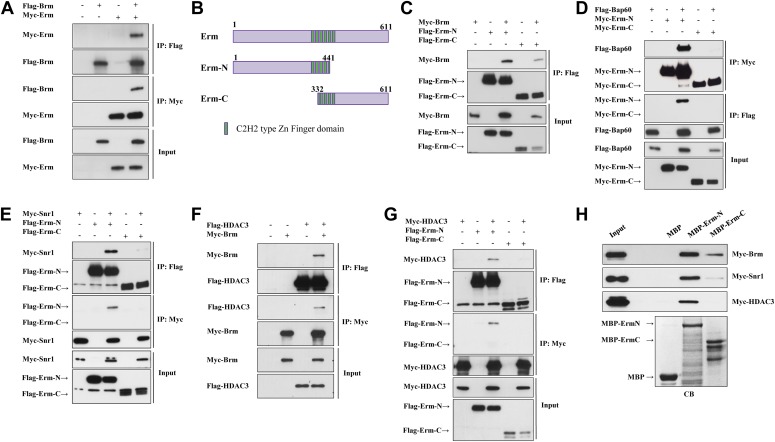
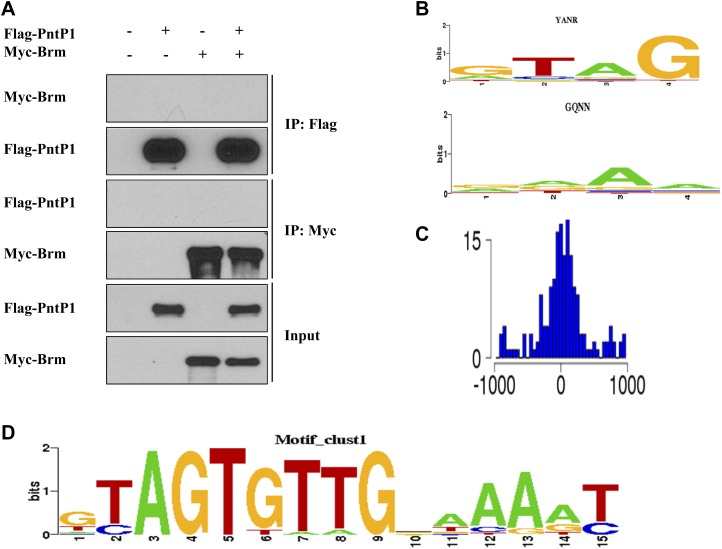
Given that Brm is ubiquitously expressed in various cell types of larval brains, including neuroblasts, INPs, GMCs and neurons (Figure 2—figure supplement 1 and data not shown), it is conceivable that the Brm complex may associate with regulatory protein(s) or co-factor(s) that is/are specifically expressed in type II neuroblast lineages to suppress the formation of ectopic neuroblasts. We therefore assessed whether Brm could associate with two such type II-specific transcription factors, Erm and PntP1. Flag-tagged Brm was co-transfected with Myc-tagged Erm in S2 cells. Following immunoprecipitation (IP) of Flag-Brm, Erm can be specifically detected in the immune complex (Figure 4A). Consistently, Flag-Brm was detected in the immune complex following the IP of Myc-Erm (Figure 4A). In contrast, Myc-Brm did not associate with Flag-PntP1 in similar co-IP experiments (Figure 4—figure supplement 1A), suggesting that Brm specifically associates in a protein complex with Erm, but not with PntP1. Since full-length Erm had very low expression levels in S2 cells, we expressed two truncated proteins, Erm N-terminal 1-441aa (Erm-N containing N-terminal region and four of six zinc-finger domains) and Erm C-terminal 332-611aa (Erm-C containing the last four zinc-finger domains and its C-terminus), and used them for the subsequent co-IP analysis (Figure 4B). In co-IP experiments, Myc-Brm associated strongly with Flag-Erm-N and weakly with Flag-Erm-C (Figure 4C). Furthermore, we ascertained whether Brm could associate with Erm in a protein pull-down assay. Full-length Erm could not be efficiently expressed when fused with Maltose-Binding Protein (MBP) in bacteria; we therefore expressed truncated MBP-Erm-N or MBP-Erm-C. These fusion proteins were then bound to amylose resin, and subsequently incubated with protein extracts from S2 cells transfected with Myc-Brm. Following the pull-down of amylose resin, Myc-Brm associated intensely with MBP-Erm-N and weakly with Erm-C, but not with the MBP control (Figure 4H). These data suggest that Brm physically associates with Erm and Erm N-terminus appears to be more important for this association.
Figure 4. The Brm remodeling complex physically associates with Erm and HDAC3.
(A) Co-immunoprecipitation (Co-IP) between Flag-Brm and Myc-Erm. (B) An illustration of Erm domains and truncated constructs. (C) Co-IP between Myc-Brm and Flag-Erm-N or Flag-Erm-C. (D) Co-IP between Flag-Bap60 and Myc-Erm-N or Myc-Erm-C. (E) Co-IP between Myc-Snr1 and Flag-Erm-N or Flag-Erm-C. (F) Co-IP was Flag-HDAC3 and Myc-Brm. (G) Co-IP between Flag-HDAC3 and Myc-Erm-N or Myc-Erm-C. IP was performed using anti-Flag or anti-Myc antibodies. Western blot was performed using anti-Flag and anti-Myc antibodies. (H) Protein pull-down assay. MBP, MBP-Erm-N and MBP-ErmC bound beads were incubated with protein extracts from S2 cells expressing Myc-Brm, Myc-Snr1 or Myc-HDAC3. Western blot was performed using an anti-Myc antibody. Coomassie blue (CB) staining showed 10% input of various purified MBP or MBP fusion proteins.
Figure 4—figure supplement 1. Brm and Erm may regulate gene expression of some common downstream targets.
We next ascertained whether Erm associates with other components of the Brm remodeling complex, such as BAP60 and Snr1. In co-IP experiments, Flag-BAP60 was detected in the immune complex following IP of Myc-Erm-N but not Myc-Erm-C (Figure 4D). Likewise, Myc-Erm-N was detected in the immune complex when IP was performed using Flag-BAP60 (Figure 4D). Moreover, Myc-Snr1 associated with Flag-Erm-N or Flag-Erm-C in co-IP experiments (Figure 4E). Consistently, Myc-Snr1 associated with MBP-Erm-N and weakly with MBP-Erm-C in protein pull-down assays (Figure 4H). Therefore, we conclude that the several components of the Brm remodeling complex specifically associates with Erm.
Given that HDAC3 functions cooperatively with the Brm complex to suppress the generation of ectopic neuroblasts, we ascertained whether HDAC3 can physically associate with both Brm and Erm. Flag-HDAC3 and Myc-Brm were co-transfected in S2 cells. Following immunoprecipitation of Flag-HDAC3, Myc-Brm was clearly detected in the immune complex (Figure 4F). Similarly, Flag-HDAC3 was detected in the immune complex after IP of Myc-Brm (Figure 4F). Interestingly, HDAC3 also physically associates with Erm-N, but not Erm-C, in both co-IP (Figure 4G) and protein pull-down assay (Figure 4H). Taken together, these results show that Brm physically associates with Erm and HDAC3 in the protein complex.
brm and hdac3 genetically interact with erm to prevent dedifferentiation of INPs to neuroblasts
Given that Brm and Erm associate in a protein complex, and both of them suppress the formation of ectopic neuroblasts, we assessed whether brm genetically interacts with erm to prevent dedifferentiation of INPs to neuroblasts. First, we ascertained whether erm knockdown can exacerbate the brm RNAi phenotype in type II neuroblast lineages. The simultaneous knockdown of brm and erm resulted in a much more severe phenotype with a large number of ectopic neuroblasts in each lineage (Figure 5D,E; 37.1 ± 7.6 neuroblasts/lineage, n = 20), in contrast to brm knockdown alone (Figure 5B,E; 9.5 ± 2.8, n = 32). It was reported that in erm- mutants, dedifferentiated neuroblasts can establish ectopic type II neuroblast lineages and form ectopic glial chambers (Weng et al., 2010). Presumably due to incomplete knockdown of erm that only led to weak ectopic type II neuroblasts phenotypes, erm RNAi under the type II driver resulted in ectopic type II lineages with each lineage containing one type II neuroblast (Figure 5C,E; 1 neuroblast/lineage, n = 60). This dramatic enhancement suggests that brm and erm genetically interact to prevent the dedifferentiation of INPs back to neuroblasts. Furthermore, knock down of erm by RNAi in the brmT362 MARCM clones (Figure 5—figure supplement 1A,B; 9.9 ± 5.5 neuroblasts/clone, n = 32) also significantly enhanced neuroblast overgrowth compared with brmT362 clones (Figure 5—figure supplement 1A,B; 4.1 ± 2.4 neuroblasts/clone, n = 30). However, the size of the brmT362 clones with erm knockdown remained smaller than the control clones, probably due to the reduced number of INPs that are required to expand the clonal size. Erm overexpression has previously been shown to result in premature differentiation of type II neuroblasts (Weng et al., 2010). Similarly, we found that overexpression of Erm in type II MARCM clones caused 100% of the neuroblasts to undergo premature differentiation; 29.3% of the clones contained a neuroblast that gained Ase expression and 41.5% of the clones contained a neuroblast that had gained Ase expression with strongly reduced Dpn expression, while the rest of the clones showed no obvious neuroblasts (Figure 5G and data not shown; n = 41). To assess whether this effect is dependent on its association with Brm, we overexpressed Erm in brm2 type II neuroblast clones. The premature differentiation of type II neuroblasts was dramatically suppressed in a brm loss-of-function mutant background, as there were still 37.8% of clones contained ectopic neuroblasts (Figure 5I), while 62.2% of type II neuroblasts underwent premature differentiation (Figure 5H; n = 37). Similarly, the simultaneous knockdown of both erm and snr1 resulted in a more severe phenotype of ectopic neuroblasts (Figure 5M–N; 862 ± 106.8 neuroblasts/brain lobe, n = 20) compared with either erm knockdown (Figure 5K,N; 76.6 ± 14.2 neuroblasts/brain lobe, n = 20) or snr1 knockdown (Figure 5L,N; 219.5 ± 52.2 neuroblasts/brain lobe, n = 20). Thus, we conclude that brm and snr1 genetically interact with erm to prevent dedifferentiation of INPs to neuroblasts. Furthermore, the simultaneous knockdown of hdac3 and erm under the control of type II driver also resulted in a more dramatic increase of ectopic type II neuroblasts (Figure 5Q,R; 565.4 ± 68.1 type II neuroblasts/brain lobe, n = 20) compared with either erm knockdown (Figure 5P,R; 76.0 ± 7.7 type II neuroblasts/brain lobe, n = 20) or hdac3 knockdown (Figure 5R; 8 type II neuroblasts/brain lobe, n = 20), suggesting that hdac3 and erm genetically interact in type II neuroblast lineages. Taken together, these results indicate that Brm, HDAC3, and Erm function as a repressor complex to prevent INP dedifferentiation into type II neuroblasts.
Figure 5. Brm genetically interacts with Erm to prevent dedifferentiation of INPs to neuroblasts.
(A–D) Type II clones of control (the type II driver; A), brm knockdown (B), erm knockdown (C) and brm erm double knockdown (D) were labeled with Dpn (blue), Ase (red) and CD8 (green). (E) Quantifications of neuroblast number per type II neuroblast lineage for A–D. (F–I) Type II MARCM clones of brm2 (F, F′), UAS-Erm (G) and UAS-Erm, brm2 (H–I) were labeled with Dpn (blue), Ase (red) and CD8 (green). (J–M) Larval brains of control (J, elav-Gal4 driver), erm knockdown (K), snr1 knockdown (L) and erm snr1 double knockdown (M) were labeled with Dpn (blue), Ase (red) and Mira (green). (N) Quantifications of the number of type II neuroblasts per brain hemisphere in various genotypes in J–M. Control (elav-Gal4), 7 ± 0; erm RNAi, 76.6 ± 14.2; snr1 RNAi, 219.5 ± 52.2; erm snr1 double knockdown (KD), 862.0 ± 106.7. (O–Q) Larval brains of control (driver; O), erm knockdown (P) and erm hdac3 double knockdown (Q) under the type II driver were labeled with Dpn (blue), Ase (red) and CD8 (green). (R) Quantifications of neuroblast number per brain hemisphere in O–Q. Central brain is to the left of white dotted lines. Arrows indicate neuroblasts. Clones were indicated by white dotted lines. Scale bars, 10 µm. *** indicates p<0.001.
Figure 5—figure supplement 1. Knocking down of erm enhanced the neuroblast overgrowth observed in brm mutants.
Discussion
Here, we report a critical function of the Drosophila Brm remodeling complex in suppressing the formation of ectopic type II neuroblasts in larval brains. Mutants of major components of the Brm complex, including Brm and Bap55, and RNAi targeting of several Brm components formed ectopic type II neuroblasts. Therefore, the Drosophila Brm remodeling complex displays a tumor suppressor-like function in larval brains. Multiple subunits of the SWI/SNF complex are associated with various cancers. BAP47 (homologous to Snr1) is a bona fide tumor suppressor and the gene is deleted in pediatric rhabdoid tumors (Reisman et al., 2009). Mutations in epigenetic regulators are found in approximately half of hepatocellular carcinoma and bladder cancers, and represent a significant portion of mutated genes in medulloblastoma (Gui et al., 2011; Fujimoto et al., 2012; Pugh et al., 2012). Drosophila Brm complex is essential for intestinal stem cell proliferation and commitment in the adult intestine (Jin et al., 2013; Zeng et al., 2013). Two other chromatin remodeling factors, Iswi and Domino control germline stem cell and somatic stem cell self-renewal in the ovary (Xi and Xie, 2005).
We have demonstrated that Brm physically associates with Erm, a type II-specific transcription factor that prevents the dedifferentiation of INPs back into neuroblasts. Furthermore, Bap60 and Snr1, two other components of the Brm complex, also physically associate with Erm in a protein complex. Therefore, we have provided the first molecular link during the regulation of type II neuroblast lineages. We speculate that the association with Erm may provide functional specificity of the Brm remodeling complex in type II neuroblast lineages. We have also shown that brm genetically interacts with the type II-specific transcription factor erm. Ectopic neuroblast phenotype resulting from brm knockdown was dramatically enhanced by simultaneous knockdown of erm. Furthermore, brm knockdown, similar to erm− (Weng et al., 2010), can be partially suppressed by loss of notch (Figure 5—figure supplement 1C,D). These functional data suggest that Erm is a co-factor of the Brm remodeling complex in type II neuroblast lineages. However, it is uncertain how the Brm–Erm protein complex functions to prevent dedifferentiation in type II neuroblast lineages.
Our bioinformatic analysis has identified a 14 bp-long motif as the de novo Erm DNA-binding motif (Figure 4—figure supplement 1B–D; and Supplementary methods) and 202 sites out of the 270 known genomic loci harboring Brm (Negre et al., 2011) also contain the de novo Erm DNA-binding motif (Table 2, Gene list). As there are many genes that are potentially co-occupied by Brm and Erm, it is possible that Brm–Erm complex results in a unique configuration of the chromatin ‘landscape’ in INPs to prevent INP dedifferentiation into neuroblasts. Therefore, disruption of chromatin remodelers may cause widespread changes to the transcriptome, thus amplifying the effect of the single genetic mutation.
Table 2.
Predicted common target genes of Brm and Erm
| S/No. | CG name | Gene name |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | CG10033 | for |
| 2 | CG10117 | ttv |
| 3 | CG10137 | CG10137 |
| 4 | CG10159 | BEAF-32 |
| 5 | CG10388 | Ubx |
| 6 | CG10610 | ECSIT |
| 7 | CG1071 | E2f2 |
| 8 | CG10844 | RyR |
| 9 | CG1100 | Rpn5 |
| 10 | CG11228 | hpo |
| 11 | CG11309 | CG11309 |
| 12 | CG11589 | VhaM9.7-c |
| 13 | CG12165 | Incenp |
| 14 | CG12321 | CG12321 |
| 15 | CG12333 | CG12333 |
| 16 | CG12387 | zetaTry |
| 17 | CG12797 | Ciao1 |
| 18 | CG12818 | CG12818 |
| 19 | CG12819 | sle |
| 20 | CG12855 | HPS1 |
| 21 | CG12994 | CG12994 |
| 22 | CG13004 | CG13004 |
| 23 | CG13016 | CG13016 |
| 24 | CG13018 | CG13018 |
| 25 | CG13117 | CG13117 |
| 26 | CG1322 | zfh1 |
| 27 | CG13316 | Mnt |
| 28 | CG13350 | Ctf4 |
| 29 | CG13366 | CG13366 |
| 30 | CG13432 | qsm |
| 31 | CG13472 | CG13472 |
| 32 | CG13688 | Ipk2 |
| 33 | CG13900 | CG13900 |
| 34 | CG13919 | CG13919 |
| 35 | CG14291 | CG14291 |
| 36 | CG14463 | CG14463 |
| 37 | CG1453 | Klp10A |
| 38 | CG14813 | deltaCOP |
| 39 | CG14814 | CG14814 |
| 40 | CG14938 | crol |
| 41 | CG14939 | CycY |
| 42 | CG15010 | ago |
| 43 | CG15027 | CG15027 |
| 44 | CG15120 | CG15120 |
| 45 | CG15387 | CG15387 |
| 46 | CG15701 | CG15701 |
| 47 | CG15706 | CG15706 |
| 48 | CG15845 | Adf1 |
| 49 | CG1600 | Drat |
| 50 | CG1616 | dpa |
| 51 | CG17033 | elgi |
| 52 | CG17035 | GXIVsPLA2 |
| 53 | CG17052 | obst-A |
| 54 | CG17233 | CG17233 |
| 55 | CG17249 | CG17249 |
| 56 | CG17259 | CG17259 |
| 57 | CG17260 | CG17260 |
| 58 | CG1765 | EcR |
| 59 | CG17803 | CG17803 |
| 60 | CG1785 | CG1785 |
| 61 | CG1817 | Ptp10D |
| 62 | CG18292 | CG18292 |
| 63 | CG1845 | Br140 |
| 64 | CG18660 | Nckx30C |
| 65 | CG18675 | CG18675 |
| 66 | CG2004 | CG2004 |
| 67 | CG2019 | disp |
| 68 | CG2051 | CG2051 |
| 69 | CG2146 | didum |
| 70 | CG2189 | Dfd |
| 71 | CG2446 | Amun |
| 72 | CG2698 | CG2698 |
| 73 | CG2720 | Hop |
| 74 | CG2813 | cold |
| 75 | CG2977 | Inx7 |
| 76 | CG3059 | NTPase |
| 77 | CG3127 | Pgk |
| 78 | CG31481 | pb |
| 79 | CG3157 | gammaTub23C |
| 80 | CG3165 | CG3165 |
| 81 | CG3166 | aop |
| 82 | CG31712 | CG31712 |
| 83 | CG31713 | Apf |
| 84 | CG3178 | Rrp1 |
| 85 | CG31794 | Pax |
| 86 | CG31852 | Tap42 |
| 87 | CG31855 | CG31855 |
| 88 | CG31911 | Ent2 |
| 89 | CG32022 | CG32022 |
| 90 | CG32556 | chas |
| 91 | CG32592 | hiw |
| 92 | CG33116 | CG33116 |
| 93 | CG33162 | SrpRbeta |
| 94 | CG3587 | CG3587 |
| 95 | CG3666 | Tsf3 |
| 96 | CG3842 | CG3842 |
| 97 | CG3857 | CG3857 |
| 98 | CG3920 | Reph |
| 99 | CG42254 | CG42254 |
| 100 | CG42311 | grh |
| 101 | CG42334 | comm3 |
| 102 | CG42362 | CG42362 |
| 103 | CG42363 | CG42363 |
| 104 | CG42365 | CG42365 |
| 105 | CG42379 | CG42379 |
| 106 | CG42380 | CG42380 |
| 107 | CG42381 | CG42381 |
| 108 | CG4400 | CG4400 |
| 109 | CG4590 | Inx2 |
| 110 | CG4619 | CG4619 |
| 111 | CG4645 | CG4645 |
| 112 | CG4798 | l(2)k01209 |
| 113 | CG4996 | CG4996 |
| 114 | CG5229 | chm |
| 115 | CG5393 | apt |
| 116 | CG5505 | scny |
| 117 | CG5548 | CG5548 |
| 118 | CG5588 | Mtl |
| 119 | CG5599 | CG5599 |
| 120 | CG5611 | CG5611 |
| 121 | CG5613 | CG5613 |
| 122 | CG5824 | l(3)07882 |
| 123 | CG5836 | SF1 |
| 124 | CG6022 | Cchl |
| 125 | CG6202 | Surf4 |
| 126 | CG6218 | CG6218 |
| 127 | CG6235 | tws |
| 128 | CG6241 | CG6241 |
| 129 | CG6272 | CG6272 |
| 130 | CG6322 | U4-U6-60K |
| 131 | CG6343 | ND42 |
| 132 | CG6401 | CG6401 |
| 133 | CG6511 | CG6511 |
| 134 | CG6556 | cnk |
| 135 | CG6565 | CG6565 |
| 136 | CG6604 | H15 |
| 137 | CG6634 | mid |
| 138 | CG6829 | Ark |
| 139 | CG6948 | Clc |
| 140 | CG6951 | CG6951 |
| 141 | CG6983 | CG6983 |
| 142 | CG7082 | papi |
| 143 | CG7085 | l(2)s5379 |
| 144 | CG7186 | SAK |
| 145 | CG7191 | CG7191 |
| 146 | CG7372 | CG7372 |
| 147 | CG7379 | CG7379 |
| 148 | CG7564 | CG7564 |
| 149 | CG7597 | Cdk12 |
| 150 | CG7632 | CG7632 |
| 151 | CG7685 | CG7685 |
| 152 | CG7734 | shn |
| 153 | CG7771 | sim |
| 154 | CG7828 | APP-BP1 |
| 155 | CG7845 | CG7845 |
| 156 | CG7849 | CG7849 |
| 157 | CG7957 | MED17 |
| 158 | CG7961 | alphaCop |
| 159 | CG8067 | CG8067 |
| 160 | CG8241 | pea |
| 161 | CG8287 | Rab8 |
| 162 | CG8360 | CG8360 |
| 163 | CG8372 | CG8372 |
| 164 | CG8396 | Ssb-c31a |
| 165 | CG8409 | Su(var)205 |
| 166 | CG8481 | CG8481 |
| 167 | CG8790 | Dic1 |
| 168 | CG8798 | Lon |
| 169 | CG8817 | lilli |
| 170 | CG9042 | Gpdh |
| 171 | CG9054 | Ddx1 |
| 172 | CG9063 | Rich |
| 173 | CG9065 | CG9065 |
| 174 | CG9243 | CG43345 |
| 175 | CG9243 | CG43346 |
| 176 | CG9244 | Acon |
| 177 | CG9249 | CG9249 |
| 178 | CG9250 | Mpp6 |
| 179 | CG9305 | CG9305 |
| 180 | CG9376 | CG9376 |
| 181 | CG9473 | MED6 |
| 182 | CG9596 | CG9596 |
| 183 | CG9635 | RhoGEF2 |
| 184 | CG9641 | CG9641 |
| 185 | CG9730 | mRpL21 |
| 186 | CG9750 | rept |
| 187 | CG9829 | poly |
| 188 | CG9865 | CG9865 |
Most class I HDACs are recruited into large multi-subunit co-repressor complexes for maximal activity (Wen et al., 2000). HDAC1 and 2 are found in multiple co-repressor complexes, while to date HDAC3 appears to be uniquely recruited to the Silencing mediator of retinoic and thyroid receptors (SMRT)/Nuclear receptor co-repressor (N-CoR) complex (Guenther et al., 2000; Li et al., 2000). Here, we report that Drosophila HDAC3 is recruited to a novel multi-subunit complex containing Brm and Erm and that this co–repressor complex prevents dedifferentiation of INPs into type II neuroblasts. The SMRT complex appears not to be important for type II neuroblasts, as knockdown of smrter that encodes a core component of the SMRT complex (Heck et al., 2012) neither resulted in any ectopic type II neuroblasts nor enhanced the phenotype of ectopic neuroblasts by brm knockdown (data not shown). We also showed that HDAC3 dramatically enhanced the phenotype of ectopic neuroblast upon loss of brm or snr1, two core components of the Brm complex. By identifying this novel repressor complex, we have provided a mechanistic link between transcriptional repression and histone deacetylation during the suppression of dedifferentiation. HDACs are typically recruited by oncogenic protein complexes in lymphoma and leukemia and HDAC3 inhibitors are synergistic or additive with anticancer agents for therapeutics (Dokmanovic et al., 2007). Our finding that HDAC3 functions cooperatively with the Brm complex in suppressing suppressing dedifferentiation of INPs into neuroblasts and induces tumors in the allograph transplantation revealed an unexpected potential involvement of HDAC3 in tumor suppression in brain tissue. It will be of interest to determine whether this effect is conserved in the mammalian central nervous system and whether it occurs in tissues other than the brain.
Materials and methods
Fly stocks and antibodies
The following flies were used in this study: brmT362 is from J Treisman; erm1, erm2, UAS-ErmCTHA, UAS-Brm (AK Dingwall), 9D11-Gal4 (erm-Gal4; GM Rubin). brm2, bap55LL05905, Erm RNAi (#26778; BDSC) are from Bloomington Drosophila stock center. VDRC RNAi lines used: Brm (GD37720 and 37721GD), Bap60 (KK103634), Snr1 (KK108599, GD12645, and BDRC#32372), Bap55 (GD24704), Moira (GD6969), Bap180 (KK108618), dMi-2 (KK107204), nurf301 (GD46645), Acf1 (GD33446) and ISWI (GD24505). The type II neuroblast driver: w; UAS-Dicer 2, wor-Gal4, ase-Gal80/CyO; UAS-mCD8-GFP/TM3, Ser (Neumuller et al., 2011).
The primary antibodies used were: guinea-pig anti-Dpn (1:1000, J Skeath), anti-Insc (1:1000); rabbit anti-aPKCζ C20 (1:100; Santa Cruz Biotechnologies, Dallas, TX); guinea-pig anti-Numb (1:1000; J Skeath); mouse anti-Mira (1:50; F Matsuzaki); rat anti-CD8 (1:250; Caltag laboratories, United Kingdom); rabbit anti-GFP (1:500; Molecular Probes, Eugene, OR); rabbit anti-Asense (1:1000; YN Jan); rabbit anti-PntP1 (1:100; J Skeath); rabbit anti-Brm (1:100; L Zhang); rat anti-phospho-Histone H3 (1:1000; Cell Signaling, Danvers, MA); rabbit anti-phospho-Histone H3 (1:200; Sigma, St Louis, MO); mouse anti-dMyc (1:5; B Edgar). Antibodies for western blotting used were: mouse anti-Myc (1:2000; Abcam, United Kingdom) and mouse anti-Flag (1:1000; Sigma).
Immunohistochemistry and immunoblotting
Third instar larval brains were dissected and fixed with 3.7% formaldehyde in PBS. Fixed brains were blocked with 3% BSA for one hour and then incubated with primary antibody in 3% BSA (in 0.3% PBS-T) over night at 4°C. Following three times washing (10 min each), larval brains were incubated with secondary antibody diluted in 0.3% PBS-T for 1.5 hr. After two times washing (10 min each), DNA was labeled by ToPro-3 (1:5000; Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA) in 0.3% PBS-T for 20 min. Larval brains were mounted in vector shield (Vector Laboratory, Burlingame, CA) for confocal microscopy. Images were obtained using a Zeiss LSM 700 confocal microscope and processed with Adobe Photoshop CS5.1.
Clonal analysis
MARCM clones were generated as previously described (Lee and Luo, 1999). Briefly, larvae were heat shocked at 37°C for 90 min at 24 hr ALH and at 10–16 hr after the first heat shock. Larvae were further aged for 3 days at 25°C, and larval brains were dissected and processed for immunohistochemistry. To generate type II neuroblast clones, UAS lines were crossed to the type II driver at 25°C and shifted to 29°C at 24 hr ALH. Wandering third instar larvae were dissected after incubation for 3 or 4 days at 29°C.
S2 cell culture, transfection and co-immunoprecipitation
Drosophila S2 cells were cultured in Shields and Sang M3 insect medium (Sigma-Aldich), and supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS; Hyclone, Logan, UT). Flag-Erm or Myc-Brm generated by Gateway cloning was transfected into S2 cells using Effectene Transfection Reagent (QIAGEN, The Netherlands). S2 cells were collected 48 hr after transfection for protein homogenization. 80 μg S2 cells are homogenized with lysis buffer (25 mM Tris pH8/27.5 mM NaCl/20 mM KCl/25 mM sucrose/10 mM EDTA/10 Mm EGTA/1 mM DTT/ 10% (vol/vol) glycerol/0.5% Nonidet P40) with Proteases inhibitors (Complete, Boeringher; PMSF 10 μg/ml, Sodium orthovanadate 10 μg/ml). The supernatants were used for immunoprecipitation with anti-Myc or anti-Flag for overnight at 4°C, followed by incubation with protein A/G beads for two hours (Pierces, Rockford, IL). Protein A/G beads were washed with cold PBS for three times. Bound proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE and analyzed by western blotting.
Protein pull-down assay
MBP or MBP fusion proteins were expressed in BL21 cells and bound on amylose resin (Cart# E8021L; NEW ENGLAND Biolabs Inc., United Kingdom). 50 μg of purified MBP fusion proteins bound on amylose resin were incubated for 3 hr at 4°C with protein extracts from 100 μg S2 cells that were homogenized in lysis buffer with proteases inhibitors. After washing amylose resin three times for 7 min each with 1 ml lysis buffer, bound proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE and analyzed by western blotting.
Transplantation
Allograft culture of larval brain tissue was carried out as previously described (Castellanos et al., 2008). Third instar larval brains are dissected and the tissue is cut into pieces. A piece of tissue is collected with the tip of a glass needle and injected in the mid-ventral abdomen of a young female fly.
Generation of plasmid constructs
Plasmid constructs were generated using either pENTR Directional TOPO Cloning Kit (Invitrogen) or In-Fusion HD Cloning Kit (Clontech, Mountain View, CA). ESTs used in this study were GH14092 (Erm), LD36356 (Brm), LD09078 (Bap60), GH08712 (Snr1) (Drosophila Genomics Resource Centre [DGRC], Bloomington, IN). Briefly, coding region of genes were amplified by PCR, inserted into the pENTR/D-TOPO vector (Invitrogen) and destination vectors (pAMW or PAFW) were generated by LR recombination.
Bioinformatics
From the previously reported ChIP–chip data, we obtained a list of 270 Brm binding sites. To determine if Erm also binds to these binding sites, we first analyzed the DNA binding domains of Erm, which contain 6 zinc fingers. Each zinc-finger domain was assigned a DNA binding preference (position weighted matrix) based on published methods (Kaplan et al., 2005). We then scanned these six DNA binding preferences of approximately +/−200 bp around the 270 Brm binding sites and found the DNA binding preferences of the 1st zinc-finger ‘GTAG’ and the 4th zinc-finger ‘RAAA’ are enriched in the 270 Brm binding sites. The sites enriched with these two binding preferences were subjected to further analysis using the de novo motif-finding program SEME (Zhang et al., 2013), and a 14 bp-long motif was identified as the de novo Erm DNA-binding motif. We scanned +/−200 bp around the 270 Brm binding sites with the de novo Erm DNA-binding motif. Among them, 202 sites (FDR<0.0001) were identified as putative Erm-binding sites with an AUC score of 0.73, which is significantly higher than the AUC score computed for random motifs (0.5). As a negative control, the same approach was also applied to predict the motif of Zinc-finger protein (Zif), which regulates asymmetric division of neuroblasts and therefore is unlikely to be a co-factor with Brm. The predicted Zif DNA-binding motif differs dramatically with the predicted Erm DNA-binding motif in sequence. Furthermore, it was not significantly enriched in the 270 Brm binding sites and had an AUC score of 0.54, similar to the AUC score (0.5) for random motifs. Thus, our data suggests that Brm and Erm can potentially regulate a set of common downstream targets.
Acknowledgements
We thank J Treisman, AK Dingwall, GM Rubin, J Skeath, B Edgar, C Doe, F Matsuzaki, J Knoblich, CY Lee, B Edgar, T Lee, H Steller, A Swan, YN Jan, L Zhang, the Hybridoma Bank, the Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center, Vienna Drosophila RNAi Center for fly stocks and antibodies, SY Chia for technical assistance and Groth C. for critical reading of this manuscript.
Funding Statement
The funders had no role in study design, data collection and interpretation, or the decision to submit the work for publication.
Funding Information
This paper was supported by the following grants:
Duke-NUS Signature Research Program funded by A*STAR to Hongyan Wang.
Singapore National Research Fondation NRF2008NRF-RF001-117 to Chwee Tat Koe, Song Li, Keng Chen, Hongyan Wang.
NUS Graduate School for Integrative Sciences and Engineering Scholarship to Chwee Tat Koe, Song Li, Jack Jing Lin Wong, Yan Wang.
Spanish Ministerio de Economía y Competitividad (MEC) BFU2012-32522 to Fabrizio Rossi, Cayetano Gonzalez.
European Research Council (ERC) ERC-2011-adG 294603-FliesCan to Fabrizio Rossi, Cayetano Gonzalez.
Genealitat de Catalunya CG041413 to Fabrizio Rossi, Cayetano Gonzalez.
Senior Research Fellowship from the National Health and Medical Research Council (NHMRC) Australia to Helena E Richardson.
National Health and Medical Research Council APP1011320 to Helena E Richardson.
Temasek Life Sciences Laboratory to Jack Jing Lin Wong, Yan Wang, Fengwei Yu.
School of Computing, National University of Singapore to Zhizhuo Zhang, Wing-Kin Sung.
Genome Institute of Singapore to Paul Robson, Wing-Kin Sung.
Additional information
Competing interests
The authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Author contributions
CTK, Acquisition of data, Analysis and interpretation of data, Drafting or revising the article.
SL, Acquisition of data, Analysis and interpretation of data.
FR, Acquisition of data, Analysis and interpretation of data.
JJLW, Acquisition of data, Analysis and interpretation of data.
YW, Acquisition of data, Analysis and interpretation of data.
ZZ, Acquisition of data, Analysis and interpretation of data.
KC, Acquisition of data, Analysis and interpretation of data.
SSA, Conception and design, Analysis and interpretation of data.
HER, Conception and design, Analysis and interpretation of data.
PR, Conception and design, Analysis and interpretation of data.
FY, Conception and design, Analysis and interpretation of data.
CG, Conception and design, Analysis and interpretation of data.
W-KS, Conception and design, Analysis and interpretation of data, Drafting or revising the article.
HW, Conception and design, Analysis and interpretation of data, Drafting or revising the article.
References
- Bello B, Reichert H, Hirth F. 2006. The brain tumor gene negatively regulates neural progenitor cell proliferation in the larval central brain of Drosophila. Development 133:2639–2648. 10.1242/dev.02429 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bello BC, Izergina N, Caussinus E, Reichert H. 2008. Amplification of neural stem cell proliferation by intermediate progenitor cells in Drosophila brain development. Neural Development 3:5. 10.1186/1749-8104-3-5 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betschinger J, Mechtler K, Knoblich JA. 2006. Asymmetric segregation of the tumor suppressor brat regulates self-renewal in Drosophila neural stem cells. Cell 124:1241–1253. 10.1016/j.cell.2006.01.038 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boone JQ, Doe CQ. 2008. Identification of Drosophila type II neuroblast lineages containing transit amplifying ganglion mother cells. Developmental Neurobiology 68:1185–1195. 10.1002/dneu.20648 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowman SK, Rolland V, Betschinger J, Kinsey KA, Emery G, Knoblich JA. 2008. The tumor suppressors Brat and Numb regulate transit-amplifying neuroblast lineages in Drosophila. Developmental Cell 14:535–546. 10.1016/j.devcel.2008.03.004 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brumby AM, Zraly CB, Horsfield JA, Secombe J, Saint R, Dingwall AK, Richardson H. 2002. Drosophila cyclin E interacts with components of the Brahma complex. The EMBO Journal 21:3377–3389. 10.1093/emboj/cdf334 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabernard C, Doe CQ. 2009. Apical/basal spindle orientation is required for neuroblast homeostasis and neuronal differentiation in Drosophila. Developmental Cell 17:134–141. 10.1016/j.devcel.2009.06.009 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carney TD, Miller MR, Robinson KJ, Bayraktar OA, Osterhout JA, Doe CQ. 2012. Functional genomics identifies neural stem cell sub-type expression profiles and genes regulating neuroblast homeostasis. Developmental Biology 361:137–146. 10.1016/j.ydbio.2011.10.020 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castellanos E, Dominguez P, Gonzalez C. 2008. Centrosome dysfunction in Drosophila neural stem cells causes tumors that are not due to genome instability. Current Biology 18:1209–1214. 10.1016/j.cub.2008.07.029 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caussinus E, Gonzalez C. 2005. Induction of tumor growth by altered stem-cell asymmetric division in Drosophila melanogaster. Nature Genetics 37:1125–1129. 10.1038/ng1632 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chabu C, Doe CQ. 2009. Twins/PP2A regulates aPKC to control neuroblast cell polarity and self-renewal. Developmental Biology 330:399–405. 10.1016/j.ydbio.2009.04.014 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang KC, Garcia-Alvarez G, Somers G, Sousa-Nunes R, Rossi F, Lee YY, Soon SB, Gonzalez C, Chia W, Wang H. 2010. Interplay between the transcription factor Zif and aPKC regulates neuroblast polarity and self-renewal. Developmental Cell 19:778–785. 10.1016/j.devcel.2010.10.007 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang KC, Wang C, Wang H. 2012. Balancing self-renewal and differentiation by asymmetric division: insights from brain tumor suppressors in Drosophila neural stem cells. Bioessays 34:301–310. 10.1002/bies.201100090 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choksi SP, Southall TD, Bossing T, Edoff K, de Wit E, Fischer BE, van Steensel B, Micklem G, Brand AH. 2006. Prospero acts as a binary switch between self-renewal and differentiation in Drosophila neural stem cells. Developmental Cell 11:775–789. 10.1016/j.devcel.2006.09.015 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dokmanovic M, Clarke C, Marks PA. 2007. Histone deacetylase inhibitors: overview and perspectives. Molecular Cancer Research 5:981–989. 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-07-0324 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimoto A, Totoki Y, Abe T, Boroevich KA, Hosoda F, Nguyen HH, Aoki M, Hosono N, Kubo M, Miya F, Arai Y, Takahashi H, Shirakihara T, Nagasaki M, Shibuya T, Nakano K, Watanabe-Makino K, Tanaka H, Nakamura H, Kusuda J, Ojima H, Shimada K, Okusaka T, Ueno M, Shigekawa Y, Kawakami Y, Arihiro K, Ohdan H, Gotoh K, Ishikawa O, Ariizumi S, Yamamoto M, Yamada T, Chayama K, Kosuge T, Yamaue H, Kamatani N, Miyano S, Nakagama H, Nakamura Y, Tsunoda T, Shibata T, Nakagawa H. 2012. Whole-genome sequencing of liver cancers identifies etiological influences on mutation patterns and recurrent mutations in chromatin regulators. Nature Genetics 44:760–764. 10.1038/ng.2291 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez C. 2013. Drosophila melanogaster: a model and a tool to investigate malignancy and identify new therapeutics. Nature Reviews Cancer 13:172–183. 10.1038/nrc3461 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guenther MG, Lane WS, Fischle W, Verdin E, Lazar MA, Shiekhattar R. 2000. A core SMRT corepressor complex containing HDAC3 and TBL1, a WD40-repeat protein linked to deafness. Genes & Development 14:1048–1057 [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gui Y, Guo G, Huang Y, Hu X, Tang A, Gao S, Wu R, Chen C, Li X, Zhou L, He M, Li Z, Sun X, Jia W, Chen J, Yang S, Zhou F, Zhao X, Wan S, Ye R, Liang C, Liu Z, Huang P, Liu C, Jiang H, Wang Y, Zheng H, Sun L, Liu X, Jiang Z, Feng D, Chen J, Wu S, Zou J, Zhang Z, Yang R, Zhao J, Xu C, Yin W, Guan Z, Ye J, Zhang H, Li J, Kristiansen K, Nickerson ML, Theodorescu D, Li Y, Zhang X, Li S, Wang J, Yang H, Wang J, Cai Z. 2011. Frequent mutations of chromatin remodeling genes in transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder. Nature Genetics 43:875–878. 10.1038/ng.907 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heck BW, Zhang B, Tong X, Pan Z, Deng WM, Tsai CC. 2012. The transcriptional corepressor SMRTER influences both Notch and ecdysone signaling during Drosophila development. Biology Open 1:182–196. 10.1242/bio.2012047 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jin Y, Xu J, Yin MX, Lu Y, Hu L, Li P, Zhang P, Yuan Z, Ho MS, Ji H, Zhang L. 2013. Brahma is essential for Drosophila intestinal stem cell proliferation and regulated by Hippo signaling. Elife 2:e00999. 10.7554/eLife.00999 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan T, Friedman N, Margalit H. 2005. Ab initio prediction of transcription factor targets using structural knowledge. PLOS Computational Biology 1:e1. 10.1371/journal.pcbi.0010001 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirilly D, Wong JJ, Lim EK, Wang Y, Zhang H, Wang C, Liao Q, Wang H, Liou YC, Yu F. 2011. Intrinsic epigenetic factors cooperate with the steroid hormone ecdysone to govern dendrite pruning in Drosophila. Neuron 72:86–100. 10.1016/j.neuron.2011.08.003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klochendler-Yeivin A, Muchardt C, Yaniv M. 2002. SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling and cancer. Current Opinion In Genetics & Development 12:73–79. 10.1016/S0959-437X(01)00267-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee CY, Andersen RO, Cabernard C, Manning L, Tran KD, Lanskey MJ, Bashirullah A, Doe CQ. 2006a. Drosophila Aurora-A kinase inhibits neuroblast self-renewal by regulating aPKC/Numb cortical polarity and spindle orientation. Genes & Development 20:3464–3474. 10.1101/gad.1489406 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee CY, Robinson KJ, Doe CQ. 2006b. Lgl, Pins and aPKC regulate neuroblast self-renewal versus differentiation. Nature 439:594–598. 10.1038/nature04299 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee CY, Wilkinson BD, Siegrist SE, Wharton RP, Doe CQ. 2006c. Brat is a Miranda Cargo protein that promotes neuronal differentiation and inhibits neuroblast self-renewal. Developmental Cell 10:441–449. 10.1016/j.devcel.2006.01.017 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li J, Wang J, Nawaz Z, Liu JM, Qin J, Wong J. 2000. Both corepressor proteins SMRT and N-CoR exist in large protein complexes containing HDAC3. The EMBO Journal 19:4342–4350. 10.1093/emboj/19.16.4342 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marenda DR, Zraly CB, Dingwall AK. 2004. The Drosophila Brahma (SWI/SNF) chromatin remodeling complex exhibits cell-type specific activation and repression functions. Developmental Biology 267:279–293. 10.1016/j.ydbio.2003.10.040 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marenda DR, Zraly CB, Feng Y, Egan S, Dingwall AK. 2003. The Drosophila SNR1 (SNF5/INI1) subunit directs essential developmental functions of the Brahma chromatin remodeling complex. Molecular and Cellular Biology 23:289–305. 10.1128/MCB.23.1.289-305.2003 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narlikar GJ, Fan HY, Kingston RE. 2002. Cooperation between complexes that regulate chromatin structure and transcription. Cell 108:475–487. 10.1016/S0092-8674(02)00654-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Negre N, Brown CD, Ma L, Bristow CA, Miller SW, Wagner U, Kheradpour P, Eaton ML, Loriaux P, Sealfon R, Li Z, Ishii H, Spokony RF, Chen J, Hwang L, Cheng C, Auburn RP, Davis MB, Domanus M, Shah PK, Morrison CA, Zieba J, Suchy S, Senderowicz L, Victorsen A, Bild NA, Grundstad AJ, Hanley D, MacAlpine DM, Mannervik M, Venken K, Bellen H, White R, Gerstein M, Russell S, Grossman RL, Ren B, Posakony JW, Kellis M, White KP. 2011. A cis-regulatory map of the Drosophila genome. Nature 471:527–531. 10.1038/nature09990 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neumuller RA, Richter C, Fischer A, Novatchkova M, Neumuller KG, Knoblich JA. 2011. Genome-wide analysis of self-renewal in Drosophila neural stem cells by transgenic RNAi. Cell Stem Cell 8:580–593. 10.1016/j.stem.2011.02.022 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugh TJ, Weeraratne SD, Archer TC, Pomeranz Krummel DA, Auclair D, Bochicchio J, Carneiro MO, Carter SL, Cibulskis K, Erlich RL, Greulich H, Lawrence MS, Lennon NJ, McKenna A, Meldrim J, Ramos AH, Ross MG, Russ C, Shefler E, Sivachenko A, Sogoloff B, Stojanov P, Tamayo P, Mesirov JP, Amani V, Teider N, Sengupta S, Francois JP, Northcott PA, Taylor MD, Yu F, Crabtree GR, Kautzman AG, Gabriel SB, Getz G, Jäger N, Jones DT, Lichter P, Pfister SM, Roberts TM, Meyerson M, Pomeroy SL, Cho YJ. 2012. Medulloblastoma exome sequencing uncovers subtype-specific somatic mutations. Nature 488:106–110. 10.1038/nature11329 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reisman D, Glaros S, Thompson EA. 2009. The SWI/SNF complex and cancer. Oncogene 28:1653–1668. 10.1038/onc.2009.4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang C, Chang KC, Somers G, Virshup D, Ang BT, Tang C, Yu F, Wang H. 2009. Protein phosphatase 2A regulates self-renewal of Drosophila neural stem cells. Development 136:2287–2296. 10.1242/dev.035758 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang C, Li S, Januschke J, Rossi F, Izumi Y, Garcia-Alvarez G, Gwee SS, Soon SB, Sidhu HK, Yu F, Matsuzaki F, Gonzalez C, Wang H. 2011. An ana2/ctp/mud complex regulates spindle orientation in Drosophila neuroblasts. Developmental Cell 21:520–533. 10.1016/j.devcel.2011.08.002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang H, Ouyang Y, Somers WG, Chia W, Lu B. 2007. Polo inhibits progenitor self-renewal and regulates Numb asymmetry by phosphorylating Pon. Nature 449:96–100. 10.1038/nature06056 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang H, Somers GW, Bashirullah A, Heberlein U, Yu F, Chia W. 2006. Aurora-A acts as a tumor suppressor and regulates self-renewal of Drosophila neuroblasts. Genes & Development 20:3453–3463. 10.1101/gad.1487506 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wen YD, Perissi V, Staszewski LM, Yang WM, Krones A, Glass CK, Rosenfeld MG, Seto E. 2000. The histone deacetylase-3 complex contains nuclear receptor corepressors. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 97:7202–7207. 10.1073/pnas.97.13.7202 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weng M, Golden KL, Lee CY. 2010. dFezf/Earmuff maintains the restricted developmental potential of intermediate neural progenitors in Drosophila. Developmental Cell 18:126–135. 10.1016/j.devcel.2009.12.007 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xi R, Xie T. 2005. Stem cell self-renewal controlled by chromatin remodeling factors. Science 310:1487–1489. 10.1126/science.1120140 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeng X, Lin X, Hou SX. 2013. The Osa-containing SWI/SNF chromatin-remodeling complex regulates stem cell commitment in the adult Drosophila intestine. Development 140:3532–3540. 10.1242/dev.096891 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Z, Chang CW, Hugo W, Cheung E, Sung WK. 2013. Simultaneously learning DNA motif along with its position and sequence rank preferences through expectation maximization algorithm. Journal of Computational Biology 20:237–248. 10.1089/cmb.2012.0233 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu S, Barshow S, Wildonger J, Jan LY, Jan YN. 2011. Ets transcription factor Pointed promotes the generation of intermediate neural progenitors in Drosophila larval brains. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 108:20615–20620. 10.1073/pnas.1118595109 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]